Signs of skin photoaging
The main signs of photoaging are changes in skin turgor, elasticity, color and pattern. The pores deepen, causing them to be more clearly visible on the face. In places that are especially exposed to sunlight, spider veins - telangiectasia - appear. After 30 years, obvious signs of degenerative processes may appear - changes in complexion, dyschromia.
One of the very first signs that the skin is suffering from constant exposure to sunlight can be considered a pigmentation disorder. Melanin, found in epidermal cells, protects the skin from UV rays. Therefore, if the skin is constantly exposed to the sun, the synthesis of this pigment increases. But this process does not occur evenly, like tanning, for example, but in a targeted manner. Affected areas of skin darken and enlarge, or may return to normal with proper care.
Under the influence of UV rays, the skin's metabolic processes are disrupted, it loses more moisture, causing it to peel and lose elasticity. Increased insolation promotes skin tumors – fibromas. Their constant exposure increases the risk of developing papillomas and ephelides (freckles), lentigo.
The degree of photoaging is determined using a special Glogau scale.
1. Slight change in pigmentation. There are no obvious wrinkles yet, but the skin is dry and requires nutrition. Observed at 20-35 years of age.
2. Formation of facial wrinkles, increased pigmentation, slight change in normal complexion. Slight change in facial design. Typically between the ages of 35 and 60.
3. Wrinkles are visible even at rest; they are deep and clearly defined. Telangiectasia and dyschromia appear on the skin. Severe pigmentation disorder, dramatic change in color of individual areas. Most often it manifests itself in people over 50 years of age.
4. The extreme degree is typical for people over 60 years of age . Wrinkles appear on the entire surface of the skin, pronounced loss of elasticity, vascular changes, sagging, sagging of certain areas. The color becomes yellow-gray.
Another unpleasant skin factor is impaired sebum secretion. This is a natural barrier that protects it from external influences. It can be reduced or increased, but in any case, it only has a negative effect on the skin. Pores become clogged and inflammation appears, dry skin flakes, loses elasticity, and the protective layer becomes thinner. Also, exposure to sunlight can lead to changes in pH, which significantly aggravates the situation.
What is facial photoaging?
The fashion for a beautiful tan arose several decades ago and is in no hurry to lose ground. A bronze body looks much more attractive than a whitish one, and therefore relaxing on a sun lounger on the beach in the summer and regular visits to the solarium are perceived as a tribute to beauty. But doctors are sounding the alarm: tanning is not only not healthy, it also takes away the very beauty that every woman strives to preserve.
“Few people think that tanning is a protective reaction of the skin,” comments dermatovenerologist Vera Malinovskaya. — Darkening occurs as a response to exposure to ultraviolet radiation. If this exposure occurs frequently, the risk of skin cancer and photoaging increases.”
How does it happen? Ultraviolet light changes the structure of the skin. Its short UVA rays affect only the top layer - the epidermis, but are destructive. Regular “burns” caused by tanning eventually lead to the appearance of foci of microinflammation, obstruction of blood flow, and damage to the capillaries that nourish the skin. Cells do not receive sufficient nutrition, dehydration occurs, and cell membranes are destroyed.
Externally, signs of photoaging do not appear immediately. The skin is capable of active regeneration, and if it experiences excess ultraviolet radiation not often, but from time to time, it manages to restore its structure. Regular exposure to ultraviolet radiation is dangerous, as is its negative effect on aging skin. In this case, chronoaging manifests itself in a variety of symptoms:
- thickening of the skin - it becomes rough, porous;
- the appearance of age spots as a result of excessive synthesis of the protective pigment melanin by the dermis;
- dryness, peeling, sagging skin, the appearance of numerous small wrinkles.
“The first signs of photoaging can be seen in young women, aged 25-30,” continues Vera Malinovskaya. — For lovers of beaches and solariums, age marks appear early, and the skin fades very quickly. Photoaging is similar in symptoms to age-related changes, but occurs faster than natural.”
Prevention of photoaging
There are several ways to prevent skin photoaging. We are constantly exposed to sunlight, so reducing their impact on the human body is one of the main tasks. You should not deny yourself sunbathing, because it stimulates the formation of vitamin D, which is very important for the body. Initially, especially in the summer, it is worth using skin care products with UV protection against photoaging with a high SPF value. You must wear sunscreen on the beach.
