When a person is bothered by dandruff and cannot cope with the problem on his own, he turns to those closest to him. Friends and relatives always “know” how to deal with such misfortunes. Some share folk recipes, others recommend shampoos that have helped them personally. In most cases, unfortunately, such recommendations are meaningless. The fact is that this unpleasant phenomenon occurs for various reasons, and experts identify several types of dandruff. It is possible to select adequate treatment only after a complete diagnosis.
What does dandruff look like?
White flakes, clearly visible on dark clothes, are nothing more than dandruff. It consists of scaly particles of keratinized skin, appears at the roots of the hair, and then easily falls off. Most often, the disease is provoked by the activity of the Malassezia fungus. It is present on the skin of every person, but only under certain conditions does it begin to multiply and cause dandruff.
When the fungus on the scalp becomes active, a person feels itchy. Depending on the reasons that caused the spontaneous reproduction of microorganisms and the characteristics of the sebaceous glands, seborrhea (this is what the disease accompanied by peeling is called) is divided into dry, oily, and mixed. It can also manifest itself in other forms.
Oily dandruff
This type of dandruff often occurs when the scalp is too oily. If the sebaceous glands work too intensely, a film forms on the surface of the skin, which closes the pores, irritates the nerve endings and does not allow the cells to receive the proper amount of oxygen.
Symptoms:
- excessive greasiness of the scalp;
- formation of large-plate dandruff;
- hair loss;
- severe itching.
Causes of oily dandruff
- psycho-emotional overload;
- insufficient hygiene of hair and scalp;
- use of alkaline detergents;
- increasing the level of male sex hormones in the body;
- decreased immunity;
- genetic predisposition;
- poor nutrition;
- avitaminosis;
- chronic pathologies of internal organs.
Oily seborrhea of the scalp most often manifests itself during puberty, when intensive work of the sebaceous glands is caused by an imbalance of male and female sex hormones.
Exceeding the level of androgens leads to a decrease in the bactericidal properties of the secretion and excessive sebum secretion, which, in turn, contributes to the active reproduction of the yeast-like fungus Pityrosporum Ovale and the natural clogging of the glands. A sebaceous film forms on the scalp, which does not allow the pores to breathe, complicates blood microcirculation and the process of nourishing the hair follicles.
Types of oily dandruff
Experts distinguish between thick and liquid forms of oily seborrhea.
With the development of a dense form
the curls become hard and dry and cannot be styled, the scalp loses its elasticity and becomes thickened, acquiring a grayish-brown tint. Patients may experience enlargement of the mouths of the sebaceous glands, upon pressure on which thick contents are released and oily, thick dandruff is formed.
In advanced cases, an epidermal cyst (atheroma) filled with a thick mass may form on the surface of the skin. Such atheromas can become inflamed, causing an increase in body temperature and soreness of the affected skin.
If treatment for the disease is not started in time, complications may arise in the form of partial or complete baldness, furunculosis and other pustular diseases.
Patients suffering from liquid seborrhea
, can observe a characteristic greasy shine on the hair, the curls seem dirty or damp even with the proper level of hygiene. Even during the day after washing, large flakes of yellowish dandruff form on the head, the hair sticks together, looks stale, falls out, and severe itching appears. In the absence of adequate treatment, sebaceous cysts form on the scalp and partial or complete hair loss occurs.
In severe forms, liquid seborrhea can cause pustular lesions of the skin, abscesses, and furunculosis.
Treatment of oily dandruff
For any diseases of the hair and scalp, you should consult a trichologist. Ignoring the problem for a long time can only aggravate the situation and lead to irreparable consequences.
Types of seborrhea
Seborrhea and dandruff are often considered synonymous. However, dandruff is only a symptom of seborrhea, the same as itching. Therefore, when considering the types of disease, we need to talk about seborrhea, and not dandruff.
