Causes of injury
A burn to the skin of the face occurs due to the action of thermal, chemical, electrical or radiation factors. The last two species are quite rare. The most likely cause of electrical burns is electric shock. It leaves small but very deep damage.
Radiation burns occur under the influence of sunlight, laser radiation, as well as radiation injuries.
Thermal and chemical burns need to be considered in more detail.
Chemical exposure
A chemical burn to the face can occur under the influence of the following factors:
Depilatory cream
Depilatory cream belongs to acid-based cosmetics. Such compositions are often quite aggressive, because their action is aimed at the complete destruction of hair and partially hair follicles.
A burn with this cream can occur in the following cases:
- Very sensitive skin.
- The product stays on the skin longer than expected.
- Poor quality cream (subject to compliance with all rules for its use).
Aggressive liquids
The composition of liquids that can cause a chemical burn includes both acids and alkalis with salts of heavy metals. These can be substances such as household chemicals, insecticides, some medications, and liquids used in agriculture.
Thermal damage
A thermal burn occurs when the skin is exposed to high temperatures. This may be caused by the following factors:
"Panthenol"
For chemical burns of the face, this cream can effectively combat injuries to the dermis resulting from exposure to chemical components. It is recommended to apply this product immediately after the aggressive drug has been washed off. Panthenol cream must be applied in a thin layer on the face. Apply the composition up to four times during the day. This number of procedures will significantly reduce the risk of scars and cicatrices. Before applying the cream, the affected dermis is treated with an antiseptic.
The drug "Panthenol" has no contraindications. It can be used by pregnant women and those who have sensitive skin.
Degrees
There are 4 degrees of burns (including on the face):
- It manifests itself only as pain, redness and slight swelling of the skin. Only the top layer of the epidermis is affected. Burns go away on their own within 4–5 days.
- In addition to the symptoms characteristic of first-degree burns, blisters with cloudy contents appear. They go away within 2 weeks, almost never leaving any traces. With this degree, the entire epidermis suffers.
- Not only the epidermis is affected, but also the dermis. Divided into "A" and "B". Grade 3 “A” is characterized by partial damage to the dermis. All the signs of the burns described above remain, only much more pronounced. A brown or black scab also appears. At degree 3 “B,” all layers of the skin die.
- The process involves all layers of the skin, subcutaneous fat, and often muscles and bones. Carbonization of tissue occurs. This is the most severe degree of burns, leaving serious scars that cannot be eliminated.
Measures taken after a burn
How will you need to care for your facial skin during the course of treatment?
- If your forehead has been burned, it should be protected from contact with hair. After all, curls will certainly bring pollution and will irritate sore skin.
- The products will need to be applied in a thin layer.
- Preparations based on alcohol will dry out the epidermis. This will cause the skin to become even more irritated. Iodine should not be used either. It will cause an even worse burn.
- A compress soaked in kombucha tincture will help bring recovery closer. This natural remedy accelerates the regeneration of damaged skin.
- A first degree burn will not require any additional measures. After all, it will not leave scars on the face and will go away within a few days. At the site of a healed wound, a thin layer of dead tissue forms, which will come off on its own after some time.
How to treat?
Treating burns is a complex, lengthy and patient process.
You must immediately call an ambulance, regardless of the severity of the injury. Treatment of any burn should take place after consultation and under the further supervision of a physician.
What to do first?
Before the arrival of doctors, it is necessary to stop contact of the facial skin with the damaging factor. You can wash the burn with cold water or apply ice to the damaged area.
It won’t hurt to treat the skin area with peroxide or chlorhexidine. These remedies will not relieve pain, but at least prevent infection. However, you can do something yourself only if the area of the burns is small.
In the hospital, doctors prescribe antibacterial agents (for example, Levomycetin or Erythromycin) to destroy possible pathogenic microorganisms in the wound. This is the main goal of burn treatment. Under no circumstances should you use these medications on your own. Antibiotic bandages are applied to the burn site.
Specific treatment when exposed to chemistry
If you know which chemical caused the burn, it can be neutralized. This means that the destructive effect of the acid will stop after it comes into contact with the alkali and vice versa. However, this must be done in the first seconds of the burn. Unfortunately, this is very dangerous, especially if you overdose on the antidote in a stressful situation.
Further treatment of chemical burns involves the use of water-based products, because the fatty ointment acts as a kind of film for the wound. Namely, in this type of damage, it is important to ensure proper peeling of the scab and not interfere with the recovery process by using oil-based products.
How to remove pain?
Painkillers will help relieve severe pain. For not too extensive burns and in the absence of painful shock, you can use drugs such as Ibuprofen, Paracetamol, Analgin, Diclofenac, Imet, Dexalgin, Nimesulide, and in some cases Ketanov (according to indications and a doctor’s prescription).
In hospital settings, for extensive injuries, narcotic analgesics (Promedol, Fentanyl, Morphine) are used.
Using them on your own is strictly prohibited.
How to heal the skin?
For further healing of burns, such products as Panthenol, Bepanten, Levomekol, Syntomycin ointment, Olazol, Dioxyzol, Radevit, sea buckthorn oil, calendula ointment, Solcoseryl (at the same time prevents the formation of scars), furacilin ointment, Actovegin are used.
Can it be cured quickly?
It all depends on the degree of damage. Whatever it is, the speed of recovery depends on timely consultation with a doctor and compliance with all his instructions.
