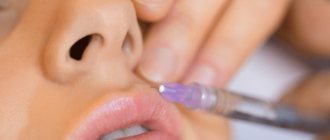
What is electrocoagulation
Electrocoagulation is one of the most effective methods for removing moles, papillomas and warts
Electrocoagulation is one of the most effective methods for removing moles, papillomas and warts from any area of the skin.
To carry out the procedure, an electrocoagulator is used - a device with a small loop that can become very hot. It is she who, in contact with the skin, eliminates unwanted tumors. In one session, you can remove either one or several growths.
The loop itself is so small that even tiny moles and warts can be treated with it. During the procedure, small vessels are cauterized, which eliminates bleeding.
An electrocoagulation session takes only a few minutes. To avoid pain, local anesthesia is given before the procedure.
Reviews
NATALIA, 28 YEARS OLD:
“I had a large mole on my neck for a long time.
In principle, she did not interfere with life, but I constantly touched her with the chain and collar of my clothes. One day I accidentally pulled the collar of my shirt particularly hard, which I thought was torn off. I was terribly scared. I've read all sorts of horror stories about cancer and how you shouldn't damage it. I decided that I should try to delete it. I live in a small town, so I signed up for such a serious procedure at a clinic in the regional center.
At the consultation, the doctor carefully examined my long-suffering mole and said that it could be removed right now. He gave an anesthetic injection, and after 5 minutes I cut it off with a small device.
My happiness knew no bounds. And when the results of histology of the cut tissue came back, I felt better. Now I’m thinking, why did I suffer for so long? It cost little money, but the result is priceless. Now at least wear a choker or wear a golf.”
ALLA, 39 YEARS OLD:
“I treated cervical erosion with electrocoagulation.
Somehow nothing was bothering me, so I delayed visiting the gynecologist and kept putting it off. When I finally got checked and found out about the erosion, I panicked. Thanks to the doctor I saw, she did everything carefully. The mucous membrane has recovered. I’m thinking of going to remove the papilloma on my back in the same way.”
SERGEY, 28 YEARS OLD:
“I’ve never had warts, but six months ago they started spreading all over my arms.
Celandine and this all didn’t help. I decided that I needed to make an appointment with a doctor, otherwise I would be embarrassed to take a girl’s hand. In principle, I knew what I was getting into, because once in college I even wrote an essay about electrocoagulation, how it works and where it is used.
There were a lot of warts, they were removed in two times. The palms and fingers looked terrible, all covered in dark crusty spots. But when they healed, I felt like a different person. So far everything is clean, not a single new wart.”
Now you understand what electrocoagulation is. It remains one of the best methods for combating tumors on the skin and mucous membranes.
The procedure is effective, safe and affordable. In just one session you can get rid of unaesthetic papillomas and warts, as well as formations prone to degeneration.
Types of electrocoagulation
Electrosurgical high-frequency devices (ECHF) are called differently in different sources. They are called radio knives, radio scalpels and coagulators. However, EHF is the most complete and accurate name, reflecting the device’s ability to produce alternating current of the required frequency.
Today, EHF devices are capable of removing various formations on the skin, both by contact and non-contact methods.
Contact methods:
- Electrical cauterization;
- Electrical agulation;
- Electrical section;
- Electrical desiccation;
Non-contact methods in which the working electrode does not come into contact with the skin:
- Plasma coagulation;
- Electrical fulguration (SPRAY-coagulation).
Each of the above methods has certain pros and cons, but in our article we will cover in detail the electrocoagulation method.
What are the advantages of laser coagulation of varicose veins
A technique such as laser coagulation of varicose veins is a modern method that allows you to get rid of the manifestations of varicose veins of the lower extremities using the thermal energy of laser beams.
This method of treatment does not require hospitalization of a person in a surgical hospital, but can be performed on an outpatient basis.
Another undoubted advantage of non-surgical laser treatment of varicose veins is the absence of the need for surgical incisions, which significantly shortens the recovery period and does not leave postoperative scars on the legs. Under the influence of laser radiation, the walls of the veins become sclerotic and the pathological blood flow in them stops. The procedure does not cause any pain.
Since endovenous laser coagulation is a surgical technique, it also has its own postoperative period. Immediately after vein obliteration, the patient is given a compression bandage (special compression hosiery can be used). This round-the-clock compression should last 5 days. This is a prevention of the resumption of pathological blood flow in the treated vein, thrombophlebitis and thrombosis. Further compression is necessary for 2 months, but only during the daytime.
