Excess weight is one of the most pressing problems of our time. According to WHO, over the past 40 years the number of people suffering from obesity has quadrupled. Today their number is 650 million people worldwide. The main cause of the disease is considered to be excess food consumption with insufficient physical activity. The body receives an amount of nutrients that it does not have time to process. Excess is stored in the form of subcutaneous fat.
It should be noted that food is psychologically addictive. At a certain stage, a person who does not have sufficient willpower can no longer stop and continues to consume excessive amounts of food. His weight increases, sometimes reaching enormous levels. To reduce the need for food and achieve weight loss, not only therapeutic but also surgical methods are used. One of the common methods of weight correction is mini-gastric bypass surgery.
Mini-bypass surgery is an operation that can not only reduce the volume of the stomach, but also slightly change the path of food in the digestive tract. Thanks to this, satiety occurs faster during meals, and the amount of nutrients entering the blood decreases. In Moscow, similar interventions are performed by doctors at the Moscow Bariatric Group bariatric surgery clinic. The center is one of the first medical organizations in the Russian Federation that began to carry out such procedures and achieved success in this area.
What is the difference between classic gastric bypass and mini gastric bypass?
The main difference between mini-gastrobypass and the classic version of the operation according to the method of the German scientist Wilhelm Roux is the number of anastomoses - artificial connections between parts of the intestine. With classic gastric bypass surgery, the surgeon cuts off a small part of the stomach and creates a small ventricle with a volume of about 20-40 ml. The small intestine is divided approximately down the middle. Its lower part is sutured to the newly created ventricle, and the upper part, connected to the remaining lobe of the large stomach, is implanted into the lower gastrointestinal tract. Thus, the doctor makes two anastomoses, one of which is located on the small stomach, the second on the final part of the jejunum.
The mini-gastrobypass technique is generally similar to the procedure described above. However, the small ventricle has an elongated shape and is directly sutured at the level of 150-200 cm from the beginning of the jejunum. Its complete intersection is not performed. Anastomosis is present only at the junction of the ventricle with the middle part of the small intestine. This approach allows Moscow Bariatric Group surgeons to significantly reduce the time of surgery and anesthesia.
Mini-gastrobypass compared to conventional gastric bypass is preferable in the following cases:
- poor tolerance to general anesthesia, need to reduce the duration of anesthesia;
- diseases of the cardiovascular system;
- high risk of postoperative complications;
- insufficient ability to recover in patients with diabetes (fewer number of anastomoses - it is easier for the body to heal damage).
The decision about the optimal method of operation remains with the surgeon. Our doctors accept it based on the results of a comprehensive examination and consultations with related specialists (endocrinologist, gastroenterologist, cardiologist), who will observe you free of charge throughout the course of treatment at the Moscow Bariatric Group.
Operations Scopinaro
Biliopancreatic bypass operations - the Scopinaro and the Fobi operation (the operations are named after their developers - the Italian surgeon Scopinaro and the American surgeon Fobi) are the most radical of all combined operations, and can reduce excess weight to a safe level in patients with a BMI > 55 kg/m2, whose body weight exceeds 180 - 200 kg. Also, these surgical interventions are indicated for pronounced pathological changes in fat and carbohydrate metabolism, and severe manifestations of somatic diseases in superobese patients.
When performing the operations under consideration, as with any combined operation, the formation of a “small ventricle” is performed, the volume of which can be 50 or 100 cm3. The small intestine is rebuilt in such a way that the long common loop (the area where bile and pancreatic juice mix with the food bolus) is only 50-100 cm. Thus, throughout almost the entire small intestine, food absorption does not occur, which makes the amount of its consumption no longer so important.