A burn is severe tissue damage caused by heat or chemicals. It is one of the most common injuries. Burns can affect large areas of the skin and leave deep scars forever. The consequences of burns negatively affect professional growth, relationships with the opposite sex and self-esteem.
Therefore, it is very important to determine the type and extent of damage, as well as to provide the necessary assistance in a timely manner. It is on these conditions that further recovery and the likelihood of consequences depend.
What information will you find out:
Treatment of superficial chemical burns of the face
Typical superficial burns are considered to be injuries of degrees I, II and III A, which leave the skin the opportunity to regenerate independently. Provided that the damage has not affected the eyes, respiratory tract and nasal mucosa, the prognosis for treatment is favorable.
Stage I is treated by accelerating skin regeneration using drugs based on pantothenic acid: panthenol spray, dexapatnenol, bepanthen. In this case, it is preferable to use aerosol forms to avoid contact with the skin and mechanical damage during application.
II and III A degree is treated based on the following principles:
- Prevention of infection. This requires antiseptic treatments with gentle drugs: Chlorhexidine bigluconate, Miramistin, furatsilin solution, isotonic saline solution.
- Local antibacterial therapy using external agents: Levomekol, Sulfargin. This measure helps to transfer the wound process from the stage of inflammation to the phase of active granulation.
- Auxiliary regenerating agents that improve the process of formation of new skin cells and normalize tissue blood circulation: Solcoseryl, Dexapanthenol, Rescuer, Actovegin, Argosulfan help accelerate the epithelization of the damaged area.
Typically, treatment of burn wounds on the face is carried out in an open manner to avoid additional trauma to the healing areas during the dressing process.
Elimination of pain syndrome is carried out during the period of first aid by injection of painkillers, then, at the discretion of the doctor, over-the-counter analgesics can be prescribed: analgin, tempalgin, baralgin, ketanov tablets, or local anesthetic drugs in anti-burn sprays: olazol, lidocaine.
All topical preparations are applied to the wound only if the effect of the chemical substance is completely stopped and eliminated.
Throughout the entire recovery period, it is recommended to carefully monitor the water-salt balance of the body, carry out an enhanced drinking regime and adhere to a gentle diet, the basis of which is proteins - the building material of our cells.
Types of burns by type of injury
Wounds received after a burn require long-term treatment
Burns are classified in different ways in medicine. One of the most used classifications is based on the type of lesion. This means that each type of burn differs from the others in the factor that caused the skin damage. Thus, the type of lesion will determine subsequent treatment, as well as the recovery period.
Thermal burns
The most dangerous type of burn. Can be obtained from exposure of the skin surface to high temperature. Among the most unpleasant consequences are not only the remaining scars, but also the likelihood of loss of vision and severe damage to the respiratory organs.
The resulting wounds after a burn require long-term treatment. If the severity of tissue damage corresponds to the third or fourth degree, then the appearance of scars after wound healing is inevitable.
Chemical burns
Today, a chemical burn to the face can easily be obtained at home by purchasing low-quality cosmetics or a strong cleaning product.
Electrical burns
Electrical burns are quite rare. It can be obtained from a place on the skin that becomes the point of entry and exit of electrical charge. A characteristic feature of this type of burn is small but very deep marks. An electrical burn wound resembles a fire burn and is caused by a short circuit.
Radiation burns
Cases of burns on the face from radiation are not uncommon. Radiation burns can occur on the street, as well as during cosmetic procedures in beauty salons.
Light burns
Light burns can occur if you do not follow the simple rules of exposure to the sun. If you don't use sunscreen or wear a hat, there is a risk of getting burned. It is characterized by superficial skin lesions that go away very quickly.
Ionizing burns
This type of damage to body tissue can occur from a laser in a beauty salon during the use of ionizing radiation.
The wound from a burn is shallow, but getting rid of it can be difficult, since the laser injures nearby tissues: the walls of blood vessels become very brittle, bleeding occurs, and the ability of cells to recover is reduced.
Combined burns
In medicine, there is also a type of combined burns. Fans of modern cosmetology and beauty salons can get this type of burn. Since this is where you can burn the skin with cosmetics and laser at the same time.
First aid
If you get a chemical burn on your face from the cream, what should you do? In order to avoid negative consequences, you will need to take simple measures. It is advisable to find out in advance what to do in this case. After all, sometimes the use of the most harmless compounds can harm sensitive skin.
On the advice of dermatologists and cosmetologists, first aid should be carried out according to the following scheme:
- If any discomfort, burning or itching occurs, it is necessary to remove the composition applied to the face. To do this, just take a large amount of cool water. You will need to rinse your face for 15 minutes. This will relieve swelling and redness. The use of detergents is not recommended, as they can cause additional irritation and pain.
- Remove any remaining moisture from your face. The skin should be completely dry.
- In the event that the skin of the face is burned by a cream that contains acid, its harmful effects should be neutralized with a soda solution (25 g per 200 ml of water).
- If injuries caused by alkaline agents occur, you will need to treat your face with a mixture of citric acid (3-5 g) and water (200 ml).
- Apply special preparations to the affected areas. How to apply chemical burns on your face? To do this, it is recommended to use products whose effects promote tissue regeneration.
- To reduce pain, it is recommended to take painkillers such as Paracetamol, Citramon and Analgin.
In most cases, the actions described above are sufficient to prevent serious consequences. After all, it rarely reaches severe degrees of skin damage when applying cream. If discomfort or severe pain occurs, women immediately try to completely remove the product.
In the case when the drug, the use of which caused a burn, did not cause any particular harm to the dermis, you can cope with the consequences by using traditional medicine recipes that have a gentle effect.