On the 2-3rd day, you must go to the clinic for a follow-up examination. In this case, it is necessary to conduct an ultrasound with color Doppler to confirm the absence of blood flow in the coagulated veins.
As a rule, the results of the manipulation are good, but in a certain number of patients, recanalization of coagulated veins occurs after a certain time.
Blood flow resumes again and the symptoms of the disease return, which requires repeating the procedure. There may be several reasons for this phenomenon: insufficient postoperative compression, the development of thrombophlebitis, thrombosis.
Hardware coagulation has great potential, and not only in cosmetology. Until recently, defects such as capillary or cavernous hemangiomas could only be removed through surgery, which left scars that distorted the face. But today, thanks to laser coagulation, such defects are corrected not only without consequences, but also painlessly. Read about other modern methods of treating varicose veins without surgery in our separate article.
When a patient has to remove a tumor, he is faced with a choice: laser or Surgitron device? Doctors believe that it is better to resort to a proven and effective method that has maximum advantages, that is, radio wave intervention using Surgitron. Why? This question can be answered by comparing the advantages and disadvantages of both methods of surgical intervention.
The advantages of Surgitron over laser are as follows:
- The recovery period after surgery takes much less time;
- either a minor cosmetic defect or no traces of the operation remain on the skin;
- the use of the drug requires greater control by a specialist during surgery;
- surrounding tissues are less injured, which is an important point for the health of the whole organism.
In addition, the device has only a few contraindications for health reasons, which cannot be said about the laser procedure, which should not be performed if the patient has a cold, an inflammatory process in the dermis, even a slight increase in body temperature and herpes.
Therapy with Surgitron is considered the most accessible and effective all over the world. Its undoubted advantage over laser is that the procedure does not have serious complications and consequences. A laser cannot allow a specialist to control the depth of penetration into tissue as precisely as possible, therefore such coagulation is considered more dangerous than radio waves. Gynecologists note that only the Surgitron device is capable of removing formations on the cervix without consequences in women who have not yet become mothers.
If a patient is about to undergo surgery using the Surgitron device, despite its many positive qualities, it is worth taking the process responsibly. It is necessary to worry about your health before surgery and ask your doctor about further actions after treatment. The doctor must explain all the pros and cons of the technology used, point out its features, talk about the possible consequences and describe the restorative course of therapy after it is carried out.
Indications for the use of electrocoagulation
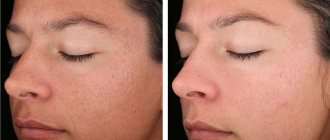
Electrocoagulation is used to remove common moles
New growths on the skin are divided into three types: moles, papillomas and warts. Electrocoagulation is equally effective against any of them. However, before the procedure, it is better to consult a doctor to rule out the malignant nature of the growth.
A common mole is a collection of pigmented cells that are dark in color due to the increased content of melanin. As a rule, such formations themselves are safe and cause inconvenience only from an aesthetic point of view. However, a damaged mole can easily become infected, which will lead to widespread inflammation of the surrounding tissues. Therefore, if the tumor is located in an inconvenient place and is constantly injured, it is recommended to remove it.
In our clinic, you can get rid of a mole on the same day of treatment. In preparation for the procedure, the doctor will also take a histological sample in order to carry out deeper tissue removal if necessary.
Warts and papillomas, unlike moles, are caused by a virus. In a passive form, it occurs in most people, but manifests itself externally in a few.
Papillomas are tumor-like benign formations that, as a rule, do not cause inconvenience. They, like moles, can be removed for aesthetic reasons or to prevent infection if they are constantly injured.
Warts are not particularly pigmented and are not the result of any pathology. They are also only benign formations. Their removal using electrocoagulation is an easy and virtually painless procedure.
These types of neoplasms are not dangerous to human health. However, any manipulation of them should only be carried out by medical professionals under appropriate conditions. Attempts to get rid of moles, papillomas or warts on your own can lead to serious consequences, including blood poisoning or degeneration of the growth into a malignant tumor.
On the contrary, electrocoagulation is the simplest and safest way to get rid of any benign neoplasm.
Laser coagulation technique
Laser medicine is developing at a rapid pace, and cosmetology is no exception. Such methods of treatment and prevention of cosmetic defects are gradually replacing all similar techniques - cryodestruction, and even electrocoagulation.