Preparing for surgery
You can complete all the necessary preparatory activities at our clinic. You do not need to waste time and effort visiting third-party medical organizations. Preparation includes the following types of examinations:
- ECG - allows you to assess the condition of the heart;
- FGDS - used to examine the esophagus, stomach and duodenum;
- Ultrasound of the abdomen - required to assess the condition of internal organs and plan the course of the operation;
- Chest X-ray - allows you to exclude severe pathology of the respiratory system;
- laboratory tests (general and biochemical blood tests, coagulogram, blood group, acid-base balance and electrolytes, test for blood-contact infections) - with their help, the doctor assesses the general condition of the body, predicts possible complications and determines contraindications to surgery, if any.
The examination plan necessarily includes a consultation with a therapist, endocrinologist, and gynecologist (for women). Immediately before the operation, the anesthesiologist who will administer anesthesia will meet with you. Tell your doctors about any health problems you have and provide medical documentation, if available. This will make the operation safer and achieve an optimal result of the procedure.
What to expect before surgery
Before the operation, consultations are scheduled with the attending physician, psychiatrist and nutritionist. You will also be informed about exactly what to expect from this surgical procedure. Here's a list of things to know:
- Your doctor will do a complete physical examination, check your blood counts, and review your medical history.
- Smokers will have to quit the habit six weeks before their planned surgical procedure.
- The nutritionist will tell you what lifestyle you should follow and what to eat and in what quantities after the operation.
- A psychiatrist will conduct an examination to determine whether bariatric surgery will help in your case.
- Having surgery will help you lose weight over a period of about 12-15 months. The weight won't disappear overnight.
- Most weight loss surgeries are safe and show good results. But excess weight can return if you do not adhere to a healthy lifestyle.
- Additional procedures may be required after surgery.
- Talk to your doctor if you have a phobia about needles, foreign objects in your body, or anything else that bothers you.
Now, let me answer the most important question - are such operations safe for health?
How is the operation performed?
Our center practices laparoscopic interventions, which means that there will be no unaesthetic scars left on your body. The surgeon, using special instruments, works through 3-4 punctures on the anterior abdominal wall. The length of each of them does not exceed 1 centimeter. Subsequently, neat stitches are placed on the punctures, so that after healing, small, barely noticeable scars remain on the skin.
The operation is performed under general anesthesia. We use anesthetics that ensure easy awakening and the absence of post-anesthesia psychosis. The duration of the procedure is on average 1.5-2.5 hours. During this time you will sleep and wake up in the recovery room. There will be no pain. During the intervention, your condition is monitored by modern expert equipment and an experienced anesthesiologist, so you do not have to worry about your own safety.
Gastric banding
Gastric banding, like vertical gastroplasty, belongs to the group of restrictive operations based on the formation of a “small ventricle.” The formation of a “small ventricle” is carried out by applying a special bandage to the initial section of the stomach, 2-3 cm below the esophagogastric junction, thus dividing the stomach into two sections: “small”, above the bandage, and “large” below it with leaving a narrow transition hole between them. There are two types of gastric banding performed in our clinic: non-adjustable and adjustable. All operations are performed laparoscopically (through 4-5 punctures), under general endotracheal anesthesia.
For non-adjustable gastric banding, a 2.0 cm wide polypropylene tape is used as a band. This material is widely used in general surgery and does not cause allergic reactions from body tissues. At the beginning of the operation, a special calibration probe with an inflating cuff at the end is inserted into the stomach.
The cuff is inflated to 20-25 cm3 and pulled up to the esophageal-gastric junction, after which a polypropylene mesh is placed directly under it around the stomach along its outer surface, the free edges of which are stitched together. The last stage of the operation is suturing the stomach tissue over the band to prevent its migration. Thus, a “small ventricle” with a volume of 20-25 cm is created? and a transition hole with a fixed diameter of 10-11 mm.
The advantage of this operation is the absence of expensive consumables, which makes this operation cheaper than others.
The second gastric banding operation, which is becoming increasingly widespread in the world, is adjustable gastric banding. According to the mechanism of its action, this operation does not differ from the one described above, however, special devices are used as a bandage to adjust the diameter of the transition hole.
