What is tubular breast shape, signs
The tubular form of the mammary glands is a developmental anomaly, against which the area of the base of the breast decreases , mastoptosis, alveoreal hernia and connective tissue deficiency develop. The glands acquire a characteristic elongated tubular shape.
There are unilateral and bilateral lesions, the areolas protrude slightly. The pathology is diagnosed in 20-25 patients out of 1000. Patients rarely seek medical help due to the fact that the disease is practically asymptomatic. Pathology is considered an aesthetic defect.
An anomaly is detected during external examination. Depending on the degree of damage, the chest has a cylindrical or cone-shaped shape. At the base, the organ narrows, the interthoracic space is enlarged.
It is possible to develop glandular ptosis. The mammologist often discovers that the areolas are underdeveloped; they are dilated and do not correspond to the patient’s age. The nipples are dense, structural anomalies are observed (for example, retraction).
In rare cases, an alveolar hernia is diagnosed, which is manifested by protrusion of the nipple complex. There are no subjective symptoms manifested in the form of discomfort or pain.
When breastfeeding, the tubular shape of the breast can become an obstacle for the baby to latch on to the nipple.
A woman may experience difficulties during breastfeeding caused by a decrease in the volume of the mammary gland.
The child cannot latch onto the breast correctly if the structure of the areolar-nipple complex is abnormal.
How is tubular breast augmentation performed?
The operation includes several stages, among which are:
- Periareolar breast lift.
- Plastic surgery of glandular tissue with subsequent formation of a normal breast shape.
- Breast augmentation with implants.
- Correction (lowering) of the inframammary fold.
The procedure begins with preoperative marking of the level of the new inframammary fold in a standing position.
During the operation, the chest is infiltrated with a solution of lidocaine and adrenaline.
To reduce the areola to the desired size, up to 4–4.5 cm, deep-epidermization of the skin of the periareolar area is performed.
Next, the skin in the lower semicircle of the de-epithermic area is dissected, the gland tissue is dissected to the pectoral fascia.
The implantation cavity is formed according to preoperative markings. The gland tissue is dissected along the posterior surface in the middle, dividing the constricting fibrous ring in half, thus creating two flaps that allow redrawing of the breast parenchyma.
If necessary, a silicone breast implant is used to enlarge the breast. The implant can be installed in a purely subglandular or biplanar position (upper part axillary, lower part subglandular). The decision to use breast implants is usually made at a preoperative consultation, where the plastic surgeon and patient discuss whether additional volume will be needed. Typically, anatomical textured silicone implants are used. The periareolar incision is sutured in layers with deep subcutaneous and intradermal sutures.
The scope of the operation may vary depending on the severity of the defect in a particular patient. For example, the surgeon may use periareolar skin resection and minor removal of glandular tissue under telescopic guidance. For some women, this operation is quite effective and allows you to restore the normal appearance of the breast without significant trauma to the mammary gland.
In some cases, the surgeon has to reduce the size of the areola or use asymmetrical implants.
Causes of tubular breasts
The tubular form of the mammary glands develops for a number of reasons.
Scientists have put forward several theories about the occurrence of pathology:
- Acquired factors. A number of researchers do not consider the pathology to be congenital due to the absence of changes in the areolar-nipple complex until adolescence. The reason for the development of the tubular form, in their opinion, is a violation of blood flow inside the mammary glands.
Tubular breast form can develop during adolescence
- Teratogenic factors. The anomaly occurs against the background of a biological or chemical effect on the fetus developing in the womb.
- Hereditary factors. Tubular breasts can be passed down the female line from mother to daughter. The key genes that are responsible for the development of the disease have not yet been identified.
With “goat breasts”, dense bridges are formed inside the mammary glands (one or two), preventing the normal growth of glandular and fatty tissues.
Tubular breasts after childbirth
The tubular form of the mammary glands cannot develop during pregnancy or while breastfeeding.
An aesthetic defect cannot be considered acquired. Pathology is not an absolute contraindication to lactation. Women suffering from grade 2 or 1 anomaly can breastfeed their baby.
