Keratosis - main symptoms:
- Itchy skin
- Hair loss
- Dry skin
- Skin pigmentation
- Hair fragility
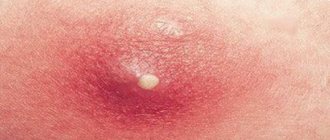
- The appearance of blisters
- Pain syndrome
- New growths on the skin
- Appearance of warts
- Dandruff
- Cracks in the skin
- Dull hair
- Scales on the skin
- Dry hair
- Split ends
- Skin roughness
- Formation of areas with keratinized skin
- Thickening of the skin
- Change in skin tone
- Bleeding skin
Causes of keratosis
The causes of keratosis are endogenous and exogenous factors, depending on the form of the disease.
Common reasons include:
- exposure to ultraviolet radiation is the most common cause of keratosis of the facial skin;
- damage by aggressive chemicals;
- injuries;
- insect bites that produce toxins;
- skin infection for various reasons;
- inflammatory processes of the skin, exposure to bacteria, fungi, viruses;
- somatic diseases, especially inflammation of the digestive system, nervous diseases, pathologies of the heart and blood vessels;
- metabolic disorder;
- decreased immune status;
- hematopoietic disorder;
- endocrine disorders;
- benign and malignant neoplasms, especially blood and skin;
- allergic reactions;
- hormonal changes;
- old age;
- heredity (Darier's disease, Mibelli's poroquetosis, Miescher-Lutz elastosis).
Keratosis in a child can develop as a result of intrauterine intoxication. There are frequent cases of pathology developing against the background of other skin diseases, for example, atopic dermatitis (allergic reactions associated with genetic disorders).
Etiology
The exact cause and mechanism of development of the pathology have not been established to date, but experts in the field of dermatology have identified a large number of predisposing factors - both physiological and pathological.
Acquired keratosis pilaris in children or adults can develop or worsen against the background of such unfavorable sources:
- hypovitaminosis - a lack of vitamins A, C, D and group B in the human body;
- poor nutrition - an excess of fatty and spicy foods, salty foods, strong coffee on the menu;
- long-term use of hormonal substances;
- prolonged exposure to stressful situations or severe emotional stress;
- cold season - clinicians note that in the summer season the nodules completely disappear;
- the course of tertiary syphilis;
- immunodeficiency conditions, such as HIV infection;
- verrucous tuberculosis of the skin;
- fungus on the feet;
- diseases of an autoimmune nature - systemic lupus erythematosus, scleroderma;
- allergic processes;
- hormonal imbalance - the appearance of characteristic signs is often observed in women during pregnancy or after childbirth;
- prolonged contact of open areas of the skin with X-ray or other types of radiation, chemicals or toxic substances;
- wearing clothes made of synthetic fabrics;
- chronic pathologies of the digestive system.
Experts have found that the disease is congenital and may even have a genetic predisposition.
The main risk group consists of children and adolescents - in them the disease is diagnosed in 50 to 80% of cases. Among the adult population, the incidence is 40%.
Classification
Conventionally, pathology is divided into several types.
By degree of distribution:
- Diffuse - almost the entire surface of the skin is affected.
- Localized (focal) - specific areas of the body are affected.
By origin:
- Congenital - the prerequisites for the disease are laid in intrauterine development.
- Acquired - occurs at any age under the influence of external or internal factors.
- Symptomatic is one of the manifestations of dermatosis.
By localization:
- Keratosis of the cervix.
- Follicular (hyperkeratosis) - blockage of the hair follicle by epidermal scales.
- Keratosis of the facial skin.
- The scalp.
- Plantar keratosis.
- Keratosis of the vulva.
- Keratosis of the feet.
For development reasons:
- Solar keratosis (actinic) is a reaction to excessive exposure to sunlight. In older people, senile keratosis, a precancerous condition, may occur.
- Actinic keratosis or seborrheic - “senile warts”, basal cell papilloma.
- Pilar keratosis (pilaris) is inherited, the most common (50–80% of all skin pathologies in adolescents, 40% in adults).
- Lichenoid keratosis - develops as a result of infection of skin formations that, when inflamed, resemble lichen planus.
- Professional – associated with constant skin contact with aggressive environments.
- Ichthyosis occurs when protein metabolism is disrupted due to a gene mutation.
The classification is conditional. As such, there is no classification of keratosis due to the variety of manifestations and causes.
Follicular keratosis photo.
Kinds
Keratinization normally occupies the following areas on the human body:
- feet;
- Hands;
- elbows;
- knees.