Today there are about 10 main models of adjustable bandages, the most common are LapBand, (USA); Swedish Band (Sweden); Soft Gastric Band (Austria). Although there are some differences, all adjustable braces have the same basic components. LapBand system, (USA). The bandage itself is a hollow silicone cuff (in some systems a rigid clamp is applied along the outer diameter of the cuff), a catheter tube connecting the lumen of the cuff with an external access device (port) - a reservoir with a diameter of about 2.0 cm, with a titanium plate at the base and a silicone membrane in the upper section. A small amount of saline is injected into the port, through a conductor into the internal cavity of the silicone ring on the stomach, which can thus be inflated, reducing the size of the transition hole, or deflated, accordingly increasing the diameter of the transition.
In this way, it is possible to regulate the rate at which food enters the lower section of the stomach and further into the underlying sections.
The operation is performed laparoscopically through 5 punctures (from 5 mm to 2.0 cm) in the anterior abdominal wall. As with unregulated gastroplasty, the volume of the formed “small ventricle” is determined using a calibration probe with a calibration cuff inflated to 20-25 cm? and installed at the esophagogastric junction. The band is passed around the stomach directly under the calibration cuff and closed using a special locking device. Sometimes, in order to prevent the band from slipping onto the esophagus, the walls of the stomach are sutured with 2-3 sutures around the band. Using a flexible catheter, the lumen of the bandage is connected to an external access device, which is installed in the subcutaneous fatty tissue.
Possible complications and side effects The most common complications specific to this operation are narrowing of the transitional foramen, migration of the band along the wall of the stomach, and a sharp expansion of the “small ventricle”. If the first complication is eliminated endoscopically, the last two often require repeated surgery
Behavior after gastric banding The fundamental difference between this surgical intervention and other restrictive operations is that it is possible to adjust the rate of food exit from the “small ventricle”, carried out by introducing or pumping out a solution from a silicone band through a port located under the skin. On the one hand, this is an advantage, since it makes it possible to select the most optimal size of the transition opening; on the other hand, some patients are tempted to independently expand the diameter of the gastric transition to take in larger amounts of food.
The selection of the optimal diameter of the transition (the bandage is installed in a deflated state) is carried out by a doctor at least 1 month after its installation under x-ray control, while monitoring the rate of passage of contrast through the transition hole.
Installation of a gastric band is not a temporary procedure and its removal requires repeated abdominal surgery, therefore gastric banding should be performed only if indicated and after the firm consent of the patient!
What causes weight loss
Weight loss after mini-gastrobypass occurs due to two mechanisms. First, due to the reduced stomach capacity, you feel full faster and eat less food. Secondly, due to the fact that food enters the small intestine much lower than it occurs under normal conditions, it does not have time to be completely processed. Accordingly, the amount of nutrients absorbed into the blood is insufficient to maintain the same body weight. Weight begins to quickly decrease as the body compensates for its energy needs by breaking down subcutaneous fat.
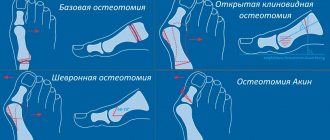
Basic surgical methods of weight loss (types of operations):
- Gastric banding.
- Gastric ballooning.
- Longitudinal gastrectomy.
- Gastroplication (suturing of the stomach).
- Gastric bypass surgery.
- Biliopancreatic bypass.
You can obtain detailed information about modern methods of surgical treatment of obesity at the Weight Loss Center (Moscow) during an individual consultation. Consultations are conducted by a surgeon of the highest category, Dmitry Vladimirovich Gladyshev. This publication discusses the main surgical methods of weight loss with a brief description of the principles of each surgical intervention, its features and advantages.
How will you lose weight after mini-gastric bypass surgery?
The effectiveness of mini-gastrobypass surgery is comparable to the classic version of the operation. After it, you can lose about 60-70% of your original body weight. This result is achieved 1.5-2 years after the intervention, subject to all doctor’s recommendations. In the first months, weight loss will be very intense, but later the process will slow down.