Classification of burns by degree of damage
It is customary to distinguish 4 degrees of burn damage to the skin of different parts of the body and face.
First degree burns
The top layer of skin is not severely affected. Manifestations: redness, slight swelling, pain. Healing occurs within a few days. Affected skin cells dry out and fall off. There are no scars left on the skin.
Second degree burns
The upper layer of skin is affected much deeper. Manifestations: the same as in the first degree, but small bubbles with liquid still form. The recovery period takes 2 weeks until the skin regenerates on its own. Consequences rarely appear.
Third degree burns
Severe damage to all layers of the skin. This type of burns is usually divided into two types:
- grade “A”: the inner layer of the skin, the dermis, is not completely affected, its lower part is preserved. Manifestations: formation of a dark scab, large blisters. If the wound does not become infected, independent regeneration occurs, but there is a danger of secondary deepening of the burn;
- grade “B”: complete destruction of all layers of the outer cover.
Fourth degree burns
Complete destruction of the dermis and epidermis, nearby tissues, burning of bones and muscles. Once the tissue has healed, the scars remain for the rest of your life.
What to do when your face is burned
How to provide first aid if you or someone else has a facial burn? Please note that first aid for a burn is carried out according to certain rules.
After an accident occurs, you need to call and wait for an ambulance. Also at this stage it is important to stop contact with the damaging factor.
- extinguish the flame, remove boiling water or steam;
- stop interaction with electric current;
- Wash your face after contact with chemicals.
Directing a stream of cold water onto the face is allowed only if the skin is intact. Do not apply sour cream or vegetable oil to the wound after a burn.
It is forbidden to remove remnants of clothing or a hot object that has stuck to the skin from the face after a burn. This should only be done by a doctor, as too large pieces of skin may come off and bleeding may occur. At home, there is a danger of infection if the wound comes into contact with any objects.
It is not recommended to treat a wound on the face and apply a bandage without special skills and medical training for this. Without painkillers, this process will cause the victim severe pain.
If transportation of a patient is required, his entire body must be examined. Check to see if he has any additional injuries (depending on the circumstances of the accident). In the absence of emotional reactions in the victim, such as screaming and crying, you need to remember that with third-degree burns a state of shock often occurs.
Not everyone knows which doctor can help with a facial burn, but this question is wrong, because the first condition for medical care is calling an ambulance team.
If the burn is minor, you can get to the hospital on your own. If you have a third or fourth degree burn, surgery will be required at a burn center. In all other cases, you need to contact a dermatologist or therapist.
Burns from creams and other cosmetics
As a rule, they develop as a result of a combination of individual intolerance to components and exposure to a chemical substance. They can occur as a result of mistaken application, for example, of a cream for softening dry calluses of the feet with phenol on the face, or out of ignorance.
Recently there was a case when a patient came in with signs of a deep burn, who used a phytopilling product as a night moisturizer: she applied the drug before bed, and by the morning she received a swollen, red face and burning pain. The injury occurred due to the fact that the inscriptions on the sachet with the drug were made in hieroglyphs, and the product itself was ordered on the Internet among other cosmetic creams.
Also, chemical damage often develops intensively and quickly if there has already been a negative reaction to this product or its components before. The body has already recognized the chemical composition as potentially harmful and has prepared an algorithm for a lightning-fast histamine response to the stimulus.
But for some reason, these types of burns from cosmetic products are quite common. Repeated application of a dangerous product is often explained by the fact that “what if there is no reaction this time” and “it would be a pity to throw away a good cream.”
Remember: if the skin once shows an allergy to a substance, this can only mean that next time this reaction will occur faster and be more severe. In this case, there is no such thing as a lucky coincidence of circumstances and the others will be “blown away.”
Dear readers, you should also be careful when using the following products as cosmetic care:
- Salicylic alcohol exceeding 10% concentration.
- New creams with labels that you find difficult to make out or are not sure that they are intended for the face.
- Homemade masks based on sour fruits and berries. Fruit acids can corrode the skin quite deeply, despite their appetizing name.
- Products that contain acidic ingredients such as vinegar. Trichloroacetic acid and ordinary table vinegar are fundamentally different substances, both are far from safe for the skin.
- Aggressive lightening creams.
- Concentrated aroma oils.
- If you have had allergic reactions to cosmetics, use new products with caution. First test for skin sensitivity by applying the substance to the inner surface of the elbow. If no signs of irritation appear within 10-20 minutes, the product can be used. But even if there is the slightest redness of the skin during the test, you should refuse to use such facial cosmetics.
- It is especially dangerous to experiment with new care products during the recovery period after cosmetic procedures, not only peeling, but also mesotherapy, plasma lifting, hardware and mechanical cleaning.
If you find it difficult to choose the optimal product for solving aesthetic problems or a cream for everyday care, seek advice from an experienced specialist, do not take risks.
First aid for facial skin burns
First aid is provided directly on site or in the hospital. If it is carried out competently, it will quickly heal the burn on the face, speed up the recovery period and reduce the risk of consequences. It consists of the following steps:
- Before treating a burn on the face, you need to administer anesthesia, which depends on the severity of the tissue damage. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (Ketoprofen, Ketorolac), painkillers and antipyretics (Paracetamol), as well as narcotic painkillers (Omnopon, Morphine, Promedol) are used. The use of local anesthesia is considered common.
- Treatment of burn wounds consists of the following stages: the affected epidermis is removed, the blisters are drained, and a bandage is made.