If pathology develops, keratinization spreads to other parts. For example, scalp, back, stomach. Keratinization is divided into 2 large groups.
It can be physiological, that is, caused by natural processes in the body. Less commonly, a pathological form occurs that occurs in the presence of diseases.
Dermatologists distinguish manifestations of keratinization of the skin:
- the formation of areas that have a brown or gray tint;
- hardening of the soles of the feet or hands;
- nodules, growths, bumps;
- yellow spots gradually increasing in size;
- pain when walking, working with your hands;
- exfoliation of the surface layers of the epidermis;
- itching causing discomfort.
Acquired keratinization of the skin is divided into types:
- symptomatic – a sign of an underlying disease, for example, with endocrine disruption;
- professional – people who use chemicals are subjected to heavy physical labor;
- oncological – benign or malignant neoplasm on the surface of the skin;
- venereal – occurs due to a sexually transmitted disease.
If keratinization is not stopped in a timely manner, it will turn into a disease. For example, keratosis (follicular, seborrheic, actinic), keratoderma, ichthyosis can form.
It is necessary to carry out the diagnostic stages and treatment prescribed by the doctor in a timely manner. Excessive keratinization is dealt with by a dermatologist.
The material was prepared specifically for the website mazikrem.ru, edited by pharmacist M.N. Aleksandrova.
Symptoms of keratosis
Provoking factors in the development of clinical manifestations may be:
- avitaminosis;
- stress;
- use of oral contraceptives;
- unhealthy food;
- lack of personal hygiene;
- cold weather.
General symptoms:
- pigmented skin;
- keratinization;
- the appearance of various formations or thickenings;
- itching;
- possible pain syndrome;
- bleeding
The nature of skin formations and symptoms vary depending on the form of the disease and location.
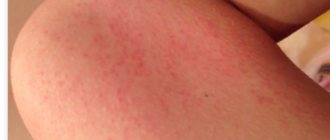
With palmoplantar keratosis, keratinization, deep cracks, and blisters appear on the heels. Roughness of the skin on the hands and feet occurs in 100% of cases, a change in the shade of the dermis from amber to brown - in 90%, increased sweating of the soles and palms - in 70%, painful cracks - in 60% of cases. Keratosis of the feet can occur when wearing uncomfortable shoes or an unsuccessful pedicure.
Keratosis symptoms
The first symptom of keratosis of the scalp is dry skin and hair, deterioration of hair condition (brittleness, dullness, split ends), dandruff. Next, keratinization appears in the area of the hair follicles, irregularities and tubercles are felt on the head, which can bleed if damaged.
As the disease progresses, hair begins to fall out in individual areas or over the entire surface at once. At the site of baldness, hair does not grow back, which is due to the death of the hair follicles.
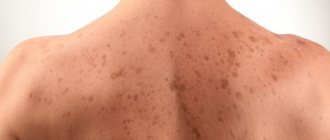
The seborrheic form is characterized by the appearance of hyper-pigmented spots, which transform into warts or plaques with clearly defined boundaries, covered with crusts. Plaques can occur anywhere on the body, plural or singular. The color of the formation varies, from flesh-colored to black. When subjected to mechanical damage (rubbing, squeezing), warts bleed.
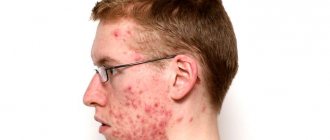
Symptoms of the follicular form usually appear at an early age. The first manifestation is dry dermis. Next, nodules with hairs on top appear, which are located symmetrically on the skin. A peculiarity in children is keratosis on the face, usually without any unpleasant sensations other than aesthetic ones. Often these manifestations disappear during adolescence due to hormonal changes.
Skin damage in the solar (actinic) form of the pathology occurs in open areas with direct exposure to ultraviolet radiation. At risk are older people, those who spend a long time in the sun, people with fair skin, HIV-infected people, and those with age spots.
The senile form is characterized by the formation of multiple fused hard scales on open areas of the body. Round or oval lesions up to one centimeter in size are difficult and painful to remove. At risk are men, people with skin photosensitivity types I – III, who are exposed to ultraviolet radiation for a long time.
Seborrheic keratosis photo.
