General information
Atheroma - what kind of formation is this?
Atheroma (trichodermal cyst or steatoma) refers to fairly common tumor-like neoplasms of the pilosebaceous apparatus of the skin. It is one of the varieties of the group of epithelial skin cysts and is a rounded encapsulated neoplasm filled with thick yellowish-white contents, which may have an unpleasant odor. ICD-10 code: D23. Other benign skin neoplasms. Atheromas occur in 7–10% of the population. At the same time, atheromas occur more often in women compared to men, and in people of the older age group more often than in people under 30 years of age. Often found in patients with acne and seborrhea.
It occurs predominantly in areas of the skin with a high concentration of sebaceous glands (scalp, breast, face, back), therefore it is often found in the literature as a sebaceous gland cyst. In most cases, the size of atheromas is 1-3 cm, less often they reach 5 cm, but in practice there are cases of large atheroma formations. The localization of atheromas may vary.
The most common are atheroma of the scalp and atheroma on the back in different places, as well as atheroma on the face (usually on the cheek and skin of the forehead, in the chin area). Less common are atheroma behind the ear, on the ears (atheroma of the earlobe or pinna), on the neck (lateral/back surface), and atheroma of the mammary gland. And much less often - on the leg, atheroma on the penis, on the scrotum or atheroma on the labia and on the skin in the groin in women.
Photo. Atheroma on the back
Photo of atheroma on the head
Photo of atheroma behind the ear
Atheroma on the leg photo
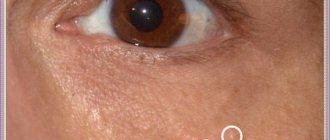
Atheroma (blockage of the sebaceous gland on the eyelid). Photo.
Often in everyday life, atheroma is called a wen. However, this is not true, since there is a fundamental difference between them. Externally, atheroma is certainly similar to lipoma, however, structurally they are fundamentally different. Lipoma consists of altered cells of adipose tissue and develops in the layer of subcutaneous connective tissue, while atheroma is a cyst of the excretory duct of the sebaceous gland.
Depending on the histomorphological structure, the sebaceous gland cyst of the skin is divided into several types:
- Epidermal cyst - occurs very rarely, is formed from the skin epithelium, which, due to disturbances in the embryonic period, was subdermally transferred, that is, submersible growth of epithelial elements occurs, their proliferation and desquamation, which leads to the formation of a cyst cavity, which is filled with keratin and components of the skin lard This type of atheroma is characterized by slower growth, occurs predominantly in females, the predominant localization is the scalp (atheroma on the head) and the perineal area (in the groin in women, atheroma on the penis).
- Retention - formed due to blockage of the excretory duct of the gland. It is characterized by faster growth and occurs in both sexes with equal frequency; in addition to the scalp, it can occur on the skin of the face, back, mammary glands, and external genitalia. They can be single or multiple, often of the same size. They tend to become inflamed and coalesce into lumpy conglomerates.
Atheromas are a pronounced cosmetic defect, which causes psychological discomfort and becomes the main reason for contacting a surgeon. Also, if an infection enters the internal cavity of the atheroma, there is a high probability of its suppuration, since the contents of the tumor are a favorable environment for the proliferation of bacterial microflora with the development of the inflammatory process and the formation of an abscess (cavity with pus).
Suppurating atheroma (there is no code according to ICD-10), since the atheroma code according to ICD-10: D23 does not provide for cyst complications. It often develops after mechanical damage to the atheroma, but in most cases the cause of its occurrence cannot be determined and therefore a diagnosis of “idiopathic purulent atheroma” is made.
Sebaceous glands
To understand the origins of the cyst, you need to understand the structural level of the skin at which the process begins. It begins with the sebaceous gland, a small skin organ.
The sebaceous glands are located in the dermis, the second layer of the skin. These are alveolar formations (consisting of several chambers) that secrete sebum (sebum) onto the surface of the skin, which acts as a natural lubricant and is part of the water-lipid mantle: moisturizes and prevents the skin from drying out, protects against the penetration of bacteria, fungi, viruses, participates in the function of thermoregulation.
