Urticaria pigmentosa. Causes of the disease
The clear reasons are unknown. The disease has not been sufficiently studied.
Sometimes it is formed without visible prerequisites. Under some circumstances, doctors believe that the disease is inherited - as an autosomal dominant gene trait. However, not all people with the problematic gene suffer from this disorder.
Usually it is caused by a gene combination of specific characteristics located on chromosomes. The defective gene can be inherited from two parents or from just one. The risk of transmission is about 50%.
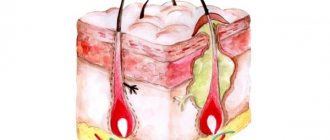
In many cases, the disease appears due to an inadequate concentration of inflammatory cells in the skin, exceeding the norm. The cells are called mast cells.
Factors contributing to an increase in the number of mast cells:
- physical irritants (such as heat or strong friction);
- excessive physical activity;
- bacteria;
- poisoning;
- dextran in eye drops;
- alcohol;
- certain foods (crustaceans, fish, cheese, spicy foods, excessively hot drinks);
- frequent use of painkillers;
- stress and depression.
Sometimes the described pathology is preceded by mastocytosis. However, the opposite situation is more common, when mastocyosis is a complication after it.
As people age, the likelihood of mastocytosis increases in those who suffer from the disease.
Urticaria pigmentosa. Symptoms and manifestations
Pathology can develop in people of all age categories. However, symptoms are dictated by age. About half suffer solely from changes to the surface of the skin.
In general, dermatologists distinguish two key types of pathology:
- Children's cutaneous mastociosis. Progresses in the first 24 months after birth. The rashes appear exclusively externally and do not affect the insides of the body. Before pubertal hormonal changes, all symptoms usually disappear without a trace and never reappear.
- Adolescent and adult mastociosis. Formed in adolescents from 12 years of age and adults. Not only the outer skin surface suffers, but also the insides. Sometimes the pathology develops into a systemic mastoid form.
READ ALSO: Ointments that draw pus from a boil (boil): list of the most effective
Pathology also has two types of external manifestations:
- single tumor (a single formation on the epidermis that appears in the mastocytoma form);
- profuse rashes over the entire surface of the body (in a generalized form).
The latter type is more common.
Urticaria pigmentosa in children
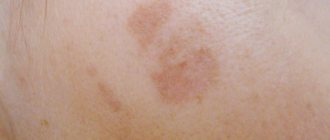
Urticaria pigmentosa in children is formed by pinkish-red marks on the epidermis (can be seen in the photo) and severe itching. As the spots develop, they turn into blisters filled with liquid. Externally, it is transparent or pinkish (due to the blood content),
The blisters are accompanied by swelling, and when irritated they react with new damage. The bubble formation swells even more intensely, turns red and itches. A similar reaction occurs when compressed and exposed to temperature.
For example, while taking a bath or being exposed to sun radiation. In some circumstances, the reaction takes place without leaving any traces. However, more often it leaves behind brown-brown pigment spots.
Occasionally, not blisters are visible on the epidermis, but nodules of a reddish tint. In this case, there is no response to new damage.
As a rule, the rash appears only on the torso. But it can spread to the face and hands. The matter does not go further than this. Rarely do rashes cover the entire skin surface.
Some other manifestations:
- Thickening of the skin. And the formation of more obvious folds.
- Yellowness. The skin gradually acquires a yellowish tint. Partly due to coarsening.
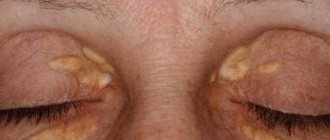
- Tumor-like nodule. Formed in the cervical and forearm areas or on the torso. In diameter - up to 40-50 mm. Usually there is only one nodule. Less often there are four, but this is the maximum. Feels like rubber. The surface is smooth or with folds. When damaged, it forms blisters or pustules. Examples can be seen in the photo of urticaria pigmentosa.
After opening, some bubbles become covered with cracks and form ulcers.
Usually the pathology occurs without malignancy and does not cause complications. At puberty, symptoms go away on their own.
READ ALSO: Rashes all over a child’s body: what to do if there is no fever or itching
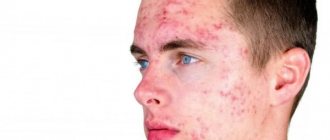
Hives on the face. Symptoms
The main symptom of the disease is the formation of blisters. They come in different sizes, small - similar to a rash and large - with a diameter of up to 10 cm. In appearance, the rashes resemble swelling like after a burn or mosquito bite. Over time, a red border may form around the papule. Smaller blisters can merge and form a large localized area.
