Bath, sauna - harm and benefit, indications and contraindications, rules for taking bath procedures
The bathhouse is a traditional place for many people to spend one or more evenings each week.
- Some consider the bath a powerful healing procedure
- Others - relaxation for soul and body
- Still others are a serious risk factor for a number of diseases.
Each of these theories has its own truth, which we will look into in this article. Baths are an active method of thermal exposure of the body surface and respiratory system to high temperatures. The therapeutic effect of bath procedures is aimed at eliminating some functional changes in the body:
- increasing the reserve of the respiratory and cardiovascular systems
- acceleration of microcirculation of blood and lymph
- improvement of immune reactivity.
The type of bath is determined by the specific microclimate of the thermal chamber (steam room):
- A traditional Russian bath is characterized by saturating the steam room air with water vapor, which forms a fog with 100% humidity. The air temperature in a Russian steam room is 40-50 C.
- The Roman bath is heated with dry air, the temperature of which in the tepidarium is 40-45 C, and in the thermal chamber - 60-70 C. Hot air is supplied through holes in the floor or walls.
- Turkish bath - in it the air temperature reaches 40-50 C, the humidity is regulated by heating the water in boilers and often reaches 100%.
- The Finnish sauna differs from all others in its special microclimate: the air temperature reaches 70-100 C, the temperature gradient in the floor and ceiling areas is 60 C, and the relative humidity is within 10-15%.
- Japanese bath - involves washing in barrels with a temperature of 40 and then 60 C. The humidity in the room can also reach 80-100%.
- IR sauna (infrared) - provides air heating to 45-60 C and humidity 45-65%. It is believed that an infrared sauna is beneficial for the body with minimal health risks, which is why many people install this type of bath even in apartments.
The physiological effect of a bath is directly related to air humidity. A steam bath always leads to more significant functional changes and faster overheating than a dry air bath. Due to the inhalation of hot steam, gas exchange and evaporation of sweat are hampered, and a significant load is placed on the pulmonary circulatory system.
The greatest danger posed by the effect of elevated temperatures on the body is the activation of the degeneration of cells into malignant ones in the presence of precancerous diseases, which one may not even be aware of, as well as in the case of a hereditary risk of oncology. Since after 40 years the risk of neoplasms increases significantly, this category of people should definitely not turn the bathhouse into a lifelong hobby.
In this paragraph, we will consider the main aspects of the positive effect of the microclimate of the bathhouse and sauna on a healthy body with strictly dosed temporary exposure agreed with the doctor, as well as the harm caused to the body by bathing procedures.
| Body system | ||
| Heat exchange |
|
|
| Metabolism |
|
|
| Autonomic nervous system |
|
|
| Endocrine glands | Level Up:
| Level Up:
|
| CNS |
|
|
| The cardiovascular system |
|
|
| Respiratory system |
|
|
| Musculoskeletal system |
|
|
At the beginning of this section, we wrote about dosing exposure, which should be taken very seriously. The fine line between the benefits and harm of a sauna and steam bath is precisely in the time period, which many ignore, staying in the steam room for half an hour and breaking useless “records”. It is also important to observe the cyclical nature of the procedure: preparation, temperature exposure, cooling and rest.
Harm from the Finnish sauna and other types of baths is most often associated with non-compliance with the time spent in the heat chamber, neglect of contraindications, and visiting the steam room while intoxicated.
General contraindications:
- Precancerous diseases
- Oncological diseases
- Acute diseases or exacerbation of chronic diseases
- Tuberculosis of any localization
- Hyperthermia
- Children's age is up to 3 years, and steam room - up to 10-12 years
- Very old age (over 75 years old)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
This list of indications does not mean that if you have such a pathology, you can go to the bathhouse without risk. In a good way, the indications for a bath are a state of absolute physical and mental health. Any person should reasonably and realistically measure their capabilities, not be equal to others and not put their health (and sometimes life) at risk for the sake of the desire to prove to someone their incredible ability to withstand high temperatures.
Contraindications to the Russian bath and other types of baths can be continued and continued on an individual basis. There are no absolutely healthy people, there are underexamined ones. There is a lot of truth in this medical joke, so you should carefully weigh the possible harm and dubious benefits of bath procedures.
- on an empty stomach and immediately after eating;
- after intense physical activity;
- after and during drinking alcohol (high risk of dehydration, burns from hot air);
- against the background of psychological stress.
- Before bathing procedures, you should quench your thirst (still mineral water, green tea, water).
- Before entering the thermal chamber, you should take a warm shower and wipe your body dry to create better conditions for sweating and natural thermoregulation.
Effect on the body
Bath procedures
High temperatures in the steam room activate the cleansing of the skin, which means more oxygen is supplied.
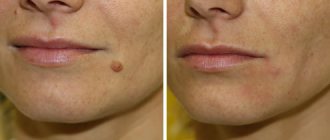
The heat in the bath trains the sweat and sebaceous glands, a kind of gymnastics that allows you to smooth out existing wrinkles and prevents the appearance of new ones.
As a result:
- blood flow improves;
- the pallor of the face disappears;
- the skin becomes soft and elastic.
The bath procedure normalizes the regeneration of epidermal cells, restores the immune and metabolic functions of the skin. During steaming, dead particles are exfoliated, bacteria and skin secretions are removed.
Botox injections
Refusal of cosmetic procedures
The following procedures are contraindicated for the first time after “beauty injections”:
- Harsh cleansing of the skin with rough products (peelings based on stones or containing large granules).
- Go to beauty salons for various skin care treatments.
- Chemical or laser peeling. You can use the service in 14-30 days. Under no circumstances should you resort to performing this procedure yourself!
- Injections with other drugs (hyaluronic acid, fillers).
- Mesotherapy, biorevitalization.
- Ultrasound and other procedures of a similar type of influence.
After Botox, you cannot ignore the recommendations and turn a blind eye to prohibitions. Botulinum therapy, although a fairly simple procedure, does not exempt you from following a number of recommendations. The client's face is not only the responsibility of the doctor, but also of the client himself. The cosmetologist is responsible for what happens in the office. What can happen outside its walls is controlled solely by the person himself.
Author: bov-bov
Article design: Mila Friedan
Is it possible to visit a sauna after biorevitalization?
These substances nourish the skin, and hyaluronic acid effectively restores its water balance and activates the body’s production of its own hyaluronic acid, as well as elastin and collagen. In this case, the change and restoration of the skin structure occurs not only through the introduction of useful substances, but also through the activation of the skin’s own resources.
After a full course of biorevitalization procedures, the following changes occur in the skin:
- Wrinkles disappear;
- The relief of the face is smoothed;
- Improves complexion;
- The skin becomes more elastic.
The introduction of beneficial substances directly into the dermis improves metabolic processes.
This procedure is included in treatment programs:
- scars;
- stretch marks;
- hyperpigmentation;
- loss of turgor;
- anti-aging programs.
The first results can be seen on the skin after the 1st or 2nd procedure. In total, to improve the skin you will need to carry out from 4 to 6 sessions. Biorevitalization takes about 60 minutes. In this case, the procedures are done with a break of two weeks. And the effect of the course will last for 12-18 months.
Biorevitalization can be done at any time of the year. This procedure is carried out not only on the face, but also on the skin in the neck, décolleté and hands.
Side effects can occur both with the injection method and with the laser method, which is considered more gentle.
After biorevitalization, the following may appear on the skin:
- Edema;
- Bruises or bruises;
- Lumps and irregularities (due to uneven distribution of nutrients under the skin);
- Itching;
- Papules, which can increase by 1.5-2 times over time;
- Feeling of dry skin;
- Painful sensations.
All these side effects go away on their own within a few days (maximum 7).
The following side effects may occur in the following cases:
- If the technique of the procedure is violated (which may occur due to the inexperience or inattention of the specialist);
- If the patient fails to comply with the cosmetologist’s recommendations (the patient’s fault);
- Feature of the body.
How do Botox injections work?
Botox was first used by US doctors back in the 1970s. Then this procedure was of a slightly different nature. Injections were used exclusively on the recommendations of the attending physician.
The patients were people with real health problems. They treated strabismus, torticollis and other diseases with Botox. Only in the early 2000s did such injections begin to be used in cosmetology without the appointment of a specialist.
The injected drug can be called differently, the “working” names of the substance are:
- Botox.
- Dysport.
- Xeomin.
The basis of all is the substance butulinum toxin type A. Each manufacturer uses its own methods of cleansing the product and fillers. Hence the difference in the final composition of the substance used for the injection.
But, despite the differences, the basic principle of action remains the same: through an injection, the muscles are affected. Neuromuscular connections are blocked, causing them to stop contracting and remain at rest. As a result, facial wrinkles are completely smoothed out.
Is it possible to go to the steam room?
A unique and absolutely safe procedure that does not tolerate heat at all. The first and most important thing that a specialist should warn about: after Botox injections, it is strictly forbidden to heat the injection sites. High temperatures contribute to the dilation of blood vessels, which can lead to the penetration of the drug into the blood and neighboring tissues. You need to understand that botulinum is a poison, and exposure to warm air will cause a number of negative reactions.
Attention! For the first 5 days after administering the drug, it is prohibited to: take a hot bath, wash with warm water and dry your hair with a hairdryer.
Prohibitions before vaccination
2-3 days before the flu shot, you should not drink alcohol or eat too fatty foods. It is necessary to measure the temperature - if it is even slightly elevated, vaccination cannot be done.
It is advisable to get a good night's sleep and not to give your body too much physical activity the day before. Smoking is prohibited on the day of vaccination and immediately before it.
Features of visiting a bathhouse or sauna when taking medications
Article from the series Bath, sauna and health.
Taking certain medications may require you to change your regime for visiting a steam room in a bath or sauna, or to abandon bath procedures.
People taking medications that affect thermoregulation, sweating, cause dehydration (dehydration), increase body temperature or make it difficult to increase cardiac output should be used with caution when visiting the sauna:1
|
Visiting a sauna can be dangerous for people who use alcohol, beta blockade and nitrates.2 Taking sympathomimetics (for example, bronchodilators) can provoke tachycardia and arrhythmia due to heat stress in the sauna. Atropine, tricyclic antidepressants, phenothiazines (neuroleptics, antihistamines, antiarrhythmics) and other antihistamines have anticholinergic effects that disrupt thermoregulation processes and may predispose to heatstroke and fainting in the sauna.
3 Taking diuretics can lead to hypovolemia, hyperosmolarity and decreased sweating. Barbiturates and beta-blockers can also interfere with thermoregulatory mechanisms and reduce heat transfer.4 On the other hand, taking atenolol reduces the increase in heart rate and decrease in systolic blood pressure during sauna use in people with hypertension.
5 However, it is better to take prescribed antihypertensive drugs in advance of visiting the steam room, so as not to enhance the hypotensive effect of the bath on diastolic pressure. You can also use the calcium channel blocker diltiazem as an antihypertensive, which does not potentiate the hypotensive and vasodilatory effects of heat stress in the sauna.6
1 Kukkonen H, Kauppinen K. Health effects and risk of sauna bathing. Int J Circumpolar Health 2006; 65: 195-205
2 Nguyen Y, Naseer N, Frishman WH. Sauna as a therapeutic option for cardiovascular disease. Cardiol Rev. 2004;12:321–4.
3 Knochel JP, Goodman EL. Heat stroke and other forms of hypothermia. Chapter 34 in, Mackowiak P. Fever: Basic Mechanisms and Management. Second Edition. Philadelphia: Lippincott-Raven;1997, pages 437-458.
4 Lee-Chiong T, Stitt J. Disorders of temperature regulation. Comprehensive Therapy. 1995;21(12):697-704.
5 Luurila OJ, Kohvakka A, Sundberg S. Comparison of blood pressure response to heat stress in sauna in young hypertensive patients treated with atenolol and diltiazem. Am J Cardiol. 1989;64:97
6 Luurila OJ, Kohvakka A, Sundberg S. Comparison of blood pressure response to heat stress in sauna in young hypertensive patients treated with atenolol and diltiazem. Am J Cardiol 1989;64:97-99.
Attention! All articles are for informational purposes only and under no circumstances can be used as a guide for diagnosing and treating diseases independently, without the participation of a doctor. Articles may contain errors and inaccuracies and reflect the subjective opinion of the author. If you or someone close to you gets sick: please seek help from a doctor and do not self-medicate!
What medications should you not take?
Both in preparation for the procedure and after it, you should not abuse medications. Tablets can provoke unwanted reactions, the most harmless of which is the absence of any result after the injection.
The interaction of Botox with a certain group of drugs can cause the development of paralysis.
These include:
- antiarrhythmic drugs (quinidine alkaloid);
- antibiotics of the tetracycline group;
- succinylcholine;
- magnesium sulfate;
- antibiotics belonging to the group of lincosamides and polymyxins.
Intramuscular injections of vitamins B1 and B2 should also be avoided. After the procedure, the specialist must list a list of prohibited medications. You should pay attention to the list and if an urgent need arises, be sure to consult a doctor.