Sebum plays an important role as a protection against chemicals, so the skin performs its function.
There are two types of glands:
- in the first type, the duct opens to the surface of the skin and is connected to the hair follicle (such glands are present throughout the body, in all areas where there is hair, even vellus hair);
- in the second type, the ducts are not connected to the hair follicle and open directly to the surface of the skin (lips, nipples, eyelids, foreskin and glans penis).
Cysts appear in different parts of the body where there are sebaceous glands. The exception is the skin of the soles and palms, where there are no sebaceous glands. The more glands in an area of the body, the larger their size, the greater the likelihood of developing atheroma in this place. Such localizations include: the head area (often on the face and scalp), neck – mainly on the back surface, back, interscapular area, chest, shoulders.
Sebaceous gland cysts can also occur in areas without hair, where the duct of the sebaceous gland breaks off directly onto the surface of the skin - the external genitalia, eyelids, nipples.
Classification
A cyst is a benign cavity formation. It can occur on any part of the body, including the face. Based on morphological features, true and false cysts are distinguished. The former have their own capsule (inner shell), while the latter lack it. True cutaneous cysts are represented by the following:
- Epidermal (atheromas).
- Dermoid.
- Implantation.
- Retentional (milia).
False cystic formations (without internal epithelial lining) are synovial, have the appearance of calcification, or are represented by pseudomilium. Each of the presented forms has its own origin, morphological and clinical features.
Depending on the origin there are:
- Congenital atheromas (primary, true) are a hereditary disease and develop from detached epidermal cells during the embryonic development of the fetus.
- Acquired (secondary, false) - are formed due to blockage of the sebaceous gland duct or difficulty in the outflow of its secretion, which contributes to the accumulation of secretion in the lumen of the gland and the formation of a sac filled with atheromatous masses (altered sebum).
Causes
Formations can develop on any part of the head, also affecting the delicate area at the edge of the eye. Palpation can reveal both a soft-bodied formation and a dense node. The mechanism of development of the pathology has not been fully studied, therefore, among pediatricians (in the case of growths in children) and surgeons (in the case of growths in adults), there are only assumptions. The main cause of proliferation in infants is a violation of intrauterine development in the form of epithelial fusion, when part of the epithelium detaches with subsequent proliferation.
In adulthood, the causes include factors that contribute to blockage of the sebaceous glands with subsequent encapsulation of the accumulated secretion. These include:
- hormonal imbalances;
- chronic diseases of the liver and gastrointestinal tract and infectious pathologies;
- low level of personal hygiene;
- weakened immunity due to psycho-emotional exhaustion, nervous strain, intense work, unbalanced nutrition.
Associated factors affecting the level of protective forces are hypothermia, prolonged disruption of sleep and wakefulness, and exposure to stress. In any case, a benign formation spoils the appearance, and the likelihood of favorable resolution of the cyst remains extremely low.
Therapy methods (4 options)
There is no hope that atheroma will disappear on its own. If your doctor recommends laser, radio wave or surgical treatment, you must follow all instructions.
Treatment of atheroma on the face without surgery does not imply obtaining a quick positive result. The effectiveness of folk recipes and pharmaceutical drugs is low, and the patient’s condition will worsen.
Experts do not recommend conservative treatment. If the tumor has opened on its own, it is necessary to treat it with disinfectants, cover it with a band-aid and contact a medical facility.
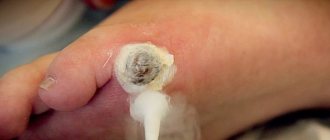
It is considered the most common method. The procedure involves cutting the skin and removing the cyst along with the pus.
A cosmetic suture is placed on the wound, which is removed after 14 days. Removal of atheroma on the face is surgically performed under local anesthesia.
Laser removal
Suitable for combating small wen in the absence of an inflammatory process. A small incision is made in the skin where the LED is inserted.