An aesthetic defect does not in any way affect the quantity and quality of milk. Women with grade 3 may have trouble latching on to the baby's areola and nipple. The mother must choose the right position during feeding so that air does not enter the baby's stomach. Breast deformation does not affect lactation in any way.
Tubular breasts in a teenager
The tubular form of the mammary gland in adolescents appears during puberty. The number of glands in the chest increases 8-12 times. Tubular lobes are intensively formed.
Only a mammologist can determine the presence of pathology in adolescents.
A mammologist can confirm or refute the diagnosis after the mammary gland is fully formed. The development of pathology is in no way connected with maintaining strict diets: the disease is inherent in a person from the moment of his birth
Tubular breasts: causes, types and degrees, consequences, correction
13 Feb
The nature and degree of development of the pathology
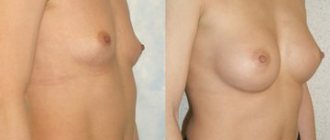
Tubular breast is a congenital defect in which the base of the mammary gland has a reduced diameter, and the breast itself is elongated and has the shape of a tube (tube). The area around the nipple is twice as large as usual, so the gland resembles a mushroom and the nipple is flattened. The developmental defect occurs both in both mammary glands and in one. In addition, the mammary glands may be located asymmetrically if the abnormal development is expressed in them to varying degrees.
The presence of such a defect can be noticed in a girl during adolescence, when sexual development begins and the formation of external signs of femininity. Pathology of mammary gland development (anatomical deviations, asymmetry) can be expressed to varying degrees.
1st degree. The defect is hardly noticeable and does not cause the woman much discomfort. Changes are observed only in the lower part of the gland, where tissue underdevelopment occurs. Its upper part is convex, the lower part is slightly concave, the nipple “looks” down. The area of the areola and nipple are not changed.
2nd degree. The lower and lateral parts of the mammary gland are underdeveloped. The nipple is strongly drooping and the areola is significantly enlarged.
3rd degree. The base of the mammary gland is underdeveloped. Its tissues are compressed by a dense frame. The gland only grows forward. It is a cone with a large areola and a flat nipple.
Causes and signs of the defect
The reason for the formation of tubular breasts is a violation of the structure of the connective tissue from which its frame is formed. The elasticity of the stroma is lost due to the formation of strong bridges. A rigid frame inhibits the development of the mammary gland. Therefore, it can be small, elongated, and devoid of fat.
Signs of tubularity are weak and abnormal development of the base of the breast (reduction in its diameter), stretching and growth of the areola, flattening and abnormal direction of the nipples, as well as too high a fold between the breast and body.
Often a hernia forms in the areola area. The space between the mammary glands is increased.
The following types of deviations exist:
Parenchymatous. The mammary gland resembles a cone-shaped tube in appearance. Fascial. Breast growth occurs only due to an increase in its axillary and lateral area; the areola and flattened nipple are greatly stretched and protruded. Unilateral development of the mammary gland occurs. Mushroom. The gland is elongated, the areola resembles a mushroom cap.
This pathology is genetic in nature and is passed on to subsequent generations. It is also believed that the congenital nature of the disease may be due to intrauterine developmental disorders of the fetus due to exposure of the expectant mother’s body to harmful chemicals or biologically active substances.
It is argued that the development of tubular breasts is facilitated by poor circulation as a result of breast diseases and previous surgeries, as well as due to wearing a tight bra in adolescence.
Possible complications
The formation of mammary glands is completed by the age of 17-20. The presence of pathology of physical development, especially improper breast formation, affects the mental health of a teenager, leading to inferiority complexes, neuroses, and complications in intimate relationships.
Due to tissue compression, a woman also experiences physical discomfort in the mammary glands, especially during menstruation and pregnancy. Complications occur during breastfeeding. The reason is a violation of the blood supply and nutrition of breast tissue, which is why lactation may be weak. In addition, due to the small size of the mammary glands, their irregular shape and the presence of flat nipples, difficulties arise when putting the baby to the breast. This increases the risk of mastitis and other breast diseases.
Diagnostics and method of eliminating the defect
The diagnosis of “tubular breast” is made by a mammologist upon examination and palpation. Already by external signs it is possible to establish the type of pathology and the degree of its development.