On average, our patients lose about 1 kilogram per week. This pace allows you to gradually get rid of obesity, while avoiding the complications associated with too rapid weight loss. The first results of treatment become noticeable by the end of the first month. Throughout the entire period required to normalize your body weight, Moscow Bariatric Group specialists will monitor you and monitor the weight loss process.
Operation efficiency, reviews
The question is often asked about how many days after surgery the stomach shrinks. Its volume decreases immediately - during surgery. The question is essentially how long and how many extra pounds you can get rid of.
The criterion for the effectiveness of such operations is the reviews of patients who managed to quickly get rid of excess fat through surgery. As practice shows, the key to success lies in the professionalism of specialists and the strict implementation of their recommendations by patients.
Indications and contraindications for mini-bypass surgery
Indications for mini-gastrobypass surgery do not differ from those for classical Roux-en-Y surgery. The intervention is carried out in the following cases:
- body mass index above 45-50 kg/m2;
- BMI is above 40 kg/m2 if the patient refuses to follow the recommended diet and rapid weight gain;
- the presence of diseases, successful treatment of which is possible only after losing weight;
- diabetes mellitus of non-insulin-dependent type due to obesity;
- lack of effect from other weight loss methods.
The choice in favor of mini-bypass surgery is made when there is a high risk of complications, the need to reduce the time spent under anesthesia or to facilitate the regeneration process as much as possible. To determine the presence of indications, choose the optimal method of work and eliminate contraindications, the clinic’s doctors will provide you with a full range of preoperative diagnostics.
After the examination, our doctor may refuse to perform surgery on you if it would jeopardize your life and health. Thus, mini-gastrobypass surgery is not performed for patients with exacerbation of cardiovascular diseases, blood clotting disorders, or acute infectious diseases. In addition, intervention is contraindicated if the patient is under 16-18 years of age, has acute mental disorders, drug addiction, or alcoholism. The procedure is not indicated for people with a BMI less than 40 kg/m2 and is rarely used as a first treatment option. First, the patient is recommended to try conservative methods of weight correction.
Surgical treatment of excess weight
We were lucky enough to talk with the leading bariatric surgeon at the Clinical Center for Obesity Surgery in Moscow, Professor Vadim Viktorovich Fedenko, who, together with his colleagues, has been performing unique surgeries for Russia for many years, helping obese people lose weight.
— Vadim Viktorovich, how many years has the Clinical Center existed and how did your journey in bariatric surgery begin?
— Our team consists of people who have been engaged in bariatric surgery for many years; the center has existed since 2000.
During this time, we changed three clinical bases, and on the basis of the Central Clinical Hospital of JSC Russian Railways No. 6 in Pechatniki, Moscow, we have been working for 5 years. At first we only performed gastric banding, then we gradually developed, mastered new techniques, and now we perform all the bariatric surgeries that exist in the world. Today there are three standard bariatric surgeries: banding, gastric sleeve (or SLIV) and gastric bypass.
About 90% of all bariatric surgeries performed in the world involve these three types of surgeries.
— If we talk about the number of patients, how many patients have passed through your hands today?
— During our practice, we had about 4,000 patients, and, accordingly, the same number of operations, since we do not treat with pills or diets.
— During this time, did you have to correct someone’s work and help patients who had unsuccessful or ineffective bariatric surgery from other surgeons?
“Not only did I have to, but I still have to do this today.” Such patients come to us very often. There is even a whole section on our forum called “Help for patients undergoing surgery in other clinics.” If we talk about statistics, about 70% are primary operations, and 30% are repeat operations.
— What knowledge do bariatric surgeons lack and what are the main mistakes made by inexperienced and young doctors?