Under the influence of a laser beam, the tumor is burned out. The duration of the procedure is 20 minutes.
If the tumor is removed from the scalp, the hair in the treatment area is first shaved off. The use of a laser protects the patient from recurrence of the disease.
Radio wave method
This method is similar to the previous one, the main difference is faster restoration of the affected tissues.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with a homemade turmeric face mask or a ready-made product
The procedure involves evaporating the tumor. It is carried out only in the absence of inflammation. If infection occurs, the abscess is incised and drainage is installed. The patient is prescribed antibacterial drugs.
The procedure is considered the safest, since the effect is carried out with high precision. There are no scars left on the skin, and signs of the disease do not reappear.
Treatment methods
Not wanting to go to the doctor, many people wonder how to cure a wen at home. This is not recommended. The only radical and complete treatment for these tumors is to remove them using various methods. Atheroma will never go away on its own; sooner or later it must be removed in one of the following ways: laser, surgical, radio wave.
In addition, the atheroma cannot be squeezed out, even if it is first pierced with a needle and a hole is formed through which the contents can escape. In this case, the contents will come out, but the capsule with the cells that produce the secretion will be in the gland duct, so after some time the free cavity will again be filled with sebum.
Causes and mechanisms
The most common is an epidermal cyst or atheroma. It occurs as a result of blockage of the excretory duct of the sebaceous gland and the accumulation of secretions there. The mechanism for the formation of such a state has three components:
- Increased secretion.
- Hyperkeratosis of the excretory duct.
- Imbalance of neuroendocrine regulation.
Sebaceous cysts can occur in people with oily or combination skin types, but under certain conditions. It is known that the glands and epithelium are under the influence of sex hormones (primarily androgens). And if the balance with estrogen is disturbed (for example, during menopause or ovarian tumors), then the risk of developing atheroma increases. They usually occur in places where the glands are most dense: on the back, face, upper chest.
Compensatory hyperkeratosis of the excretory ducts accompanies not only sebaceous gland cysts on the face, but also occurs during trauma or inflammatory processes (acne, seborrhea). Mechanical damage can lead to the penetration of the epidermis into the skin, which will become the source of an implantation cyst.
Milia or retention cysts, unlike atheroma, are filled not with sebaceous secretions, but with horny masses. Therefore, their main development mechanism will be hyperkeratosis with increased division of epidermal cells. If we talk about dermoid cysts, they most often arise when embryogenesis processes are disrupted, i.e. they are congenital in nature.
Reasons for education
The main reason for the formation of a sebaceous cyst is blockage of the passage, that is, the creation of an obstacle to the release of sebum. As a result, a cavity is formed, which is gradually filled with horny masses.
Since epidermal cysts are often observed in blood relatives, it is likely that a hereditary predisposition can lead to their formation.
Pathogenesis
The formation of atheroma occurs as a result of the cessation/impairment of the release of the secretion of the sebaceous gland. As the secretion accumulates, it expands the duct of the sebaceous gland, forming a cavity in it with contents of a dough-like consistency, which includes particles of fat, detritus (a product of the breakdown of necrotic tissue) and keratinized cells of the epidermis.
The skin above the gradually enlarging cyst rises, and a round-shaped compaction with a soft-elastic consistency is formed. As it grows, a capsule of connective tissue begins to form around the overstretched walls of the sebaceous gland. At the same time, the inner surface of the cyst produces secretion.
Complications
Adverse consequences of a dermoid cyst usually occur in case of late consultation with specialists. If the size of the dermoid increases, the likelihood of suppuration and the development of inflammatory reactions increases. It is strictly not recommended to squeeze out or open the bag on your own. Otherwise, purulent secretion filled with pathogenic microorganisms can enter the blood and cause a serious complication - sepsis.