How to treat
If the diagnosis has determined hyperkeratosis of the feet, treatment is prescribed depending on the cause and nature of the pathological condition. To eliminate hyperkeratotic manifestations, it is important to adhere to the following treatment method:
- moisturizing and softening the surface of the skin - achieved through the use of special medicinal products recommended by the doctor;
- destruction of dead horny compaction - removal of the keratinized layer of the upper layer of the epidermis is carried out by a podiatrist using a special scalpel. Essentially, this is a professional blade with attachments;
- grinding the upper skin - done independently, for example, with a pumice stone or a special brush with attachments, sold in a pharmacy. A more effective method is a procedure performed in a salon using a laser or radio waves. This method is called hardware.
All techniques are aimed at moisturizing and softening the skin in the foot area, as well as destroying the rough and dead stratum corneum. Any therapeutic measures aimed at treating hyperkeratotic foot disease are carried out after coordination with the doctor.
At home, it is possible to improve the condition of the affected areas by using special ointments and traditional medicine. Only with an integrated approach is it possible to get rid of unpleasant violations. The dermatologist prescribes treatment based on the degree and severity of the disease.
In addition to general symptoms, other internal factors are also taken into account, for example, increasing the body’s immune properties by taking special medications. An effective addition would be vitamin complexes, especially group B, since this element has a powerful regenerating effect and protects the skin from drying out.
Note. In winter, when the body especially suffers from a lack of vitamins, it is important to take additional complexes containing minerals and elements. Severe vitamin deficiency serves as an impetus for the development of hyperkeratosis.
Drug treatment
As a rule, the doctor prescribes ointments and products that are aimed at moisturizing and softening rough skin. The preparations provide healing and regenerating properties, while saturating the skin with essential elements and nutrients:
- Ointments and creams containing urea and salicylic acid - salicylic-zinc ointment, Kerasal, Elixin.
- Hormonal agents - hydrocortisone ointment, Prednisolone.
- Antimycotic drugs - cream “Fundizol”, “Sinalar K”, “Dermozolon”.
- Healing preparations - “Fulex”, balm “Flexitol”, “Lekar”, “Radevit”.
Please note that any product is selected individually. You should not self-medicate, as this leads to even greater irritation of the skin and aggravation of the condition.
How to treat at home
Hyperkeratosis of the skin of the feet at the initial stage can be treated at home. Natural remedies help improve skin condition, tighten cracks, relieve inflammation and pain.
- Wraps using sea buckthorn oil, known for its healing and soothing effects. They are done before bedtime. To do this, a large amount of oil is applied to the skin of the feet, steamed and treated with pumice, the feet are wrapped in cling film, and socks are put on top.
- Warm baths based on mineral water with the addition of calendula, chamomile and essential oils are used.
- Compresses using aloe juice and castor oil are also used. A mixture of two components mixed in equal proportions is applied to the feet, covered with film, and socks are put on top.
Often a panacea is a bath with one tablespoon of salt and one spoon of soda. The components are dissolved in water, into which the feet are then immersed for half an hour. After this, you should apply pumice, lubricate the skin with moisturizers and put on socks.
Diagnostics
The clinical picture of the disease is pronounced, so an experienced specialist can make a diagnosis based on a visual examination. To clarify the form of pathology and differentiation, a microscopic examination is carried out. Modern devices have great capabilities and provide information sufficient for a clear understanding of the disease.
The main method for the final diagnosis is histological examination of a biopsy specimen, which makes it possible to establish the type of skin formation, stage, nature of the pathological process, and obtain other accurate indicators based on which adequate treatment is selected.
Treatment of keratosis
You can get rid of keratosis with the help of comprehensive treatment after identifying the cause of the disease. The treatment is carried out by a dermatologist; you may need to consult a geneticist, endocrinologist, nutritionist, or oncologist.
The treatment complex includes:
- systemic therapy;
- diet therapy;
- symptomatic treatment;
- surgical intervention;
- local treatment;
- traditional methods.
Vitamins (A, D), fish oil, calcium and iron supplements are prescribed, and, if necessary, painkillers. The specific treatment regimen is selected individually, taking into account the causes and manifestations.
For topical use, creams, sprays, and gels based on sodium chlorite are used with a moisturizing and anti-inflammatory effect.
If you have hyperkeratosis of the feet, you should consult a podiatrist. For keratosis of the foot, treatment is aimed at careful care and hygiene procedures. First, you should soften the stratum corneum using salt baths or softening cosmetic products. The hard layer is then removed and then sanded.
A competent podiatrist carefully removes the rough layer to reveal healthy skin. To remove corns and rough skin, using a sugar cone is effective - a pedicure milling machine with a garnet-coated cutter can be used both at home and in beauty salons. Hardware procedures are hygienic and effective.