In some cases, it becomes necessary to exclude the presence of mastopathy, which is also characterized by a change in the shape of the breast and the appearance of asymmetry (if one of the mammary glands is affected). For this, an ultrasound or mammography is performed.
Indications for correction
The indications for such an operation are, first of all, the desire of the patient herself to get rid of the pathology, as well as the presence of obvious signs of ailments that she experiences due to impaired development of the mammary glands.
Contraindications
Surgery to correct tubular breast defects is not performed during pregnancy or breastfeeding.
Important: It is recommended to correct the tubular mammary glands no earlier than 1 year after the end of feeding, when the condition of the tissues and the size of the glands have stabilized.
Contraindications to such an operation are the presence of skin diseases (at the acute stage), diabetes mellitus (due to difficulties in wound healing), cardiovascular diseases (for which it is impossible to perform general anesthesia), as well as infectious and inflammatory processes. If a woman has such pathologies, then the decision on the possibility of correction is made individually.
The operation is not performed if the woman has breast cancer, has a mental illness, or has bleeding problems.
Preparing for surgery
The operation is carried out only on the condition that the patient quits smoking and stops drinking alcohol 1 month before the operation, since the effects of nicotine and alcohol on mammary gland tissue slow down the healing process and restoration of their structure.
Carrying out the operation
Correction of the shape of the glands is carried out using various methods of plastic surgery. If necessary, mammary glands are enlarged (less frequently reduced), breast tissue and hernia are removed, glandular tissue is stretched and plastic-coated implants are installed, and the shape and size of the nipples and areola are corrected.
The operation is carried out in a certain sequence:
First, incisions are made along the perimeter of the areola, and its diameter is immediately reduced. Excess tissue of the inframammary fold and hernia are removed. The fold is moved lower. The cords (septa that interfere with the development of the mammary gland) are dissected. The gland tissues are straightened and stretched using a special device (expander). Implants are inserted underneath them, and the remaining clotted blood is removed from the gland through special drainage tubes under vacuum. The internal tissue incisions are sutured. External cosmetic sutures are applied. The operation to correct the shape and size of the tubular breast lasts 1-2 hours. It is performed under general anesthesia. To correct the shape of the glands, lipofilling (transplantation of the patient’s own fat tissue into certain areas of the mammary gland) or the introduction of a filler made of silicone or other substances may be required.
The advantages of lipofilling are the impossibility of rejection of the material and the occurrence of allergies. Breast restoration occurs faster than with fillers. Its disadvantages are that this method can only enlarge the breasts only slightly. In addition, fat can be absorbed, and the shape of the mammary gland will change. It may be necessary to repeat the procedure after some time.
Recovery period
After surgery to correct tubular breasts, until the tissues have completely healed, slight swelling of the breasts and pain in the area of the incisions are observed. Complications after surgery such as bruising, scarring, inflammation and swelling of the suture (seroma) are rare. In this case, the woman is prescribed antibiotics (in tablets or in the form of ointments) and painkillers.
The final result of the correction can be seen in about six months. During the entire recovery period, a woman must refrain from swimming in hot water, visiting a solarium or sauna.
You should avoid sports and other physical activities for the next few weeks. You will need to wear a support bra around the clock for 1 month.
Types and degrees of tubulation
Tubular breast cancer is not considered a life-threatening condition. The disease does not require urgent mammoplasty. The gland is usually shaped vaguely like a mushroom. There are several main degrees of tubulation.
Among them, the type of disease characterized by:
- cone-shaped and tube-shaped;
- predominance of vertical size over horizontal;
- small base of the mammary gland;
- deficiency of breast volume.
Tubular form of the mammary glands: degrees
The lower part of the breast is narrowed, the areolas and nipples are drooping. There is pronounced asymmetry.
Initial degree
Stage 1 tubulation of the mammary glands is considered the mildest form that does not require correction. The aesthetic defect is mild: the breast is slightly raised, the areolar-nipple complex is not changed.
The growth of the mammary gland is hampered by the formation of bridges formed from connective tissue. They are located in the lower and medial quadrants.