Dry seborrhea
If there is a lack of activity in the sebaceous glands, dry seborrhea can occur. The reason is not only low sebum production, but also:
- stress, anxiety, psychological shocks;
- hereditary factors;
- hormonal disruptions (puberty or abnormalities in the functioning of the glands);
- use of incorrectly selected cosmetics, as well as cosmetic paints with ammonia;
- poor hygiene, excessively frequent hair washing and blow-drying;
- lack of vitamins (this affects the general health and functioning of the glands).
A deficiency of sebum contributes to the appearance of inflammatory processes on the scalp, which provoke the proliferation of Malassezia fungi. Symptoms of dry seborrhea:
- discoloration, dryness and brittleness of hair;
- formation of cracks in the epidermis;
- the appearance of large scales that quickly peel off.
If measures are not taken, dry seborrhea moves into the next stage. In addition to dandruff, a person is bothered by redness of the skin and seborrheic spots. Sometimes dry seborrhea is an advanced form of oily seborrhea, in other cases the problem arises on its own.
The role of the sebaceous glands in the development of seborrhea
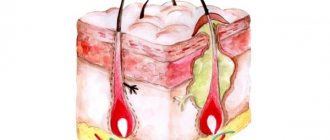
Seborrhea is based on a violation of the mechanisms of sebum secretion and the quality of the secretion of the sebaceous glands. The largest number of sebaceous glands are associated with hair follicles, into the mouths of which their ducts open. A minority of the sebaceous glands are located in isolation. The main places of their localization are the area of the nasolabial triangle, the red border of the lips, forehead, corners of the eyes, the peripapillary zone and nipples, in men in the area of the glans penis, in women in the clitoris and labia minora. Places where there are as many sebaceous glands as possible are called seborrheic zones. These are the forehead, central part of the face, ears, scalp, décolleté, shoulders and interscapular area.
Sebaceous glands have different sizes. The largest of them are associated with vellus hair follicles, the small ones are associated with long hair.
The sebaceous glands contain sebocytes. They accumulate lipids. When moving outward, the sebocytes are destroyed and their contents are poured out into the hair follicle in the form of sebum.
In children, the sebaceous glands are in a calm state. Their growth and active sebum secretion begins during puberty, which is associated with hormonal changes in the body. Women experience increased sebum secretion during the ovulation phase. At the end of puberty, seborrhea normalizes and signs of skin lesions disappear. In old age, the glands decrease in size. Secretory function decreases.
Rice. 2. The sebaceous gland, the duct of which opens into the hair follicle (picture on the left). Isolated sebaceous gland (picture on the right).
Sebum
Sebum, secreted from the sebaceous glands, spreads over the skin and covers almost its entire surface with a layer 7 to 10 microns high. Within one week, a person secretes from 100 to 200 grams. secretion, for seborrhea - 300 g. and more. Mixing with sweat, sebum emulsifies and turns into a water-lipid film (sebum), which protects the skin from drying out and waterlogging, and protects against the harmful effects of environmental factors and infections.
With increased sebum secretion, the yeast-like fungi Pytyrosporum ovale and Pytyrosporum orbiculare are activated. Normally, they are found in small quantities on human skin and feed on the secretions of the sebaceous glands. With increased sebum secretion (seborrhea), fungi multiply intensively and acquire pathogenic properties. They cause increased flaking (dandruff) and itching of the skin. When the production of sebaceous secretion decreases, the skin dries out and cracks.
With seborrheic dermatitis, the concentration of linolenic acid in the secretion of the sebaceous glands decreases. This leads to an increase in the pH of the skin, the permeability of the epithelium changes, and the growth of microorganisms is activated. Seborrhea creates conditions for the development of diseases such as juvenile acne and pyoderma. Corynebacteria and staphylococci produce lipase, which breaks down triglycerides in the secretion of the sebaceous glands. The fatty acids formed as a result of this reaction irritate the skin, which creates conditions for the development of microbes. All this leads to the development of seborrheic dermatitis and seborrheic eczema.
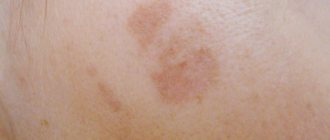
Rice. 3. The photo shows seborrheic dermatitis on the face.
Rice. 4. The photo shows dry seborrhea of the scalp in a child.
