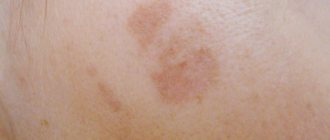
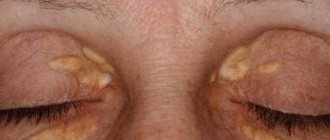
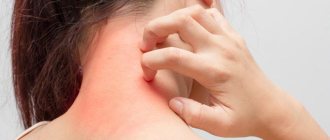
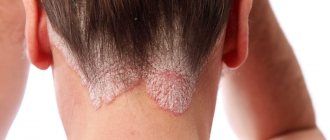
What is keratosis
The pathology consists in the compaction of epithelial cells, which provokes the development of a neoplasm with defined boundaries.
A keratoma may look like:
- plaque;
- spot;
- crust;
- node;
- growth
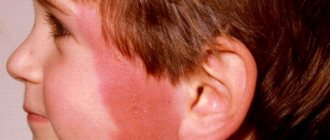
Keratosis of the skin, photos in adults are presented below, belongs to the category of age-related pathologies. But some types can be diagnosed in children. Keratosis usually affects people over 40 years of age. The peak incidence occurs between the ages of 55 and 65 years.
The disease develops in both men and women. In some cases it disappears without therapy. The neoplasm is classified as benign, but can develop into a malignant form. Flat cells are similar in morphology to malignant cells, so if pathology appears, it is advisable to immediately seek help from a specialist.
Classification
In order to somehow understand the many forms and manifestations of dermatological diseases, they were divided into 2 large groups:
- hereditary keratosis;
- acquired keratosis.
Some experts isolate actinic keratosis, considering it a separate pathological condition with its own causes and symptoms.
Hereditary forms
This is the largest and most diverse group. Hereditary keratoses develop with equal frequency among men and women, affecting both very young people and the elderly.
Common genetic forms:
- Ichthyosis . Distributed throughout the body, keratinization of the epithelium resembles fish scales;
- Palmoplantar keratosis (hereditary keratoderma). The disease usually begins in childhood and only progresses with age. It affects the palms, soles, fingers and toes. In its advanced form, it spreads to the elbows and knees;
- Follicular keratosis simplex. It occurs against the background of blockage of hair follicles by overgrown scales. Appears at an early age and reaches its peak during puberty. Localized in the area of the shoulders and elbows, on the hips, less often on the stomach and back;
- Hereditary polykeratosis. The disease includes signs of other forms of keratosis and proceeds in waves, with periodic exacerbation of one or other manifestations.
Each of these forms is combined with numerous lesions and disorders of body systems and has many subtypes with varied symptoms.
Acquired forms
This group includes keratoses formed against the background of adverse external influences or as a result of chronic pathologies, hormonal imbalances and disorders of nervous trophism.
Among the acquired forms the most interesting are:
- Menopausal keratosis. It is observed in women during menopause. Accompanied by obesity, hypertension and thyroid dysfunction;
- Professional keratosis. Caused by constant exposure to traumatic factors. Manifested by callus on the hands;
- Infectious keratosis. Develops against the background of sexually transmitted diseases, tuberculosis.
Horny epidermis can also appear from a lack of vitamins A, E and C, a one-sided diet or constant adherence to strict diets. In some cases, keratosis develops as a symptom of metabolic disorders in the body.
Senile
It occurs due to degenerative changes in the tissues of the epidermis and dysfunction of the sebaceous glands. It can be senile and seborrheic. In the first case, the provoking factor is excess ultraviolet radiation. Actinic keratosis occurs on exposed areas of the skin.
The seborrheic form resembles flat, loose, dark-colored warts. Such growths can be located throughout the body.
Stages and degrees of the disease
Keratosis of the skin develops gradually. Each type has its own clinical picture. In the cyanide form, as the tumor grows, the area of the skin affected by the pathology becomes dark and loose. At the second stage, cysts form in the tissues.