You should not sunbathe between 12 and 15 hours , because at this time the penetration of sunlight is increased and there is a risk of burns. You cannot ignore the standard methods of protection against photoaging - a hat or cap. They do an excellent job, significantly reducing the level of insolation.
It is important to take care of nourishing the skin not only from the outside, but also from the inside. A great way to help your skin recover from increased sun exposure is with antioxidants. They help get rid of free radicals resulting from cell damage and promote regeneration.
Causes of photoaging
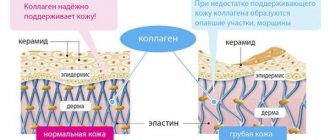
If the body's defense system against exposure to UV rays malfunctions, then damage to the epidermis occurs and hyperpigmentation appears, which persists for a long time. Ultraviolet radiation also penetrates into the deep layers of the skin, which helps activate the oxidation process. As a result, the healthy collagen fibers of the skin that make up its frame are damaged, the contour of the face becomes blurred and a network of wrinkles appears on it.
Signs of photoaging can appear as early as 20-25 years of age. The reason for this may be overuse of tanning, which will manifest itself in a decrease in skin elasticity, the appearance of wrinkles and excessive dryness.
But, if young skin can be saved from the effects of ultraviolet radiation with the help of cosmetics, then with age irreversible changes occur that cannot be compensated and cannot be masked by any cosmetics.
Photoaging of the skin can occur in parallel with natural ageing. In this case, all the signs of aging of the epidermis appear, but at the same time they are more pronounced.
How to improve the condition of your facial skin
Unfortunately, skin restoration processes slow down with age, which is why the negative effect of the photo factor is more pronounced. When it becomes rougher, loses its natural elasticity, and degenerative changes appear, it is worth thinking about procedures that can help change the situation for the better.
You can resort to the biorevitalization procedure - artificial saturation with hyaluronic acid. It provides optimal hydration and restores protective properties. After the procedure, the skin looks more toned, fine wrinkles are smoothed out, and signs of facial photoaging are removed.
Laser resurfacing will help get rid of the rough layer. The principle of its action is aimed at several processes - removal of hardened cells, restoration of the synthesis of its own collagen. After the procedure, you can notice a significant result - the skin pattern is evened out, shallow defects and age spots disappear. Over the course of 3-6 months, the effect only increases, because the process of synthesis of collagen and elastin fibers and the formation of fibroblasts is intensified.
Peels have a combined effect against photoaging of the face. They not only help exfoliate dead cells, but also improve blood circulation and stabilize the formation of sebum.
Sunscreens - as protection against photoaging
“The best sunscreen is your hat, clothes and of course an umbrella.
But we can’t hide from the sun and we have to turn to sunscreen cosmetics.” The main task of sunscreens is to prevent UV from penetrating the skin. For these purposes, sunscreens use ultraviolet filters, which can be divided into two groups:
- Organic filters (or "chemical" filters) that absorb ultraviolet photons
- Inorganic filters (or "physical" filters) that reflect ultraviolet photons.
Methods to combat photoaging
Photoaging can be successfully combated with the help of cosmetic procedures. The most accessible of them include medium or deep chemical peels with trichloroacetic or fruit acids, phenol, retinol, etc. Peels for photoaging have a complex effect on the skin: whiten, exfoliate, moisturize the skin. During photoaging, the use of various physical methods of influence is recommended to smooth the skin surface. These include laser skin resurfacing, dermabrasion, microdermabrasion. The method of photorejuvenation, in which a complex effect on the skin is carried out by a system of pulsating thermal and light energy, is gaining increasing popularity these days. This method of combating photoaging of the skin has proven itself to be excellent due to the minimal number of undesirable consequences, good tolerability, and effective effect on improving the condition of the skin. After the photorejuvenation procedure, skin pallor and a decrease in the number of lentigines and telangiectasia, improved skin texture, increased skin turgor and elasticity are noted.
Premature skin aging, photoaging
Premature skin aging - what is it and when should you think about it? What can lead to premature skin aging?
Genetically determined aging develops rather slowly and is accompanied by gradual thinning of the skin, a decrease in its elasticity, and a slowdown in the rate of its renewal and regeneration.
And the appearance of the first wrinkles is not explained by age, but by the damaging effects of unfavorable environmental factors, the main ones of which are solar radiation, free radicals and skin dehydration.
Premature skin aging is primarily associated with chronic sun exposure of the skin. Residents of hot countries age earlier than their northern neighbors and this is an indisputable fact.