The development of the inflammatory reaction is accompanied by fever, weakness, nausea and vomiting. Another complication of epithelial proliferation is dizziness and disruption of the normal functioning of internal organs. If the course of the disease is ignored for a long time, the dermoid cyst in 5-8% of observed cases degenerates into a malignant tumor. At the same time, large formations spoil the appearance, reduce social activity and communication abilities.
Symptoms
The standard complaint of patients is the presence of a superficial tumor-like neoplasm with a dense elastic consistency, often easily movable when pressed with a finger and painless when palpated. In uncomplicated cases, the skin over the cyst remains unchanged; less often, on the most elevated part of the skin above the cyst, an enlarged obstructed duct of the sebaceous gland is noticeable.
In this case, there is severe pain during palpation and the patient’s general condition suffers (weakness, general malaise, increased body temperature). If the outcome is favorable, the pus breaks through the capsule or comes out through the ducts of the sebaceous glands. However, in some cases, pus can escape into the subcutaneous layer with the development of an abscess.
In a normal course, when there is no infection by microorganisms, the formation does not bother the person in any way. Upon careful examination, a yellow-pink color will be visible, but when pressed, a person will not feel anything.
When the color of the atheroma changes to dark red or brown, the formation will be accompanied by symptoms such as pain, inflammation of the tissue around the formation, and also if there is a large amount of pus inside the tissue, the tissue may not be able to withstand, so some of the contents come out.
Atheromas do not manifest pronounced clinical manifestations. The main sign of a cavity is enlargement and compaction. Visually, a hollow node appears in the form of a dense wen. In most cases, formations are formed in areas where hair follicles are present: head, ear area, back and neck, facial area, groin.
The main signs of a cyst include:
- The formation has a dense elastic structure;
- Mobility of the capsule is observed;
- Placed on the surface of the skin;
- A cyst on the face or body has clear contours;
- The gland duct may be located in the center of the formation;
- The occurrence of an inflammatory process and suppuration of atheroma. Severe redness of the borders of the formation, pain when palpating, and swelling appears. Possible rupture of the capsule and eruption of purulent contents.
Symptoms of cystic formation of the sebaceous gland are visual signs. Cavity neoplasms are identified quickly, at the first appointment with a dermatologist during examination and palpation.
A mass formation on the skin of the face (even a small one) is not a cyst on the leg, which no one will pay attention to. And when a similar problem arises in a child, it brings even more anxiety. But only a doctor can dispel all doubts regarding the benignity of the tumor and methods for its elimination. After conducting an examination, the specialist will give answers to all your questions.
Atheroma
An epidermal cyst of the facial skin is a closed formation containing horny masses mixed with sebum. The epithelium above it remains unchanged, probably only the expansion of the pores and the appearance of a vascular mesh. The size of the atheroma is usually in the range of 5–10 mm, but can also be significantly larger.
Atheroma develops gradually over quite a long time. Such a cyst is localized in various areas: on the head under the hair, on the forehead, cheeks, in the area of the lower or upper eyelid. The latter is also called atheroma of the eye, although the apple itself, of course, is not affected.
An epidermal cyst does not cause physical discomfort. But there are two situations when a tumor is cause for concern: when it becomes large and becomes inflamed. In the first case, there is likely to be pressure on neighboring structures, including vessels and nerves, and in the second, an abscess (microabscess) may form. Then other signs appear in the clinical picture:
- Redness of the skin.
- Swelling.
- Soreness.
An infected atheroma proceeds like a boil, only without a necrotic core. Despite this, pus accumulates in the center of the tumor, which can break out or, much worse, spread to neighboring tissues. Therefore, if you suspect an inflammatory process, you should not hesitate to consult a doctor.
Dermoid
Another subcutaneous cyst is a dermoid. It has an oval or spherical shape, has a dense capsule and can be multi-chambered. The contents of the cyst are various elements of the skin and its appendages:
- Epidermal cells.
- Sebum.
- Hair.
- Nails.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with Facial skin care Japanese massage
Dermoid cysts are usually found in children or young adults. This is a painless and fairly dense tumor, not fused with surrounding tissues. It grows slowly, but under certain conditions (heredity, the influence of carcinogens) it can degenerate into malignant.