Using a special installation that generates laser beams (the length, intensity of the beams and other characteristics depend on the purpose of the method), the defective areas are affected. The rays penetrate deep into the skin, but they do not injure the skin itself, heat and coagulate unwanted elements. During the procedure, the impact on surrounding tissue is minimal.
Laser coagulation is most successfully used for vascular defects (hemangiomas, vascular mesh, telangiectasia, spider veins, port-wine stains, varicose veins) and pigmentation (freckles, birthmarks, lentigo, tattoos).
The mechanism of laser action on capillary formations is as follows. The beam penetrates the skin and is absorbed by blood cells that are currently in the vessels of the area being affected. The blood heated in this way coagulates in the middle of the capillary, and the vessel sticks together and sticks together.
To achieve the effect, you need to conduct from 2 to 5 therapy sessions. Laser coagulation of blood vessels on the face is especially popular, as it is painless, quick, and most importantly, it does not leave scars, which is very important in such cases.
Using a laser you can get rid of the following defects:
- rosacea (visible network of subcutaneous capillaries);
- capillary hemangiomas;
- varicose veins on the lower extremities;
- port-wine stains;
- congenital pigment defects;
- spider veins;
- seborrheic keratosis;
- tattoos
There are no absolute contraindications to the procedure. Relative ones can be:
- pregnancy (read a separate article on how to deal with varicose veins during pregnancy);
- oncological diseases;
- diabetes;
- diseases of the cardiovascular system;
- skin diseases in the area of application;
- active infectious process.
Electrocoagulation methods
Electrocoagulation can be used on any area of the skin
Electrocoagulation is a medical procedure during which soft tissue is cauterized in the desired location using an electric current. The electrocoagulation method involves the use of a device in monopolar or bipolar mode, which provides radical removal, or electrical destruction, of non-cancerous formations that have arisen on the integument of the body. Such formations include: moles, warts and calluses, inflammatory elements of acne and rosacea, tattoos, genital warts and papillomas. Electrical coagulation is also carried out to achieve hemostasis, remove hair, nail matrix and destroy individual blood vessels.
This procedure can be used on any area of the skin. Before electrocoagulation, local anesthesia is administered to avoid pain. The procedure has proven effective in treating and getting rid of senile keratomas and hypertrichosis. Electrocoagulation is a relevant and effective method, and the results of the procedure are comparable to the effect of laser skin treatment.
What is the difference?
Despite the common thermal mechanism of tissue destruction, these procedures have significant differences. Electrocoagulation involves exposure to a constant electric field, i.e. it is necessary to ensure that the heated electrode touches the skin. To remove flat and convex formations, a nozzle with a ball is used, which is moved over the skin until the pathological structures are completely destroyed.
In the case of a growth “on a stalk”, use a loop attachment, with which it is simply tightened at the base and burned out. One of the advantages of this method is the immediate “soldering” of blood vessels, which significantly reduces the risk of infection.
Laser exposure is conventionally called non-contact , since the electrode only produces a beam that already touches the epidermis. However, it is still painful and requires prior anesthesia. In this case, a high-frequency alternating field is used, which penetrates deep into the tumor, accompanied by a uniform distribution across the cell layers.
Another characteristic difference is the order of biopsy to assess the histological picture of the affected tissue. With conventional electrical stimulation, a sample can be taken both before and after the procedure, while laser radiation completely destroys the cells, so a biopsy is performed in advance.
Although it is believed that laser has fewer contraindications than electrocoagulation, the possibility of using a specific technique is determined strictly on an individual basis.
Specifics of the method
The procedure is carried out exclusively in specialized beauty salons. New growths are removed using electrodes - active and inactive. A lead plate or foil is used as an inactive electrode. The material is placed under the thigh, buttock or other part of the body, and basic manipulations are performed with the active electrode.
To make it easier to remove defects, there are different types of active electrodes, which can look like a ball, a thin needle, a knife, a straight or curved loop.
The electrodes are connected to a device that operates in several modes and generates several types of waves:
- Long electric waves. They have a cutting effect. In this mode, they mainly work to cut the subcutaneous tissue and the skin itself. In addition, in medical cosmetology they use this method to cut off and eliminate pathological neoplasms - large warts and pedunculated moles.
- Short electric waves. Their action is more gentle. Such waves are used to cauterize wounds during the destruction of a cosmetic defect. Birthmarks, spider veins, hemangiomas, papillomas, tattoos, and genital warts can be removed in a similar way.