— First of all, surgeons performing bariatric surgery need to have knowledge of abdominal surgery, and, of course, specialized knowledge. It is difficult to answer about common errors, since there are a lot of them, as well as problems that arise against this background. Moreover, if you look at specialized journals on obesity surgery, almost half of the articles that are published there are devoted to errors, problems, complications... Surgeons who are just starting their journey in bariatrics will most likely make all the mistakes that exist, because It is impossible to learn this in theory. Only when the surgeon begins to operate himself will he learn from his own experience. And that means based on your mistakes.
— When is bariatric surgery performed?
— Surgeries are performed when a BMI (Body Mass Index) is 30 or higher, when a medical diagnosis of obesity is made.
But if we are talking about a patient with a BMI of 30, he should not undergo gastric bypass, in this case only a band can be considered.
Although, if we talk about indications for bariatric surgery, now the approach around the world is becoming more and more liberal. Previously, it was possible to perform bariatric surgery only with a BMI of 40 or more, but now the American organization FDA (Food and Drug Administration), which also licenses medical techniques, in February 2010 officially allowed the bandage to be placed on people with a BMI of 30 or more. This organization has such high authority that sooner or later its decisions are accepted as a standard throughout the world. This limit is lowered today because if a person is truly obese, experience shows that the weight will sooner or later return, no matter how effective the diet was at first. In addition, if we are talking about a bandage, this is an operation with virtually no risk: it is 100% reversible and does not make any changes to the body.
If the bandage is then removed for some reason, the situation immediately returns to its original state, there is no point of no return. By and large, the installation of a bandage could be done for all overweight people. But these operations are not considered cosmetic - these are operations that are done for health. Therefore, in order to do them, the patient’s desire alone is not enough. We are limited by medical indications.
— All surgical weight loss operations have one goal, to lead to the loss of excess weight. Are there clear indications for this or that operation? How do you decide which surgery will be performed?
— This question is one of the most difficult in bariatric surgery, and there is no answer to it yet. Let me explain, if a person has a BMI of 40 or more, from a formal point of view, he can undergo any bariatric surgery, and this will not be a medical error.
Moreover, different clinics take different approaches to this issue. There are clinics that offer only one operation, for example, a bandage, and they perform it on all patients.
In this regard, it is much more difficult for us, since we do all types of bariatric operations, we know the pros and cons of each of them, so the choice is extremely difficult. As a doctor, I can say that with a BMI of 40 and above, any operation can be performed, but from a subjective point of view, I may have my own approach. Take even our team: we, three doctors, operate on the same patients, see the same results, but, nevertheless, we do not have a consensus on what kind of operation should be performed in each specific case. It would be good if there was some kind of set of examinations, by doing which you can understand that you need to do this or that operation, but unfortunately there is nothing like that... And this is not only Russian realities - the situation is the same in the world.
— Does it ever happen that a patient comes to you with a request for a specific operation, that is, with a ready-made solution?
- Often. Most patients come to us from the Internet, because general practitioners - therapists, endocrinologists - do not know about our methods and do not send patients to us. As a rule, patients find us themselves: they look for information, analyze, think about this issue, sometimes for more than one year. During this time, they have studied the data inside and out, know the procedure perfectly and come with a ready-made solution. And if this decision fits within the formal framework (BMI - 40 or more), then we have the right to perform any operation on him. If he wants a bandage, then why not? Sometimes we can suggest something, based not so much on medical, but on paramedical data. For example, a person lives very far away, in Khabarovsk or Vladivostok, and wants to have a bandage made in our clinic. We will most likely recommend something else to him, because the bandage requires adjustments, and in the first year after surgery, a person must come to us on average 5 times so that the size of the narrowing can be selected to suit his individual needs. As practice shows, it is not possible to come from Khabarovsk or Vladivostok regularly. And this cannot but affect the result.
Or, another option: a person has type 2 diabetes. In this case, it is better to undergo gastric bypass, since it cures type 2 diabetes in 90% of cases. But this is a big problem, and we have the opportunity to completely cure a person.