The forehead and bridge of the nose, behind the ear area, and neck are most susceptible to the formation of such cysts. But dermoid can also appear in other areas: on the back, abdomen, lower extremities, above the sacral spine, in internal organs (ovaries).
Milia
White spots on the face, especially common in adolescents and adults, but also common in the newborn period, are milia. These are intradermal cysts containing horny masses, not sebaceous secretions. They do not connect to the ducts of the glands, and therefore cannot empty themselves spontaneously.
Small nodules up to 3 mm in size are white or yellowish in color and rise slightly above the surface of the skin. Usually they are located in groups, but never merge with each other. Milia are prone to spontaneous disappearance, which is associated with the natural renewal of the skin.
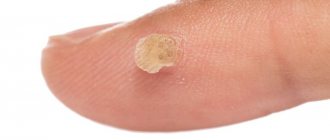
Symptoms of an epidermal cyst
Epidermal cyst photo.
Epidermal cyst is the most common neoplasm. True atheroma visually resembles a subcutaneous node; the surface of the skin is clogged with pores. It can be located on the cheeks, ears, back and other parts of the body.
The node quickly grows and opens into the dermis, which causes severe pain and inflammation. The growth of the pathology is slow, the lesion has a tendency to thicken. A false epidermal cyst grows quickly.
You should consult a doctor if the following signs appear on your skin:
- inflamed nodules;
- pain in the tumor;
- rapid cyst growth.
A quick response and medical assistance will protect the patient from possible complications.
Folk recipes
The use of traditional methods for the treatment of atheroma is possible only with mild symptoms of the pathology and only after consultation with a specialist.
The most effective are ointments, rubs and compresses made from natural ingredients.
Burdock ointment
The plant must be thoroughly washed with running water, passed through a meat grinder, and then mixed with pork fat.
For 3 days, the product is infused in a cool, dark place. After this, the ointment is applied in a thin layer to the wen, no more than 3 times a day.
Onion compress
The onion is baked in the oven, cooled, crushed and mixed with the same amount of laundry soap (pre-grated).
The resulting mass is applied to the wen and secured with a sterile bandage. The compress is changed 2 times a day.
A small amount of the product must be melted, then gently rubbed into the surface of the new growth until completely absorbed.
Treatment
If the epidermal cyst is small in size and does not cause concern to the patient (including aesthetic concerns), then it does not require treatment. It is necessary to monitor the development of education in dynamics.
If the sebaceous cyst interferes, then it should be removed. It is imperative to carry out treatment in case of infection.
There are two methods for treating epidermal cysts:
- Husking using laser coagulation.
- Radical removal of the formation simultaneously with the capsule using traditional surgical methods.
If the atheroma is inflamed, then before the operation, treatment with anti-inflammatory methods is prescribed. When an abscess forms, it is opened with mandatory drainage.
Procedure for performing an operation to remove an epidermal cyst:
- an incision is made at the most protruding place of the cyst;
- The contents of the cyst are carefully squeezed onto a napkin;
- the cyst capsule is removed;
- a suture and an antiseptic bandage are applied.
It is possible to perform an operation without damaging the cyst capsule; in this case, the entire capsule is removed through one or two incisions.
Treatment with traditional methods
Treatment of epidermal cysts with folk remedies is not effective enough. However, if radical removal of the formation is impossible or undesirable, you can use the following recommendations:
Vishnevsky ointment is used to treat education.
- Every day at night, apply a bandage with Vishnevsky ointment to the atheroma. Carry out the procedure until a hole is formed on the surface of the skin for the contents of the formation to exit. Unfortunately, after such treatment there is a high risk of relapse.
- Fresh leaves of coltsfoot for the treatment of atheroma. It is necessary to rinse the fresh leaves and wash them a little so that the plant produces juice. Apply compresses to the formation at night.
- An ancient way to treat atheroma is to apply a silver coin or other suitable silver object to the affected area.