- If the burn is determined to be first or second degree, the victim is prescribed treatment at home and a prescription for the required drug is issued. After this, the patient comes for a medical examination.
- For third and fourth degree burns, competent medical care is provided in hospital treatment and consists primarily of the use of infusion therapy.
Depilation burn
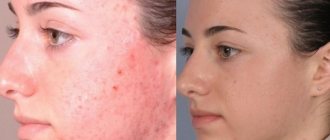
Removing unnecessary hairs using a special cream is one of the least expensive and easiest ways to get the desired result, which does not require any special skills. To carry out the procedure, simply apply the cream to the skin and wait a few minutes. Next, you just need to remove the product along with the hairs. Such ease of use does not mean that the procedure is completely safe. After all, such creams contain active synthetic acids. It is under their influence that those hairs that are located on the treated area dissolve. The surface layers of the skin also react with acids. This leads to a burn on the face after depilatory cream. It is accompanied by burning and redness of the skin. Such a chemical burn on the face (see photo below) most often appears on the most sensitive areas.
Proper treatment of burns
Further treatment of burns consists of the use of local disinfectant preparations to prevent wound infection:
- antiseptic oxidizing agents: potassium permanganate and 3% hydrogen peroxide solution;
- antiseptics: Dioxidin, Ethacridine lactate, Quinoxidin, Furacilin, Nitazol, Furagin;
- cationic disinfectants (Chlorhexidine, Decamethoxin), ionophores (Gramicidin, Valinomycin), silver nitrate;
- antibiotics: Levomycetin, Erythromycin;
- streptocid.
The listed drugs make it possible not only to remove redness of the skin after a burn, but also to avoid infection in the wound, which promotes speedy healing. But using them on your own initiative is strictly prohibited. It depends solely on the doctor’s decision what the patient should apply to the damaged skin.
To localize pain in a hospital setting, the following means are used:
- Droperidol;
- Ketamine;
- Midazolam;
- Sodium hydroxybutyrate;
- Propofol;
- Sodium thiopental;
- Ftorotan;
- Fentanyl.
Once you have a burn wound, you will need to choose a drug to treat it. First, consult a doctor who will prescribe medications based on the severity of the burn and the type of injury. If the burn is superficial, then to heal the skin you can use drugs such as:
- Bepanten;
- Panthenol;
- Rescuer;
- Olazol;
- Levomekol;
- Solcoseryl;
- Eplan;
- Ebermin;
- Furacilin ointment;
- Actovegin;
- Radevit;
- Syntomycin ointment;
- Dermazin;
- Sea buckthorn oil;
- Argosulfan;
- Calendula ointment.
This variety of medications should not replace a visit to the hospital and consultation with a doctor. Remember that the burn is on the face, so it is very noticeable. And any side effects from improper use of the drug can greatly harm your appearance.
Considering that most often women get burns from cosmetics or cleaning substances, it should be noted that only a dermatologist is able to choose the right treatment package. In addition, you need to find out from him about the possibility of using folk remedies.
"La Cree"
This is an excellent regenerating agent. Its active components are panthenol, as well as some medicinal plants, including licorice, chamomile and string. In addition to them, the cream also includes avocado oil. Thanks to its healing ingredients, the cream perfectly relieves irritation, eliminates pain, and also helps restore the surface of the skin after first-degree burns and minor injuries.
Even a small amount of the drug, which is recommended to be applied once a day, will significantly alleviate the condition. Apply the product to cooled skin and apply until the problem completely disappears. As a rule, such a course of therapy lasts 5 days.
This cream has no contraindications. Its use is not prohibited for pregnant and lactating women. No side effects were identified during the use of the drug. It contains no hormonal or antibacterial substances.
Relief from the condition after applying La-Cri is felt almost immediately. In cases where the resulting burn is shallow, the surface of the skin can be restored with its use within just a few days. In addition, this cream can be used constantly, because it does not cause any addiction.
Treatment of facial burns at home
To treat first- and second-degree burns on the face, your doctor may recommend using some folk remedies that help wounds heal faster. These can be daily external compresses to the burn site based on medicinal herbs and food products:
- lingonberry juice;
- decoctions from oak, aspen or elm bark;
- apple puree;
- chokeberry berries;
- compress of water and baking soda;
- warm cottage cheese;
- mask of egg white and 3 tablespoons of vegetable oil;
- white cabbage leaves;
- mumiyo solution (3 g per glass);
- crushed charcoal.
If a chemical burn is treated at home, then medical supervision must be a prerequisite.
Typically, such therapy comes down to the use of such means as:
- Dexpanthenol to prevent inflammation.
- Preparations based on vitamins A, B, E and vegetable oil.
- Mephenate is an analgesic and anti-inflammatory drug.
- Levosin, Olazol, Dioxyzol - for wound healing.
- Actovegin accelerates skin regeneration.
- Sudocrem, Alfogin, Panthenol are drugs with analgesic, antimicrobial and healing effects.
- Miramistin is an anti-inflammatory drug.
When it is necessary to treat a sunburn of the face at home, a complex of traditional medicine and medications is used:
- Lubricate your face with sour cream, kefir or sour milk.
- Use raw potatoes as a compress.
- Apply an aloe leaf cut in half to the affected skin.
- Make a compress from chamomile infusion.
- Apply Panthenol to the burn site.
- Apply hydrocortisone ointment against skin inflammation.
- Apply Indomethacin and Diclofenac against swelling and pain.
- Use cooling gels for pain relief.