Types of effects of electrical impulses on the skin
The effect of high-frequency electric current on living epithelial cells is divided into several types:
- Physico-chemical impact – as a result, the physico-chemical balance inside the cell is disrupted.
- Thermal effects - after strong heating of the fabric, a burn forms on its surface.
- Electro-dynamic effect - blood, lymph or interstitial fluid is heated until a certain amount of steam is released, which provokes a sharp rupture of tissue.
- Biological effect - irritates healthy tissue around the damaged one, thereby accelerating the healing process.
Specifics of the electrocoagulation process
The procedure for removing skin tumors is carried out using a special medical device - an electrocoagulator.
The procedure for removing skin tumors is carried out using a special medical device - an electrocoagulator. The working element of this device is a loop heated to a high temperature by electric current. The tissue around the defect is affected after contact with a heated loop, and a crust forms at the site of contact, which should be treated for several days after electrocoagulation with a five percent solution of potassium permanganate. The healing process lasts a week and a half, during which the crust should not be removed or wetted. After healing, the crust falls off on its own, leaving behind a pink area of young skin, which after some time takes on a healthy appearance. If small-sized condylomas were removed, then no trace remains at all. The duration of removal using electrocoagulation is from ten minutes to a quarter of an hour.
Electrocoagulation can also be used for hemostasis. In this case, a monopolar mode of operation of the device is used, which involves direct contact of the working electrode with the vessel from which bleeding must be stopped.
Before starting the procedure, the wound is dried with tampons, and then the vessel is touched with an electrode at least for a short moment.
The achievement of complete coagulation can be judged by the discoloration of the operation site, after which the device is turned off and its effect on the vessel stops to avoid injury to surrounding tissues.
Rehabilitation after electrocoagulation of tumors
During the first week, skin wounds are treated with an antiseptic. This may be a solution of potassium permanganate. Treatment must be carried out daily. During this period, visiting the pool, sauna and bathhouse is not recommended.
Prolonged exposure to the sun should be avoided and the surgical site should not be exposed to ultraviolet light. Do not rub the treatment area with a hard washcloth.
Dermatologist Marty Gidon
The postoperative crust is a natural barrier against microorganisms. Its removal, as well as accidental or intentional mechanical impact on the treated area of skin can provoke the formation of scar tissue at the site of the cut.
If the epidermis in the area of electrocoagulation changes color or any other changes are observed, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Procedure
Just a few seconds are enough to remove a wart, mole or other cosmetic defect using electrocoagulation. The procedure is well tolerated, but it is quite painful, so local anesthesia is used for the patient’s comfort and peace of mind. Immediately before the start of manipulation, the desired area is disinfected using a special antiseptic solution. To remove a formation that rises above the surface of the skin, a knife electrode or loop electrode is selected. Flat cosmetic defects are destroyed by cauterizing them in layers in several approaches. In this case, a flat or ball electrode is used. All layers of the tumor are removed with great care. If a visible “pit” remains at the site of a mole or papilloma, the edges of the depression are smoothed using the same electrode and then cauterized. Point defects, such as small spider veins, are eliminated using a needle electrode.
Mole removal procedure
No additional preparation is required for electrocoagulation. The manipulation itself takes from 15 to 30 minutes. First, the doctor does an allergy test for medications. If there are no allergic reactions to medications, you can safely proceed to anesthesia. The patient is given local anesthesia or a special cream is applied to the skin. Next, using the device, the mole is excised layer by layer. At the time of removal, the skin at the site of the growth is cauterized. Cauterization of the epidermis and blood vessels occurs due to exposure to very high temperatures. Electrocoagulation allows you to solve the problem of bleeding, swelling and infections.
During the manipulation, a person will not feel discomfort or unpleasant sensations. The patient may only feel a slight tingling sensation in the area where the nevus is excised. After manipulation, a scab (protective crust) forms in its place. The scab protects against infections from entering the wound and prevents bleeding. The wound healing period varies from 7 to 10 days.
Advantages of the electrocoagulation technique
Electrocoagulation has gained recognition and sympathy among many beauty salon clients for several reasons:
- Using this method, you can get rid of any neoplasm (warts, moles, papillomas and many others) in just one step.
- Samples of removed tissue can be submitted for histological examination (to determine the nature of the disease).
- If a small area is being treated, there is no need for anesthesia.
- Absolutely any benign neoplasms are susceptible to exposure.
- Affordable cost of electrocoagulation.