- For epidermal cysts, it is recommended to take 0.5 - 1 glass of watercress juice daily.
Additional diagnostics
Diagnosis of atheromas in the presence of characteristic clinical symptoms does not present any particular difficulties. If necessary, an ultrasound examination of soft tissues can be performed, which allows visualization of the cavity and capsule with curd contents. Additional histological diagnosis is carried out during surgery by taking atheroma tissue for histological examination.
What caused the atheroma on the face or what the nature of the other cyst is - all this will become known based on the results of additional diagnostics. After a visual examination, the doctor must make sure that the formation is benign and make a final conclusion. They will help him with this:
- Complete blood count (leukocyte count, ESR).
- Blood biochemistry (hormonal spectrum, immunogram).
- Content analysis (microscopy, culture).
- Histological examination.
- Ultrasound of soft tissues.
When a cyst suppurates, it should be distinguished from acne or boils, and nodes under the skin require differential diagnosis with lipomas. But each case requires individual consideration.
Reasons for the development of cysts
There are many reasons for the formation of cysts in a child. Some of them are associated with disruption of the normal circulation of interstitial fluid and blockage of the gland duct. Such cavities are called retention cysts; they are usually localized in the mammary, salivary, sebaceous glands, as well as in the pancreas and thyroid gland.
A ramolation cyst may appear as a result of damage to organ tissue due to inflammation or other pathology. Such cysts appear anywhere.
A parasitic cyst develops in a child after certain parasites enter the body. For example, if tapeworm eggs enter the baby’s body, the parasite settles in the liver, protecting the larva with a chitinous capsule, which is a parasitic cyst.
Displacement of the epithelium in the abdominal cavity, joints or spine after injury leads to the appearance of traumatic cysts.
Children often have congenital cysts, the causes of which are usually pathologies during pregnancy, as well as chronic diseases of the woman.
Prevention
The main types of hollow neoplasms include:
- Secondary formations (retention follicular cyst). These neoplasms are formed as a result of complications of acne and acne. In most cases, these formations are localized on the facial area, back, neck;
- Congenital benign formations (epidermoids). This type of neoplasm is formed from epidermal cells. In most cases, epidermoids are multiple formations that are localized in the area where hair follicles are present;
- Trichodermal cystic nodules;
- Steacystoma;
- Various unspecified follicular formations of the skin and tissue.
Neoplasms arise due to a violation of the outflow of sebum, which occurs due to blockage of pores, therefore the prevention of atheroma on the face should be based on regular cosmetic procedures for cleansing the skin. These include:
- visiting the sauna;
- steam baths;
- cleansing masks;
- massages.
To reduce facial skin oiliness, you should use special tonics and cleansers. In addition, preventing the development of tumors on the skin of the face should include proper, balanced nutrition. So, with high fat content of the skin, you need to exclude fatty and carbohydrate-rich foods from your diet.
Atheroma in a child is a fairly rare occurrence, since the sebaceous glands in young children still function poorly. If adult patients require surgical removal of atheroma, then in most cases children under three years of age do not undergo surgery at all. An operation to remove atheroma in a child is undesirable, since general anesthesia is required, which is harmful to a still fragile body.
- There is rapid aggressive growth of the cyst.
- The surrounding tissues/vessels swell and are compressed.
- Signs of inflammation of the cyst appeared.
- The tumor is disturbing the child.
In rare cases, the neoplasm may disappear without surgical intervention, but you should not hope that the atheroma will resolve on its own. If your doctor advises you to remove the tumor, you should listen to him. A tumor under the skin can be removed in one of three ways: radio wave, surgical excision or laser.
A subcutaneous cyst can form after injury to the skin, inflammation of the hair follicles, improper squeezing of acne, and other circumstances. The fact is that the sebaceous duct becomes increasingly constricted, and the glands continue to produce deposits. Since the duct to the outside for sebaceous deposits is closed, it turns into a cyst, gradually increasing in size. It is in this way that the formation of a subcutaneous tumor occurs.
