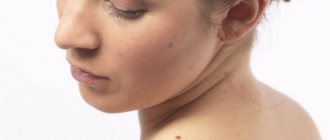
Every person, adult and child, has moles of different sizes and colors on their body. For some, pink moles are a particular concern. There is no need to worry about this, since such formations are the safest and are always benign in nature. They appear especially often on the child’s body and suggest a vascular origin. Sometimes pink moles appear from birth and remain for life, but in some cases such a nevus is temporary in nature and goes away on its own after a while.
Initially, the pink color of a mole is not a cause for alarm unless there is a change in its color, structure or size.
general information
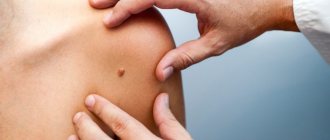
A pink mole is a benign neoplasm that does not exhibit any symptoms and does not cause any discomfort. In most cases, pink nevi appear in childhood, but they can also occur in adults. These are vascular formations that do not affect the work and functions of the body. A mole on pink skin can be convex or flat. If the formation is convex or hanging, then you should be more careful about such a nevus, since cases of injury are not uncommon. Pink nevi range in size from a couple of millimeters to several centimeters.
Like all moles, pink nevi have a minimal chance of degenerating from benign to malignant.
Causes and risk factors for degeneration
The development of melanoma from an ordinary nevus can occur either spontaneously, for no apparent reason, or under the influence of certain factors, namely:
- Mole injuries;
- Ultraviolet irradiation;
- Damage by microorganisms ( bacterial or fungal skin diseases ).
In addition to direct damage to the mole, using one of the listed methods, there is a hereditary predisposition. According to various data, 25–70% of people with skin cancer suffered from a similar disease in one of their first-degree relatives.
The main causes of pink moles on the skin
A pink mole on the face or anywhere else on the body appears when the function of capillaries and vessels, the main task of which is to supply blood to the skin, is impaired. This nevus includes many microscopic vessels. In adults, the appearance of pink moles is influenced by prolonged exposure to the sun on the skin. If the formation is pink in color and appears in old age and has a convex structure, then you need to see a doctor, as this may indicate a malignant nature.
Nevi of this type can form on different layers of the skin, and are also common in the capillary, arterial or venous circulatory systems. The following main reasons for education are identified:
- hormonal imbalance in the body;
- abnormalities in the gastrointestinal tract;
- increased functional functioning of blood vessels;
- disturbances in the functioning of pigment cells.
Moles can appear, disappear, or be on the body from birth.
Pathogenesis
In medicine, nevi of this type are called angiomas, which do not require special control. In children, a pink mole has a special pathogenesis: a nevus can appear and disappear on its own, without being affected by any external factors. First, a small tumor appears, pink or red in color. Over time, it may change shape and size, or it may not change at all. If a mole is constantly changing, growing or changing the structure of the formation, you should see a doctor, since such changes may indicate complications.
Reasons for asymmetry
Melanocytes are cells containing a special pigment, melanin, which is responsible for the color of the skin. When they accumulate, a birthmark is formed. Under the influence of a number of factors, the DNA structure of pigment cells is disrupted and mutations occur. Healthy melanocytes are degenerated. Atypical cells continue to grow and multiply progressively. The skin around the tumor begins to turn red and become inflamed. A malignant form of skin cancer – melanoma – is formed. Approximately 75% of patients with an established diagnosis die. Treatment is effective only with early diagnosis of the formation. There are the following risk factors for atypical degeneration:
- Skin phototypes I and II (persons with fair skin);
- sunburn. WHO has equated ultraviolet radiation to obligate carcinogens along with arsenic, asbestos, and smoking;
- Excessive ultraviolet radiation in solariums. According to experts, one session of artificial tanning is equivalent to a whole day of exposure to the open sun on the beach. In Europe and the USA, children under 18 years of age are prohibited from visiting a solarium;
- genetic predisposition. It has been proven that the risk of developing melanoma increases by 15% if close relatives have a similar diagnosis;
- the presence on the body of pigment spots from the cancer risk group (nevus of Ota, blue nevus, giant nevus, borderline nevus);
- injury;
- endocrine disorders;
- harmful production factors (electromagnetic radiation, chemicals).
Features of a child
Moles in children can appear and disappear in the first couple of years of life.
A mole of this type in a child is not uncommon. This is due to congenital pigmentation in the body. Children's moles are divided into hemangiomas, port-wine stains and pigmented formations at the base of the skull. In the latter case, pigmentation does not require any treatment and goes away on its own within 2 years. Hemangioma is a benign formation, the presence of which indicates an abnormal position of the blood vessel. This nevus is bright pink or red in color.
Hemangiomas appear in the first days after birth and can disappear on their own by the age of 3.
Port-wine stains or flaming nevi appear when the blood vessels on the head or face dilate. Such formations do not disappear and remain the same color as they were originally. In this case, the nevus grows with the child. It is recommended to consult a dermatologist as soon as possible and treat the formation so that a significant cosmetic defect does not arise in the future.
Are light moles dangerous and what symptoms to look out for?
Light ones do not pose a danger to the human body; normally they are benign formations, regular in shape, small point size (often do not exceed 0.1 - 0.5 mm).
Light moles increase the risk of malignant degeneration under the influence of unfavorable triggers, pay attention to atypical symptoms:
- rapid change of color with a tendency to darkening, heterogeneous inclusions (red dot on a white nevus);
- the appearance of a red rim around the mole;
- addition of bleeding, serous discharge, pus (layering of secondary infection);
- uneven torn edge, change in shape, asymmetry;
- the appearance of peeling, cracks on the surface, pain when pressed, itching.