Disadvantages of electrocoagulation
- The disadvantage of electrocoagulation in the treatment of plantar warts is the painfulness of the procedure
not for use on large areas of skin
- longer healing period due to the involvement of nearby healthy tissues in the process
- very painful removal of warts, especially those located on the soles and feet, as well as prolonged and painful healing, often with scarring
- when removing large elements, healing with scar formation
- not recommended for removing large elements in cosmetically significant areas (face, open décolleté, neck)
In what cases is it contraindicated?
There are cases when electrocoagulation has contraindications. The reason for this is possible negative consequences in the form of deterioration of the condition, as well as other clinical cases.
It is not recommended to apply for the procedure to patients who have the following diseases and pathologies:
- acute reaction of the body to the current;
- allergy to disinfectants;
- problems with blood clotting;
- the presence of viral diseases;
- blood sugar problems;
- psychical deviations;
- cancer diseases.
Also, those who have implants or a pacemaker should not sign up for a session.
Features of recovery after the procedure
In the first days after the electrocoagulation procedure for moles, papillomas, acne and other elements that spoil the appearance, the patient needs to carefully monitor the condition of the area on the surface of which the electrode was used. A scab gradually forms at this site. Dead tissue needs to be treated with a solution of potassium permanganate 5%.
It is impossible to tear off the crust from a dried wound, otherwise an infection will penetrate there - suppuration will form on the vulnerable tissue and, most likely, a scar will remain.
You need to wait until the wound disappears on its own. On average, this occurs 10–12 days after electrocoagulation. If you do not interfere with this natural process, new healthy skin without scars will appear at the site of the defect.
How is the procedure performed?
Electrocoagulation of the skin is carried out using a mono or bipolar electrode in the form of a needle, knife, loop or ball - depending on the type of tumor.
Preparation for removal involves disinfecting the surface of the problem area and applying local anesthesia. When eliminating minor defects, there is no need for anesthesia.
The current passing through the tool nozzle locally heats the tissue at the base of the formation and destroys the protein.
The entire protruding part is rejected and a neat hemorrhagic crust forms on the surface of the epidermis or mucous membrane.
As a rule, the mini-operation lasts no more than a minute, after which the patient can return to normal activities.
During the procedure, the doctor can remove up to 30 small tumors located in one area.
Dermatologist Karen Beasley
The scab that forms at the cut site should be treated with a special solution for the first time.
You cannot remove the crust: with a high degree of probability, the open wound will fester, and an ugly scar will later form in its place. The complete healing process lasts from 8 to 12 days. The scab will fall off on its own, leaving virtually no mark on the skin.
When the vascular mesh is removed, a thin needle electrode is used. The doctor pierces the skin surface with it. Anesthesia is required.
Dermatologist Karin Litani
Before performing electrocoagulation, you should consult a specialist. Depending on the location of the tumor, this may be an oncologist, gynecologist, dermatovenerologist, or otolaryngologist.
The doctor will conduct an examination, determine the type of formation using dermatoscopy (hardware examination) and evaluate the possibility of its removal.
Electrocoagulation of ingrown toenails is always performed under anesthesia. After the operation, the patient is prescribed analgesics and recommended to remain in bed for 24 hours.
Dressing is performed as necessary. Complete healing requires 2–3 weeks, during which physical activity should be limited.
Electrocoagulation technique on the face
Electrocoagulation of papillomas on the face allows you to quickly and painlessly remove a tumor
Electrocoagulation is a very simple procedure, which is confirmed by the video.
First you need to treat the skin with an antiseptic. When sealing the vessel, the electrode in the form of a needle is inserted into the thickness of the skin, approximately a millimeter. After all the vessels have been treated, the skin must be treated with an antiseptic again. Next, corticosteroid ointment is applied.
After electrocoagulation, in order to avoid suppuration and inflammation of wounds received during the procedure, you need to lubricate the skin with any of the antiseptic solutions twice a day. Preferably not with alcohol, because it dries out the skin a lot. Chlorhexidine or potassium permanganate is best.
After a coagulation session, crusts will appear on the skin, which under no circumstances should be touched, and especially not picked off, because this can cause scarring.
Vascular electrocoagulation is one of the few procedures that are aimed specifically at combating these unsightly spider veins on the face, and quite successfully, as evidenced by reviews from many patients.
Is it better to remove papillomas with laser or electrocoagulation?
1757
Papilloma is a benign neoplasm that can appear on almost any part of the human body. Externally, papilloma resembles a wart or genital wart.