How urticaria manifests itself on the face is clearly visible in the photo, the symptoms in all cases demonstrate the need for treatment.
Urticaria on the face is accompanied by painful itching and pain in the areas where the rash is located. The general condition worsens: weakness, headache, joint aches occur, and body temperature may rise slightly. The inability to tolerate discomfort can even lead to nervous breakdowns.
There are acute and chronic phases of the disease.
During an exacerbation, symptoms appear suddenly, quickly disappear and leave no traces.
If the rash on the face does not go away for more than 1-1.5 months, the disease enters the chronic stage.
Left untreated for a long time can have serious consequences. The most dangerous of them is Quincke's edema. A person develops a hoarse, barking cough, and the face and lips swell at lightning speed. If the attack is not stopped quickly, swelling of the larynx will occur and death from suffocation will occur within a few minutes.
Urticaria pigmentosa in adults
Urticaria pigmentosa in adults manifests itself in the form of streamlined spots. Diameter - no more than 5 mm.
The edges of the formations are clearly defined and have a smooth surface. Color - dull gray or brownish-pinkish. As a rule, they appear on the body, without initially affecting the face.
Migration to the face and limbs occurs over time - with the evolution of the disease. Then the formations take on the shape of a sphere and change color to a darker color - brown, pinkish-red or dirty brown. The distribution process can occur intermittently and drag on for years.
For urticaria pigmentosa in adults, treatment is predominantly medicinal.
With age, the pathology progresses. A complication arises - mastocytosis of a systemic type, that is, it affects the insides of a person. This leads to death because the functionality of the organs is impaired.
Hives on the face. Disease prevention
Urticaria on the face is an insidious and unpredictable disease. It can be caused by a whole range of interrelated reasons. It will take a long time to treat it, methodically going through expensive options.
It is much easier to defeat an illness without letting it begin.
This is possible if you follow simple rules:
- limit your time outdoors in sunny or frosty weather;
- protect exposed areas of the body with clothing;
- cancel field trips during the flowering period of plants and herbs;
- regularly rinse the nasal cavity with a solution of table salt and special sprays based on sea water;
- refrain from eating foods that can trigger a relapse;
- keep your skin clean, shower regularly, use only hypoallergenic cosmetics;
- in clothing, give preference to natural, breathable fabrics, choose a style that does not hinder movement and does not tighten the skin;
- promptly treat any diseases of internal organs, undergo scheduled preventive examinations once a year;
- Do not self-medicate, do not take medications uncontrollably.
Urticaria on the face is an ailment that can and should be combated. Now you know how to do it. Be careful, monitor your health and the health of your children. And then instead of unpleasant red spots on your faces there will always be a radiant smile.
Urticaria on the face is an aesthetically unpleasant and painful phenomenon, manifested by blisters, swelling, and itching. The disease can occur in chronic or acute forms. Inflammation on the face, characterized by a bothersome rash, occurs for various reasons. Insect bites, medications, foods, chemicals, infections - all this can cause a sharp reaction of the skin on the face. The disease was named for its similarity to the micro-inflammations that appear on skin burned by nettles. The method of treatment is directly related to the cause that caused such a reaction.
- Why does hives appear on the face?
- Symptoms of different forms
- Possible complications and consequences
- Diagnostic methods
- How to quickly cure hives on the face
- Basic principles of treatment
- Drugs
- Traditional methods
- Diet
- How soon will the rash go away?
Urticaria pigmentosa. Treatment
First, some precautions:
- Do not injure your skin. Try not to rub or comb it. Under no circumstances should you puncture the bubbles or squeeze out the contents.
- Limit skin contact with environmental factors. Reduce the amount of clothing, wear looser clothes. Spend less time in the sun. Avoid hot baths, they will only harm you.
- Don't take aspirin. And codeine.
Understanding the causes of the disease and avoiding its symptoms can become a residual measure in a mild form of the pathology.
Treatment methods
The main difficulty in treating idiopathic urticaria is the fact that it is extremely difficult to accurately determine the cause of the development of the pathological process!