Second degree
In the second degree, tissue deficiency is formed in the lower quadrant. The mammary gland is slightly lowered or displaced downwards. During a visual examination, thickening of the nipple and expansion of the areolar lobe can be detected.
Third degree
Stage 3 tubulation is considered the most severe. In a woman, a sheath of connective tissue forms inside the mammary gland, narrowing the glandular base and preventing its growth. There is a shortage of tissue. There is a high risk of developing alveolar hernia.
Tubular form of the mammary glands of the 3rd degree threatens the development of alveolar hernia
Due to the sharp expansion of the areola-nipple complex, the breast grows towards the nipple. In the third degree, experts recommend choosing an implant to eliminate the defect.
Causes
Usually the shape of the mammary glands is hemispherical. The glands are located evenly over the entire surface of the pectoral muscle; in the case of tubular changes in the breast, they acquire an elongated shape and are distinguished by asymmetry. For any woman, such a problem will be sexual and personal in nature.
It is not completely clear what exactly causes this pathology of tubular breast development, but it is absolutely known that it is associated with a defect in the mammary glands and a genetic predisposition. Therefore, such pathology is almost always inherited.
This is explained by the excessive density and strength of the connective tissue, which does not allow the breasts to expand and acquire the correct shape. As a result, the breast grows exclusively towards the nipple and this, accordingly, leads to a hernia.
Such deformation is extremely rare, approximately 1:50.
Methods for correcting breast shape, indications
A woman with tubular breasts must make her own decision about the need for surgical intervention.
Specialists offer patients with mild forms of the disease a lift. Endoprosthesis replacement or mammoplasty is indicated for grade 3 tubulation. Breast prosthetics refers to improving the shape and increasing the size due to the revitalization of the implant in the tissue.
A breast lift is an operation during which endoprostheses are not installed. After surgery, the geometry of the mammary glands changes, sagging is eliminated and the correct shape is formed. The main indications for mammoplasty include not only tubulation, but also ptosis.
The disease is considered a complication of “goat breast”, due to which the tissues that form the mammary gland are stretched. There are 1, 2 and 3 degrees. Pathology is detected by visual examination: the mammologist pays attention to the location and size of the nipple.
There are several main methods of tightening. They are distinguished by the volume of tissue to be cut and the geometry of the incisions. The rehabilitation period and the duration of the operation directly depend on the complexity of the surgical intervention.
Mammoplasty or endoprosthetics is indicated for tubular breasts of the 3rd degree
A semi-monthly lift is indicated for women with moderate deformities of the mammary glands (1-2 degrees of tubulation). An incision is made on the falciform lobe, capturing the upper areolar semicircles.
After the operation, the breast takes on the correct shape, and the nipple is moved to the right place. Periareolar mastopexy involves an incision along the contour of the pigment spot. Scars after such operations are almost invisible.
To eliminate significant deformations due to tubulation or grade 3 ptosis, a long incision is made from the areola to the inframammary fold. Endoprosthetics is also very popular.
Indications and contraindications
The main indications for breast correction surgery should be the presence of the disease presented, as well as a positive psychological attitude. Speaking about contraindications, we can note a much wider list. In the first place are diseases of an infectious and inflammatory nature - they are a direct contraindication for intervention to change the shape of the mammary gland. Traumeel for lactostasis and features of its use here.
No less significant contraindications include menstruation, type 1 and 2 diabetes mellitus, which is in an aggravated form.
In addition, it is important to pay attention to the fact that the operation is not performed in the presence of any hematoma, malignant neoplasms, or mental illness. Additional cases in this list should be considered poor blood clotting and asymmetry, which sometimes characterizes the mammary glands, which can be seen even in the photo. Not only the mammologist, but also the surgeon is obliged to familiarize the woman with the presented list. This will be the key to a successful operation and a short, fairly easy rehabilitation after breast augmentation.
Contraindications and consequences
Surgical interventions for the tubular form of the mammary gland have a number of contraindications.
Mammoplasty cannot be used during pregnancy and breastfeeding.
