Dermatoscopy is an instrumental non-invasive study in which the doctor examines moles and other formations on the skin using a special device that creates multiple magnification. In oncology, dermatoscopy helps to distinguish harmless formations from skin cancer and identify melanoma in the early stages.
- Indications for dermatoscopy
- Why are moles dangerous?
- How is dermatoscopy performed?
- Equipment for dermatoscopy in the European Clinic
- Analysis of the received data
- Advantages of dermatoscopy using the FotoFinder system
- Prices for dermatoscopy at the European Clinic
Indications for dermatoscopy
- the appearance of any red, brown or black formation on the skin;
- injury to a mole; uneven change in color of the mole;
- an increase in the total number of moles and age spots;
- itching and tingling in the mole area;
- increase in size of the mole.
For preventive purposes, dermatoscopy is recommended:
- fair-skinned people with moles and age spots;
- with a family history of melanoma (if it was diagnosed in close relatives);
- people who have many moles and freckles on their body;
- when taking oral contraceptives for more than 1 year;
- when working in hazardous industries;
- with regular trips to hot countries;
- For dysplastic nevi, it is recommended to undergo dermatoscopy every six months to a year.
No special preparation is required for dermatoscopy. It is not recommended to use cosmetics or topical medications on the day of the examination. To obtain a clearer image, a small amount of gel is sometimes applied to the test site to reduce the reflection of light from the surface of the skin.
Modern digital dermatoscopes have many advantages over conventional ones. The device tube is connected to a computer monitor, on which the image is displayed. Digital dermatoscopy serves as a monitoring method for patients at high risk for developing melanoma. It also allows you to map moles over the entire surface of the body and observe their changes in dynamics, comparing the results with previous ones. The technique of digital dermatoscopy is simple, safe and fully automated. Within 3 minutes you can get a detailed analysis of all neoplasms.
It should be remembered that dermatoscopy does not allow a definitive diagnosis of melanoma to be made: this requires a biopsy and histological examination of a tissue sample.
Characteristics of the method
Dermatoscopy refers to instrumental methods for examining the skin of the human body.
For this purpose, a special device is used - a dermatoscope. This method is used by many doctors - cosmetologist, dermatologist and oncologist. Dermatoscopy is a modern diagnostic method. Before the development of the technique, histology was used to examine suspicious formations on the upper layer of the dermis. Partial excision of the nodule was carried out with further examination for the presence of malignant cells. This technique is quite painful for humans and is accompanied by certain risks of complications - it can provoke rapid growth and infection of the nevus.
A dermatoscope allows you to enlarge a suspicious area (enlarged nevus or inflammation) and study the structure of the neoplasm in detail. The non-invasive method is distinguished by accuracy and accessibility. Error in the study is excluded.
Diagnostics helps to identify:
- Enlarged nevus, papillomas with warts;
- Change in color of the neoplasm associated with cell degeneration;
- The structure changes density;
- Capillaries located nearby are injured, microbleeding occurs;
- The skin around the mole and other formations changes color and cracks appear.
The procedure is often prescribed for:
- Determining the results of treatment;
- Determining the correct method of excision of a dangerous formation;
- Establishing a course of treatment for the degeneration of a mole;
- Differentiation of diseases of the scalp;
- Diagnosis of nail plate pathology;
- Controlling the development of nevi.
The formation of nodules suspected of being malignant is studied by an oncodermatologist using a dermatoscope.
Why are moles dangerous?
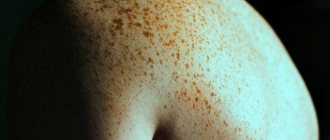
Moles (pigmented nevi) are benign neoplasms, but some of them can transform into an aggressive, dangerous malignant tumor - melanoma. Risks are increased in the following conditions:
- A large number of moles on the body.
- Dysplastic nevi are special moles that are large in size, uneven edges, and uneven in color.
- Congenital melanocytic nevi are moles that are present on a child’s body from birth. Usually children are born without moles - they appear throughout life. The most dangerous are giant congenital nevi with a diameter of more than 10 cm. They degenerate into melanoma with a probability of 30%.
Important to know: Scientific research shows that only 30% of melanomas develop from pre-existing pigmented nevi. In 70% of cases, a malignant tumor occurs on unchanged skin, where there were no moles.
How is dermatoscopy performed?
Classic dermatoscopy is carried out using a special instrument resembling a magnifying glass - a dermatoscope. With its help, the doctor examines the skin and assesses the size and appearance of the detected tumors.
A more modern technique, which is used in the European clinic, is videodermatoscopy using the German PhotoFinder device. The device takes pictures of the entire surface of the patient's skin, creates a “mole map” and stores the images in a computer. The procedure is absolutely painless.