Proper treatment of this type of urticaria helps eliminate the symptoms of the acute form of the pathology in the first 6 weeks. The main goal of therapy is to reduce the intensity of itching, eliminate watery blisters and relieve swelling of the skin.
Treatment of non-allergic urticaria consists of the following steps:
- determining the causes of pathology;
- relief of disease symptoms using drug therapy;
- identification of disorders that develop against the background of the disease;
- carrying out measures to prevent secondary development of the disease.
Drug therapy
As mentioned earlier, therapeutic therapy for idiopathic urticaria is aimed at eliminating the rash and reducing itching. In addition, the goal of drug treatment is to reduce the sensitivity of the immune system, detoxify the body and eliminate the main cause of the pathology, which was determined through a series of examinations.
Therapy for idiopathic urticaria is carried out with the following drugs:
- Antihistamines – Suprastin, Prednisolone, etc.
- Sorbents – Enterosgel, activated carbon, etc.
- Ointments, gels containing glucocorticosteroids.
- Other means that help eliminate the symptoms of pathologies. These can be sedatives and antifungal drugs, agents to relieve swelling, inflammation, etc.
Traditional medicine in the fight against urticaria of unknown origin
Important! Self-medication can be dangerous to health. Therefore, before trying any folk remedies, it is better to consult your doctor.
When choosing folk recipes as a tool in the fight against the manifestations of idiopathic urticaria, it is extremely important to take into account the increased sensitivity of the affected areas of the skin.
First of all, it is necessary to review your wardrobe - in such a pathological condition, it is better to wear loose-fitting clothes and it is desirable that they are made from natural fabrics. It is best to dry yourself with soft towels that do not rub the skin and do not cause irritation.
In the fight against idiopathic urticaria, you can use the following traditional medicine:
- Freshly squeezed celery juice. Take 2/3 cup on an empty stomach. The remaining 1/3 of the juice is used to wipe the affected areas of the skin.
- Calamus root. Chopped root in powder form, ½ tsp. at night with warm water.
- Soda baths. Treating damaged skin areas with soda solution.
Nutrition adjustments
It is extremely difficult to create an adequate menu for idiopathic urticaria, since it is almost impossible to determine the allergen/trigger. But at the same time, it is better to coordinate the diet with your doctor.
After all, an ill-designed diet can lead to a deficiency of nutrients in the patient’s body, which will negatively affect both the course of the disease and the patient’s health as a whole.
The basic principles of dietary nutrition for idiopathic urticaria are as follows:
- The basis of the diet is foods with low allergenic properties. Chicken, beef, kefir, cottage cheese, apples, pears, rice, oatmeal.
- Fatty foods, smoked meats, chocolate, citrus fruits, red fruits and vegetables are prohibited.
- Complete abstinence from alcoholic beverages.
Drug treatment of urticaria pigmentosa includes:
- Antihistamines type H1. Reduce symptoms such as itching and hyperemia.
- Antihistamines type H2. Reduce acidity levels.
- H1 and H2 blockers. Reduce the likelihood of anaphylactic shock. In serious cases, the patient is given a special medical bracelet, which lets them know about the release of histamines. Then the patient needs to inject himself with adrenaline.
- Mast cell stabilizers. Needed for abdominal pain, diarrhea, bone pain and headaches. Drink for a week.
- Products containing aspirin. Prescribed carefully and in small dosages. Needed for those suffering from vascular insufficiency.
- Photochemotherapy. UVA rays. Reduces total mast cell volume. Therapy is carried out in sessions - 2-3 sessions per week. Reduces the degree of itching and externally transforms the skin surface.
- Steroid drugs. Internal or in cream format. Used for general mastocytosis.
READ ALSO: Lump on the back under the skin: what it could be, which doctor to see and how to get rid of the lump
Sometimes treatment is not enough for urticaria pigmentosa. Some resort to cosmetic measures and remove dark pigmentation.
Treatment of urticaria pigmentosa with folk remedies
Therapy can be supplemented with traditional home remedies. Several recipes:
- Aloe juice. Squeeze a little mixture onto a sterile bandage. Apply a compress to the affected areas. You cannot massage the areas or rub juice into them. This will make matters worse. A course of aloe compresses is 8-10 minutes once a day.
- Ginger. Pour boiling water over the root parts (5-7 pieces per 0.5 liters of boiling water). Let cool. Soak gauze in the mixture and apply a compress to the affected areas. No more than 10 minutes a day.