Treating keratosis at home
To treat keratosis at home, caring emollient oils (lavender, rosemary, pine oil), hand and foot baths, special lotions, and gels are used. It is especially effective to use herbal baths in the morning and evening hours before abrasive procedures, after which a medicinal ointment or oil is applied. Compresses are made from herbs with anti-inflammatory and healing effects (chamomile, sage, aloe, etc.). The main goal is to soften the formation and carefully remove it.
Lavender oil photo.
The healing properties of tar soap in the fight against skin diseases have been known since ancient times. Tar soap removes excess sebum, preventing clogging of pores, reduces sweating, dries out inflammation on the skin, fights dandruff, and makes hair stronger and thicker. Due to the content of tannins and oils in soap, it has an anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, and moisturizing effect. Skin and hair look well-groomed after using soap.
It is recommended to eat a diet that excludes canned foods, spicy, fatty, pickled foods, baked goods, sweet carbonated drinks, alcohol and those foods to which the patient may develop an allergic reaction. It is recommended to consume large amounts of vitamins contained in fresh fruits and vegetables, seafood, and cereals.
How to remove skin tags
Gentle surgical and cosmetic techniques are used to remove growths:
- Cryotherapy is indicated for large lesions; the technology involves the effect of liquid nitrogen on the formation. After freezing, the plaques undergo necrosis and are removed. A possible complication of cryotherapy is hyperpigmentation.
- Laser therapy - laser removal. The manipulation involves the impact of a laser beam on pathological lesions. This is the most effective method of combating keratotic formations, characterized by painlessness, speed, and absence of consequences.
- Diathermocoagulation - removal of lesions with electric current is performed under anesthesia. There is a high risk of scarring and pigmented spots.
- Phototherapy is the treatment of keratotic lesions with a special agent that increases the sensitivity of the epidermis to light waves of a certain length. The plaques are then exposed to light rays without damaging healthy tissue. After the procedure, you should not stay in the sun for 48 hours.
- Plasmolifting - plasma injections to stimulate local immunity and skin regeneration.
- Biorevitalization - injections of hyaluronic acid improve the condition of the skin, rejuvenate it, and increase its ability to regenerate.
For minor lesions, chemical peeling (glycolic, lactic, glycolic-salicylic) helps - the use of acids for a chemical effect on warts.
Solar keratoses are treated using curettage, a surgical technique in which localized affected areas are scraped out using a curette. Curettage is not used to remove actinic lesions on the face, since the manipulation may leave a scar.
For ichthyosis skin lesions (“fish scales”), warm alkaline baths (up to 39 degrees) help, after which the patient is wrapped in a blanket for two hours and given hot herbal tea to drink. Heat dilates blood vessels, promotes sweating, exfoliation, moisturizing the skin, and stimulates the muscle and vasomotor reflex.
An hour after the bath, the body is lubricated with salicylic acid in combination with oil or fat. Combining baths with massage is effective. The treatment is long-term.
Treatment
Medicine is currently not able to completely cure this disease. The disease occurs with periods of chronic relapses and remissions.
On this topic
- Keratosis
Let's find out what keratosis is
- Inna Viktorovna Zhikhoreva
- August 17, 2020
All treatment is aimed at temporarily improving the condition of the skin and obtaining the best result. It is worth noting that this disease does not affect the entire body as a whole, is not transmitted from one person to another through close contact, and is rather of an aesthetic nature.
To achieve the best result, you need to undergo complex treatment prescribed by a dermatologist. It includes:
- a diet rich in vitamins A, B, C and E;
- drinking 2.5 liters of clean water per day;
- separate intake of vitamins necessary for the body;
- normalization and restoration microflora ;
- restoration of liver cells;
- restoration of the endocrine and digestive systems;
- avoiding contact with allergy substances.
Many doctors recommend laser therapy, which will remove visible formations.
During treatment:
- It is worth avoiding damage to the rash, so you should avoid chemical and mechanical peeling of the skin. This can lead to the development of the disease and transition to a chronic form.
- There is no need to wear tight clothing, especially if it is made of rough and synthetic fabric.
- It is necessary to dress in accordance with weather conditions, and also avoid hypothermia or, conversely, overheating of the skin.
- You need to moisturize your skin. Glycerin, castor oil, fish oil or Vaseline and baby cream are suitable for this.
- It is necessary to limit the use of steroid drugs, especially during complications.
