Blue spots on a child's face
The skin is one of the first to signal a malfunction in the body; purple spots on the skin are confirmation of this.
Often people simply do not pay attention to the so-called bruises, mistaking them for the consequences of careless movement and injury resulting from this reason.
But in some cases, such neglect is unacceptable, since purple spots on the body can become evidence of a serious illness.
Purple or blue spots that form on the surface of human skin can be symptoms of many diseases. Of course, these can be ordinary bruises that form after a bruise, but they can also tell about internal pathologies that are not always noticeable to a person, or become symptoms of genetic diseases.
Considering that the purple spots themselves on human skin may differ from each other, we can say that the color, shape, and also the location of such a spot can suggest a disease from which the person is suffering.
Among the possible causes of purple spots on the human body are the following diseases:
- liver diseases;
- avitaminosis;
- rheumatoid arthritis;
- thrombocytosis;
- leukemia;
- marbled skin syndrome;
- Cobb syndrome;
- Fabry disease;
- flaming nevus;
- Kaposi's sarcoma.
This list is by no means complete. There are still many diseases in which one of the obvious clinical manifestations is violet, cyanotic or port-wine stains.
Of course, if any suspicious spot occurs, no matter where it appears - on the hands, on the face or on the back, it is better to consult a specialist and rule out possible serious diseases.
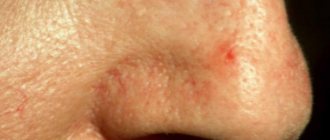
Port-wine stains on the face in medical practice are called the complex term “telangiectatic nevus” or flaming nevus.
At its core, this is a type of dysplasia, characterized by a violation of the integrity of the structure of blood vessels, which are located quite close to the surface of the skin.
Due to the characteristic color of the marks that appear on the surface of the skin, this pathology is popularly called port-wine stain disease.
A flaming nevus is very similar in appearance to a hemangioma, but there are some differences. Firstly, the disease has a very good prognosis for cure, and secondly, it does not pose an oncological threat.
This pathology develops during the prenatal period. Flaming nevus is found in 2-3 babies out of 1,000.
The shape of the nevus is usually irregular. Often, nevus does not go away on its own, leaving a mark for life. It is often pink in color in babies, but over the years it can thicken and darken, turning purple.
In some cases, a flaming nevus can become a symptom of the following serious genetic diseases:
- Cobb syndrome;
- Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome;
- Sturge-Weber-Krabbe syndrome.
These diseases require special treatment and attention from medical specialists.
Even in the recent past, a nevus was removed using a scalpel, but such treatment often led to the fact that the cells remaining after an unsuccessful operation became malignant and provoked the development of cancer. Today, there are more humane, and most importantly, effective methods for removing such a purple spot from the surface of the skin. We are talking about cryotherapy and laser removal of nevus.
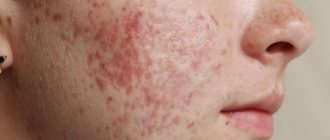
Another disease in which violet-blue spots can be found on the surface of the skin is Kaposi's sarcoma. If we talk about the territorial prevalence of the disease, it should be noted that patients with this diagnosis live mainly in countries such as Ukraine, Belarus, Russia, and in countries belonging to Central Europe.
The purple spots themselves during the development of Kaposi's disease are only the beginning of pathogenesis. At this time, the tumor core itself begins to grow in various parts of the human intestine or in his stomach.
Externally, violet-blue spots with Kaposi's sarcoma are similar to the rashes characteristic of lichen planus, that is, they are round discs or nodes, the size of which can reach 50 mm in diameter. Such spots are painful when you press on them.
Among the patients who may be diagnosed with Kaposi syndrome, there are people belonging to the following risk groups:
- HIV-infected;
- AIDS patients;
- men;
- people who have undergone organ transplantation;
- people infected with HPV type 8;
- people from African countries.
Treatment of this disease involves systemic and local use of chemotherapy drugs, interferons, as well as radiation exposure to the tumor and cryotherapy.
Source: https://kozhnye.ru/sinie-pjatna-na-lice-u-rebenka.html
Recipes for folk remedies for blue spots
For minor defects in the form of blue spots on the surface of the face, you can try to get rid of them using traditional methods.
Mix bodyaga powder with hydrogen peroxide in a 1:1 ratio to a paste, apply to blue spots for at least 5-7 minutes. After removing the mixture, you need to treat the skin with kefir to relieve inflammation. This product is suitable exclusively for oily skin. This product must be used with caution, avoiding contact with mucous membranes and eyes.