And if a person lives somewhere nearby, if he does not have diabetes, then we listen to the opinion of the patient himself. The moment of choice here can be not only medical, it is largely psychological. Often people say that they do not want to risk removing part of the stomach and ask for a band. This is a completely normal approach. And there are other people who don’t want any foreign bodies, don’t want to go for adjustments every month, but want to solve the problem once and for all - get a bypass and forget about the problem. Such a radical approach is also quite legitimate. Of course, if a girl with a BMI of 23 comes and asks to perform the most “scary” operation on her, of course, in this case we will not perform the operation. And such girls often come to us.
— Which of these operations is considered the most complex, modern and high-tech?
— The most difficult operation is gastric bypass. A standard gastric bypass operation lasts 2.5 hours. And it provides for an intestinal stage, which is not present with the bandage and DRAIN. Banding and draining are operations only on the stomach itself, while gastric bypass also affects the small intestine. Therefore, it is the most difficult technically. All operations use high-tech equipment, disposable instruments and modern stitching machines.
— If we talk about absolute medical indicators, when will you not perform this or that operation?
— If a patient has a BMI of 40 or more, there are already medical indications for any operation. But there are situations when the case is severely advanced, when the BMI is 60 or higher, the so-called supermorbid obesity, when people weigh 200 kg or more. They have a very high risk of complications, for example, during the operation, blood clots can form in the legs, which break off and clog the pulmonary arteries. It is impossible to fight this. They also have a lot of medical problems with both the heart and lungs, and the risks of undergoing major surgery are very high. Even from a technical point of view, it is very difficult for such people to undergo surgery due to the large amount of adipose tissue. The operation in this case does not last 2.5 hours, like a standard bypass surgery, but 4-5, sometimes even 6 hours...
And the duration and risk of the operation are in direct linear relationship - the longer the operation, the greater the risk of complications. And we have to either refuse to operate on this person, because the anesthesiologist does not give the go-ahead for the use of anesthesia, or perform the smallest operation, for example, bandaging, which lasts about 20 minutes. This is done so that the person loses 50-70 kg, and after that, when the risks decrease, he will undergo a more serious operation. In this case, we divide the operation into two stages, each of which is not very risky.
If we talk about the clinical picture of the development of the disease, often such people gradually and imperceptibly gain weight, weigh 150 kg, then 180, then 200, and everything seems to be “fine” with them, and then suddenly a breakdown occurs and their health immediately and sharply deteriorates. Blood circulation in the legs worsens, trophic ulcers form, blood clots begin to clog the pulmonary artery, chronic pulmonary embolism develops - shortness of breath appears, they cannot breathe. Only when a person becomes very ill do they come for surgery. But it is no longer possible to operate on such a person, because the point of ultra-high risk has already been passed. In this case, you should try to at least moderately lose weight (by 30-40 kg), more or less restore your health, and only after that you can operate on it.
— Speaking about surgical weight loss, how many kilograms do patients lose per month, how long does the weight loss program last?
“Everything here, of course, is individual and depends on the patient’s initial parameters, but this can be calculated and predicted. The optimal rate of weight loss is 1 kg per week, sometimes 2. As a rule, the process lasts a year, and this does not depend on what operation is performed.
— What are the absolute contraindications to surgical weight loss? Do your patients need to be completely healthy at the time of surgery?
— Metabolically healthy people among obese patients are about 50%.
As a rule, healthy patients are young women with a BMI of 30 or more. They come to us not to improve their health, but for aesthetic reasons - for beauty. If people come with great obesity, then, naturally, there is no longer any health. An absolute contraindication to surgery is a person’s condition when he cannot be given anesthesia. These are serious diseases of the heart and blood vessels; as a rule, all these diseases are complications of obesity.
— Describe the ideal patient for surgical weight loss, in which case will the person get an excellent result?