These include:
- period of pregnancy and breastfeeding;
- benign and malignant neoplasms in the breast area;
- childhood or adolescence (up to 18 years).
Mammoplasty can be considered a safe procedure. The operation must be performed by a highly qualified specialist in compliance with all standards of asepsis and antiseptics.
The consequences that arise after endoprosthetics include:
- Pathological swelling. Most often, tissue swelling goes away on its own within 3-5 days after surgery. If a woman is plagued by severe pain, temperature fluctuations, local low-grade fever, and hyperemia are observed, then it is necessary to consult a doctor as soon as possible.
- Gray. In this case, lymphatic fluid accumulates in the subcutaneous fat. The condition can be triggered by non-anatomical tissue dissection.
Signs include redness of the scar, severe aching pain in the incision area, discharge of clear fluid from the scar, and severe swelling. In case of serous syndrome, drainage or dissection of the wound is necessary, followed by pumping out the fluid.
- Subcutaneous hemorrhages. Due to unqualified actions of the plastic surgeon, improper stopping of bleeding or tissue injury during excision. Small hematomas are considered normal; they disappear on their own after 5-7 days.
Extensive hematomas that affect the armpit area and shoulder indicate the need to consult a doctor. Most often, patients complain of severe pain and fever. The doctor must first stop the bleeding.
Breast sagging occurs when the implant size is incorrectly selected
- Sagging breasts. A complication occurs when the implant size is incorrectly selected. It forms after 3-6 months. after operation.
Sagging can be pronounced and artificial (if a woman has a small prosthesis installed, then the breasts sag or the body reacts to a foreign body in this way). The defect can be corrected only with repeated mammoplasty.
- Implant contouring. Complications are detected in women who have a thin subcutaneous fat layer. In this case, the contours can be visible through the skin. Characteristic symptoms include unnatural protrusion. Corrective fillers that are injected into the mammary gland will help correct the situation.
- Suppuration. This is the most dangerous complication that occurs against the background of non-compliance with the rules of antisepsis and asepsis. Women complain of redness, temperature fluctuations, severe swelling and pain.
Pus may drain from the nipple or surgical scar. It is easiest to stop inflammation at the initial stage through antibacterial drugs and antieptics. In advanced cases, repeated surgery is required.
- Capsular contracture. Connective tissue forms around the implant. If growth occurs incorrectly, capsular contracture occurs. The breasts become deformed, when palpated, dents and lumps are revealed, and the woman experiences severe pain.
Stage 1-2 contracture is eliminated with the help of anti-inflammatory drugs, massage and physiotherapy. Stage 3-4 can only be corrected through surgery.
- Skin rash. Ripping is characterized by the formation of folds that vaguely resemble fingerprints. The defect is most noticeable when bending. The condition develops against the background of an incorrectly sized implant. To eliminate it, lipolifting is used.
To minimize the risk of complications after surgery, it is necessary to contact highly qualified specialists who have the appropriate certificates and diplomas.
ACQUIRED BREAST DEFECTS
Acquired breast defects —deformations of the ribs and sternum. Predisposing factors to the development of acquired defects can be fractures of the ribs, sternum, purulent-inflammatory processes in the organs of the sternum and its bones.
Acquired breast defects lead to a decrease in breast size and, as a consequence, abnormalities in the spine. Injuries suffered in childhood rarely lead to significant deformations of the chest, since children's bones are quite pliable, and in addition, the treatment of such injuries is much easier for them. Most often, sternum injuries can lead to chest deformation in childhood. Rib fractures cause such deformities in very rare cases.
At one time, a significant role in acquired deformation of the chest may be played by a lack of vitamin D - rickets. This is the so-called rachitic deformity of the chest. In this case, the child’s body is unable to absorb calcium and the bones become soft, changing shape. In this case, the chest may take the shape of a keel, with a protrusion at the top and retracted hypochondrium.
One of the rarest diseases, syringomyelia, can also be accompanied by chest deformities. This disease is characterized by the formation of cysts in the spinal cord. The disease is accompanied by muscle weakness and spasms, pain in the legs, numbness and tingling, as well as curvature of the spine. This is due to a decrease in calcium content in the bones, as a result of which the shape of the chest is curved and a depression appears in the center - the so-called. scaphoid chest.