Combine green clay with rosemary essential oil and make masks no more than 3 times a week, applying the mixture for 10 minutes. Continue the course until the stains are completely removed. Green clay can be replaced with blue clay, and it is best to add lemon juice as an additional ingredient.
- Combine tomato pulp – 1 tablespoon with starch – 1 teaspoon, bring to a homogeneous consistency and apply to problem areas.
- Combine egg white with lemon juice (2 teaspoons) and apply spotwise to dark spots for 15 minutes. The composition can also be used to lighten the entire face. You can wipe stains with cucumber juice or its pulp.
- Cinnamon and honey in equal quantities - mix 1 teaspoon each well and apply the resulting mixture to the stains, rinse off after 20 minutes. If you are intolerant to honey, you can replace it with white or green clay and add a little water until the required thickness is obtained. The mask is not recommended to be used daily.
- Dilute water with apple cider vinegar - 3:1 and wipe your face with this product daily.
Infusions of medicinal herbs are good to use for washing in the presence of blue spots. Chamomile works better than others, relieving inflammation, soothing and refreshing the skin.
Small wounds, where red from scratches will be disinfected, and scars will not appear.
?Pour-wine and purple spots on the skin: why do they appear?
What are the harbingers of purple spots on the skin? Should we be afraid of them? Can we ignore them? What are the factors in the development of this unusual phenomenon and how does skin damage occur in adults and children?
Subcutaneous hemorrhage is a common consequence of a mechanical shock, but the appearance of a wine-colored rash for no reason suggests that something is wrong with your health.
When to panic and run to the doctor if you find a green coating
In the morning, almost all people develop a small white-yellow coating on the tongue, which disappears after hygienic cleaning of the oral cavity. If this does not happen and the plaque is difficult to remove, dense, and of an uncharacteristic color, you should consult a doctor. This symptom can appear in an adult, a child, and even an infant.
The tongue can have absolutely any color - from white to black, and sometimes even green. Such plaque on the tongue in adults and children most often occurs due to fungal infections, as well as as a consequence of natural aging of the body, HIV infection, diabetes mellitus or cancer.
Read more about what this symptom means, why it occurs and how to treat it in today’s material.
Dark spots
Dark pigmentation is disorders such as melasma or melanosis, blue-gray dispigmentation.
Melanosis is promoted by any long-term and severe chronic disease. This causes the deposition of melanin in the skin. Common pathologies are:
- Endocrine melanosis, which occurs with insufficiency of the adrenal cortex, dysfunction of the gonads, diabetes mellitus, thyrotoxicosis, etc.
- Hepatic melanosis, developing against the background of impaired liver function.
- Cachectic melanosis in tuberculosis.
- Uremic - occurs in chronic renal failure.
Becker's melanosis
Or it is also called Becker's nevus. Often occurs in boys aged 10 to 15 years. Men and women are rarely affected by them.
The reasons for the appearance of nevus are still not clear. There are suggestions that this may be due to a hereditary predisposition to this type of pigmentation or the body’s reaction to ultraviolet radiation.
Dubreuil's melanosis
It appears as a flat, dark-colored spot, possibly slightly raised above the skin. The size on average reaches 5 cm, but after a few years it grows to 10 cm.
The color varies from light brown to dark and sometimes black. This melanosis is considered a precancerous condition. Often accompanied by papillomas and nodular elements.
The damaged areas are dense, with peeling and erosion. The skin around such a formation reacts with the appearance of redness, freckles, and foci of keratosis, which are indicators of the degeneration of melanosis into melanoma (a malignant tumor).
The causes of Dubreuil's melanosis are:
- age;
- abuse of ultraviolet radiation;
- skin sensitivity to light;
- skin injury;
- overdrying of the skin.
A common disease in children. Hives look like red-pink spots that develop into blisters with liquid. The spots are very itchy.
And after opening the blisters, brown-brown marks remain on the skin. Urticaria occurs more often in children. As a rule, the spots disappear during puberty.
If an adult falls ill with urticaria, the situation is complicated by the appearance of systemic mastocytosis, which often leads to disability or death.
The causes of urticaria pigmentosa are still being studied. Presumably, provoking factors are:
- immune system response;
- stress;
- climate change;
- inflammation and infections;
- genetic predisposition.
The spots are never hairy and have dark or black dots on the surface. Presumably the reason for the formation is heredity.
