A. A. Hmayakyan Dental surgeon, implantologist
Today, implantation surgeons rarely do without mucoplasty. This is a very important component of implantological rehabilitation, since high-quality soft tissues ensure patient comfort and a favorable treatment prognosis, both functionally and aesthetically.
There are patients (for example, with a thick mucosal biotype) for whom additional work with soft tissues is not indicated. In such situations, it is possible to achieve high-quality tissue volume around the implant without any plastic surgery. And there are those for whom work with soft tissues is indicated, consisting of several phases at different stages of treatment.
When is soft tissue plastic surgery necessary?
- Deficiency of soft tissue volume, as a result:
- long-term absence of a tooth (with edentia, atrophy occurs both in bone tissue and soft tissues);
- wearing a Maryland prosthesis (mechanical impact on soft tissues, even in a short period of time, leads to a loss of gum volume);
- thin biotype of the mucosa (here we are talking about the prognosis of future restoration and prevention of volume deficit of hard and soft tissues).
- Lack of attached keratinized mucosa due to:
- the need for directed bone regeneration or an already performed GBR operation (the suturing technique afterward is such that part of the keratinized mucosa is often lost, not counting the already existing atrophy);
- past mistakes during implantation or soft tissue plastic surgery.
- In order to improve the prognosis of treatment. Creating a reserve of soft tissue in the frontal region increases the favorable prognosis of treatment.
To achieve success, it is necessary to comply with parameters that must be taken into account at the planning stage. Some factors may influence directly, others indirectly. Factors such as the accuracy of sampling the SDT or SST, the processing method, the quality of the graft, the preparation of the material fixation zone and the quality adaptation to the receiving bed directly influence.
Indirect ones include careful planning and compliance with the surgical protocol (position, inclination and size of implants, correct choice of suprastructures, compliance with the necessary timing and stages of treatment).
Before we go any further, let's refresh our memory a little. The purpose of dental implantation is to restore a functionally and aesthetically missing element of the dental system. In the dental system, we are interested in bone tissue, mucous membranes, and adjacent teeth. The function of bone tissue is support, retention of the implant, perception and distribution of load. The function of the mucosa is to protect and nourish bone tissue and ensure adequate hygiene.
Based on the above, it turns out that for high-quality implant treatment it is necessary to have high-quality bone tissue in the right volume and the right place (if there is not enough, create it), and high-quality soft tissue (not only in volume, but also of the desired histological structure). Below are examples in different clinical situations.
Examination of the condition of the front tooth, development of a treatment plan
During the examination, the orthopedic dentist found that the front tooth was loose due to severe inflammation of the tissues around the tooth, and pus was leaking from the gum pocket near the tooth.
A CT scan was performed to evaluate the condition of the bone around the tooth. CT scan sections show an extensive bone defect (gray area above the problem tooth).
There are two reasons that led to such inflammation: too deep an edge of the crown (made in another clinic), which injured the gums and led to the formation of a gum pocket, and treatment of the tooth canals in another clinic without the use of a microscope, as a result of which an infection remained in the canals (in Dial -Dental root canal treatment is always carried out with a microscope).
In this case, it is necessary to urgently remove the front tooth so as not to aggravate the inflammation. It will not be possible to install a dental implant at once, since before installing the implant it is necessary to relieve inflammation and restore the jaw bone.
The dentist proposed a treatment plan :
- Removing the front tooth and waiting for the socket to heal completely.
- Bone grafting to build up the jaw bone and install a dental implant in place of the front tooth, waiting for bone restoration and implant healing.
- Soft tissue transplantation (gum volume restoration).
- Installing a crown on a front tooth.
It was necessary to decide the question of what to make the front tooth out of for the healing period after removal, since the soft tissues could not be injured by anything. All the teeth in the upper jaw were previously covered with zirconium crowns, and the patient refused to replace the crowns on two adjacent teeth in order to make a temporary bridge. The option of gluing an artificial tooth to adjacent crowns during surgical procedures was very unreliable. Future bone and soft tissue grafting did not allow inserting the front tooth as a classic removable microprosthesis. An unusual solution was proposed - to make a thin-walled mouth guard for all the upper teeth, and insert the front tooth into the mouth guard. This design eliminated pressure on the surgical area and restored acceptable function and aesthetic appearance of the teeth.
Clinical case No. 1
Simple implantation for long-term missing teeth. An implant is installed, GTR (guided tissue regeneration) is carried out using a SST (connective tissue graft), and a FDM (gingival cuff former) is installed. After 3-4 months you can begin prosthetics.
Rice. 1.
Fig.2.
Rehabilitation period
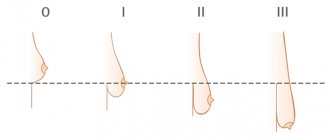
The duration of healing depends on:
- type of plastic;
- presence of diseases (immune status, diseases of the endocrine system);
- its individual characteristics.
On average, the rehabilitation period lasts from 2 days to 2 weeks. With reduced immunity, diabetes and other diseases, recovery is more difficult and takes longer.
After patchwork extension, the tissues are restored within 12 days, after installation of the shaper - from 7 to 14 days.
Features of care after gum augmentation surgery
To quickly restore gums during implantation after plastic surgery, you must adhere to the following recommendations:
- To protect the gingival surface and improve healing, use a special nylon overlay - a mouth guard.
- Try not to mechanically impact the area after the operation. Use a toothbrush with soft bristles; movements should not lead to pain or discomfort. Supplement cleaning with rinses.