Scoliosis, a curvature of the spinal column, can also cause chest deformation. In addition, it can lead to dysfunction of the mediastinal organs (lungs and heart). Some chronic obstructive pulmonary diseases may be accompanied by changes in the shape of the chest. The airiness of the lungs increases (so-called emphysema), their volume increases, and the chest becomes barrel-shaped.
There are also iatrogenic causes of chest deformation, when the cause is medical invasive interventions, for example, when taking a section of a rib for transplantation, etc. Some diseases of the mediastinal organs, for example, tumors, expansion of the cavities of the heart, etc., may be accompanied by a change in the shape of the chest.
Diagnosis of acquired chest deformities consists of methods such as radiography, digital radiography, computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging. It is also important to find out not only the type, but also the cause of the deformation.
Acquired breast defects are usually treated surgically. The shape of the breast and ribs is corrected and the cause of the defect is corrected.
Make an appointment with thoracic surgeon Pavel Alekseevich Korolev
You can fill out an Application for Treatment, or:
+7 (495) 517-66-26 — call
or
[email protected] — write
Stages of surgery to correct tubular mammary gland
Surgical interventions on the female breast are considered one of the most complex plastic surgeries. The procedure should be carried out by a specialist who has extensive experience in this field and intuitively understands the problem. Each anomaly is individual, so an integrated approach is important.
The operation includes four stages:
- correction of the shape of the mammary gland;
- mammoplasty (implantation of hydrogel or silicone implants);
- moving the areolar-nipple complex to the desired point;
- formation of the inframammary fold.
During surgery, the specialist must eliminate the periareolar hernia (if present) and correct the asymmetry of the mammary glands, reducing the interbreast space.
Selection of implant
Before the operation, the specialist must agree with the patient on all stages of the surgical procedure.
Endoprostheses should be selected as high quality as possible, meeting the following criteria:
- Low risk of rupture. It is recommended to select the most durable implants that do not break due to injuries or falls.
- Safety. Almost all fillers present in dentures are completely safe for women.
- Biocompatibility. The main component is a gel, which remains in place when cut. The implants are made of modern materials, so the prostheses take root well in the woman’s body.
For tubular breasts, hydrogel or silicone implants are implanted.
The first contains:
- Highly cohesive gel. Dense material does not leak when damaged, the risk of rupture is minimal.
- Cohesive standard gel. The consistency resembles jelly. If the prosthesis ruptures, the gel dissolves in the body on its own.
Bioimplants contain carboxymethylcellulose, a natural polymer of natural origin. The substance is completely safe for the human body. When a prosthesis ruptures, carboxyl methylcellulose breaks down into carbon dioxide, water and glucose.
After implantation, a woman can examine her breasts using x-rays: the implant transmits x-rays well. Today, prostheses with a smooth surface texture are rarely implanted.
For tubular breasts, implants with a textured surface are used. They are not overgrown with connective tissue, which minimizes the risk of complications after implantation.
There are drop-shaped (anatomical) and round. Prostheses belonging to the first category are suitable for women suffering from ptosis or tubular form of the mammary gland of the 3rd degree. The structure of these dentures is quite dense, so they retain their shape well.
When choosing a prosthesis, the doctor must take into account the individual structural features of the patient’s body:
- breast density;
- body proportions;
- sternum size (hypersthenic, normosthenic, asthenic);
- elasticity of the skin;
- natural breast size.
After receiving all the data, the doctor conducts an analysis and selects the most suitable implants in terms of volume and shape.
Prosthetics
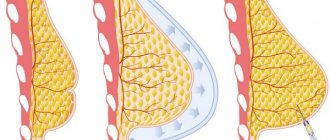
The implant is implanted in 2 quadrants: in the lower part of the breast (under the mammary gland) or in the upper part of the breast (under the pectoral muscle). The specialist makes a tissue incision along the border of the areola and pushes the skin flaps apart. The bridges that interfere with the growth of the mammary gland are cut off.