"Levomekol"
This ointment is an anti-inflammatory agent with an antimicrobial effect. Its active components are methyluracil and chloramphenicol. This combination of ingredients allows you to get the fastest results, which leads to the fact that damaged areas of the skin are restored in the shortest possible time.
To treat a burn on the face, you will need a small amount of ointment. Apply it 2-3 times a day to the damaged area of the epidermis. Treatment must be carried out for 10 days.
This remedy is contraindicated in case of individual sensitivity to its components. Its use by pregnant and lactating women, as well as young children is allowed. Side effects are extremely rare and are expressed in the form of allergic reactions.
Levomekol ointment is recommended for deep wounds with purulent discharge. In this regard, it can be used to eliminate second-degree burns, when blisters form on the surface of the skin. Within a few minutes after applying the ointment, the pain subsides. Next, the inflammation of the damaged areas is gradually eliminated.
Classification of burns on the face
Due to lack of protection, facial injuries occur quite often, approximately 2% of them are burns.
A burn is a superficial or deep tissue injury that occurs under the influence of air, high-temperature liquids, chemical compounds and other external factors.
In medicine, several classifications of burns are used; the most common ones are based on the cause of damage and the depth of the affected tissue. The clinical picture, treatment methods, recovery time and prognosis depend on this.
Provoking factor
According to the reason that caused the burn, they distinguish:
Thermal burns
One of the most common and dangerous burns is thermal; under the influence of high temperatures, proteins that form tissues are destroyed. Thermal damage to the face can be caused by several factors, and the clinical picture of the burn is somewhat different:
Under its influence, a fairly large area of the face is affected, but the tissues are affected shallowly. The danger of steam burns lies in the high probability of damage to the mucous membranes, organs of vision and breathing.
Such burns are small in area, but tissue damage can be deep, especially if hot oil comes into contact with the face.
Tissue damage caused by open flames is usually extensive and deep, with a high likelihood of complete or partial loss of vision and serious respiratory damage.
They leave a burn with clear boundaries, which is often accompanied by detachment of part of the epidermis (when trying to remove the object). Very often, after such an injury, noticeable marks remain.
Chemical
The second most common cause of facial burns is the action of chemicals. Today this can happen in the workplace (in a medical laboratory, at an industrial enterprise), at home (household chemicals, improper use of cosmetics) and even in beauty salons if the cosmetologist is insufficiently qualified.
Burns can be caused by acids, alkalis or salts of certain metals.
Alkaline burns are the most complex; when a chemical gets on the face, it literally eats away soft tissue, and sometimes even bone.
Damage to the face with various acids does not cause such deep damage, although the extent of the damage can be quite large. Under the influence of acid, scabs form on the skin, which prevent the substance from penetrating further. Deep tissue damage can occur when concentrated acids come into contact with the skin, while superficial damage occurs accidentally.
The same thing can happen at home: when using low-quality or inappropriate cream, face mask, when cauterizing acne, insect bites, and damage from antiseptics. For example, iodine burns the edges of the wound; healing will take longer and leaves an unattractive mark.
Damage to the facial skin by salts of heavy metals (bismuth, gold, antimony, iron, mercury, copper, lead) occurs relatively rarely. They occur upon contact with medications, pest control products for plants, and fertilizers. In appearance, such burns are similar to acid burns.
All types of chemical burns are dangerous due to general intoxication of the body.
Electrical
Electrical shock to facial tissues is extremely rare. In appearance it resembles a thermal burn, has a small area, but tissues can be damaged to a great depth.
Ray and solar
Complaints of radiation burns are very common. They arise under the influence of ultraviolet radiation, laser rays and other radiation. There are several varieties:
The most common burns in this category are light or sunburns. They occur during prolonged exposure to the street during sun exposure, without the use of creams with a UV filter, and in solariums. The affected area is extensive, but the damage is superficial.
Typically, light burns are relatively mild and almost never leave marks.
They occur during intense laser exposure during cosmetic procedures. In this type, the outer integument is slightly injured; the danger comes from damage to the deep layers by rays. Treatment is complicated by impaired cell regeneration ability and capillary fragility.
Radiation burns can occur as a complication of therapy for malignant tumors.
In addition to the main types of facial burns, there are combined ones - injuries combined with other injuries.
Acid or alkali: fundamental differences in the mechanism of injury
When receiving chemical damage to the face, the following factors play a huge role:
- type of aggressive substance;
- concentration;
- duration of contact;
- skin type;
- volume of aggressive liquid or quantity (for dry forms of chemicals);
- quality of first aid provided;
- the presence of an allergic reaction in the victim.
Taking into account all these points, appropriate drug treatment will be prescribed.
A chemical burn has a different development mechanism depending on the type of damaging agent. Injury from acids is always accompanied by increased tissue dehydration and protein coagulation, so its sign is the presence of dry necrosis at the sites of injury. The dense crust serves as a kind of protection against the penetration of substances into deeper layers.
Moreover, each type of chemical is characterized by a special color of the scab:
- hydrogen peroxide: grey-white;
- nitric acid: bright yellow, dense;
- sulfuric: black or brown;
- hydrofluoric: milky white, dirty gray;
- salt: light green;
- salicylic: brown.
The method for determining a dangerous substance according to the classification of the scab is not reliable, however, for primary diagnosis, if the reagent is unknown, it helps to determine further tactics for providing assistance.
An alkali burn is accompanied by deep damage to the skin of the face, this is due to the presence of a large number of sebaceous glands in this area and the special oiliness of the skin, and, as is known, fats bind well to alkalis, enter into a saponification reaction and increase the destructive effect on tissue.