Preparation for the procedure
The procedure does not require special preparation, as it does not pose any danger. So, how is dermatoscopy done:
- A special solution or gel is applied that increases the transparency of the skin and prevents glare from appearing in the image;
- The light of a halogen lamp is directed at an angle of 20 degrees onto the area of skin being examined;
- If a mole or other formation is not painful, a special glass is pressed onto it;
- A photograph of the surface of the formation is taken. The image is transferred to a digital medium, where the state of education is assessed using the above scale. This depends on the chosen dermoscopy method. When using modern equipment, the software provided in it itself issues a conclusion. But the final verdict is still given by the doctor;
- When the malignancy of the tumor is confirmed, the specialist carefully examines the tumor, takes pictures to study further dynamics, for comparison after subsequent treatment procedures.
Equipment for dermatoscopy in the European Clinic
The European clinic performs dermatoscopy using a modern PhotoFinder installation from the German company FotoFinder Systems GmbH. This manufacturer has been producing high-tech turnkey solutions for visualizing skin tumors and image analysis for more than 20 years. The device takes pictures of the entire surface of the body and loads them into a computer, where they are saved and processed by a special program.
Analysis of the received data
During dermatoscopy, a number of characteristics of formations found on the skin are assessed:
- Dimensions.
- Does the tumor rise above the skin?
- Shape, symmetry.
- State of boundaries: smooth/uneven, clear/blurred.
- Color, its uniformity.
- Character of the surface.
- The presence of ulcerations and other pathological changes.
In the PhotoFinder system, a computer program automatically analyzes images, thereby achieving greater diagnostic accuracy.
Advantages of dermatoscopy using the FotoFinder system
- The diagnostic accuracy is 99%.
- While a dermatologist using a conventional dermatoscope does not examine the entire surface of the skin and may miss pathological neoplasms in hard-to-reach places, the FotoFinder system provides the most complete scanning of the body surface.
- The ability to detect melanoma and other small skin tumors in the early stages.
- If videodermatoscopy is performed regularly, the doctor is able to assess the condition of the skin over time, and this further increases the accuracy of diagnosis.
- The system can automatically analyze images.
- The study is completely safe, painless, and has virtually no contraindications.
Dear friends!
If you have single neoplasms:
1. Dermatoscopy.
It is a modern, fast, non-invasive research method, which is carried out using a special optical device - a dermatoscope.
The principle of the method: the technique of epiluminescent microscopy is used - a magnification system, a source of unpolarized light and a transparent lens that is in direct contact with the skin, previously coated with a transparent gel.
The image is magnified 10-20 times, which allows you to study in detail the structure of the formation, as well as deeper layers of the skin than is possible when viewed with the naked eye. The doctor examines the surface of the skin and mucous membranes using a dermatoscope, identifying all suspicious formations
This procedure is performed by a dermatologist during a daily appointment; it is a common procedure. Residents of the Nevsky district can make an appointment in the “Inspection of neoplasms” section. Residents of other areas or if there is no time to wait, examination is possible for a fee - 700 rubles.
2. Photodermatoscopy.
When examining a neoplasm with a dermatoscope, there may be doubts about its benignity. The changes may be so minimal or a variation of the norm that they are not sufficient grounds for immediate removal. In this case, photographic recording of images with subsequent observation is necessary.
Unlike classical photodermatoscopy, digital photodermatoscopy provides the ability to photograph and save a dermoscopic image of skin formations in a database.
This solution allows you to most objectively monitor the dynamics of formations, evaluate the effectiveness of treatment and make a timely decision on removal if signs of malignancy (malignant degeneration) appear.
The examination is carried out using the latest equipment using polarization and cross-polarization technology.
Residents of the Nevsky district are registered for this examination by dermatologists, since this procedure is not required for every patient. For residents of other areas, examination is possible for a fee - 1,700 rubles.
For multiple neoplasms:
It is recommended to make a map of neoplasms of the human body (videodermatoscopy FotoFinder dermoscope).
Typically, it is not necessary to remove all lesions, but each one should be monitored for early signs of malignancy. The system allows you to mark all formations on macro photographs and link them with dermoscopic images. All images are stored in a database for comparison with subsequent images during regular examinations.
This strategy helps avoid unnecessary surgical procedures and allows the patient to feel more secure.
Residents of the Nevsky district are registered for this examination by dermatologists, since this examination is extensive and not required for every patient. For residents of other areas, examination is possible for a fee - 3,000 rubles.
The office of fluorescent diagnostics, photodynamic therapy and dermatoscopy is a unit of routine oncological care. During the year, on average, more than 350 sessions of photodynamic therapy with domestic photosensitizers are carried out in the office, and more than 1000 dermoscopic examinations are performed.
The method of fluorescent diagnosis of malignant tumors makes it possible to diagnose malignant tumors of the skin and internal hollow organs in the early stages of development, which makes it possible to cure in most clinical cases using methods of organ-preserving and functionally sparing treatment without removing the affected organ. This examination method is based on determining differences in the intensity and spectral composition of the intrinsic fluorescence of healthy and tumor tissue, the ability of a number of drugs (photosensitizers) to selectively accumulate in the tissue of a malignant neoplasm and the possibility of their detection by characteristic fluorescence (glow). During a fluorescent diagnostic session, a thorough examination of the examined organ or skin is carried out using special fluorescent equipment (fluorescent endoscopes and telescopes) in order to search for and detect pathological foci.
Photodynamic therapy using domestic photosensitizers is carried out for primary, recurrent and metastatic malignant tumors of the skin, soft tissues, gastrointestinal tract, lung, bladder, vulva, cervix, larynx, oropharyngeal zone. Photodynamic therapy is used as an independent treatment method or in combination with surgery, radiation or chemotherapy. Sessions of intraoperative photodynamic therapy are also conducted. The method is based on the ability of a number of drugs (photosensitizers) to selectively accumulate in the cells of a malignant neoplasm and cause tumor destruction when irradiated with laser light of a certain wavelength.
Dermatoscopy is the study of a pigmented skin tumor with a magnification of up to x10, using the effect of epiluminescence when creating an oil environment between the object of study and the dermatoscope. Dermatoscopy is a new, promising non-invasive method for diagnosing skin melanoma, which can increase the frequency of detection of early forms and significantly reduce the number of cases of unjustified surgical removal of benign pigmented neoplasms.
The office’s specialists remove moles (“nevi” - pigmented skin formations).
The office is equipped with diagnostic equipment that meets international standards:
- Laser installation for PDT – LFT 630-01 “Biospec”
- Laser installation for PDT – LFT 675-01 “Biospec”
- LED video fluorescent device “UFF-675-01 Biospek”, “UFF-630-01 Biospek”
- Endoscopic stand “D-light AF system” with attachment for photodynamic diagnostics
- Fluorescent bronchofiberscope
- Endoscopic stand EVIS EXERA II “OLYMPUS”
- Videogastroscope “OLYMPUS 1TQ160”
- Video bronchoscope “OLYMPUS BF-1T180”
- Laser installation Medilas Fibertom 8100,
- Modern dermatoscope DELTA 20 from HEINE, digital SLR camera Canon EOS, photo adapter HEINE DELTA 20/Canon
Types of Dermatoscopes
A dermatoscope consists of a magnifying lens and a light source to improve the visibility of subsurface structures of the skin. There are different types of dermatoscopes:
Digital and analogue dermatoscopes
Analog dermatoscopes
Analog dermoscopy is also called epiluminescence microscopy (ELM). When using an analog dermatoscope, dermatologists look through a magnifying lens to analyze skin lesions in detail. An analog dermatoscope can be combined with a digital camera or smartphone for clinical imaging and monitoring of lesions over time.
Digital dermatoscopes
On the other hand, in digital epiluminescence microscopy (DELM), or videodermoscopy, dermatologists use a digital dermatoscope that comes with a built-in camera. This means that the dermatologist does not look through a magnifying lens to analyze the disease, but at the screen of a digital camera.
Using digital dermatoscopes, dermatologists can take dermoscopic images of skin lesions during patient examinations. Some digital dermatoscopes also allow you to take close-up photographs and/or clinical reviews without the need for an external camera.
Smartphone-based dermatoscopes
Dermatoscopes connected to a smartphone are becoming increasingly used. These devices consist of a smartphone combined with special additional lenses and lights through which skin lesions can be observed. High-end smartphones can produce high-quality images. However, medical imaging requires extremely high imaging standards, as well as other conditions regarding medical compliance, sanitation, and safety.
Polarized and non-polarized dermatoscopes
Non-polarized dermatoscopes
When using a non-polarized dermatoscope, dermatologists must use a coupling fluid, such as a gel or oil, to suppress reflections from the skin surface when the lens makes contact with the skin. This means that the device must be cleaned and disinfected after each use, making it less convenient. However, some superficial structures of the skin can only be seen with a non-polarized dermatoscope.
Polarized dermatoscopes
Polarized devices use polarized light with or without a coupling fluid to more accurately visualize subsurface structures located in the dermal or dermal-epidermal layer. Polarized dermatoscopes can be used in both contact and non-contact modes. Polarized light can be multi-spectral or white. This is an important distinction because with multispectral illumination, dermatologists can visualize the different chromophores in the superficial layer of skin that determine skin color (melanin, hemoglobin, etc.). Spectral imaging thus allows the extraction of additional information that the human eye cannot see. This technique is based on the specific optical absorption properties of these pigments in the skin. Red light, for example, penetrates deeper into the skin, while blue light is better for viewing superficial structures.