Oily seborrhea
If too much sebum is produced, this can also lead to dandruff. The fact is that the secretion does not contain enough antibacterial substances. Favorable conditions are created for an increase in fungal colonies. The active activity of Malassezia leads to detachment of the epidermis and the appearance of oily dandruff.
Symptoms of oily seborrhea:
- greasy hair;
- itching;
- The scales stick together and peel off very poorly.
Oily seborrhea is often accompanied by acne and furunculosis. The skin of the scalp becomes crusty; scratching during itching leads to bloody wounds. If adequate treatment is not carried out, hair will begin to fall out.
Seborrhea, associated with increased sebum production, occurs not only on the scalp. It also appears on the face, especially in the area of the nasolabial triangle, behind the ears and on the chin. On the face, the disease is characterized by enlarged pores and graying of the skin.
The most common cause of oily seborrhea is hormonal imbalances. The disease often plagues adolescents during puberty. Most often, young men suffer, because it is male hormones that provoke the activity of the sebaceous glands.
Normally, seborrhea is temporary; by the age of 25, it goes away in most people. In 10% of cases the disease becomes chronic.
Another common cause of oily seborrhea is genetics.
Also, the impetus for the disease can be:
- frequent stress;
- deviations in the functioning of the nervous system;
- taking hormones;
- problems with the gastrointestinal tract;
- diseases of the genitourinary system.
Why dandruff appears and how to deal with it
Dandruff is small scales on the scalp that appear as a result of a pathological acceleration of skin cell renewal. It is one of the symptoms of seborrheic dermatitis. This is a source of social and psychological discomfort for every sixth inhabitant of the planet.
The problem is not only medical. The presence of dandruff reduces self-esteem and self-confidence, and forms an inferiority complex.
Causes of dandruff
Dandruff is the initial stage of seborrhea. Most often incorrectly regarded as a cosmetic problem. Untimely treatment leads to further development of the disease, worsening symptoms, and the appearance of severe forms with a chronic course that are difficult to treat.
Scales appear on the scalp. This is due to the structure of the skin. It contains a large number of large sebaceous glands due to the presence of hair: the hair follicle and the sebaceous gland are a single complex. Their number reaches 460–480/cm2. The sebaceous glands perform the barrier function of the skin.
Physiological renewal of the skin occurs constantly, unnoticed by humans. Desquamation (cell exfoliation) normally occurs within 25–30 days. In pathological conditions, this process is accelerated and takes 4–10 days.
The scales, which in a healthy person dry out during the process of exfoliation within 1 month of rejection and become invisible, do not have time to lose water due to adverse effects on the body. They mix with the sebum of the glands and turn into grayish or yellowish flakes. This is dandruff.
The presence of large scales indicates excessive sebum production and too rapid rejection of skin cells. The most common location of dandruff is the occipital-parietal region of the head.
There is no single point of view on the causes of dandruff formation. There are a number of factors that indirectly influence this process:
- Hormonal
- imbalance between androgens and estrogens in favor of androgens. Dandruff is more common in men than in women - androgens control the activity of the sebaceous glands. In women, this imbalance develops during pregnancy. - Yeast fungi Malassezia.
In 90% of the population they are permanent inhabitants of the skin and belong to the opportunistic microflora. By feeding on sebum, they secrete oleic acid, which irritates the skin and causes it to peel in people with individual high sensitivity to it.
Additional causes of dandruff:
- genetic predisposition;
- pathology of the endocrine system and gastrointestinal tract;
- chronic infectious diseases;
- hypovitaminosis A and C;
- nature of nutrition;
- stressful situations (acute and chronic);
- improper care of hair and scalp.
All of the above leads to dandruff:
- all over the head;
- on the head in one place;
- in the beard.
Partial skin damage is mainly associated with the use of a hair dryer, curling iron, chemical curling agents, and various hair dyes.
Uneven exposure to aggressive factors leads to the appearance of dandruff on the head in one place. As a rule, their consequences appear in the form of small lesions on the back of the head or crown. As the process progresses, it spreads throughout the entire head.
and even beyond.