Prerequisites for the appearance of atheroma:
- Seborrhea caused by hormonal or inflammatory imbalance;
- Pimples and blackheads;
- Tendency to sweat heavily;
- Metabolism;
- Diseases caused by genetics;
- Rare adherence to hygiene standards, improper application of cosmetics;
- Injury to the skin.
In addition to the above prerequisites, a cyst can be a complication of the clinical manifestation. Thus, the auxiliary factors contributing to the appearance of atheroma include the following:
- Skin injuries;
- Diabetes mellitus, the protective functions of the skin in this case are weakened;
- Inflammatory lesion of the epidermis;
- Irregular structure of the sebaceous glands;
- Applying excessive amounts of cosmetics to the skin;
- Congenital diseases that affect the synthesis of fats in the body.
As a result of the increased work of the exocrine glands and their low permeability from the excretory duct, the secretion is retained and, as a result, the glands become swollen, which become like sacs filled with curdled contents.
It is possible to minimize the risk of atheroma formation by following simple rules:
- compliance with hygiene requirements;
- use of high-quality hypoallergenic cosmetics;
- conducting systematic vitamin therapy;
- including only healthy foods in the diet;
- careful care of delicate facial skin, prevention of injury and irritation;
- timely elimination of any diseases of the endocrine and hormonal systems, as well as pathologies of the skin.
We invite you to read How to grow nails in 2 days at home?
At the same time, self-medication is unacceptable, since it often aggravates the situation. Atheromas are diagnosed and treated only by qualified doctors.
One of the types of cysts on the face are mammary cysts, or so-called milia. They are also called whiteheads or milletheads. They occur in children and infants. The main reason is that the child’s hormonal background has not yet been formed. A certain amount of hormones enters the baby’s body with mother’s milk, which intensifies the work of the sebaceous glands and clogs the pores.
In any case, it is recommended to show the baby to a doctor, who will make the correct diagnosis and recommend treatment if necessary. It is important not to confuse milia with allergies or heat rash. It is strictly forbidden to scratch or pierce the milia, as in the process of these manipulations it is possible to introduce an infection.
Breast cysts in adolescents and adults are recommended to be treated by cosmetologists. There are many procedures to help eliminate this cosmetic skin defect.
The most important rule that will help avoid the appearance of tumors on the face is personal hygiene, as well as regular visits to the doctor. In addition, the following prevention methods may help:
- Steam baths, with which you can easily remove sebum.
- Vitamin therapy.
- Proper nutrition (reducing the consumption of spicy, fatty and smoked foods; it is better to add foods that contain fiber, vitamins and minerals to the diet).
- Removing makeup before bed is mandatory.
Monitor the health of your skin and use preventative methods.
A cyst on the face is not a malignant tumor, so you should not worry too much if you have one.
The main thing is to consult a doctor in time for professional help to avoid complications.
Prognosis and prevention
Prevention of the development of epidermal cysts is not effective enough. To prevent its formation it is recommended:
- avoid skin injury;
- monitor metabolism and hormonal balance. If necessary, carry out corrective treatment;
- maintain body hygiene.
The prognosis for epidermal cysts is favorable. After incomplete removal of the formation, the likelihood of relapse is very high. Malignization (transition to a malignant form) with this disease is extremely rare.
Preventive actions
Diagnosis of formations occurs already at the first appointment with a dermatologist. The presence of a cyst is determined visually; the doctor feels it to determine its density and degree of mobility. The most important point of the examination is to identify the excretory duct. This indicator is the dominant sign of atheroma, allowing it to be distinguished from other formations of the skin and subcutaneous tissue.
In cases of emergency need to remove skin formations, during the operation, the tissue of the capsule and the secretion contained inside are taken for histology.
Histological examination allows one to accurately differentiate cavity formation, since the symptomatic manifestations are similar to various neoplasms:
- Fibroids;
- Hygromas;
- Lipomas;
- Hemangiomas.
