All girls remove unwanted hair from their bodies using different techniques. However, the side effects after any method of hair removal are the same. Quite often, after performing the procedure incorrectly, women have a question: hair grows ingrown after hair removal - what to do? In fact, eliminating ingrowth is not difficult if done in time. Otherwise, a strong inflammatory process may occur, in which case you will have to consult a doctor.
Why do they grow?
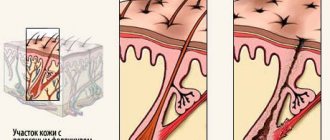
An ingrown hair is a hair that cannot penetrate the structure of the skin and begins to grow in the opposite direction or curl in the skin in the form of a spiral.
It is quite easy to recognize ingrown hairs after hair removal, especially immediately after the procedure, since that is when they are very noticeable on smooth skin.
The ingrowth area may look like local redness, the appearance of a small bump on the skin, or a dark dot located under the epidermis layer. Sometimes the hair is visible in full length or twisted in a “ring”, but it is hidden under a layer of skin, which is why it cannot be removed using regular depilation.
To understand why hair grows after hair removal, you should study all the possible causes of this side effect:
- Hard hair structure.
- Skin too thick.
- Illiterate performance of depilation. Ingrowth occurs due to damage to the hair follicle when it is pulled out incorrectly.
- Regular use of machines and epilators to remove unwanted hair.
- Ignoring recommendations for skin care after the procedure.
From the cause of the appearance of ingrown hairs, you can understand how to deal with ingrown hairs after hair removal and prevent their occurrence in the future.
Sometimes ingrown hairs appear after hair removal due to the girl’s hormonal characteristics. Then it will not be possible to radically correct the problem.
Your dermatologist
Photoepilation (foto = light) - hair removal, in which damage to the hair follicle is ensured by the absorption of light energy by its tissues.Mechanism of action
When light energy is absorbed by tissues, various reactions occur, the main of which is thermal.
When a sufficient amount of light energy is absorbed, the tissue is heated to a temperature that leads to its destruction - this is the process of thermolysis (thermo = temperature, lysis = destruction).
Since during photoepilation thermolysis occurs under the influence of light energy, it is called photothermolysis .
The absorption of light with different wavelengths in tissues of different colors occurs with different intensities (just as if you place two objects - black and white - under direct sunlight, the black one will heat up faster and stronger).
Hair color is mainly provided by the content of dark pigment (melanin) in its composition. It is found in both hair and hair follicle. The darker the hair, the more melanin it contains. Therefore, in most cases, photoepilation uses light sources with a wavelength that is best absorbed by melanin and less absorbed by other pigments present in the skin.
Photothermolysis of some tissues (in photoepilation - tissues of the hair follicle) with minimal damage to surrounding tissues is called selective photothermolysis (selective = selective, photo = light, lysis = destruction).
If, as a result of selective photothermolysis, photoepilation heated up to 70-80°C and all the cells of the hair follicle responsible for hair growth (primarily the cells of the hair papilla) died, hair growth from it will not resume. If the hair follicle does not die, but is damaged to a sufficient extent, atrophy of the follicle occurs, a disruption of the normal cycle of hair growth from it, a decrease in the thickness and degree of pigmentation of the hair shaft.
Selectivity problem
Melanin is not a specific pigment for hair and hair follicle. It is also found in the skin (the darker the skin, the more melanin it contains). Therefore, light radiation during photoepilation is absorbed not only by the melanin of the hair follicle, but also by the melanin of the skin. At the same time, skin cells containing melanin are located more superficially than the hair follicle. Accordingly, they will be the first to be damaged by light.
The presence of such a problem is due to the fact that photoepilation methods are better at removing dark hair on light skin, and removing light hair on dark skin is either less effective or is a contraindication for some photoepilation methods.
Engineers working on the creation of systems for photoepilation use various technologies designed to protect skin cells while maintaining a fairly effective effect on the hair follicle. Most often, this is cooling the skin surface before light exposure (cooling also helps reduce the pain of the procedure). Various options for the wavelength of light generated by the emitter, the “shape” of the light pulse, “fragmentation” of the pulse, etc. are also used.
Photoepilation methods
During photoepilation, light sources can be:
- laser (Alexandrite, neodymium, ruby, diode, YAG laser)
- broadband photoepilation based on the IPL principle
Differences between IPL and laser photoepilation
There is no fundamental difference between laser photoepilation and IPL. In both cases, light energy is used, which has a single mechanism of action.