The reasons for the development of beard dandruff in men are different:
- local malfunction of the sebaceous glands, which begin to produce sebum in large quantities;
- hormonal imbalance (especially during puberty, when the level of androgens in the blood rises sharply);
- development of allergies to personal hygiene products;
- frequent consumption of alcohol, spicy and fatty foods, fast food, sweets;
- smoking.
Ways to get rid of dandruff
Treating dandruff is a long process. The appearance of skin scales is one of the symptoms of pathological changes in the body. Therefore, therapy must be comprehensive. Using only special shampoos can give only short-term results, then a relapse will occur again.
Full adequate treatment is prescribed by a trichologist after examination and clarification of the cause and severity of the process.
To get rid of the discomfort associated with dandruff, you must first eliminate all risk factors:
- strictly adhere to a hypoallergenic diet;
- get rid of bad habits, minimize alcohol consumption;
- remove stress from your life;
- bring chronic diseases to the stage of remission.
Antimycotic medications are prescribed individually in each case by a trichologist. If the examination reveals the presence of secondary bacterial microflora, additional antibiotics are prescribed.
Antifungal shampoos should be used several times a week. They are prescribed by a doctor if the process lasts many months and ordinary hygiene products are no longer effective. The exposure of the foam is at least 5 minutes, after which it is washed off. The course of treatment can last up to 2–2.5 months.
The shampoo must contain zinc, sulfur and its compounds. These microelements restore the condition of the scalp well. Products containing alkalis or alcohol are contraindicated. They dry out the skin and lead to increased flaking.
In some cases, during a long-term process with profuse dandruff, glucocorticoids are prescribed in combination with antifungal and keratolytic drugs for external use.
In the absence of a therapeutic effect, a detailed examination by related specialists is required: dandruff may be a manifestation of another serious pathology that needs to be treated.
Prevention of dandruff
There are no special methods for preventing dandruff. General measures are aimed at changing lifestyle.
Necessary:
- healthy diet - exclude spicy, fatty, sweet foods;
- complete rest;
- limiting excessive physical and emotional stress.
To prevent dandruff it is important:
- observe the rules of personal hygiene, do not use other people’s combs, towels, wash your own combs and hairpins;
- Avoid hair coloring, curling, long-term styling, using a hair dryer or curling iron;
- after washing your hair, massage with your fingertips - this improves blood circulation and makes it easier to remove dandruff;
- take courses of multivitamin and mineral complexes;
- wash your hair no more than once a week; if you wash more frequently, choose a special shampoo for daily care.
To prevent re-peeling of the skin (after an effective course of treatment), proper care is necessary: properly cleanse the scalp, soothe and moisturize it to prevent relapse.
During the period of remission, mild shampoos with a neutral pH are used that do not irritate the scalp. Twice a month it is necessary to use antimycotic detergents with zinc and sulfur. At the same time, ointments and creams containing zinc, as well as hypoallergenic local products, are prescribed.
If dandruff does appear, it is recommended to consult a specialist who will individually select treatment and care products for your hair and scalp.
ru.freepik.com
Elena Kornilova
Read the original article on the website:
https://health2.ru/zabolevaniya/perhot.html
If you liked the article, give it a thumbs up and subscribe to the channel
Source: https://zen.yandex.ru/media/id/5ca35f40d677b400b3b89a26/5e0a4c8dfe289100b000164d
Mixed seborrhea
Mixed seborrhea has characteristics of dry and oily varieties. In particular, patients note that the skin on the face in the middle part is oily, and on the cheeks it is dry. Especially a lot of fat is released in the areas of the crown, chin, forehead, and nose. In other places the fat content is moderate or insufficient.
Doctors also note that a person may be bothered by dry dandruff and oily skin on the face.
Symptoms of mixed seborrhea:
- inflammatory process on the cheeks, scalp, chin, forehead, chest, nose;
- in the area of inflammation, the skin becomes rough;
- redness, itching;
- increased secretion of sebum on the forehead, but decreased secretion in other areas of the face;
- peeling in the area of increased activity of fat-secreting glands, yellowish or gray scales;
- peeling of dry areas of skin.