The analysis is of particular importance for differentiating formations in the axillary region, groin area, and scalp, since in these areas the risk of degeneration of a benign formation into a malignant tumor is highest.
Histology allows us to determine the nature and nature of the formation, because it is externally similar to the syphilitic gumma that forms on the knees and forehead area. In the area of the reproductive organs, bartholinitis may form, resembling a cavitary node at the initial stage. At the initial stage of development, lymphadenitis can be confused with a cyst.
Histological examination allows one to accurately determine the nature and form of the pathology and determine the treatment direction.
The main signs of neoplasms, allowing to identify the cavity formation of the sebaceous gland
| Dominant trait | Lipoma | Fibroma | Lymph node | Cyst | |
| External manifestations | In most cases, they appear visually in the case of an increase in size or growth of large formations. | Visualizes well. It appears as an elevation above the skin. Visually it is a round formation of regular shape. | |||
| The degree of mobility of the skin over the formation | The skin is characterized by good mobility, which is due to the location of the formation: it is formed deeper. | The displacement of the formation occurs along with the skin, due to the fact that the atheroma is formed in its thickness. It is impossible for the skin and formation to move relative to each other. | |||
| Formation Density | Soft to the touch | Have a dense structure | The formation is quite soft to the touch. | ||
| Presence or absence of pain on palpation | No pain is felt | Painful | In the absence of inflammatory processes, there is no pain. The inflammatory process, suppuration of the formation is manifested by pain on palpation. | ||
These signs make it possible to differentiate a cyst already at the first appointment with a dermatologist, to separate it from skin formations that have similar signs.
In some cases, an ultrasound examination of a neoplasm similar to atheroma is performed. If a cavity is detected during the examination, the possibility of a sebaceous gland formation is high.
Various methods of laboratory and instrumental diagnostics are not used due to their low information content.
It is within the power of every person to reduce the risk of pathology; to do this, all you need to do is follow simple hygiene requirements, properly care for your skin, and use high-quality cosmetics.
Dermatologists recommend periodic professional facial cleansing, but a home procedure is also suitable: using scrubs and mud masks.
For complete prevention, additional tips are needed:
- regular visits to the dermatologist’s office, especially when skin diseases appear;
- periodic steam baths;
- healthy diet, supplement the menu with fresh vegetables, fruits, herbs and other foods high in vitamins;
- avoidance of fried and spicy foods;
- using sunscreen in the summer and nourishing creams in the winter;
- strengthening the body’s protective functions: taking vitamins, physical activity, giving up bad habits;
- daily removal of decorative cosmetics.
Treatment of epidermal cyst
An epidermal cyst cannot be eliminated mechanically. If the lesion is squeezed out, after a while it forms again in the same place. To prevent relapse, the tumor should be surgically removed along with the capsule.
If the cyst is severely inflamed, treatment will be as follows:
- eliminate the inflammatory process;
- conservative therapy.
The purulent inflammation is opened with drainage; only after the wound is cleansed and healed is it possible to remove the capsule to prevent the risk of blood poisoning.
The operation is performed with local anesthesia and can have the following types:
- traditional surgical removal;
- use of laser;
- radio wave technique.
Classic surgical removal involves cutting the skin over the cyst. The surgeon, using a special clamp with a gauze swab, carefully peels off the surrounding tissue from the cyst and removes the lesion along with the capsule. Stitches are then applied.
The following techniques are used to eliminate pathology with laser:
- Photocoagulation. Applicable for cyst diameters of no more than 5 mm. It is removed along with the capsule without suturing. During healing, a crust forms, which disappears at the final stage.
- Excision with capsule. Prescribed when the tumor is from 0.5 to 2 mm. Removal is similar to surgery, but a laser is used instead of a surgical instrument. The wound heals quickly.
- Vaporization of the capsule. The procedure is performed with a tumor larger than 2 cm.
It is worth undergoing treatment in a high-quality clinic with modern equipment and experienced staff.