Causes of neoplasms
One of the main reasons leading to the appearance of papillomas is HPV (human papillomavirus). In addition, the tumor may be to blame for:
- unprotected sex or indiscriminate change of sexual partners;
- disruptions in the hormonal system;
- pathologies of the digestive system;
- various pathological addictions: smoking, drugs, alcohol abuse;
- reduced immunity;
- contact with an infected person in the presence of wounds, scratches, burns, etc.;
- neglect of personal hygiene rules, etc.
In addition, an infected mother can pass the virus to her baby during natural childbirth.
It is impossible to cure HPV, it is only possible to drive it into a stage of stable remission with the help of immunomodulators and by changing your usual lifestyle.
To identify the human papillomavirus, it is necessary to donate blood for general and biochemical analysis, a biopsy from the affected area and conduct a PCR test.
Methods for removing papillomas
Today, there are 4 main methods for combating skin tumors:
- Surgical removal . The papilloma is removed with a scalpel under local anesthesia;
- Cryodestruction . Cauterization of the growth with liquid nitrogen;
- Electrocoagulation . Cauterization of skin tumors with high frequency current;
- Laser therapy . Exposure of the tumor to a red or infrared laser beam.
Electrocoagulation and laser removal are currently the most popular, each having its own advantages and disadvantages.
Removal of papillomas using electrocoagulation
Electrocoagulation is used to remove almost all skin tumors. The manipulation device vaguely resembles a soldering iron with a set of attachments; to remove papillomas, a loop attachment is used that wraps around the tumor.
The exposure time to alternating current depends on the size of the build-up and varies from 20 seconds to 20 minutes. On average, it takes no more than 7 minutes to remove a skin growth.
Since electric shock can cause discomfort to the patient, adults are given local anesthesia, and children are given general anesthesia.
After removing the growth, the affected area is treated with an antiseptic solution and the patient is given recommendations on taking antiviral and immunomodulatory drugs.
A crust appears at the site where the papilloma was removed, which disappears on its own after a few weeks. You can’t rub or wet it, much less rip it off, because infection can get through an open wound.
Contraindications to the procedure
Electrocoagulation is prohibited for any pathology of the circulatory system, including impaired coagulation. In addition, the procedure is not carried out if:
- persistent hypertension;
- decompensated diabetes mellitus;
- hormonal disorders;
- during periods of exacerbation of viral and infectious diseases.
Laser removal of papillomas
Laser therapy is one of the newest and highly effective techniques that can be used to remove tumors reaching a diameter of 2-3 cm.
Removing papillomas with a laser does not take much time. Before using the laser beam, the patient is given local or general (depending on the area of exposure) anesthesia. The type of beam and intensity of the laser beam directly depends on the size and number of skin tumors. Small papillomas can be removed in one procedure; large ones may require up to 4 sessions.
Under the influence of the laser, the cells of the virus that causes papillomas are destroyed, and the blood flow that feeds the tumor is cut off.
However, the above complications occur extremely rarely and are often the result of the actions of an unqualified specialist or due to the patient’s neglect of the recommendations given to him.
Contraindications to laser removal of papillomas
There are a number of absolute contraindications to laser therapy:
- pregnancy;
- heart pathologies;
- exacerbation of chronic diseases;
- diabetes;
- viral, fungal or bacterial infection of the skin.
Contraindications to electrocoagulation
- intolerance to electrical procedures and drugs for local anesthesia
- blood clotting disorder
- suspicion of a malignant nature of the skin formation
- acute infectious diseases
- herpes skin rash
- presence of a pacemaker
- rapid growth of benign neoplasms
- systemic blood diseases, leukemia
- increased skin sensitivity to light (photodermatoses)
- endocrine diseases (decompensated diabetes mellitus, etc.)
- diseases of the cardiovascular system (crisis course of arterial hypertension, heart and pulmonary failure stage 3)
Contraindications (10 prohibitions)
Electrocoagulation should not be performed if one or more of the following factors are present.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
- malignant neoplasms;
- herpes in the active stage;
- blood diseases and blood clotting disorders;
- allergy to anesthetics;
- individual intolerance to electrical procedures;
- presence of a pacemaker;
- tendency to form keloid scars;
- inflammatory process in the treatment area;
- any somatic diseases in the acute phase;
- pregnancy and breastfeeding.
The procedure costs 350-1200 rubles. It all depends on the amount of work.