All the factors listed above as causes of other types of the disease can provoke mixed seborrhea. Most often the problem is associated with hormonal changes or disruptions. Heredity plays an important role. Stress and anxiety can also contribute to the growth of fungi.
Dandruff on women's legs
cure dandruff at home
It's no secret that it is important for every girl to know that she is the most attractive and pretty. To achieve perfection, ladies spare no time in caring for their face, body and hair, do not skimp on sports exercises and try to lead a healthy lifestyle. But other times some offensive flaw will spoil the whole picture. Either an inopportune pimple that popped up right on the nose, or an inopportunely broken nail. And other times the mood drops due to the fact that the skin is very flaky. And if it’s easier than usual to cream your hands while in any place, then with your feet the situation is more difficult. They spoil the entire memory of the look, and even a small skirt and prestigious stiletto sandals do not help the situation. What should you do when the skin on your legs peels? What does this process depend on and how to stop it? This is exactly what we will talk about next. dandruff and seborrhea
Tubular seborrhea
This is a special type of seborrhea, the main symptom of which is the formation of scales not on the scalp, but on the hair. This is explained by the fact that the active reproduction of the Malassezia fungus began precisely on the hairline. Dandruff looks like small tubes, which are sometimes confused with nits.
Tubular seborrhea is also characterized by severe itching and redness. Most often it occurs in adolescence, when hormonal levels are actively restructured.
Also, the causes of tubular dandruff can be:
- lack of vitamins;
- metabolic disease;
- improper or insufficient hygiene;
- improper or poor nutrition, diets;
- physical and emotional stress;
- skin diseases;
- chronic illnesses, hepatitis, HIV and other diseases that reduce immunity.
How to get rid of dandruff
Medicated dandruff shampoos, like medicated creams, should be used during the active stage of seborrhea. As the manifestation of the disease decreases, it is necessary to reduce the use of medications and, subsequently, switch to the use of everyday hygiene products. In case of the next appearance of the disease, creams and shampoos can be reused.
It may happen that if the disease reappears, the remedies that you used in previous times may now be ineffective. In this case, it will be necessary to use other shampoos and/or creams with the above components.
Basic rules for using medicated shampoos. The shampoo should be applied to damp hair and left on the scalp for about five minutes. If the shampoo is rinsed off too quickly, the active ingredients will not have enough time to work.
Basic rules for using medicinal creams (masks, lotions). Therapeutic creams are used in combination with medicated shampoos. Leave masks and lotions on the scalp for 20-30 minutes.
In parallel with the use of medicinal products, you must follow the following simple diet. The food you eat should be rich in vitamins and fiber. The diet should include fermented milk products. Consumption of fatty and sweet foods should be limited. It is also recommended to drink at least two liters of clean water daily.
Seborrheic dermatitis
When listing the types of dandruff, one cannot fail to mention seborrheic dermatitis. This is a general term for diseases that are associated with the active proliferation of fungi, the formation of crusts, redness, itching and peeling.
Seborrheic dermatitis can occur with infectious diseases such as lichen, or non-infectious diseases - psoriasis, neurodermatitis. Symptoms appear on the skin in areas with impaired sebum secretion.
The fungus produces lipotic enzymes that break down fatty acids. When there are too many enzymes, an inflammatory reaction occurs on the skin. Outwardly, at first it looks like peeling. Scratching leads to the formation of bleeding wounds.
The symptoms of seborrheic dermatitis are similar to dandruff. However, we are talking about it only if more than 83% of the microflora of the scalp consists of pathogenic fungi. For dandruff, this figure is 74%. Thus, dandruff is the first stage of seborrheic dermatitis. If left untreated, it will lead to serious consequences.