On this topic
- Keratosis
All about solar keratome
- Inna Viktorovna Zhikhoreva
- August 17, 2020
You can also use physiotherapy, but you should remember that although the result is achieved quickly, it does not last long, because the symptoms are being treated, and not the factors that influence the appearance. The most popular are:
- Quartzization of the skin, during which inflammation is reduced and bacteria trapped on the skin are destroyed.
- Laser hair removal helps reduce the number of ingrown hairs, which reduces the number of bumps and rashes.
- Treatment of the skin with photosensitizing substances and various radiations with red and blue colors in several stages.
- Taking baths with baking soda or sodium chloride. The amount of substances that should be added to warm water is determined by the doctor. After completing the procedure, it is worth moisturizing the skin.
Often, treatment for keratosis pilaris is based on taking various tablets, as well as creams and ointments containing salicylic acid. Any medications must be taken in strict accordance with the doctor's instructions.
Each treatment and diet is tailored to the individual characteristics of the body. You should not resort to using medications on your own, because this can worsen the general condition of the body, disrupt digestive processes, and also harm the stomach and liver.
Also, to quickly get rid of the disease you should:
- Take care of your skin and moisturize it regularly . To do this, you need to use cosmetics that contain petroleum jelly.
- Take baths with decoctions of chamomile, sage, and calendula. They contain soothing and anti-inflammatory substances. The procedure must be carried out every day.
- Avoid direct sunlight on the skin, especially during treatment. This is due to the fact that dry skin is prone to frequent damage and cracks, through which various pathogenic bacteria and infections can penetrate.
- Use steroid creams. It can help relieve inflammation and ultimately remove dead skin.
- All affected areas should be cleansed twice daily using gentle cleansers.
- If there is no inflammation or irritation, then you can use lotions for washing, which should be applied with light movements without damaging the skin.
- If keratosis appears on the face, then you need to choose loose cosmetics.
Since there is no universal remedy for getting rid of this disease, it is worth remembering that remissions and exacerbations are directly related to the general condition of the body, as well as seasonal and age-related factors, including hormonal disruptions and changes that can be caused by pregnancy or menopause.
With regular skin care, you can achieve fairly good results and also get rid of the symptoms that usually appear with keratosis pilaris.
All treatment, as well as the use of various cosmetics, must be permanent, otherwise frequent interruptions may cause recurrence of keratosis.
On this topic
- Keratosis
Best Treatments for Keratosis
- Inna Viktorovna Zhikhoreva
- July 28, 2020
There is no specific program that could save all patients from the disease; it is developed individually for each. It is also worth considering that constant use of the same cosmetics reduces the effectiveness of treatment.
It is worth noting that in very rare cases, a complex of various procedures and taking medications led to the complete disappearance of the disease.
Forecasts
The outcome of the disease depends on the type and extent of the keratotic process. In general, the prognosis is favorable with timely treatment and compliance with medical recommendations. In the absence of proper treatment, the development of microbial eczema, malignant neoplasm, tooth loss, hyperpigmentation, disruption of the endocrine system, and the development of depression are possible.
The most unfavorable prognosis is considered to be the senile form of keratosis. Plaques do not disappear on their own, as, for example, with the follicular form. This is a precancerous condition: in the absence of treatment, irrational therapy, and constant trauma to the lesions, degeneration into squamous cell carcinoma is possible. Malignancy occurs in 2–5% of cases.
Ichthyosis can be complicated by metabolic disorders, folliculitis, progression of chronic diseases, and the addition of new systemic diseases. If ichthyosis is detected in the fetus, it is recommended to terminate the pregnancy.
The risk group includes people with fair skin, a family history, those living in a sunny, hot climate, those who have undergone radiation and chemotherapy, and those who are HIV-infected.
Causes and symptoms of plantar keratosis
Dermatologists say that pathological growth of the upper layer of skin is not an independent disease. It often manifests itself as a result of other disorders of the keratinization process:
- ichthyosis;
- depriving;
- erythroderma;
- keratoderma;
- psoriasis.
The cause of the development of hyperkeratosis can be bone deformations:
- flat feet;
- clubfoot;
- Hallux valgus or deformity of the big toes;
- wearing tight, uncomfortable shoes.
Factors that caused significant thickening of the upper layer of the epidermis may be internal problems:
- atherosclerosis of blood vessels of the lower extremities;
- diabetes;
- metabolic disorders;
- being overweight;
- avitaminosis;
- heredity.
Pressure on certain areas of the skin provokes the activation of its protective mechanism. In places where the skin is subjected to regular compression and rubbing by shoes, the cells of the stratum corneum begin to rapidly divide, forming compactions, the thickness of which can reach several millimeters, and sometimes centimeters.