An implant is implanted into the space created after these manipulations. After installation of the endoprosthesis, the blood that has entered the cavity is removed. The fabrics are slightly stretched and stitched together, and cosmetic stitches are applied to the surface.
Mammoplasty: options for implantation
If a woman has small breasts or the skin does not stretch well, then after excision an expander must be installed in the cavity to facilitate tissue stretching. It must be regularly pumped up with solution. Stretching is carried out for 5-8 months. This is the safest and most painless method.
Breast lift (mastopexy)
Mastopexy is an operation to restore the shape of the breast.
The procedure has contraindications, which include:
- eczema at the incision site or pustular lesions of the epidermis;
- the period of bearing a child and breastfeeding;
- psychosomatic diseases;
- the presence of malignant and benign tumors inside the mammary gland;
- diabetes;
- poor blood clotting;
- severe pathologies of internal organs (including renal, liver and heart failure);
- cysts, mastopathy, cicatricial changes in the gland;
- acute infections.
Mastopexy or breast lift is contraindicated in case of mastopathy.
Before the operation, the patient must undergo a series of studies and consult with specialists (gynecologist, neurologist, cardiologist, therapist).
She may be assigned:
- electrocardiogram;
- mammography or ultrasound;
- tests for syphilis, hepatitis and HIV;
- General analysis of urine and blood.
14 days before the proposed operation, the doctor must completely stop hormonal and blood-thinning medications. A woman should get rid of bad habits (smoking, drinking alcohol) in advance.
Types of mastopexy
Breast lift is performed in several ways:
- mastopexy with implantation;
- periareolar mastopexy;
- vertical mastopexy.
The operation includes several stages:
- the skin is treated with an antiseptic;
- make a cut along the lines outlined in advance;
- Excess skin is excised and the nipple is moved to the desired point;
- apply a cosmetic suture;
- treat the skin with antiseptics;
- cover wounds with napkins.
Anchor breast lift
If there is blood left inside the cavity, it is necessary to install a drainage that will ensure the outflow of biological fluid. Types of mastopexy are distinguished by the size and location of the incision. During the operation, excess skin is excised, the edges of the wound are sutured together, and a cosmetic suture is applied.
Stage 3 breast tubulation can be corrected with an anchor or vertical lift. The incisions are placed under the breast or near the nipple line. The operation is considered complex - it leaves more scars compared to other surgical interventions.
Rehabilitation period after plastic surgery
If the operation was successful, the patient is discharged 24 hours after surgery. During this time, specialists will once again examine the woman and identify possible complications. After discharge, you must follow a number of recommendations to speed up the wound healing process.
You can’t spend a lot of time lying down; it’s better to rest while sitting or reclining. Food can be taken no later than 5 hours after surgery, and water - after 3 hours. Cold compresses will help relieve pain.
After mammoplasty, it is recommended to rest sitting or reclining
You can take a shower on the 5th day after surgery. The seams are pre-sealed with adhesive tape. You cannot wash your hair yourself : for 30 days you must limit your hand movements.
The bath is taken 6 weeks after surgery. In the first 7-10 days after plastic surgery, the patient should take analgesics and anti-inflammatory medications. During this period, the risk of side effects is high. Diarrhea or constipation usually goes away on its own.
Sutures are removed 14-16 days after plastic surgery. It is recommended to abstain from sports and intimate relationships for 10-14 days. People return to physical activity gradually, 30-35 days after plastic surgery. It is strictly forbidden to consume alcohol and tobacco products for 45-60 days after surgery.
Cost of correction
The cost of the operation may vary depending on the type of tubulation and the severity of the defects.
Approximate prices:
| Type of intervention | Price |
| Mammoplasty (endoprosthetics) | 120,000 – 240,000 rub. (including the cost of prostheses) |
| Periareolar mastopexy | 165,000 – 245,000 (excluding cost of prosthesis) |
| Vertical mastopexy | 210,000 – 220,000 (without implants) |
| Anchor mastopexy | From 240,000 rub. |
The total amount includes the cost of consultation, examination, anesthesia and the implants themselves. If a complex intervention is planned, the patient will need to pay for her hospital stay.