Freckles
These are small dark spots on the face or body. Pigmentation becomes more noticeable in the warm season with solar activity. Freckles may disappear as you age.
It is more common in people with light hair, eyes, and skin. Scientists have proven the dependence of the appearance of freckles on hereditary predisposition.
The spots look like clusters of freckles, appear in unusual places and take on a café-au-lait hue.
Such formations can appear from birth or in childhood. The color varies, but brown shades predominate.
Rarely does the spot acquire a gray-blue color. Formations appear on the surface of the arms, legs or torso in an amount of at least 5 pieces. The patient is affected by nerofibroma, which subsequently spreads to other organs - nervous tissue, adrenal glands, etc.
Such spots degenerate into cancer from 3 to 15% of cases. The nervous system and musculoskeletal system suffer. Epilepsy, depression, fatigue occurs, vertebrae are destroyed, cysts appear, etc.
The mutating gene of chromosome 17, which is inherited, is to blame for the appearance of this disease.
Nevus Ota and Ito
Ota manifests itself as a single spot of black-bluish or dark blue color in the eye area, upper jaw or cheek. Sometimes you can find merging spots. Even less commonly, pigmentation can be bilateral.
The disease sometimes spreads to the sclera and nasopharyngeal mucosa. The spots appear from birth and do not go away on their own.
Scientists have not yet determined the cause of nevus of Ota. Often this disease affects people of the Mongoloid race and very rarely Europeans and the Negroid race.
Nevus of Ito is similar to nevus of Ota. The only difference is in its location - neck, chest and shoulder blades.
What does pathological plaque on the tongue look like?
Before deciding what a coated tongue means and what it is talking about, that is, before making a final diagnosis, the specialist needs to carefully examine the patient’s oral cavity, and also take into account all the accompanying symptoms and complaints.
A slight yellowish coating is not a reason to worry. Its formation may be associated with natural physiological processes occurring in the body. If the surface of the tongue has acquired a greenish tint, you should consult a doctor. Perhaps it is a matter of some hidden pathology.
Thus, plaque may differ in the following characteristics:
- color, its intensity (we repeat that the norm is a white or slightly yellowish, easily detachable coating),
- consistency (oily, dry, curdled),
- thickness,
- localization.
Why might there be a green coating on the tongue? What can this mean if a patient has a greenish film on his tongue and a fever? Most often, such symptoms indicate the development of an infectious process in the body. In any case, it is better to immediately consult a doctor so that he can detect the problem at an early stage and offer timely treatment.
Warning sign: skin cracking in the sun
In fact, an allergy to sunlight is extremely rare (unless you're a vampire!). However, with some people their immune system can play such a cruel joke. A more realistic explanation of the causes of skin inflamed in the sun, which becomes covered with a rash like eczema,
. In fact, we are talking about the components contained in some medications. They are the ones that can increase a person’s sensitivity to light. Experts also believe that this phenomenon is typical for northerners who do not experience any problems throughout the winter, but begin to suffer from a specific rash in the summer.
Why does the symptom occur?
So, now let’s figure out why a suspicious green coating forms on the surface of the tongue of a child or adult. The cause of this symptom is most often associated with certain disturbances in the functioning of individual organs or internal systems:
- decreased immunity and, as a consequence, the body’s vulnerability to attack by pathogenic bacteria, or more precisely, fungi,
- improper functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, increased stomach acidity,
- irritating toothpastes and rinses,
- food products containing dyes,
- smoking,
- tongue injuries, including piercings,
- pregnancy,
- taking certain medications: hormone replacement therapy, oral contraceptives, certain antibiotics and corticosteroids.
This is what a fungal infection on the tongue looks like
“This morning I discovered green spots on my one-year-old son’s tongue. We made an appointment with the pediatrician. The doctor examined him. It turned out that antibiotics weakened the baby’s immunity. A month ago we suffered from pneumonia. The pediatrician told me to treat my mouth with a special solution.”
Yulia Egorova, 28 years old. Tobolsk
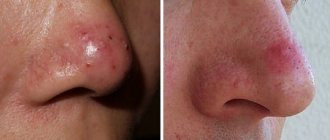
Removal methods
When talking about how to get rid of red dots on the body, the removal of these tumors is most often used. But such therapy is carried out only in case of aggressive growth of spots. The specialist prescribes a histological examination, which is carried out in cases where one or several red spots appear, associated with a cosmetic defect. Methods for removing hemangiomas:
Source: https://kcdc.ru/lico/sinie-pyatna-na-lice.html
Dangerous conditions - what are they?