Especially if you look at open areas of skin - face, hands. The role of sunlight in the process of early aging is so significant that scientists began to call this type of aging photoaging.
Sunlight is divided into ultraviolet light, visible light and infrared radiation.
The ultraviolet spectrum is divided into 3 regions:
- UV-C rays are the rays with the shortest wavelength and are the most dangerous because they have the highest energy. Fortunately, all UV-C rays are trapped in the stratosphere.
- UVB rays reach the Earth's surface by passing through the ozone layer. In the skin, they penetrate the epidermis but do not enter the dermis. These rays are highly damaging and cause sunburn, tanning and skin cancer.
- UV-A rays are the longest, have the least energy, but at the same time have the highest penetrating ability, reaching the deep layer of the skin - the dermis, and provoke the formation of free radicals in skin cells - oxidative stress. They are responsible for photoaging and skin cancer.
Small doses of UV radiation are essential for human life. It has been proven that they play a major role in the synthesis of vitamin D and calcium metabolism in the cells of our body.
In winter, with a lack of sun, there is an exacerbation of some skin diseases. And a person’s psycho-emotional state depends on ultraviolet rays - in winter, “loss of strength”, chronic fatigue and depression are more often observed.
Excessive UV radiation has damaging effects on the skin, which can be divided into acute and chronic.
When the skin is acutely damaged by the sun's rays, tanning, thickening of the skin and sunburn develop. In the modern world, a tan is considered a sign of health, but from a medical point of view this is not entirely true.
The fact is that tanning is a protective reaction of the skin to damage from the sun's rays. The main purpose of tanning is to prevent further damage to the skin, which can lead to irreversible consequences.
It is important to remember that the skin produces the pigment melanin according to the amount of solar radiation that hits it, and that sunburn is a natural way of limiting a person's exposure to the beach, a protective reaction of the skin to damage.
Immediate tanning is caused by UV-A rays and is the result of redistribution of the melanin pigment in the superficial layers of the skin. It appears 2 hours after active insolation and does not protect against sunburn.
Delayed tanning occurs several hours or days after exposure to UVB rays. Its formation is associated with the activation of the enzyme tyrosinase, which leads to increased production of melanin and an increase in the size of cells - melanocytes. Delayed tanning remains for weeks and even months after UV exposure.
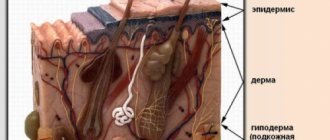
Premature skin aging or photoaging is characterized by the fact that, unlike genetic aging, there is not thinning, but thickening of the surface layer of the skin - the epidermis.
Elastin fibers in the dermis are damaged, but the ability of skin cells to synthesize collagen and hyaluronic acid is not impaired, that is, photoaging is a reversible process.
Also, with photoaging, the number of spider veins increases, age spots appear, and skin immunity decreases.
Sunburn is familiar to anyone who has been sunburned on the beach. To avoid this very unpleasant, and most importantly, harmful condition for the body, you must remember that the skin of different people tans differently.
Premature skin aging and Fitzpatrick skin phototypes:
- Type 1 - people who never tan, always get sunburned - usually people with light hair - blondes, redheads, pale skin and blue eyes. Tanning is generally contraindicated for such people; in the summer they should use sunscreen with SPF-50, and it is advisable not to go out in the sun without protective clothing. This is the so-called “Celtic type”, unfortunately, their risk of developing skin cancer is very high.
- Type 2 - such people sometimes manage to tan, but most often they get burned. Light skin, light brown or brown hair. Such people also do not want to tan at all; they can stay in the open sun for no more than 10-15 minutes without using sunscreen.
- Type 3 - in such people, the tan develops gradually and moderately, light brown in color, and sometimes a sunburn occurs. They can be in the open sun without protection for no more than 30 minutes.
- Type 4 - they always tan, never burn, or the burn is rare and minimal, the tan color is brown. These are people with dark skin and dark hair. You can be in the sun without protection for up to 1 hour.
- Types 5 - 6 - these people always tan immediately, getting a dark tan, and never burn. As a rule, these are representatives of the Negroid race.
These time intervals for exposure to the sun without protection are given very approximately, but they must be adhered to if, instead of a beautiful tan, you do not want to get a sunburn, the consequences of which your skin will remember for the rest of your life.
Premature skin aging or photoaging, unlike normal skin aging, is treatable, since skin changes caused by UV irradiation are reversible.
And in the next article we will talk about the prevention and treatment of skin photoaging.