“This is a person with a BMI of 40, that is, moderate obesity, so there will be no special technical difficulties during the operation. Next, an educated person, that is, he can understand the technical details and understand the problem. And this should be a person who cares about his health, wants to take care of it and will follow all the recommendations.
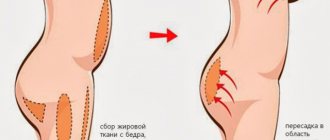
— If we talk about the aesthetic side of the issue, do all patients develop large excesses of skin and tissue after losing weight, and how should this problem be solved?
“The situation here is very simple: if excess skin has formed, and if the patient does not like it, there is almost a 100% chance that some kind of plastic surgery will have to be done to correct it. But not everyone develops excess soft tissue. It depends on the quality of the patient’s skin, on his genetics. If we see that a patient has stretch marks on the skin, there will most likely be sagging, since the very fact of the presence of stretch marks indicates poor skin tone. This does not depend on gender, age, or even weight, but only on the genetic properties of the skin. We had men aged 50, very obese, who then lost weight and nothing sagged. And there are young girls, 20 years old, whose sagging is very strong. We collected statistics, among our patients, 83% then undergo plastic surgery in order to correct the situation. And accordingly, 17% do without plastic surgery.
Besides this, there is one more very important question. Very often people who have previously undergone abdominoplasty due to obesity come to us for bariatric surgery. The aesthetic result looks extremely unattractive. The algorithm here should be exactly the opposite: first bariatric surgery, then abdominoplasty, and in no case the other way around! If you do abdominoplasty first and then bariatric surgery, the person will lose weight and everything will sag again, but in much worse conditions, with adhesions and so on.
— You recently announced cooperation with the European Medical Center (EMC), what will it consist of?
— Yes, we are getting another clinical base. Patients who want to undergo surgery in an EMC setting will have this opportunity.
— Finally, I would like to hear your recommendations for patients trying to lose weight. What advice can you give them? What should you try and what should you never do?
— We are surgeons, that is, we do not treat with diets or pills, but only perform operations. Therefore, it would be more logical to ask nutritionists this question. If the patient is “ours” (BMI 35 and above), there is only one recommendation - come to us for a consultation. On average, several months pass from the first visit to the operation.
www.VES.ru +7
Advantages and disadvantages of mini-bypass surgery
The advantages of mini-gastrobypass surgery include:
- weight loss that is many times greater than that achieved with other treatment methods;
- reducing the risk of heart attacks, strokes and other diseases associated with excess weight;
- complete cure of type II diabetes mellitus in 98% of cases;
- less surgical trauma compared to classic bypass surgery;
- shorter and easier recovery period;
- significant reduction in operational risks;
- reversibility of changes - if necessary, the intestines can be returned to their previous state.
The main disadvantage of the procedure is insufficient absorption of vitamins. They must be taken in tablet form. In addition, dumping syndrome may occur when eating foods rich in simple carbohydrates and fats. In most cases, it manifests itself with vomiting, diarrhea, dizziness and a feeling of heat in the upper half of the body. It should be noted that this is only conditionally a disadvantage. In fact, this reaction to energy-dense foods will keep you from eating them and will provide additional protection against weight gain again in the future.
What recommendations should be followed after surgery?
The recovery period after mini-gastrobypass surgery takes on average 1.5-2 weeks. In this case, discharge from the hospital becomes possible within 5-7 days. Until the sutures are completely healed, it is necessary to avoid significant physical activity, however, walking and exercise therapy with the permission of a doctor are mandatory. Later, you will need to maintain some activity, such as walking or swimming. This will increase calorie consumption and ensure that their intake into the body is lower than energy expenditure.
Correction of the diet is of great importance. It is important that immediately after surgery the diet is liquid and gentle. It is possible to use protein concentrates or broths. After a few days, you will be allowed to eat rougher foods, but the amount of foods with excessively high energy value will need to be significantly reduced. Food intake should be in small portions, 5-6 times a day.