The history of photoepilation began with the advent of laser systems created for this purpose. But, since such features of laser radiation as coherence, collimation, and a high degree of monochromaticity are not so important when carrying out photoepilation, IPL systems for photoepilation have been developed as a cheaper alternative to lasers.
| IPL (abbreviation Intensive Pulse Light) - intense pulsed light. In IPL systems, the light source is a flash lamp that generates a polychromatic spectrum of light radiation. To influence specific pigments (melanin in photoepilation), filters are used that narrow the spectrum of emitted light | |
| Wavelength: ruby laser - 694 nm alexandrite laser - 755 nm diode laser - 800 nm, neodymium laser - 1064 nm | Wavelength range: from 380 to 1200 nm. Using light filters, it is possible to isolate a narrower spectrum, but monochromatic radiation, like lasers, cannot be obtained, therefore the selectivity of the effects of IPL systems is less than that of lasers. |
| A neodymium laser allows photoepilation on dark, tanned skin. | Dark, tanned skin is a contraindication for photoepilation using IPL systems. |
| A very small divergence angle of the laser light beam allows more energy to penetrate into the deeper layers of the skin. | A large divergence angle of light rays in IPL systems requires more energy and unnecessary heating of tissue occurs. |
| Lasers are more expensive to produce. But they do not contain expensive consumables that require regular replacement. | IPL systems are less expensive to produce. But lamps that generate light in IPL systems are an expensive consumable item. |
| A laser can only generate light of one wavelength. The variety of lasers used in cosmetology is due to the fact that each type of laser is designed to solve a specific problem. | The wide spectrum of radiation of IPL systems, the ability to use removable filters to receive light with different wavelength ranges from one device makes them more versatile, allowing you to solve a wider range of cosmetological problems using one device. |
| Light spot diameter: up to 1 cm2. The relatively small impact area makes epilation on small areas and uneven surfaces more convenient. | Diameter of the light spot: from 2 to 20 cm2 (i.e., in one “flash” an area of skin up to 20 cm2 can be affected). The large area of the applicator makes the procedure quick and cheap when epilating large areas. |
Photoepilation methods based on selective photothermolysis cannot remove gray hair (since they do not contain melanin); they can only be epilated with a neodymium laser or electrolysis.
In cases where excess hair growth is caused by hormonal imbalances, photoepilation is usually ineffective.
In terms of the degree of pain, both types of photoepilation are comparable. Theoretically, broadband photoepilation (IPL) should be more painful than laser: due to the greater amount of energy transmitted to the skin, a larger area of exposure per unit of time, and less selectivity of exposure. Pain can be reduced by using systems for local cooling of the skin, which are included with most modern lasers and IPL devices.
Which photoepilation method is better?
The variety of lasers and IPL devices for photoepilation does not allow comparing them as groups. A good, modern laser for photoepilation will be more effective than an outdated, low-power IPL installation. And vice versa.
In general, with the right settings, the effectiveness of both methods is comparable. In specific cases, the optimal method of influence can be chosen. For example, for photoepilation of light hair on dark skin, it is most advisable to use a neodymium laser.
The effectiveness of photoepilation
Since hair removal using photoepilation methods is possible only during its growth period, called anagen, epilation of all hair on the desired area of the skin in one procedure is impossible.
To achieve the desired effect, it is necessary to carry out from 2 to 15 procedures. After completing the course, 90-100% of black hair and 70-80% of blond hair are removed. The remaining hair cannot be photoepilated, but it also does not violate the aesthetics of the body, since it looks like “light fluff.”
As a rule, it is recommended to carry out “maintenance sessions” of photoepilation once a year, since due to the regeneration of hair follicle cells and/or the activation of “sleeping” follicles, hair growth partially resumes.
Ingrown hairs
Unlike depilation methods, photoepilation does not lead to ingrown hairs. On the contrary, “ingrown hairs” are an indication for photoepilation.
Side effects
Since the mechanism of action of photoepilation is based on causing burns to the hair follicles, during and after the procedure, swelling and redness of the treated areas of the skin, accompanied by painful sensations, may be observed.
Swelling and redness occur a few minutes after exposure, their intensity depends on the thickness, color, density of the hair and the density of the light energy flux. As a rule, these phenomena disappear without any treatment within a few hours. If necessary, after the procedure, local cooling and anti-inflammatory creams (including corticosteroids) can be used.