- Green tea. Drink 200 ml of this tea daily. Before lunch. It is a natural antioxidant that will help promote the release of toxic elements and reduce the degree of skin inflammation.
- Milk of magnesia. Soak a cotton pad in milk and apply it to the affected area for 5-7 minutes.
- Avoid alcohol.
- Avoid spicy foods and fried foods.
- Add unrefined olive and coconut oils to your diet.
- Increase the amount of water you consume.
- Avoid saturated animal fats (milk).
- Consume more omega-3s.
- Eat plenty of fiber (whole grain baked goods).
- Reduce the level of sweet and salty foods in your diet.
- Give preference to vegetables.
Physical activity may also improve the condition.
Hives on the face. Treatment
To get rid of urticaria on the face in adults, in most cases the following treatment tactics are used:
Avoid contact with the allergen. To eliminate directly from the skin, you need to wash your face with cool water without using cleansers. For internal cleansing, sorbents and an enema are recommended. Eliminate itching. Applying topical ointments and gels to the affected areas of the skin will help alleviate discomfort.
Caution should be exercised when using hormonal drugs. They should not be allowed to get into the eyes or mucous membranes. To relieve swelling and itching, you can use traditional medicine recipes. You can apply cotton pads soaked in an infusion of medicinal herbs to the affected area: chamomile, string, nettle.
You can also make masks from raw potatoes grated on a fine grater. Take antihistamines. Before taking it, you must carefully study the instructions and become familiar with the contraindications.
It is also necessary to keep in mind that many antihistamines inhibit the nervous system and reduce concentration. Review your diet, give up spicy and sweet foods, soda, fast food, allergenic foods, smoking and alcohol. Follow the diet for a month after the disappearance of external manifestations.
If there are cases in the medical history with transient complicated development, immediately contact an ambulance for hospitalization.
Important:
Urticaria on the face is a systemic disease; only a doctor can prescribe the correct treatment. When the first signs appear, you need to consult an allergist, dermatologist or local physician.
Urticaria pigmentosa. Preventive measures
With such a pathology, it is worth considering specific rules that will prevent the development and progression of the pathology.
- Remove foods that provoke degranulation of mast cells. These are: seafood, cheese products, hot and spicy foods, alcohol, hot dishes.
- Avoid certain medications: non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (especially aspirin), drugs with antibiotics, narcotic analgesics, vitamin B1. In case of extreme need to take such a remedy, you need to take an antihistamine in advance.
- Pay attention to household and cosmetic products. The composition should not include methylparaben. It also provokes degranulation of mast cells.
Most often, urticaria pigmentosa goes away on its own. However, you should not neglect treatment and let everything go on its own. If suspicious spots form on the skin surface, you should immediately make an appointment with a specialist.
News MirTesen
Hives on the face. Causes
The mechanism of development of the disease is simple. After contact with the allergen, symptoms of urticaria appear on the face in a short time. This is how the body reports the ingestion of unwanted substances.
Allergies can be caused by:
food products taken orally (cocoa and chocolate, citrus fruits, red berries, chicken eggs, fish, food additives and dyes); substances applied directly to the skin (cosmetics, food masks, hair care products, perfumes); household chemicals (washing powders, dishwashing detergent, etc.); insect bites (mosquitoes, bees, midges); inhalation of tiny allergen particles (pollen from flowering plants, aerosols, house dust).
Immune cells recognize and prevent the spread of foreign structures in the body. In this case, urticaria on the face is an immune response to the presence of substances potentially dangerous to humans.
A similar reaction may occur if:
- vaccinations;
- taking medications.
Under the influence of certain factors, mast cells of the skin and mucous membranes secrete an increased amount of enzymes and biologically active substances. The result is a pseudo-allergic reaction - the development of urticaria on the face in adults, children and pregnant women.
Factors that trigger anaphylactoid processes:
- exposure to ultraviolet and infrared radiation from the sun;
- sudden change in ambient temperature (cold or warm).
If the symptoms of urticaria on the face do not go away for more than 6 weeks and spread to other parts of the body, the cause should be sought in the existence of internal pathologies.
Hives on the face may indicate the presence of the following diseases:
liver dysfunction; gastrointestinal diseases; infections of viral or bacterial origin; fungus; disruption of the endocrine system; tumor formations; nervous disorders.