Alternative options for breast correction
You can correct the shape of your breasts without resorting to surgery. Alternative methods may help women with mild tubularity.
If the defect is barely noticeable, the specialist prescribes a number of physiotherapeutic procedures to the patient:
- Microcurrents. The procedure stimulates metabolism, accelerating the process of collagen production. Under the influence of microcurrents, skin elasticity increases.
- Myostimulation. During the session, an electric current is applied to the pectoral muscles. It increases the onus of the pectoralis minor and major muscles.
At home, you can perform a number of exercises on your own to restore the shape of your mammary glands.
Exercises to restore the firmness of sagging breasts
A set of exercises to tighten the pectoral muscles and restore the shape of the mammary gland:
- Bench press.
You need to lie down on a bench with your feet on the floor. Take dumbbells in your hands. Bend your right and left arm at the elbow and lift it up. Fix the position. You need to perform 4-5 sets of 10 repetitions per day.
- Push ups. Perform from a lying position on the floor or leaning against a wall. When doing push-ups, your arms must be fully straightened. The exercise is repeated 4 times, performing 10 approaches.
- Palm press. Stand leaning against the wall, bend your arms at chest level, placing your palms together. Inhale, hold your breath for 10 seconds and forcefully press your palms together. After 15 seconds, repeat the exercise. The number of approaches is 6-8.
You can tighten your chest only if the above exercises are performed regularly.
Cosmetology procedures
Cosmetic procedures can help correct tubular breast shape. Meso-cocktails and preparations containing hyaluronic acid are injected into the mammary glands.
If a woman has small breasts, then you can restore their shape using lifting threads:
- Aptos. The active ingredient is polylactic acid. There is no need to remove them; the threads dissolve on their own in the tissues. Participate in the formation of a framework of elastin and collagen.
- Mesothreads. The main component is polydioxanone, the coating is polyglycolic acid. Completely dissolve in 250-280 days.
- Platinum and gold threads. They are made of precious metals (999 standard, 24 carats). They do not dissolve on their own; after they become overgrown with connective tissue, they tighten.
During the implantation of threads, the patient is not put to sleep; she can observe the process. The procedure is completely safe and painless.
Tubular breast shape is corrected after puberty. Surgeries on the mammary glands are not performed in adolescence. The final result depends on the individual characteristics of the body - in some cases, implants take a long time to take root.
Breast correction surgery
There are several methods for correcting the shape and size of the mammary gland, but doctors believe that installing implants will be the best option - less traumatic and with a stable result. Another advantage of installing an implant in the mammary glands is that the structure of the tissues and milk ducts does not change, so the woman will be able to breastfeed her child in the future.
Algorithm for performing breast correction surgery:
- The surgeon opens access to the areola (the pigmented area around the nipple) and makes two circular incisions. If there are indications, the doctor immediately reduces the size of the areola.
- Tissue detachment is carried out, which allows the formation of a “pocket” for the implant. The dimensions of this space are agreed upon in advance with the patient and depend on what size breasts the woman would like to see in the future.
- An implant is inserted into the formed “pocket”. Drainage must be done - a narrow tube with a vacuum is fixed to the side of the mammary gland, through which blood clots will come out in the first 1 or 2 days after the operation.
- The surgeon connects the edges of the wound and sutures it in two stages. First, internal sutures are applied with special self-absorbing threads. Then the external seams are made exactly according to the previously made markings.
- Cosmetic stitches are applied. They make it possible to make traces of surgical intervention almost invisible and finally fix the edges of the wound.
Watch the video about the procedure for tubular breast surgery:
The duration of the operation is maximum 2 hours. Often, instead of artificial implants, doctors use the patient’s own fat tissue, in which case the intervention will be classified as lipolifting. This method of solving the problem of tubular breasts has undeniable advantages:
- the material is not rejected, as it is natural and is adequately accepted by the body,
- the rehabilitation period proceeds quickly and without complications,
- an allergic reaction does not develop.
The doctor should warn that adipose tissue can be absorbed over time, so lipolifting will have to be done in a few years. In addition, it is impossible to increase breast size by several points in this way.