Painful sensations can occur both during photoepilation and continue after the session. In order to reduce their intensity, local anesthesia can be used (application - applying painkillers to the skin, infiltration - administering anesthetics by injection) and local cooling.
Complications of photoepilation
Early complications
Skin burns can occur when treating tanned skin, in areas of thin and sensitive skin, when using too high a flux density of light energy, applying pulses, incomplete contact of the handpiece with the skin, or inadequate cooling of the skin.
Folliculitis (see folliculitis) occurs more often in patients suffering from hyperhidrosis, as well as in people who abuse water procedures and visit the pool in the first days after the procedure.
Acneiform (acne-like) reactions occur more often in young patients, with dark skin color, when using a neodymium laser. Typically, these rashes resolve within a week without treatment.
An exacerbation of herpetic infection (see herpes simplex) occurs during photoepilation in patients who previously had herpetic manifestations in the treated area. In order to prevent this complication, before undergoing photoepilation in the lips or genital area, patients are recommended to take prophylactic antiviral drugs.
Allergic reactions after photoepilation can manifest themselves in the form of allergic dermatitis, urticaria, and be accompanied by itching. Allergies can develop to local anesthetics used before the procedure for pain relief, cooling gas, or products prescribed for skin care after hair removal.
Eye damage (photophobia, decreased visual acuity, catarrhal conjunctivitis, uveitis) can develop in patients who did not use eye protection during the procedure (metal contact lenses, special glasses). More often, eye damage occurs during photoepilation in the eyebrow area when trying to protect the eyes by covering the upper eyelids with fingers.
Late complications
Skin pigmentation disorders (hyper- and hypopigmentation) - most often occur as a result of skin burns that occur during photoepilation. Also, the appearance of hyperpigmentation is possible in patients who do not follow the rules of post-procedure care and do not use sunscreen after photoepilation.
Scars also occur due to skin burns. More often they form in the mandibular region and on the neck. They can be atrophic, normotrophic, hypertrophic and keloid.
Paradoxical hypertrichosis is the effect of increased hair growth after photoepilation. This phenomenon is most often observed on the face and neck, at the border between treated and untreated areas, in women with dark skin color. Paradoxical hypertrichosis can be caused by insufficient light energy flux density, which does not destroy the hair follicle, but stimulates it, or by a thermal-inflammatory effect: in areas bordering the epilation zone, the transition of hair follicles from the telogen phase to the anagen phase can be stimulated.
Graying of hair in the photoepilation zone is a rare complication when gray hair begins to grow instead of pigmented hair.
Hyperhidrosis, bromhidrosis (see hyperhidrosis) - disturbances in sweating in the area subjected to photoepilation are caused by damage during the procedure not only to the hair follicles, but also to the sweat glands.
Malignant degeneration of skin tumors . Any new growths on the skin should not be exposed during photoepilation. There are special protective devices for this. Irradiation of pigmented nevi (moles) is especially dangerous; exposure to intense light flux on them can lead to both local burns (due to the high concentration of melanin in them) and their malignant degeneration into melanoma.
Contraindications to photoepilation:
- Common systemic diseases
- oncological diseases
- decompensated stages of hypertension, coronary heart disease
- decompensated stages of diabetes mellitus,
- febrile conditions (flu, ARVI)
- tendency to form keloid scars
- hemophilia and other bleeding disorders
- photodermatoses (skin diseases accompanied by increased sensitivity to sunlight).
- taking photosensitizing medications (tetracyclines, fluoroquinolones, hormonal contraceptives, retinoids, etc.)
- mental illness
- epilepsy, increased convulsive readiness
- pregnancy
- breastfeeding (hormonal changes that accompany lactation reduce the effectiveness of photoepilation)
- polycystic ovary syndrome (hormonal levels must be normalized with drug therapy before photoepilation)
- hyperthyroidism (hormonal levels must be normalized with drug therapy before photoepilation)
- Local (on the skin at the site of the procedure)
- tattoos, permanent makeup
- varicose veins
- fresh tanning or self-tanning
- external use of preparations containing photosensitizing substances (most often these are essential oils in cosmetics)
- presence of “golden threads” in the skin
- multiple pigmented nevi, other skin neoplasms
- inflammatory, infectious skin diseases
Once again about the important:
The effect on pigmented nevi (moles), both those that rise above the surface of the skin and those that are “flat,” is especially dangerous. Intense light radiation during photoepilation can lead not only to their burns, but also to malignant degeneration into melanoma.