Excessive rashes on the back, as well as other parts of the body, are a sign of a complex disorder in the body. During this period, they refuse to visit the bathhouse and sunbathe.
Diseases with a risk of acquiring disability:
- Thrombocytopenic purpura. The disease is dangerous due to the risk of internal hemorrhages, including in the brain. Laboratory confirmation of purpura is an extremely low number of platelets in the blood. Vascular dysfunction is often inherited, but sometimes occurs spontaneously.
- Capillary toxicosis. A sharply manifested symptom is the result of the entry into the body of an allergen (usually a food product) to which the person is intolerant. It often develops in children as a hypertrophied reaction to sore throat.
- Venous dilatation of veins (from stage 3). Although the defect appears in many patients in old age, the greatest risk is in those who have a complication. Advanced varicose veins lead to the appearance of dark areas of the dermis, which sometimes turn black. In this case, immediately consult a doctor: a change in shade is a symptom of necrotization. Appears in the arm area in 5% of cases.
- Kaposi's sarcoma. A malignant process that spreads chaotically throughout a person’s integument. The main danger is the rapid degeneration of small “marks” into 5-centimeter (in diameter) nodes.
A small red rash, especially in the legs, is sometimes the initial stage of thrombocytopenia, but more often the phenomenon occurs due to excessive exercise.
Intensive scratching of the skin with nails can also cause pinpoint but harmless changes. If vascular tone is disturbed, then formations - red moles - can remain on the body for a long time.
Facial erythema causes redness of the epithelium, and its complicated form causes a purple tint to the damaged dermis. Sharp but temporary changes are also possible with the development of drug photosensitivity in the chronic stage.
In the photos attached to the article, it is easy to determine which rashes appeared due to the oncological process, and which due to vascular pathology.
Blue Mongolian spot in a newborn: photo, why does it appear in children?
Surely many parents have heard about such a thing as a Mongoloid spot. Most often, this defect appears on the skin of newborn Mongoloid children.
According to statistics, every year only 1% of Caucasian infants are diagnosed with this phenomenon in the first days of life. Despite the low rate, none of the Caucasian children are immune from the formation of a blue Mongolian spot.
Why does it appear and how dangerous is it for the child’s health? How can you get rid of it?
What is a Mongolian spot called, what does it look like and who gets it?
In medicine, this skin defect is classified as one of the types of congenital benign nevus and its origin is explained by the special occurrence of melanin in the connective tissue layer of the skin. This phenomenon received its name due to the fact that it was first identified in newborn children of the Mongoloid race. However, subsequently such spots began to be recorded in children of other races.
After numerous studies, scientists came to the conclusion that initially only Mongoloids were susceptible to the appearance of Mongolian spots. Subsequently, when mixing blood, this defect began to be transmitted to other races. This explains, for example, the fact that a Russian child with a Tatar grandfather at birth has blue pigmentation on the tailbone.
Mongoloid spots are diagnosed in newborns in the maternity hospital in the first days of life. You can see what they look like in the photo. There are many superstitions associated with this phenomenon. Many peoples consider such a stain a good sign. Because of its location, it received the unofficial name “sacred spot.”
The Mongols call it “Genghis Khan’s spot”, and the Uyghurs call it “Tengri’s mark”. Buryats believe that a child born with such a spot - “Menge” - is blessed by the Almighty and will be protected by a guardian angel all his life.
According to the legends of the Kyrgyz, during the birth of a baby, the goddess Umai-ene, who patronizes children and women in labor, pinches his tailbone, thereby marking him and granting protection from slander, sorrows, illness and poverty.
Clinical manifestations of Mongolian spots
The defect manifests itself in different ways in newborns. The spots can vary in shade, size, location and shape. In Mongolian babies and babies of peoples with fair skin, such formations stand out strongly against the background of the surrounding skin. In newborns of the Negroid race, they are practically invisible on the body. The table shows the main characteristics of this phenomenon.