Plus, wet necrosis develops, which does not create any barriers to the penetration of the reagent into the deep layers of the dermis. During the healing period, bleeding, non-healing ulcers form. Therefore, such burns pose a particular danger.
Oxidizing agents and salts of heavy metals can come into contact with the skin as a result of working with herbicides, as well as in the composition of medications. They cause a superficial acid-type burn, with the formation of a dry scab.
Phenolic burns are accompanied by severe intoxication due to rapid absorption through the skin.
Damage level
When a face is burned, different layers of skin and muscle tissue can be damaged. On this basis they distinguish:
It is diagnosed when only the superficial layer of the epidermis is affected by any aggressive factors. Clinical picture: slight swelling, redness of the skin, pain when touched.
During the healing process, peeling begins, which disappears without a trace after a few days.
They differ from the milder form by the formation of fluid-filled skin bubbles (blisters) on the surface. The healing of such an injury lasted 1-2 weeks, the restored tissues did not differ from undamaged ones. On the face, such burns often occur after cosmetic procedures.
They are differentiated into 2 types: A and B. With tissue damage of grade A, huge blisters filled with serous fluid form on the surface of the skin. The epidermis partially dies, brown or black scabs appear. Degree B is diagnosed when all parts of the skin are completely affected.
The most difficult and dangerous. The destruction of the epidermis, fatty tissue, part of the muscle tissue, and sometimes bones occurs.
Burns of the 1st, 2nd, 3rd (A) degrees are classified as superficial; the skin can recover on its own. With proper treatment, they do not leave scars, or they can be easily eliminated with special ointments and procedures. Treatment of such facial injuries can be carried out at home.
Deep burns (third (B), fourth degree) can be accompanied by complications; they leave deep scars that are difficult to correct. Treatment of a deep burn is carried out in a hospital and can last several weeks or months; without professional help, infection can occur.
Main symptoms
Signs of a chemical burn to the face vary depending on the extent of the injury. There are four of them in total:
- First. This degree can be determined by redness, inflammation, burning and pain.
- Second. In addition to the first degree symptoms, watery blisters also appear on the dermis. In this case, the body takes much longer to restore its skin. If the burn area is the size of a child’s palm, you should seek medical help.
- Third. With a burn of this degree, deep tissues are affected. A scab begins to form on top of the wound.
- Fourth. This degree is characterized by damage to the deep layers of the skin and even to the bones.
What to do first: emergency care
If a burn occurs on the face, first aid must be provided to the victim. This will prevent damage to deep tissue layers and reduce the likelihood of complications.
What to do in these cases? Actions depend on the cause of the burn and can vary significantly:
- In case of thermal burns caused by an open flame, you must first extinguish the flame (cover your face with a thick cloth).
- The next step is to cool the skin. You can place your face (if the integrity of the epidermis is preserved) under a stream of cool water, or wash the skin manually or irrigate it with a spray bottle.
- For chemical burns, it is important to know what exactly caused the tissue damage. Contact of some products (containing aluminum) with water is unacceptable, as the reaction intensifies. If the skin is damaged by acid, it is neutralized within a quarter of an hour with a solution of soap or soda, alkali, table vinegar.
- Examine the victim to ensure the absence or presence of other injuries.
- In case of electric shock, remove the source from your face and check your pulse. If necessary, perform artificial respiration.
- If the burn is small and the person feels relatively well, you should go to the burn department of the nearest hospital as soon as possible. In all other cases, it is necessary to call an ambulance, explain the situation and strictly follow their recommendations.
Deep burns often cause painful shock, when the victim does not experience discomfort, but performs chaotic actions. In this case, he needs to be calmed to prevent mechanical damage to the burned tissues and infection.
Methods of traditional therapy
How to cure a chemical burn on the face? If the lesion is minor, then a remedy based on honey will eliminate it. This bee product has many advantages, including eliminating pain, stimulating tissue repair processes and relieving inflammation.
The preparation of such a product should be carried out in stages:
- Warm honey (20 g) in a water bath. Exposure to heat should completely dissolve the sugar grains.
- Beat the yolk until white. After this, it is sent to already cooled honey.
- Add 20 ml of vegetable oil to the mixture.
Features of treatment
Treatment for facial burns differs from treatment for other injuries. Such injuries are considered the most complex.
Firstly, the skin and subcutaneous tissue layer are much thinner here, so the damage can be deep. Secondly, healing occurs faster if the tissues are at rest, which is almost impossible to do with the face: facial, chewing movements lead to permanent damage to the healing areas.
After visiting the burn department, the patient is examined, the severity of damage to facial tissues and treatment tactics are determined. First aid consists of several stages:
- Anesthesia (local or general). The type of anesthesia used depends on the depth of the injury. Local anesthesia is carried out through applications with Novocaine or Lidocaine. Several types of medications are taken orally: Paracetamol, Analgin, Baralgin, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (Ketoprofen), strong narcotic painkillers (Morphine, Promedol).
- Patients in a state of shock (after electric shock or very deep burns) undergo antishock therapy - intramuscular injection of a solution of analgesics and antihistamines.
- Removal of affected tissue, drainage, antiseptic treatment (Chlorhexidine, isotonic solution, hydrogen peroxide).
- In some cases, additional antibacterial treatment and tetanus vaccination are required.