The keratinizations are characterized by excessive dryness, roughness, and sensitivity is lost in these places. Hyperkeratosis can affect individual areas (heels, inner lateral parts, metatarsal area, phalanges of the big toes) and be called “limited” or spread to the entire surface of the feet and be called “diffuse hyperkeratosis.” When wearing small shoes that compress the forefoot, thickening of the skin of the fingers and nails may occur. Fungus also causes overgrowth of the nail plates.
We recommend reading
- Is it possible to remove moles on the foot?
- Treating plantar fasciitis at home
- Celandine for spines: proper treatment and use
Symptoms of the disease are the following changes:
- the skin becomes rough;
- seals appear;
- sensitivity is lost in the affected areas;
- calluses or “corns” form;
- skin elasticity disappears;
- peeling and cracks form.
When the pathology starts, the cracks become deep, pain and bleeding appear. There is a risk of infection and the onset of an inflammatory process.
In addition to hyperkeratosis of the feet, there is follicular keratosis of the skin of the lower extremities. It is a symptomatic sign of the presence of a dermatological problem or internal disorder. Follicular keratosis is divided into: acquired, congenital. The latter does not necessarily appear in the child from birth. This type of disease is caused by damage to the skin in the form of single or multiple keratinized papules and blockage of hair follicles. Problem areas are often the legs, thighs, and back of the feet.
ICD 10 code – L87.0.
Prevention
Keratotic skin lesions are a complex problem that is difficult to eliminate. In order not to encounter the disease, it is recommended:
- avoid prolonged exposure to the sun, especially for people at risk, do not be in the sun from 10 a.m. to 4 p.m.;
- do not sunbathe in the sun or in a solarium, especially if the patient has solar keratosis;
- use sunscreen, wear glasses with UV filters, sick people - wear natural, light clothing with long sleeves, comfortable shoes;
- take care of the immune system, strengthen it, eat rationally;
- do not overcool;
- maintain hygiene;
- avoid injury to the skin.
People suffering from dermatoses should undergo regular medical examinations with a dermatologist and preventive treatment, and eliminate irritating and provoking factors.
Treatment of the disease
Treatment should be carried out by a dermatologist.
You need to visit a specialist after the first appearance of keratomas, since it is important to exclude the malignant nature of the formation. Treatment is long-term and complex, usually including a number of activities.
Conservative therapy
It is carried out with the aim of reducing the number of keratoses before moving on to radical methods of treatment.
Therapeutic agents reduce symptoms and alleviate the course of the disease, but do not cure completely.
Therapeutic agents reduce symptoms and alleviate the course of the disease, but do not cure completely.
To soften keratonic areas, applications using drugs with urea (content - from 12 to 30%) are used: Keratosan, Ureaderm, Ureatop, Akerat..
The following drugs are used in therapeutic treatment: Fluorouracil, Efudex cream, Diclofenac Gel 3%, Imiquimod. Special shampoos are used to treat keratosis of the scalp. Retinoids are taken internally, which help reduce the growth rate of formations, as well as vitamins of groups A, B and C. Additionally, courses of physiotherapy are prescribed.
Radical methods of treating keratosis
Since conservative therapy for keratosis does not guarantee complete cure, it is often necessary to proceed to radical measures - direct removal of the formations. The use of drastic techniques is especially justified if there is a risk of keratosis degenerating into cancer.
The following radical methods of therapy exist:
- Cryodestruction - freezing with liquid nitrogen.
- Radio wave removal. The formation is excised using a radio knife under the influence of radio waves.
- Electrocoagulation - the doctor performs cauterization using high-frequency electric current.
- Laser destruction - a targeted effect of a carbon dioxide laser is applied to the keratoma.
- Photodynamic therapy - methyl aminolevulinate is applied to the affected area with further exposure to a light wave of a certain length. All this leads to necrosis of the affected tissues.
- Surgical removal - the skin is scraped with a curette (special instrument).
- Dermabrasion – removal using an abrasive brush.
What to do?
If you think you have Keratosis
and symptoms characteristic of this disease, then doctors can help you: dermatologist, podologist.
We wish everyone good health!
Diseases with similar symptoms
Ringworm (overlapping symptoms: 5 out of 20)
Ringworm is a fungal disease that affects the human skin. The disease is accompanied by skin rashes (in the form of spots), peeling and slight itching. The disease mainly affects children and people aged 30 to 70 years. Ringworm affects both men and women equally.
Did you like the article? Share with friends on social networks: