Frequent mechanical injuries to the face lead to the development in the basal layer of the dermis of a disease such as basal cell carcinoma or basal cell carcinoma. The skin is very sensitive to various damages, including constant ultraviolet exposure from the sun. Being uncovered by clothing, the face is exposed to the negative effects of natural and other factors. Men, especially, often injure their faces while shaving.
Few people know what it is, although the pathology is very common. Everyone has seen people with basal cell carcinoma, and many have personally encountered this skin disease. With basal cancer, a neoplasm forms on the skin of the face, which is not too dangerous and can be treated if diagnosed in a timely manner. However, during relapse, basal cell carcinoma can become aggressive.
This disease is common among skin cancer pathologies. If we take all malignant skin diseases, then in seventy percent of them basal cell carcinoma is diagnosed. Despite the fact that a nodule protruding above the surface of the skin never metastasizes, tumor cells can grow into other tissues, and basal cell carcinoma itself is highly likely to recur after successful treatment. Before thinking about treatment, it is necessary to understand the causes, types, and symptoms of these tumors.
Causes
There is no specific reason that would definitely lead to such a tumor as basal cell carcinoma on the face. Scientists were able to find out that older people (after forty or fifty years) who have fair skin and spend a lot of time in the sun are at risk of cancer. It is ultraviolet radiation that stimulates the growth of basal cell carcinoma of the facial skin.
Factors that provoke the appearance of a tumor are the following:
- Prolonged sun exposure. The stronger the influence of ultraviolet rays, the greater the risk of basal cell carcinoma.
- Hereditary predisposition. More often, people get sick in cases where they already had a similar disease in their family, and also if they have fair skin or freckles.
- Elderly age. With age, the risk of developing this pathology only increases. Almost ninety percent of facial skin cancer cases occur in people over fifty years of age.
- Professional factor. Working in hazardous industries where there is contact with chemicals increases the risk of basal cell carcinoma formation.
- Long-term or recurrent damage to the skin on the face (minor cuts, sunburn, frostbite, dermatological problems).
- Exposure to radioactive or x-rays in the treatment of other oncological pathologies.
- A decrease in the body's protective functions, which is associated with taking certain medications or with the presence of immunodeficiency conditions such as HIV or AIDS.
We recommend reading Causes of melanocytic nevus, its types and treatment
This form of skin cancer does not occur in childhood and adolescence, but prolonged exposure to the sun can lead to consequences in the form of basal cell carcinoma in the future.
Advantages of the technique
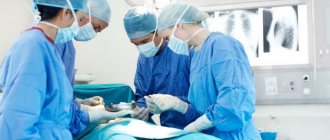
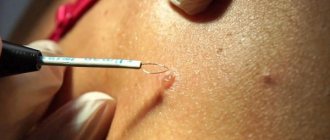
The main advantage of traditional surgical treatment is the ability to examine excised tissue under a microscope. At the same time, specialists pay special attention to the edges of the removed skin and examine whether there are any tumor remnants there. During the operation, the incision is made in width and depth. It reaches the subcutaneous fat, sometimes affecting the muscle fascia, the outer shell of cartilage and bone (if the tumor lesion also affects them).
Attention! The tumor is always removed along with some healthy tissue. “Allowances” are made taking into account the form of education.
For example, when removing a nodular basal cell carcinoma, 4-5 mm of surrounding tissue is captured. This prevents relapses. When removing a sclerosing tumor, areas are removed with a margin of 15 mm.
What is the danger
Before you think about how to treat basal cell carcinoma of the face, you need to understand what danger this pathology poses. This form of tumor is characterized by slow growth, at the beginning of which there are practically no signs of disease.
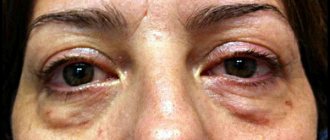
A person does not pay attention to small nodules, and sometimes may consider them moles or other harmless neoplasms, while the tumor grows into the deeper epidermal layers and leads to the destruction of muscles, bone tissue and cartilage structures. Gradually, basalioma spreads along the nerve trunks, muscles and periosteum.
When the tumor is localized near the natural openings of the face, there is a high risk that the cartilage and bone structures in the nose, eye sockets, or ears will begin to deteriorate. As a result, these organs are subject to deformation. Along with the destruction process, basal cell carcinoma ulcers, open wounds and erosions appear. This leads to infection and purulent abscesses. A neoplasm from the nose can spread to the mucous membrane of the oral cavity, destroy the bone of the orbit, leading to visual disturbances, including complete loss of vision. If the ear is damaged, a person runs the risk of hearing loss.
What is basalioma
In medical practice, basal cell carcinoma is an infiltrating neoplasm originating from epidermal cells or hair follicles. The disease is characterized by slow progression and extremely rare cases of metastasis. The cells of a non-aggressive basalioma tumor are similar to the cells of the basal epidermal layer of the skin, which explains its name.
This oncology is perhaps the most common form of cancer, diagnosed annually in 80% of malignant skin tumors. Statistical studies prove that every third man and every fourth woman encounters basal cell carcinoma throughout their life. Despite this, many people do not know what basal cell carcinoma is, how to treat it, and how dangerous the tumor is until they encounter the disease. The localization of basalioma is usually the skin of the face and neck; the neoplasm is practically not found on other organs. Most often, the characteristic localization of this tumor is the following areas of the skin:
- nose;
- cheeks;
- lower or upper eyelid;
- nasolabial folds;
- ears;
- neck;
- forehead;
- scalp area.
In fact, the disease does not pose a serious threat, as it is characterized by slow progression with minimal risk of metastasis. The most effective way to remove basal cell carcinoma is with a laser, but since the disease does not pose a serious threat, many people try to get rid of it on their own at home. More often than not, this is the reason for diagnosing tumors already at advanced stages of development.
It is worth noting that despite the minimal risk of metastases, basal cell carcinoma still belongs to the list of malignant neoplasms. In some cases, a tumor-like formation can grow into adjacent soft tissues and bones, causing their destruction, as a result of which the prognosis for patients is fraught with significant consequences.
Kinds
This pathology has several types:
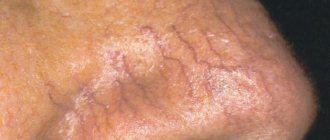
- Nodular (exophytic) - grows inward, has a round shape and pink color. Has an increased tendency to bleed. It looks like a nodule with a depression in the center.
- Ulcerative is a subtype of nodular form that is neglected without treatment.
- Solid basal cell carcinoma is nodular, large-nodular, and has the appearance of a single spherical node growing outward.
- Flat - a tumor in the form of a plaque with raised and clearly defined ridge-like edges.
- Superficial - is a rare type of pathology and is more often found not on the face, but on the body. It looks like a pink spot, the surface of this type of basal cell carcinoma is shiny, the edges are raised. Despite its rarity, this form is the safest and can grow for decades without causing damage to human health.
- Warty - is the most common, has the appearance of numerous light, dense hemispherical nodules that rise above the skin and resemble cauliflower.
We recommend reading Papillary thyroid carcinoma - causes, symptoms and treatment
According to histological classification, basalioma is divided into:
- Superficial multicentric;
- Sclerodermal;
- Fibrous-epithelial.
The tactics of its treatment depend on the type of tumor.
Stages
The initial zero stage indicates a basal cell carcinoma that has not fully formed.
After its formation, the tumor goes through four stages of development:
- Stage 1 – size is about two centimeters, the tumor does not extend beyond the dermal layer, there is no transition to adjacent tissues;
- Stage 2 – the size of the basal cell carcinoma is five centimeters, it grows through all layers of the skin, but does not affect the subcutaneous fat;
- Stage 3 – the neoplasm grows deeper than five centimeters, an ulcer appears on the surface, subcutaneous tissue is destroyed, muscle tissue and tendons are damaged;
- Stage 4 – cartilage and bone tissue are destroyed.
A simpler classification involves the initial, advanced and terminal stages.
Stages
Based on the size of the tumors and the depth of damage to healthy tissues of the body, in medicine there are five stages of basal cell carcinoma:
- stage 0 - cancer cells are already in the skin, but the tumor itself has not yet formed;
- stage I - the tumor size does not yet exceed 20 mm;
- stage II - tumor size can vary from 20 to 50 mm;
- stage III - the neoplasm grows into the dermis, bones, muscles and other tissues, the tumor is more than 20 mm in diameter and has ulcerations;
- stage IV is a papillary basal cell carcinoma, the size of which exceeds 50 mm, with ulceration and soft, muscle and bone tissue destroyed under the neoplasm.
If basal cell carcinoma is not treated promptly, the development of the tumor can lead to serious complications and consequences, which can not only cause dysfunction of important organs, but also lead to the death of the patient.
Symptoms
An experienced doctor can easily distinguish the visual symptoms of this pathological neoplasm from other skin diseases.
The tumor has a peculiar appearance:
- dense consistency;
- clear boundaries;
- thickening along the edges in the form of a roller;
- small depression in the center.
As a rule, at the initial stage of development, the tumor does not cause any discomfort or pain, therefore, with few or no signs, people often do not pay attention to it. As it grows, when the destruction of the underlying structures and ulceration begins, the patient begins to experience pain and consults a doctor.
Indications and contraindications for surgical tumor removal
The method of surgical removal of basal cell carcinoma is prescribed by doctors in most cases of detection of the disease.
Indications for the operation are:
- diagnosed superficial, ulcerative, scar or nodular tumor;
- rapidly progressing basal cell carcinoma (with a growth rate of more than 5-7 millimeters in six months);
- the presence of a neoplasm that changes its color and becomes darker;
- change in the shape of basal cell carcinoma.
Before choosing a treatment method for a particular patient, the doctor observes the growth of the tumor over time for some time.
Among the contraindications to surgical tumor removal are the following factors:
- disorders of blood clotting properties, if they cannot be corrected;
- general serious condition of the patient;
- the presence of an acute infectious or inflammatory process.
In some cases, doctors recommend that pregnant women postpone surgery until the baby is born.
Diagnostics
When a person comes to the hospital, diagnosing skin cancer begins with a visual examination. Next, the doctor takes fingerprint smears or scrapings from the surface of the tumor and refers the patient for cytological and histological examination. If nest-like clusters of spindle-shaped, oval or round cells are present, then to confirm the diagnosis it is necessary to determine the cellular composition, for which a scraping is taken from the bottom of the ulcer.
With the help of analysis for tumor markers, cancer can be diagnosed more quickly, however, with malignant basal cell carcinoma, specific tumor markers are not produced. Therefore, in all cases, a laboratory blood test is performed, during which an increased level of leukocytes, an increased ESR (erythrocyte sedimentation rate), a positive thymol test, and an increase in C-reactive protein are noted.
Since these laboratory indicators can be present in many inflammations, and the histological and clinical picture of the tumor can be varied, it is necessary to carry out differential diagnosis to help exclude or confirm other skin diseases, such as lupus erythematosus, lichen planus, seborrheic keratosis.
We recommend reading Breast lipoma - causes, symptoms, treatment
An inexperienced doctor may confuse flat superficial basalioma with Bowen's disease, the pigmented form with melanoma (cancer of a mole), sclerodermal tumor with scleroderma and psoriasis. Due to the fact that basal cell carcinoma may have more common symptoms than other tumors, the examination must be carried out very carefully and only in a good diagnostic center.
What does basal cell carcinoma look like?
Skin diseases of basalioma during fully formed neoplasms have a characteristic appearance, thanks to which the doctor can make a diagnosis immediately after examining the patient. In the early stages of development, the tumor looks like a simple pimple, which does not cause discomfort to the patient at all. Gradually, as basal cell carcinoma grows, the tumor becomes nodular, and even later an ulcerative or erosive surface of the affected skin area forms.
Treatment
For basal cell carcinoma on the face, treatment can be carried out in different ways and depends on the degree of development of the type of tumor and associated complications.