After antiseptic treatment and receiving treatment recommendations, patients with superficial burns are treated at home, while those with deep burns remain in the hospital. Treatment for severe burns is as follows:
- treatment several times a day with antiseptic and anti-inflammatory agents;
- applying bandages with medications that accelerate healing;
- removal of infected or dead tissue.
After healing, physiotherapeutic procedures or plastic surgery may be prescribed to restore facial tissues after deep burns.
How to treat with medications and creams
Several groups of drugs are used to treat burns:
- anesthetics;
- antiseptics;
- means to eliminate swelling and hyperemia (redness) in 1st and 2nd degree burns;
- antibiotics if there is a threat of infection;
- drugs that accelerate tissue regeneration.
Each group includes a large number of medications; it is not recommended to use them without a doctor’s prescription.
Pain of varying intensity may be felt until the facial tissues have completely healed. To relieve pain, you can use the well-known Nurofen, Ketanov, Analgin, but more often they use products for external use in the form of gels and ointments. Mephenate and Dioxyzol ointments have proven themselves well. In addition to pain relief, they have a pronounced antiseptic and wound healing effect.
The affected area must be treated daily with antiseptics to avoid infection: alcohol, Miramistin, Chlorhexidine, hydrogen peroxide. The use of Chlorhexidine and Miramistin is tolerated very well by patients - no discomfort occurs when applied to tissue.
To soothe the skin for superficial burns, use external remedies:
- Panthenol;
- ointment "Rescuer";
- Actovegin;
- Bepanten;
- furatsilin ointment;
- Levomekol;
- ointments of plant origin (sea buckthorn, with calendula).
Panthenol has proven itself well; it not only removes the feeling of tightness, but also accelerates regeneration and reduces the intensity of pain. In some cases, antihistamines are prescribed: Claritin, Diazolin, Loratadine.
Actovegin can be used in the treatment of burns of various types. The drug activates blood circulation and accelerates metabolic processes, which will help get rid of the consequences faster.
When a burn suppurates, antimicrobial agents are used: Levomekol, syntomycin ointment, streptocide (in the form of powder or ointment), Methyluracil, Baneocin, preparations with silver (Dermazin, for example). It is better not to use fat-containing products; they interfere with the outflow of fluid.
How to get rid of it using folk remedies
When treating superficial burns without complications, it is permissible to use traditional methods; they reduce discomfort, moisturize and accelerate tissue regeneration.
- dairy products;
- vegetable juices: cabbage, potatoes;
- applesauce;
- lotions with decoctions of oak bark, chamomile, elm;
- juice from lingonberries or chokeberries;
- a squeeze of boiled and then fried egg yolk;
- mumiyo dissolved in water;
- lotions with aloe leaf;
- dusting the wound with powder obtained from charcoal;
- a mixture of whipped egg whites and refined vegetable oil;
- lotions from burdock juice;
- sea buckthorn oil in pure form or mixed with fir oil in equal quantities.
Treatment of burns at home
Outpatient treatment is acceptable:
- in mild form (1st and 2nd degree) for all types of burns;
- for a small area - less than 1% of the entire surface of the skin (visually no more than the palm of a person);
- no high fever or signs of tissue infection.
The treatment tactics in each case are determined by the doctor, in general terms it looks like this:
- antiseptic treatment 1-2 times a day;
- applying bandages with epidermis-restoring agents;
- taking painkillers.
If the face is damaged by chemicals, even to a minor extent, regular monitoring of the tissue condition during home treatment is necessary.
In case of a radiation burn of the face, it is enough to periodically apply softening and soothing substances to the skin: sour cream or kefir, cucumber juice, Panthenol, cooling gels with menthol, Indomethacin to eliminate swelling and pain.
A prerequisite for a facial burn is daily intake of fluid in large quantities (more than 2 liters) and consumption of food enriched with light protein, vitamins A and E: carrots, fresh vegetables and fruits, turkey and chicken meat in liquid or puree form.
Causes
Burns on the face are tissue damage caused by either chemicals or high temperature. They are among the most common injuries.
There are a huge number of classifications in medicine, but one of the most frequently used is based on the type of lesion, i.e. what specific external factors caused the burn. Not only the symptoms, but also further treatment, and even the rehabilitation period with subsequent prognoses for the future will depend on them.
Thermal
The most dangerous of all is a thermal burn of the face, which destroys complex proteins - the basis and foundation of cells and tissues. Occurs due to exposure of the skin to high temperatures. How you can get burned:
- Fire can burn the entire surface of the face, and not just a separate area; among the most dangerous consequences are not only scars, but also loss of vision, as well as damage to the upper respiratory tract.
- The liquid does not have a broad effect, usually it is a local tissue damage, but very deep: a burn to the face with boiling water is common in everyday life.
- Steam is an extensive injury to the skin, but not deep, although it affects the upper respiratory tract.
- Hot objects leave marks for life, the wounds have clear boundaries and differ in depth, and when an object is removed from the face, the dermis peels off, which becomes a new traumatic factor.
Such wounds require long-term treatment and often have a disappointing prognosis. If the depth of tissue damage is determined to be degree III or IV, scars are inevitable.
Chemical
The modern chemical industry is experiencing extraordinary prosperity in the 21st century. More and more new formulas developed in laboratories are finding wide distribution in everyday life.
And today, a chemical burn to the face can easily be obtained at home by purchasing low-quality cosmetics or a powerful cleaning product. The following aggressive substances may affect the skin.
- Acids
Acids are considered very dangerous, but in fact they do not differ in the depth of tissue damage, because after them a scab forms, preventing further penetration of the substance.