Dandruff in the ears: causes and methods of getting rid of it
Ear dandruff bothers many people, although the formation of whitish scales in the organ of hearing seems strange, to say the least. However, there is nothing surprising in the appearance of keratinized scales in the ears: the auricles contain an abundance of fat glands and hair follicles, and in addition, the skin in this area is home to the causative agent of a fungal infection, which for the time being remains in a “dormant” state. It is clear that all the factors are present that, under certain conditions, lead to the formation of dandruff, which is not dangerous to health, but does not have the best effect on a person’s self-esteem. Dandruff in the ears, scalp, face and body appears, as a rule, simultaneously , which is caused by a decrease in the body's defenses, exacerbation of chronic, including dermatological diseases, changes in hormonal levels and neglect of a healthy lifestyle.
There are also specific reasons that cause dandruff in the ears - this is past otitis media, as well as boils formed in the ear canal . In such cases, dandruff is only an unpleasant addition to much more serious problems - hearing loss and purulent discharge. That is why, if scales are detected in the organ of hearing, you should go to an otolaryngologist , because self-medication can result in damage to the eardrum and even hearing loss. In cases where a general disease leading to peeling of the skin has not been identified, ointments containing salicylic acid, sulfur, tar, as well as pharmaceutical drugs with antifungal action, for example, Cycloperox and Ketonazole, are prescribed.
Attention! Do not wipe the inner surface of your ears with alcohol or wash them with anti-dandruff shampoo - these degreasing agents will only worsen the condition of the skin of your ears. To clean the ear, you can use tampons soaked in chamomile infusion or vegetable oil.
Psoriasis and dandruff
Dandruff on the head appears not only due to the activity of the sebaceous glands and fungi. Sometimes scales on the hair occur with psoriasis. This is a common disease associated with heredity and the body's immune system. The disease is chronic, its therapy is designed to reduce symptoms.
Signs of psoriasis:
- the appearance of pink or red spots (occur not only on the head, but also on the arms, legs, and other parts of the body);
- gray scales on plaques;
- itching, sometimes pain.
An outbreak of this autoimmune disease can easily be confused with seborrhea. It is important to see a doctor on time, because the treatment of these ailments is very different.
Psoriasis appears between the ages of 15 and 35 years. Outbreaks of the disease can be caused by:
- poor nutrition;
- cold or dry air;
- stress.
The causative agent is not fungi, but the person’s own immunity, which attacks healthy cells, which causes active growth of the epidermis.
Therapy requires close supervision by a dermatologist. Both local and oral medications can be prescribed. Phototherapy, IV courses, and injections help relieve symptoms.
Signs of dandruff
It is incorrect to talk about the symptoms of dandruff, because we are not talking about an independent disease. However, you can guess its appearance by the following signs:
- The scalp becomes untidy: the hair splits and loses its shine, and when parted, you can see that the skin and bases of the hair shafts are “powdered” with scales.
- It is impossible to keep the upper part of clothing (shoulders, lapels) clean - it very quickly becomes “dusty” and loses its freshness.
- The skin of the scalp looks inflamed, it swells a little and itches. Severe dandruff is always accompanied by itching.
Attention! White scales are naturally more visible on dark hair, and many people think that if they lighten their hair, the problem will disappear. However, this is a misconception, because changing your hair color will not stop the formation of dandruff , which will fall onto your clothes with the same intensity (and maybe even more, since lightening compounds are not at all good for the scalp).
Dandruff: what to do to cleanse the scalp of flakes?
It is quite difficult to determine why dandruff appears, since the causes are not always obvious and their detection requires the intervention of specialized doctors (gastroenterologist, endocrinologist and other specialists). At the same time , it will not be difficult to confirm the fact of the activation of a fungal infection; you just have to look at the scalp dotted with scales . However, you should not self-medicate, because it is not enough to make sure that dandruff is present, it is important to accurately determine its type, and this can only be done by a professional who can prescribe the correct treatment.
The patient will help himself if he decides:
- change hair care products;
- sharply reduce the proportion of spicy, fatty, smoked and fried foods in the diet;
- eat more foods rich in fiber and vitamins, especially group B;
- maintain the body's water balance by drinking at least two liters of water per day;
- Do not blow-dry or straighten your hair, and also put off coloring and curling your hair for a while.