A nutritionist at the Moscow Bariatric Group clinic will develop a diet for you that will meet your needs. Our specialists select the diet in such a way as to provide the patient with adequate nutrition, but to avoid the intake of “harmful” calories. In addition, you will need to take dietary supplements containing calcium, iron and vitamins.
How much does gastric reduction surgery cost?
The price for surgeries can range from $14,000 to $23,000. You can find specialists at a much lower cost - around several thousand rubles. Depending on the country and clinic you choose, make sure they have qualified specialists and quality post-operative care to help you recover. Under no circumstances do anything if you have even 0.1% doubt.
Before we wrap things up, let me explain the benefits and side effects of gastric reduction surgery so that you can make a fully informed decision.
What complications exist and how to deal with them
Like any other operation, mini-gastrobypass surgery may be accompanied by certain complications. During the intervention and in the early postoperative period, you will be under constant medical supervision. They have many years of experience and know how to deal with any undesirable consequences of the procedure. There is no need for you to worry about your safety, our specialists will do this. Later, especially after discharge from the hospital, you may experience the following reactions:
- Dumping syndrome. Occurs immediately after eating or shortly after eating. As a rule, it is associated with errors in diet. Manifested by general weakness, dizziness, feeling of heat. It is easily eliminated by following a diet and goes away within the first year after surgery.
- Deficiency of protein and microelements. You may experience dry skin, weakness, and hair loss. It is necessary to review the diet and add to it foods rich in protein and other substances for life.
- Insufficient weight loss. It is extremely rare. Requires additional examination, lifestyle and nutrition adjustments.
We are ready to support you if any post-operative problems arise. So that you always know who to turn to for help, the Moscow Bariatric Group bariatric surgery center will assign you a personal curator who will listen to you, determine further tactics of action and make an appointment with the necessary specialists. Most often, our patients need additional consultation with a nutritionist, since the vast majority of their problems can be solved by revising their diet and eating regimen.
Longitudinal gastrectomy
Longitudinal gastrectomy is a surgical method of weight loss based on the actual reduction of the total volume of the stomach due to resection of the lateral part of the organ. Other names of the technique: longitudinal gastrectomy (gastric bypass), sleeve resection (Sleeve).
Operating principle
. Sleeve resection is performed under anesthesia. During the operation, the surgeon removes the side part of the gastric wall, the volume of the organ is reduced to 100 milliliters. The valve system is preserved, which ensures normal motility and physiological functioning of the digestive tract after surgery.
The surgical method of weight loss gives excellent results due to a decrease in the total volume of the stomach. The excellent effect is explained not only by a sharp decrease in food consumption, but also by a decrease in the secretion of ghrelin - the “hunger hormone”, which was produced in the removed fragment of the gastric wall before the operation.
Reference
. Ghrelin is a hormone that is produced in the stomach and acts on the hunger centers in the brain, causing and increasing appetite.
Advantages.
After longitudinal resection of the stomach, no foreign objects remain in the abdominal cavity. The motility of the digestive tract is not affected, the physiology of digestion is not disturbed. Essential vitamins, amino acids and microelements are absorbed in full. The absorption of drugs is not impaired.
Effect.
Sleeve resection normalizes the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract and promotes the formation of correct eating behavior. After surgery, patients manage to lose 65% of excess weight. This surgical method of weight loss provides long-term stable results.
What is the cure for diabetes mellitus?
Cure from non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus occurs through two mechanisms. First of all, the concentration of fatty acids decreases in the body of a losing weight person. Their negative impact on the receptors responsible for processing sugar is reduced. Glucose begins to be better absorbed and its content in the blood returns to normal.
The essence of the second mechanism is as follows. In the human duodenum, anti-incretins are formed - substances that impair the absorption of carbohydrates. Since after mini-gastrobypass surgery food from the stomach goes directly into the jejunum, anti-incretins are no longer created in the same amount. This promotes better processing of sugars and their absorption by the body's cells.