The skin becomes lumpy and begins to peel. When the keratoma is damaged, it begins to bleed and becomes painful. Sometimes an inflammatory process occurs.
In the initial stages of angiokeratoma, blue-black vascular nodules, the diameter of which is 2-5 mm, form on the patient’s skin. They are based on dermal cells. At the second stage, the nodules become rough and begin to peel off. At the last stage, the nodules begin to bleed and become inflamed. This form of disease also occurs in newborns.
The pathological process is localized in the area:
- scrotum;
- belly;
- hips;
- buttocks;
- armpits;
- oral cavity;
- vulva;
- stop;
- lips;
- cheeks;
- fingers.
Keratosis of the skin.
Photos of adults show what neoplasms may look like. The follicular form most often develops in women. It is characterized by the formation of flesh-colored keratinized plugs on the hair follicles. New growths are uneven. Their structure resembles flat, silvery scales. The size of the neoplasms is no more than 1.5 cm.
Most often localized in the area:
- faces;
- buttocks;
- neck;
- armpits.
Keratosis of the skin (the photo in adults shows only external symptoms) begins in the cold season. In warm weather, the symptoms are erased. At a late stage of the disease, the nodules increase in size. The surface of the skin becomes rough. At the last stage, they may begin to bleed and hurt. The seborrheic appearance is characterized by slow development and chronic course.
A spot on the skin of a yellowish tint reaches a diameter of 3 cm. It has a dense morphology with scabs. At the second stage, the spot begins to increase in size and many layers form in it. The neoplasm becomes crusty. The thickness of the stain reaches 1.5 cm. On the last steel, the seal begins to turn black, crack and bleed.
The pathology is localized in the area:
- backs;
- breasts;
- faces;
- neck;
- scalp.
This type of pathology does not develop into an oncological form. In the actinic form, which often develops into a cancerous tumor, nerve rough spots appear in the first stage. At the last stage, they transform into keratinized scales of burgundy color.
Keratomas are located singly. They grow very slowly, reaching 2 centimeters. This form can disappear on its own, and appear under mechanical stress or injury.
In the initial stages of solar keratosis, a large number of small spots appear that begin to peel off. They rise above the epidermis. At the last stage of the disease, the spots transform into plaques covered with hard scales.
This form of pathology is localized in the area:
- faces;
- backs;
- soles;
- legs;
- hands
This form of the disease is considered precancerous. It is triggered by radiation. The initial stage of cutaneous horn is characterized by the appearance of gray or brown spots on the skin. At the second stage of keratosis of the skin, the spots begin to become covered with keratinized scales.
Externally, in the photo of adults, they resemble a tubercle that rises greatly above the skin. Some neoplasms take the form of a flat, silvery plaque. At the last stage, keratomas begin to peel off and bleed.
The pathology is localized in the area:
- lips;
- nose;
- century;
- forehead;
- mucous membranes of the genital organs;
- ears;
- scalp.
This form can turn into an oncological form.
What is skin hyperkeratosis
The name of a skin disease can tell about the mechanism of its development. Protein compounds - keratins - are found on the keratinized surface of the epidermis, starting their way up from the basal layer of the skin. The cells have to spend two to four weeks doing this. The upper scales of the epidermis die off, and a new layer appears in their place.
If the process accelerates, the surface of the skin begins to thicken as a result of the connection of young cells with old ones. When the rejection of scales is delayed, compactions also appear in various parts of the body. If the epidermal tubercles are located on the face, they cause a lot of inconvenience to a person and spoil his appearance.
Symptoms of keratosis
Symptoms of the cyanide form include:
- the presence of multiple formations of brown or black color;
- the formation of round-shaped plaques with pronounced boundaries;
- the appearance of loose scales;
- the presence of small elevations above the level of the skin;
- formation of round or oval spots;
- formation of tumors on the back, chest and forearms;
- the appearance of plaques with a diameter of 1 mm to 2 cm.
Symptoms of angiokeratoma include:
- the presence of red or dark burgundy nodules with a diameter of 1-5 mm, rarely 1 cm;
- blurred boundaries of nodules;
- irregular shape of nodules;
- arrangement of spots in groups;
- elevation of tumors above the skin level;
- expansion of capillaries.
Follicular keratoma is characterized by:
- dry dermis;
- colored nodules gray or pink;
- clear boundaries of the nodule, the diameter of which is 1.5 cm;
- tuberosity of neoplasms.
The distinctive signs of seborrheic keratoma are:
- oval or round shape of neoplasms;
- slight elevation of tumors above the skin level;
- spot diameter up to 6 cm;
- yellow or dark brown spots;
- group arrangement of spots;
- itching;
- peeling.
The actinic form, whose texture resembles sandpaper, is distinguished by:
- absence of itching and peeling;
- rashes in the form of seborrheic warts;
- plaque diameter up to 4 cm;
- bleeding and painful growths.
The main signs of solar keratosis include:
- the presence of formations in the form of groups;
- plaque formation;
- slight elevation of plaques above the skin;
- the appearance of rough scales that are easily separated.
The cutaneous horn is characterized by:
- the appearance of gray or brown spots;
- compaction of neoplasms;
- keratinization of spots;
- peeling of tissue;
- bleeding.
Causes
Various diseases can cause changes in the functioning of epidermal cells. Thickening of the skin is associated with:
- fungal infections;
- diabetes mellitus;
- ichthyosis;
- psoriasis;
- insufficiency of the thyroid gland;
- vitamin deficiency.
In this case, skin problems can be eliminated by acting on the underlying disease.
Common causes of hyperkeratosis include external actions on the layers of the epidermis while wearing tight shoes and clothes. With a large body weight, the feet experience a lot of pressure. At the same time, the protein cells begin to grow rapidly, which leads to the appearance of thickenings.
Passion for smoking and alcohol dries out the skin. Keratoderma occurs due to improper use of cosmetics, due to neglect of hygiene rules. Sunbathers often experience similar skin problems.
A combination of external and internal causes can cause extensive formations in various parts of the body.
Causes of keratosis
The causes of senile keratoma include:
- genetic predisposition;
- malfunction of epithelial cells;
- the presence of chronic pathologies of internal organs;
- accumulation of toxins in the body;
- violation of metabolic processes;
- degeneration of the skin.
The causes of angiokeratoma are still unclear. Some forms have a genetic basis. Most patients are diagnosed with metabolic disorders.
Provocateurs include:
- mechanical damage;
- frostbite;
- burn;
- presence of calluses;
- injuries;
- insect bites.
The follicular form can develop under the influence of the following factors:
- lack of vitamins A, C, D and group B;
- abuse of fatty, hot, spicy and salty foods;
- frequent consumption of coffee;
- use of hormonal-based drugs;
- stress and emotional stress;
- presence of syphilis;
- exposure to cold;
- HIV infection;
- tuberculosis of the skin;
- fungal infection of the feet;
- damage to the body by systemic lupus erythematosus;
- presence of scleroderma;
- allergy;
- hormone imbalance;
- prolonged exposure to x-rays;
- exposure to chemicals and poisons;
- wearing synthetic clothing;
- dysfunction of the digestive organs.
Experts have found that the pathology may have a genetic basis. The disease among adolescents and children is diagnosed in 50-80% of cases. Adult patients account for 40%.
The causes of seborrheic form include:
- heredity;
- malfunction of the immune system;
- skin aging;
- endocrine disorders;
- hormone imbalance.
Actinic form provocateurs include:
- living in a hot climate;
- presence of blond hair and freckles;
- presence of blue or green eyes;
- frequent sun burns;
- age above 45 years.
Keratosis of the skin (photos of adults indicate that this is a serious skin pathology) of the actinic variety, unlike the solar form, develops very slowly due to constant exposure to sunlight.
Causes of solar keratosis include:
- living in southern regions with a hot climate;
- exposure to stress;
- use of hormonal drugs;
- presence of blue eyes and blond hair;
- frequent sunburns.
The development of a cutaneous horn provokes:
- exposure to ultraviolet rays;
- endocrine system disorders;
- viral infection;
- presence of oncological tumors;
- skin trauma;
- genetic basis;
- obesity;
- lack of vitamins;
- malfunction of the gastrointestinal tract;
- disorders at the cellular level;
- alcohol and drug use;
- stress;
- burns;
- exposure to sunlight;
- poor hygiene.
Causes
The causes of keratosis are endogenous and exogenous factors, depending on the form of the disease.
Common reasons include:
- exposure to ultraviolet radiation is the most common cause of keratosis of the facial skin;
- damage by aggressive chemicals;
- injuries;
- insect bites that produce toxins;
- skin infection for various reasons;
- inflammatory processes of the skin, exposure to bacteria, fungi, viruses;
- somatic diseases, especially inflammation of the digestive system, nervous diseases, pathologies of the heart and blood vessels;
- metabolic disorder;
- decreased immune status;
- hematopoietic disorder;
- endocrine disorders;
- benign and malignant neoplasms, especially blood and skin;
- allergic reactions;
- hormonal changes;
- old age;
- heredity (Darier's disease, Mibelli's poroquetosis, Miescher-Lutz elastosis).
Keratosis in a child can develop as a result of intrauterine intoxication. There are frequent cases of pathology developing against the background of other skin diseases, for example, atopic dermatitis (allergic reactions associated with genetic disorders).
Diagnosis of keratosis
Keratosis of the skin (photos in adults indicate the stage of development of the disease) is diagnosed as a result of a medical visual examination. If the lesion has become large, bleeds and thickens, then there is a possibility that the neoplasm has degenerated into a malignant form.
To exclude a dangerous pathology, a biopsy is performed. The procedure involves taking skin samples. It is performed by a therapist using local anesthesia. The sample taken is sent for microscopic analysis.
Also, to diagnose keratosis, dermatologists carry out:
- dermatoscopy (the procedure is carried out using a dermascope apparatus that can detect morphological changes in the skin;
- Ultrasound of neoplasms.
The most common methods are biopsy and dermatoscopy. The cost of dermatoscopy in Moscow ranges from 500 to 3000 rubles. The cost of a biopsy is 1,480 rubles. The cost of dermatoscopy in Samara ranges from 250 to 2500 rubles. The price for a biopsy is 1,500 rubles.
Diagnostics
The clinical picture of the disease is pronounced, so an experienced specialist can make a diagnosis based on a visual examination. To clarify the form of pathology and differentiation, a microscopic examination is carried out. Modern devices have great capabilities and provide information sufficient for a clear understanding of the disease.
The main method for the final diagnosis is histological examination of a biopsy specimen, which makes it possible to establish the type of skin formation, stage, nature of the pathological process, and obtain other accurate indicators based on which adequate treatment is selected.
Prevention of keratosis
In order to avoid complications, you should adhere to the following preventive rules:
- use creams with a moisturizing effect for the skin;
- include more foods containing vitamins in your diet;
- limit exposure to sunlight;
- wear special clothing and gloves when working with chemicals;
- do not sunbathe in the sun or in a solarium;
- strengthen the immune system;
- avoid skin injuries;
- maintain hygiene;
- When diagnosing dermatosis, undergo regular examination by a dermatologist.
Diagnostic methods
A dermatologist makes a diagnosis of a skin disease based on an external examination of the patient. Hyperkeratosis is determined by the location of the papules, their structure and color. In some cases, if another disease is suspected, the patient is referred for a biopsy.
The collection of material for analysis is carried out by scraping or excision of part of the pathological formation on the skin. The procedure is carried out using special instruments and is completely painless.
The results of the study become known in one to six days. After taking biological material, no strict rules of behavior are required; you just need to avoid exposure to water on the damaged area of the skin.
A correct diagnosis and determination of the type of hyperkeratosis is an important step towards the patient’s recovery.
Treatment methods for keratosis
Keratosis is eliminated through drug treatment. Folk remedies are used as additional therapy and only after consultation with a specialist. Physiotherapeutic procedures are used to relieve pathology. In case of complicated course of the disease, they resort to the surgical method.
Medications
| Antibiotics | Zinnat, Doxycycline, Azithromycin |
| Ointments | Efudex, Fluorouracil, Imicvod, Fluoroplex, Solcoderm |
| Vitamin complexes | Milgamma, Bnevron BF, Vitamin A Bartel Drugs, Retinol |
The drug Zinnat is used for the inflammatory process. Prescribed 500 mg 2 times a day. The course of treatment is 7-10 days. The cost of the drug 500 mg is 420 rubles. There are 10 tablets in a package.
Imicvod ointment is used 3 times a week. Treatment should continue until symptoms disappear completely. The maximum course of treatment is 4 months. The price of the drug 5% is 5087 rubles. The tube contains 250 mg of the substance.
Vitamin A capsules Bartel Drugs take 1 tablet per day 15 minutes after meals. The duration of treatment is determined by the doctor. The cost of the drug is 150 rubles. There are 50 capsules in a package.
Traditional methods
To relieve the symptoms of keratosis, you can use folk remedies:
- Agave leaves, after three days of freezing, are applied to the affected area overnight. After removing the compress, the keratome is treated with salicylic alcohol. The course of treatment lasts 3 weeks.
- Grated raw potatoes are applied to the affected area. The top of the potatoes is covered with a clean cloth and cellophane. After 40 minutes, the bandage is removed and the potatoes are washed off with water.
- Take 2 tbsp. l. dry leaves of celandine. They are filled with 250 ml of boiling water. The mixture is infused for several hours. Lotions are made on its basis. You can wipe the skin with the infusion.
- Take 1 tbsp. l. onion peels. Pour 1 tbsp of vinegar into it. Leave the mixture in a dark place for a week, then strain. It is recommended to make lotions. They are left on the affected area for 30 minutes. It is important to avoid contact with healthy areas to avoid burns.
Other methods
Since conservative treatment is not effective in all cases, they resort to drastic measures - removal of growths. They are especially used when there is a possibility that the tumor will degenerate into a cancerous tumor.
The following types of treatment are used:
- Cryodestruction . It involves freezing the growths using liquid nitrogen. The method is used when the skin lesion is extensive. When frozen, plaques undergo necrosis. A possible complication of the operation may be increased skin pigmentation.
- Removal via radio waves . This manipulation involves excision of the tumor with a radio knife under the influence of radio waves.
- Electrocoagulation. Represents cauterization using high-frequency electric current. Performance involves anesthesia. There is a risk of scarring and age spots.
- Laser destruction . A targeted effect on the keratoma with a carbon dioxide laser is used. This is the most effective method of treating keratosis, which is characterized by painlessness, speed and absence of side effects.
- Photodynamic therapy involves the application of methyl aminolevulinate followed by exposure to a light wave of a given length. This process causes tissue necrosis. In this case, healthy tissues are not damaged. After the procedure, you should not be in the sun for 48 hours.
- Curettage is used to treat solar keratosis . This is an operative method in which individual areas of the lesion are scraped out using a curette. Curettage is not used to treat the actinic form, as it can cause scarring.
- Dermabrasion . Removing tumors using an abrasive brush.
- Plasmolifting involves the use of plasma injection, which stimulates local immunity and promotes skin regeneration.
- Biorevitalization involves injections of hyaluronic acid, which improve the morphology of the skin, promote rejuvenation, and increase the level of regeneration.
- Chemical peeling . It is used for minor lesions. For chemical treatment of warts, lactic or glycolic-salicylic acid is used.
Symptoms
Facial hyperkeratosis causes symptoms such as:
- excessive dryness of the skin;
- thickening of certain areas of the skin;
- pain, itching, sometimes burning and tingling;
- redness of the affected areas;
- the appearance of crusts and peeling;
- the appearance of papules, nodules, pimples.
When the facial muscles move, the crusts usually burst and bleeding, painful cracks appear. Often there is a light stripe around the lips, which flakes and causes a feeling of tightness of the skin.
Possible complications
The main complications of keratosis include:
- development of microbial eczema;
- dysfunction of the nervous system;
- degeneration of growths into a cancerous tumor;
- tooth loss.
Keratosis of the skin is fraught with serious complications, and the photo of adults shows that this pathology is a serious skin disease that requires treatment by a dermatologist and excludes self-medication.
Article design: Oleg Lozinsky
Forecasts
The outcome of the disease depends on the type and extent of the keratotic process. In general, the prognosis is favorable with timely treatment and compliance with medical recommendations. In the absence of proper treatment, the development of microbial eczema, malignant neoplasm, tooth loss, hyperpigmentation, disruption of the endocrine system, and the development of depression are possible.
The most unfavorable prognosis is considered to be the senile form of keratosis. Plaques do not disappear on their own, as, for example, with the follicular form. This is a precancerous condition: in the absence of treatment, irrational therapy, and constant trauma to the lesions, degeneration into squamous cell carcinoma is possible. Malignancy occurs in 2–5% of cases.
Ichthyosis can be complicated by metabolic disorders, folliculitis, progression of chronic diseases, and the addition of new systemic diseases. If ichthyosis is detected in the fetus, it is recommended to terminate the pregnancy.
The risk group includes people with fair skin, a family history, those living in a sunny, hot climate, those who have undergone radiation and chemotherapy, and those who are HIV-infected.
Symptoms of hyperkeratosis + skin photo
The main symptom of the pathology is thickening of the skin in areas where strong pressure occurs. The affected areas look like lumps, sensitivity in them is reduced, and the skin color may change to lighter or darker. At an early stage, the skin simply appears rougher than the surrounding tissue, then thickening appears. Severe foot hyperkeratosis can impair gait.
Follicular keratosis is manifested by the appearance of epidermal scales on dry skin in the area of hair follicles (“goose bumps”). It is quite difficult to see the affected areas if they are single - these are small white or brown dots. If they are removed, normal skin is revealed underneath and they do not affect hair growth. Multiple keratosis pilaris can greatly spoil the appearance.
What does hyperkeratosis look like in the photo?
Hyperkeratosis on the face
Skin hyperkeratosis
Treatment
Patients often treat skin hyperkeratosis at home. However, if the disease is associated with chronic pathologies, it is quite difficult to cure it without a course of appropriate therapy . It is possible to get rid of skin hyperkeratosis only in a comprehensive manner; patients must follow the doctor’s recommendations and carry out constant cosmetic skin care.
How is hyperkeratosis treated? Main areas of treatment:
- Therapy of chronic diseases (lichen, diabetes, psoriasis, dermatitis, etc.).
- Use of drugs with topical corticosteroids and topical tretinoin. These medications come in the form of ointments and gels. The drugs relieve inflammation and normalize the process of “exfoliation” of the skin. The most effective drugs are Dermovate, Sinaflan ointments, prednisolone ointment, etc.
- Including foods rich in vitamins A, B and C in your daily diet.
- Constantly moisturize the skin, use cosmetic creams, body milk, oils to soften and moisturize the epidermis.
- Chemical and mechanical peelings (for foot hyperkeratosis).
- Taking baths with added salt, baking soda and starch.
Advice! Peels using AHA acids are perfect for removing dead skin.
Treatment of skin hyperkeratosis is long-term, periods of remission are replaced by exacerbations. To speed up the healing process, doctors recommend:
- wear comfortable shoes and clothes that fit;
- Healthy food;
- lead a healthy lifestyle;
- treat chronic pathologies in a timely manner;
- constantly moisturize the skin and use suitable care products;
- do not stay in the sun or frost for a long time, etc.
A prerequisite for a speedy recovery is compliance with the rules of personal hygiene. Otherwise, when microbes enter, skin problems may be aggravated by the development of an inflammatory process.
We recommend studying this topic:
Keratosis: types, causes and treatment of skin keratoma
9642
0
5
reading information