Hair from nevi cannot be epilated using any method; they can only be cut.
If there is such a need, the mole must be removed, and if after its removal the hair growth continues, only then can it be epilated (preferably by electrolysis).
| Search the site “Your dermatologist” |
Why are ingrown hairs dangerous?
Ingrown hairs themselves are not so dangerous, since visually they are simply imprisoned in the structure of the epidermis and cannot break out. The consequences that can result from prolonged ingrown hairs and neglect of treatment can be dangerous.
There are two types of ingrown hairs:
- Superficial. It is quite simple to extract such hairs; they are located in the upper layers of the epithelium. They usually look like an ordinary hair growing under a thin layer of the epidermis, and at first glance it is impossible to understand that it is ingrown.
- Internal. They lie in the deeper layers of the epidermis, and visually they usually look like hairs twisted into a ring.
If a superficial ingrown hair can spontaneously break through a thin layer of skin over time, then serious problems can arise with the internal one.
Leaving the hair in this state for a long time can lead to serious inflammatory processes, which are accompanied by pain and swelling. Then you will have to contact a surgeon to open them. However, even with careful removal of the ingrowth, a small scar may remain on sensitive skin.
Is hair removal with an epilator suitable for preparing for a solarium?
Some people use an epilator to remove unwanted hair. Depending on individual characteristics, it gives the result of smooth legs for up to 3-4 weeks. But this method of depilation is quite painful and traumatic. After the procedure, the skin becomes irritated, loose and sensitive. But a solarium after epilation with an epilator is not contraindicated.
Watch the video about tips for removing hair with an epilator:
In addition to pulling out hairs, the upper, keratinized layer of the epidermis can be removed. Therefore, an epilator procedure can also act as exfoliation. It is recommended to carry it out only before tanning in a solarium, as preparation for the procedure. But this needs to be done several days in advance, so that the skin has time to calm down, recover, redness goes away, and a natural protective layer forms.
How to get rid of it?
You need to take measures to remove unwanted ingrowth immediately after you notice it. This way you will prevent the occurrence of negative consequences when ignoring the defeat.
There are other ways to eliminate ingrowth yourself:
- Steam the affected area thoroughly with hot water and then use an abrasive scrub. It will help remove dead epithelial cells from the epidermis and allow the hair to come out on its own.
- In the early stages of ingrowth, you can use acne cream. It also eliminates inflammation and helps restore normal hair growth.
- Removal with a needle or tweezers. The skin must first be steamed, the instrument must be treated with a disinfectant solution, and then the ingrown hair must be carefully lifted, pulling it out along with the hair bulb.
Be careful - if you cannot eliminate the ingrowth on your own, it is better to abandon this idea so as not to aggravate the situation. Contact a surgeon to carefully restore the integrity and health of the skin.
Solarium after hair removal
Is it possible to go to a solarium after hair removal? Experts do not recommend sunbathing, including in a solarium, after the procedure for removing unwanted hair.
Also interesting is Solarium with aquabreeze, description, advantages and disadvantages
During epilation, not only hair is removed, but the skin is also injured. Redness and pimples may appear. It takes several days to restore damaged cells and relieve all side symptoms. Only then can you sunbathe without harm to your health. If you immediately go to a solarium, you can aggravate all the side effects, namely, increased redness, age spots and even burns of the upper layer of the epidermis.
What should I do to prevent them from growing in?
You can prevent such a side effect as ingrowth before performing the procedure, and this can be done quite simply if you follow some aftercare recommendations.
Recommendations are prescribed both for preparing for depilation and for skin care after it:
- Before depilation, use a scrub to remove the dead skin layer, providing access to the hairs;
- Immediately before and after the procedure, treat the skin and all instruments used with a disinfectant solution of Chlorhexidine;
- After manipulation, apply a soothing lotion;
- After removing unwanted hair, use special anti-ingrowing creams that further slow down hair growth.
Also, after depilation, it is recommended to avoid visiting the bathhouse, sauna and swimming pool for two days.
Skin care after photoepilation
Immediately after light hair removal, the skin looks healthy, but requires special care. The epidermis has been exposed to heat, so redness and slight itching are normal.