| Criterion | Characteristics of spots | Probability of subsequent change |
| Age at which spots appear | In the first days after birth | Absent |
| Quantity | As a rule, children are born with one spot. However, there may be several of them. Merging, they form one vast formation. | |
| Dimensions | From a small diameter to 6-10 cm. The spot can also completely cover one of the parts of the body. | Gradually decrease until they disappear completely. In some cases, with large scale pigmentation, spots remain for life. |
| Color | Blue-gray with a green or black tint. The entire surface of the neoplasm has a uniform color. | During the first weeks of a child's life, the color of the formation becomes more intense; as time passes, the color loses saturation. |
| Form | Round, elongated with clearly defined edges, or irregular with blurred boundaries | Absent |
| Localization | Most often, pigmentation occurs on the sacrum, less often on the butt, back, lumbar region and inner part of the lower leg. In exceptional cases, a child is born with spots on other parts of the body. | Unlike birthmarks, such formations tend to move around the body. |
Causes of spots
The exact reasons why Mongolian children and children of nationalities with light skin tones are susceptible to the appearance of such a skin defect have not been fully studied to date, but the mechanism of its occurrence has been established. Scientists believe that the development of this phenomenon is based on genetic characteristics that lead to disruption of the production of skin pigment and its penetration into different layers of the epidermis.
To understand how this defect is formed, you need to know the definition of the following values:
- Epidermis. This term refers to the outer layer of skin. This stratified derivative of the epithelium in thick skin consists of 5 layers that are located above the dermis and perform a barrier function.
- Dermis. It is the connective tissue part of the skin and consists of glands, blood vessels, lymphatic tracts, nerves, receptors, and hair follicles.
- Melanins. These dark pigment elements are responsible for coloring the skin in shades of brown, yellow and black. Such substances are found in the epidermis of every person with the exception of albinos.
- Melanocytes. They are cells responsible for the production of melanins in the form of microscopic capsules with this pigment inside.
Caucasians with fair skin produce melanin when exposed to natural or artificial ultraviolet radiation.
Dark-skinned peoples are characterized by constant synthesis of pigment. Based on this, we can conclude that the natural color of the skin does not depend on the amount of melanin, but on the activity of its production.
For this reason, even a Caucasian can get very tanned and then regain his natural skin tone.
The formation of Mongolian spots occurs as follows. During the development of the embryo, the outer germ layer is formed, from which the nervous system, tooth buds and skin are subsequently formed.
As the skin develops, melanocytes move from it to the epidermis.
Sometimes this process fails, and a certain number of cells that produce skin pigments accumulate in the epidermis, resulting in the formation of pigment spots on the body of the newborn.
Diagnostics of education
If this defect was not detected in the maternity hospital during the first examination of the newborn, if a stain is discovered at home, the baby must be shown to a dermatologist. The doctor will prescribe a complex differential diagnosis for the small patient. This measure will eliminate dangerous dermatological diseases that require immediate therapeutic measures.
The following diagnostic procedures are used for differentiation:
- dermatoscopy - visual examination of an area of skin using a magnifying device;
- siascopy – determination of the dermoscopic picture of the neoplasm and the nature of the distribution of skin pigment using a siascanner;
- biopsy - examination of removed skin cells to determine whether they contain cancerous elements.
Is there a need for treatment?
This phenomenon is not considered a disease and does not threaten the health and life of the baby. Experts unanimously classify the defect as cosmetic. In most cases, pigmentation goes away on its own as the baby grows older.
As a rule, this happens when he reaches 4-5 years of age. Much less often, the spot disappears closer to 13-15 years. In some situations, large areas of pigmentation remain for life, and the pigments become light.
Elimination methods
Today, there are several completely different methods that can help remove blue spots. After reviewing them, everyone can make their own choice.
The medical method of treatment uses a variety of medications that help remove spots on the face:
- a special cream that has an anti-pigment, strong brightening effect. True, it should be used with great caution so as not to provoke allergies or, even worse, skin cancer;
- scrubs that contain various hydroacids: lactic, citric, salicylic;
- drugs that suppress melanin production: azelaic acid, arbutin, kojic acid.
Cosmetic treatment offers salon procedures that allow you to quickly tidy up your skin by removing blemishes on your face:
- chemical peeling based on trichloroacetic or glycolic acid. To improve the quality of the procedure, it is recommended to combine peeling with the use of retinoids;
- Fractional photothermolysis and microcurrent therapy are those procedures that are performed directly on spots or scars and are used to accelerate metabolic processes, improve skin health, and enhance blood microcirculation. These methods have the additional effect of improving the production of substances such as collagen and elastin, which help even out the tone and surface of the skin;
- dermabrasion or laser resurfacing - this procedure does not completely remove spots, but noticeably smoothes and brightens the skin.
Traditional medicine offers a wide variety of remedies suitable for eliminating blue spots.
The only drawback of these methods, despite the naturalness of the ingredients, is the long-term treatment required to achieve results.