- For rinsing, use salt, Chlorhexidine, Miramistin. The rinse solution should be warm and at a comfortable temperature.
- The diet should be gentle in taste and temperature.
- To improve healing after plastic surgery and prevent jaw injuries, you should give up sports, alcohol and smoking, limit physical activity, and not attend thermal procedures (sauna, bathhouse, beach, solarium).
- If pain occurs, it is possible to use special pain-relieving gels for the gums.
- Seams require careful care. They should not be touched with dirty hands or scratched.
If complications or unpleasant symptoms occur, it is necessary to contact the clinic without waiting for a scheduled visit.
As a result of plastic surgery, the tissue is restored to the proper volume and a tighter fit of the prosthesis is ensured.
Source: DesnaZub.ru
Clinical case No. 2
Plastic surgery using SST in 2 stages (after implantation, and during installation of FDM), to compensate for a greater soft tissue deficit than in case No. 1.
Rice. 3.
Rice. 4.
Rice. 5.
Rice. 6.
Applied systems
To implement the methodology under consideration, a special kind of system is used, which differs significantly from classical models.
Implants are significantly smaller in size than standard systems and have a special structure:
- Cone shape.
- Wide thread pitch in the apex area.
- Narrow thread pitch.
- Sharpening in the apical part of the structure, which allows you to quickly and accurately insert the rod into the bone tissue.
Clinical case No. 4
The same protocol for directed bone regeneration in a separate stage. The creation of the PCD zone and subsequently NTR using SST is carried out after implantation.
Rice. 7.
Rice. 8.
Rice. 9.
The conditions for achieving success are:
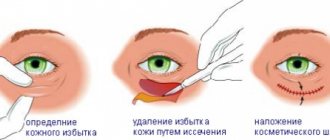
- Qualitative translation of SDT into SST. Careful removal of the epithelium, since the presence of pieces of epithelium on the SCT will, at best, complicate the healing process.
- Achieving immobility of the graft in the recipient area, which makes it possible to receive adequate nutrition.
- Correct position of the implants. The proximity of implants to each other may not allow the creation of the required volume of soft tissue. The buccal inclination of the implant and/or the buccal position worsens the aesthetic prognosis of the future restoration, also from the soft tissue side.
Possible complications
Like any operation, an implantation procedure based on the technology of splitting the gingival ridge has the potential for complications:
- Worsening of the defect. If the technology is violated or the procedure for installing the structures is carried out incorrectly, the amount of bone tissue may be further reduced.
- Structure falling out . This happens if the structure is not planted deeply enough into the bone tissue.
- Injuries to blood vessels or nerves. This can happen if soft tissue is damaged during implant placement.
Complications when working with soft tissues
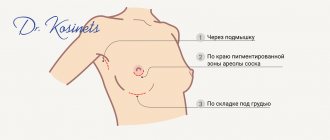
When taking SST or SDT:
- loss of material (the assistant may accidentally aspirate the graft, which entails an increase in the donor zone, or there is a need for another zone);
- taking the wrong volume of material (if there is not enough, it will be necessary to add it in a separate fragment, which complicates the process of fixing the grafts and increases the duration of the operation);
- bleeding in the immediate or delayed time after taking the graft from the palate (increased healing time, discomfort for the patient).
Particular attention should be paid to the technique of collecting SDT and SST, and the technique of suturing on the palate, to ensure comfortable healing and the absence of significant discomfort for the patient during the period of regeneration of the donor area.
Rice. 10.
In preparation:
- insufficient cleansing of epithelium;
- perforation or injury to the flap;
- drying of the graft (humidity throughout the operation ensures the viability of the graft).
When fixing:
- too much suture material (impairs blood supply and injures the graft, complicates vascularization);
- poor adaptation (healing = immobility, this is an important rule that largely determines success).
Rehabilitation period
A patient who has undergone bone grafting associated with dental implantation should be aware of the possible complications of the procedure and be able to distinguish the normal from the pathological process. For example, if we are talking about bleeding, then small amounts of blood in saliva are considered normal during the first hours after plastic surgery. Saliva may remain pale pinkish in color for several more days, but regression of this phenomenon should be observed. The duration of bleeding may increase if the patient took antiplatelet agents and anticoagulants (most often acetylsalicylic acid) before surgery.
General recommendations for the recovery period:
- Food should be soft, crushed as much as possible;
- The operated areas are not cleaned for the first 10 days after bone grafting;
- It is not recommended to drink drinks through a straw during the rehabilitation period;
- To stop bleeding (if it occurs), you can use cold water (hold in your mouth), a damp tea bag (apply to the operated area) or a clean finger (press);
- At night, the head should be elevated to prevent swelling of the face;
- In the first days, to combat pain, take analgesics prescribed by a doctor no more than once every 6 hours (if they do not help, you should consult a dentist);
- To relieve swelling, which maximally manifests itself 1-2 days after surgery, use medications prescribed by a doctor, an ice pack wrapped in a towel (after 3 days the swelling should subside or you should immediately go to a specialist);
- To prevent infectious processes, you should take an antibiotic and rinse your mouth with chlorhexidine.
Oral care should include constant monitoring of the cleanliness of the operated area. Do not brush your teeth with a hard toothbrush for the first two weeks. It is recommended to use cotton swabs to remove food debris from the stitch area and periodically clean them. Tampons are moistened with Chlorhexedine. To speed up healing, a special dental ointment is applied to the sutures, which is first prescribed by the dentist. It is prohibited to use any folk remedies, except those approved by the doctor.