Whether photoepilation was carried out at home or in a salon, to consolidate the result and reduce the impact of negative factors, it is recommended to do the following:
- Limit water treatments (hot baths, saunas) and sunbathing.
- In the first 2-3 days, do not use cosmetics containing alcohol and chemical components (only natural ingredients), fatty oils that form a film on the skin.
- Soothe the treated areas with panthenol cream or chamomile or aloe juice.
- To replenish the water balance in the body, drink more water.
When photoepilation is performed, contraindications and consequences must be taken into account so as not to expose yourself to negative factors and side effects. If the procedure is carried out independently, without visiting a cosmetologist, taking precautions before, during and after skin treatment will help reduce the risk.
How to epilate?
If you use an epilator to remove unwanted hair from your body, it is important to follow the rules for its use. Do not press too hard and operate it as smoothly as possible, without sudden movements. If you notice that the epilator does not pull out hairs, but cuts them off, you should replace the attachment.
If you use waxing or sugaring as a method for hair removal, you should apply the working paste exclusively in the direction of hair growth, and pluck it in the opposite direction. This is the only way you can prevent ingrown hairs after the procedure.
It is recommended to change procedures periodically. Don't do this too often - one shift every 6-8 months is enough.
How is photoepilation done?
Modern innovative methods of getting rid of unwanted hair include photoepilation, how is it done in salons and clinics? Various equipment is used for manipulation; the devices differ in power, speed, number of programs and other parameters, but the essence is the same - radiation with pulsed light.
Conventionally, the procedure is divided into several stages:
- Preparatory.
You should not sunbathe before radiation, and the length of the processed hairs ranges from 1 to 1.5 mm. If there is a need to shave off the hair, this will be done by a specialist at the clinic. It is recommended to visit a dermatologist before photoepilation is performed, he will evaluate the contraindications and consequences. - Session.
The patient sits on a chair, and the cosmetologist exposes an area of skin and treats it with a special gel that protects against burns. The specialist moves the tip of the device over the skin for 5-10 minutes, then removes the remaining gel and applies the cream. - Consolidation of the result.
It is not recommended to use cosmetics or visit the bathhouse for 2-3 days after the procedure; it is forbidden to be in direct sunlight for at least 2 weeks.
How to shave?
You also need to be careful with the razor. Despite the fact that most girls use it, many still do not know how to use it correctly.
Firstly, the recommendation for moving the razor is the same as when using other methods of depilation - you need to move it strictly according to hair growth. If you choose a sharp razor with the right attachment, it will completely cut off hair, leaving you with perfectly smooth skin.
Secondly, before the procedure you should apply shaving foam or lotion. Good gliding of the razor over the skin will reduce the risk of cuts and also increase the efficiency of manipulation.
It is better to buy reusable razors that have the ability to change heads. Disposable razors are always stiffer and more uncomfortable, which is why the risk of ingrown hairs when using them is higher.
The principle of photoepilation
The method involves the impact of light waves emanating from a special sensor on the hair shaft and its absorption of this energy. A “thermal effect” occurs in the subcutaneous tissue, that is, tissue heating. This leads to the destruction of hair structures at the molecular level.
The IPL method uses the principle of selective photothermolysis - the selective effect of light waves specifically on the hair pigment. But the skin, despite the fact that it contains the pigment melanin, is not affected at all. Unpleasant consequences occur only in extremely dark-skinned people or those with a strong tan.
It is the presence of a tan and dark skin that are contraindications to the procedure. The hairs under the action of the laser are heated to 80 degrees, at this temperature the follicle is destroyed (partial or complete). During a course of procedures, the bulb is deformed as much as necessary. This action helps prevent the growth of body hair, and also thins it and makes it lighter and more invisible.
The most problematic areas on the face for women are the cheeks, chin and the area above the upper lip. The increased formation of “vegetation” on the face is influenced by hereditary factors and dishormonal disorders in the body (excess of “male” hormones).
Treatment of the upper lip, cheeks, forehead and chin is one of the most popular procedures to get rid of unwanted hair. Due to its high efficiency, this method has gained great popularity among women.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yfVUtBC-lkM
Before processing the antennae, a gel is applied to protect the skin from thermal burns. Subsequently, with the help of a special device that emits bright flashes of light waves, the hairs are “burned out” over certain areas of the face. To remove whiskers, only 5-6 such flashes are enough. During the procedure, many will feel a slight tingling sensation. But there shouldn’t be any severe pain!