Basalioma can be cured in the following ways:
- Drug treatment - the method consists of taking cytostatics in small doses. Drugs such as Spirobromine, Prospidin, Cyclofafamide are used. Additionally, creams and ointments can be used to treat basal cell carcinoma. Doctors often prescribe an ointment for facial skin basal cell carcinoma based on imiquimod, for example, Keravort or Aldara.
- Surgery for basal cell carcinoma on the face is allowed only for small tumors. Surgical removal is very effective, but it leaves behind scars, which is undesirable given the location of the tumor.
- Laser removal of basal cell carcinoma has a more gentle outcome, but still, large tumors are not removed by laser.
- Treatment with radiation therapy is possible at the very beginning of tumor formation.
- Electrical burning (electrocoagulation) is an inexpensive, but painful and traumatic method. Scars remain at the site of basal cell carcinoma removal.
- Cryogenic therapy (cryodestruction) is the best option, which has no contraindications and does not require anesthesia.
Treatment with folk remedies is permissible only as an addition to the main method of therapy and must be agreed with the treating doctor. For bleeding wounds or ulcers, such therapy is unacceptable.
Advantages and disadvantages of the technique
Using a laser, you can remove tumors located in hard-to-reach places. The operation lasts 15-20 minutes. After it, a black crust forms on the wound. It creates additional protection for the penetration of pathogenic bacteria. Natural skin healing processes take place underneath it. Therefore, if you follow the doctor’s recommendations, you can count on a good cosmetic effect: after the crust falls off, a section of new epidermis forms at the site of the wound. It has a bright pink color. Over time, it fades and the hole becomes less noticeable. The absence of scars is another undeniable advantage of laser therapy.
The patient is discharged home on the day of surgery. With proper care of the wound area, the rehabilitation process lasts a week. This is half the cost of traditional surgery.
Nutrition
Proper nutrition is equally important for skin cancer. The diet must contain all the necessary complex of microelements and vitamins. It is important not to forget that by following a diet, especially at the time of treatment with chemotherapy or radiation therapy, the patient tolerates treatment much easier, which can improve his quality of life.
It is strictly forbidden to eat:
- roast;
- various pickles and marinades;
- smoked meats;
- dairy products;
- mushrooms and dishes prepared with them;
- yeast baked goods;
- fish and meat broths.
Authorized products include:
- greenery;
- citrus;
- garlic;
- cabbage of any variety;
- carrot;
- red pepper;
- beet.
You can drink natural juices, compotes, non-carbonated mineral water.
Recovery after surgery: wound care and rehabilitation process
The rules of care may differ slightly depending on whether the edges of the wound were sutured or left open.
When closing the wound with flaps, as well as if the edges of the wound were sutured, the doctor, upon completion of the operation, applies a tight bandage to the excision site, which provides the necessary pressure on the surface. After the procedure, swelling is likely to occur, so the patient is advised to apply cold compresses. Twice a day, the wound must be carefully washed with soapy water, avoiding rough movements and friction.
Open wounds must be treated with bactericidal ointments and solutions daily, mainly by the surgeon himself. Taking vitamin complexes helps speed up skin healing. Be sure to apply sterile gauze bandages to the operated area.
The entire healing process can take from 3 weeks to one and a half months. At this time, until the wound has completely healed, the patient is prohibited from visiting saunas and baths, swimming in open reservoirs and pools. To avoid relapse, it is necessary to avoid exposure to ultraviolet rays for a year after surgery.
For cancer patients, even after surgical treatment, doctors prohibit working with toxic substances, especially if they come into contact with the skin during the process. In the first year after surgery, the patient must undergo a preventive examination with an oncologist every three months, then once every six months. This measure reduces the likelihood of tumor recurrence.
Probability of relapse
Basalioma can recur. This suggests that even after removal of the formations, it is possible that the tumor will reappear in the same place after some time. There is also a possibility that the formation of basal cell carcinoma may occur in other places.
According to statistics, the probability of a recurrent condition within five years after tumor removal is 50 percent.
In most cases, relapses occur in the ears, lips, and nose.