A specially caused facial burn after peeling with fruit acids is a vivid example of this, when renewed, beautiful and young skin appears under the burnt skin, and charred cells fall off without any further scar formation. But if a cosmetologist takes a more concentrated acid or makes a mistake and accidentally increases its dosage, such a procedure can end very badly.
Due to the rejuvenating and renewing effect of acids, many manufacturers of the modern beauty industry include them in the formulas of their skin care products. And she may react to them differently.
The result is a shallow, but very unpleasant, hyperemic cosmetic burn of the face, which will require long-term treatment. Moreover, it will not guarantee the absence of consequences in the future.
Therefore, it is strongly recommended to first test all products intended for skin care. Most often, women get burned by a cream that, as it seems to them, contains no danger.
There are often cases when acids become the culprits of so-called drug-induced injuries, because they are also present in many medications. Wanting to get rid of hated pimples on their faces, women so often like to burn them out with pharmaceutical products. The result is a burn from iodine, for example. After all, few people know that from a chemical point of view it forms a number of numerous acids.
- Alkalis
This is the most severe chemical burn, since alkali literally corrodes tissue and penetrates very deeply. A barrier from the scab, as with acid, does not form. This substance may come into contact with the skin accidentally due to careless handling of chemicals or cleaning agents.
- Heavy metal salts
Facial burns from heavy metal salts are superficial and resemble acid damage in appearance. The most common ones include mercury, copper, gold, cadmium, iron, lead, bismuth, thallium, and antimony. They are found in industrial organic and inorganic compounds, agricultural herbicides and insecticides, and medical preparations.
Electrical
Electrical burns to the face are very rare, as they occur at the point where an electrical charge enters and exits the body. A distinctive feature of such a lesion is several small but very deep marks. A voltaic arc resembles a fire burn and occurs in the event of a short circuit when the current does not pass through the body.
Radiation
Radiation burns on the face are also far from uncommon, as they are caused by radiation that can be caught both on the street and become victims of it in numerous and so popular beauty salons today.
- Light
If you do not follow the basic rules of being under the scorching rays of the sun (not using cream with SPF filters, not wearing a hat), you can get a sunburn on your face - a common occurrence in summer. It is characterized by superficial tissue damage, which, with proper care and treatment, goes away without a trace.
- Ionizing
These include laser burns, which can be obtained in a beauty salon after a series of procedures that use ionizing radiation. The damage itself is shallow, but treatment can be difficult, since the same laser injures nearby tissues and organs: the vessels become brittle, bleeding begins, and the cells’ ability to regenerate is reduced.
In medicine, combined and combined burns are also distinguished. The first involves tissue damage under the influence of several factors at once. This often happens to lovers of modern cosmetics and beauty salons: you can get a facial burn from the cream and laser at the same time.
Combined ones are diagnosed when a burn and any other injury (for example, a jaw fracture) coincide in time. And this is not the only classification - there is another, no less well-known, but already based on the depth and extent of the wound received.
Through the pages of history. In the Middle Ages there was a practice of branding criminals, convicts, and slaves. In a number of cases, the mark was placed directly on the face, and it was nothing more than a burn with a hot iron, which caused extreme pain, but at the same time was relatively safe for life and left marks on the skin until the end of days.
Cautions: how to avoid unpleasant consequences?
The result of burn healing depends on the treatment tactics and behavior of the victims. The face is a sensitive place; any mistake can leave a mark for life, which can worsen the quality of life and cause complexes.
Mistakes to avoid:
- Smearing the burned area with oil is perhaps the most common and dangerous misconception. Oil, even sterile, forms a dense film that will reduce the access of oxygen to the wound and block the outflow of physiological fluid. In the worst case (if you do not use an unrefined product), infection may occur.
- When trying to cool the damaged area during a thermal or radiation burn, blot it with cotton swabs or apply ice and cooled objects. Intense pressure will lead to mechanical damage to tissues, disrupt blood circulation and complicate treatment.
- In case of thermal burns from hot objects, molten metals or plastic, you should never remove them. This action further injures the tissue and can cause bleeding.
- Treating a fresh burn with alcohol-containing substances.
- Cover the burn with a thick cloth, and even more so with an adhesive plaster. The wound must “breathe.”
- Open the resulting blisters yourself. At home, it is impossible to make the process sterile; this will only increase the risk of infection.
- In case of a chemical burn, on the first day, any external actions are prohibited, except for washing with water or special solutions.
Recommendations for the recovery period
Complete healing and tissue regeneration for facial burns can take several months. To ensure recovery without consequences, you must follow the following recommendations:
- strictly adhere to the prescribed treatment;
- do not apply decorative cosmetics to damaged skin;
- if possible, reduce facial movements;
- solarium, sauna, beach and swimming pool are strictly prohibited;
- postpone cosmetic procedures in the salon and at home;
- monitor the healing process with a dermatologist.
"Rescuer"
This drug is a homeopathic complex remedy. It contains such active ingredients as milk lipids and sea buckthorn oil, beeswax and tea tree oil, as well as vitamin E. The drug helps to quickly and effectively eliminate facial burns.
During treatment, the balm is applied to damaged areas 2 or 3 times during the day. The skin should be clean and dry. The course of therapy is until complete recovery.
It is not recommended to use the balm in case of individual sensitivity to the components that are in its composition. A possible side effect is an allergic reaction.
Improvement in the condition occurs within the first minutes after applying the balm. Pain and burning go away, and then the epidermal tissue is gradually restored.