Senas on the face lasts 15 minutes. A month later, the procedure can be repeated. To completely get rid of “vegetation” you will need 5-7 visits to the salon.
Armpits
Treatment of armpits lasts no more than 30 minutes. The number of sessions is 4–5, with a break between procedures of a month. The technique is the same as for facial hair removal - a sensor is passed over the area of the armpits, from which light flashes emanate. It is important that you should not shave your armpits between sessions, otherwise the entire effect of exposure to light waves will disappear.
Epilation of the abdomen does not last longer than the work of a cosmetologist on other areas of the body. All manipulations will take about 20–30 minutes. The time depends on the area of the surface being treated. The break between sessions is 4–5 weeks. The procedure is completely painless for the client, however, mild tingling or tingling may occur.
The chest and abdomen area is no different from the general principles of preparation before going to the salon: do not visit the solarium or sunbathe two weeks before the procedures, do not use other methods of hair removal (including shaving or waxing). For a high-quality procedure, the length of the hair should be at least 2 mm.
Hair removal on the inner thigh and pubic area, despite the fears of clients, is a completely painless procedure. These methods are especially successful before the summer holidays. Deep bikini areas are treated in the same way as other methods of hair removal with an ipl laser. Most salons guarantee complete painlessness, but judging by the reviews of women, in some cases (women with hypersensitivity) unpleasant sensations may occur.
Intimate photoepilation (removal of hair on the surface of not only the pubis, inner thigh, but also the labia, anus) is often called “Brazilian”. Cosmetologists recommend starting with a classic bikini, and then switching to a deep bikini to make it easier to get used to the procedure.
This zone has a higher cost compared to others, however, there is no fundamental difference between manipulations when removing hair on the lower extremities or when photoepilation of the abdomen is used. Hair removal occurs from the entire surface of the legs. But in almost all salons there is the possibility of hair removal of individual areas. For example, the area of the lower leg or thigh.
Typically, high-quality hair removal will require about 8 visits to a cosmetologist (or more when epilating the entire surface). The break between sessions is approximately 30 days.
The best means
After each depilation, it is recommended to use special compounds to slow down hair growth and prevent ingrown hairs.
Let's consider popular lines that are often recommended by cosmetologists:
- DEPILFLAX;
- ARAVIA PROFESSIONAL;
- SAONA COSMETICS;
- CRISTALINE;
- Veet.
They need to be applied an hour after the procedure, as well as the next day after it. This way you will protect yourself from ingrowth.
Folk remedies against ingrown hairs
You can eliminate ingrown hairs yourself, but this should only be done when superficial ingrown hairs form.
To soothe the skin and relieve inflammation, it is recommended to make herbal lotions. To do this, you need to pour boiling water over any pharmaceutical herb for 30-40 minutes, then strain it and moisten the gauze. Gauze is applied as a compress to the affected area for 20 minutes twice a day.
You can also make a natural scrub; there are many similar recipes:
- Scrub with salt. Mix olive oil, sea salt (coarsely ground) and moisturizer in equal proportions. After treating the skin with such a scrub, it is recommended to wipe it with a mixture of salicylic acid and calendula tincture. This will help reduce inflammation.
- Scrub with bodyaga. Bodyagi powder is mixed in equal parts with hydrogen peroxide and applied to the girl’s skin.
- Sugar scrub . Mix 2 parts cane sugar, 1 part olive oil and a little tea tree oil for a soothing effect.
Any scrub should be used only on a previously steamed body; this will increase the effectiveness of manipulations and speed up the removal of ingrown hairs.
Types of photoepilation
There are several types of photoepilation:
- IPL hair removal . The flash lamp targets areas of the skin with a series of high-intensity flashes. Applicable on all areas except areas with red, blond and gray hair.
- Elos hair removal . Thanks to the light, which distributes the temperature in the direction of the hair, the skin is protected from overheating, thereby reducing the risk of skin burns and irritation. With the help of elos hair removal, light hair is removed.
- LHE hair removal . The procedure does not use cooling gels. It is done only on dry, clean skin and is painful. Used on areas with blond and gray hair. One of the advantages of LHE hair removal over IPL and Elos hair removal is the large surface area being treated (up to 11 sq. cm), which significantly reduces the procedure time.