Possible complications
If the formation does not change and does not show any signs, then complications do not threaten. A nevus becomes dangerous when its asymmetry is observed, it acquires a heterogeneous color, and its size increases (more than 6 mm). A pink mole can be dangerous if it is damaged. There is a high probability of its degeneration into melanoma (malignant tumor), which has the following features:
| Risks of occurrence | Features of manifestation | Treatment and prevention |
|
|
|
Classification of convex growths
Convex moles can appear on any part of the body, but are most often localized on the face, eyelids, neck, back and décolleté. Neoplasms bring discomfort, so patients seek help from a specialist.
Some moles are removed to correct imperfections, and some are removed because of health risks. It all depends on the type of growth:
- Fibroepithelial - neoplasms have clear boundaries and a round shape, light brown or pinkish in color. A large number of such growths carries a serious risk of both the development of cancerous tumors and disruption of liver function.
- Mixed and intraepidermal - they rise slightly above the surface of the skin, have a dark color and sharp outlines. Despite the fact that moles are flat, the danger lies in their degeneration. If the growth becomes bulging, you should consult a doctor.
- Papillomatous - differ depending on the number: single moles have a filamentous shape, and multiple moles have a warty shape. Most often they appear in mature women and are flesh-colored or light brown.
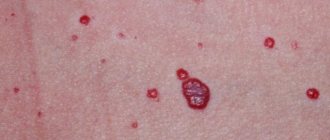
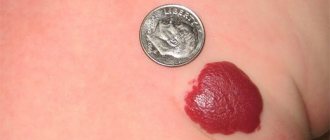
- Hemangiomas are benign growths of blood vessels that are red, burgundy or purple in color. Injuring them can lead to bleeding, so this type of growth poses a great danger. Hemangiomas usually appear in children and grow until the age of 6 years.
- Red growth - appears in adults and affects large areas of the body. Its appearance is associated with pathologies of internal organs. Among them are: problems with the liver, pancreas, gastrointestinal tract, cardiovascular system;
- weak immune system;
- cancerous tumors;
- hormonal disorders.
Dangerous moles
Some moles pose a serious danger to humans, including:
- blue growths - reach 10 mm in diameter. They can appear in infancy or during the period of hormonal changes in the body. Mechanical trauma or incomplete removal can lead to degeneration of the tumor.
- borderline - it can be considered in childhood. During adulthood, the size reaches 8-15 mm and even more. The color of the growth darkens as it approaches the center. Locations include the back, chest, arms and feet.
- giant - a congenital neoplasm of gray or brown color. The size can reach 20 mm or more. The cause may be hormonal imbalances and infections.
Moles of this type most often form on the back, face and neck. They may cause discomfort or injury from clothing. Therefore, to avoid serious consequences, they should be removed.
Harmless moles
Most moles do not pose a serious danger to humans.
- Fibroepithelial - they are light in color and reach no more than 1-2 cm in size. Such growths are removed for aesthetic reasons.
- Intradermal - formations resemble a dark wart. Their size varies from 2 mm to several centimeters.
- Angiomas are neoplasms consisting of damaged blood vessels. They grow mainly on the back or face. Rising above the skin, they cause aesthetic discomfort, so they are removed.
Pigmented nevus, which has a dark color and a discolored halo around it, does not pose a serious danger. It usually appears in children, but there are cases of formation in adults. The cause is a severe skin burn.
Halonevus (Setton's nevus)
Diagnostics
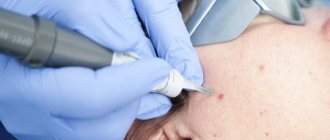
Patients who have formations on the chest, face or other parts of the body require at least one examination by a dermatologist. The specialist must assess the condition of the neoplasms and find out their nature. It is especially necessary to examine people who often stay in solariums or hot countries, as well as those who have been treated with ultraviolet radiation. If the doctor has concerns about some kind of nevus, then a comprehensive diagnosis is prescribed. First of all, such a formation is removed and then sent for histological examination to determine its nature.
Instrumental examination
If a malignant formation is suspected, a biopsy and histological examination of the nevus is performed. Instrumental diagnostics includes such a modern research method as computer dermatoscopy. Thus, specialists are able to study changes occurring on the surface and in deep layers. Only after computer dermatoscopy is therapy or surgical removal prescribed.
Signs of colorless moles that need to be seen by a doctor
A benign flesh-colored mole does not often change into a threatening shape. Oncology can begin due to excessive production of melanocyte cells. The most common negative consequence is melanoma.
Serious signs of colorless neoplasms that require special attention include:
- the appearance of a white halo;
- if a small birthmark grows;
- presence of plaque on the surface;
- there was pain when touched;
- began to bleed;
- the presence of white inclusions;
- the mole has become discolored;
- It started to get dark.
If the corresponding symptoms are present, you should immediately consult a doctor. A specialist will carefully examine and find out how the colorless growth began to appear. A dermoscopic analysis is required, which shows whether the pigmented formation needs to be eliminated or not.
You should contact a dermatologist or surgeon if you develop new colorless birthmarks, as well as when modifying existing ones. Modern equipment allows you to track the dynamics of the development of a mole and measure the level of pigment. The specialist will determine the nature of the tumor and, if necessary, prescribe therapy.
A person who is at risk needs to be careful on the beach and avoid mechanical injuries.
Treatment methods
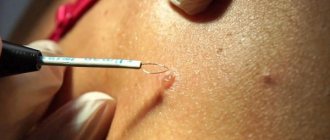
Surgical removal
Surgical removal involves the following basic methods:
- Cauterization, which is used extremely rarely because it is not particularly effective. This is explained by the fact that most of the nevus is located in deep layers, and the cauterization method affects only the top layer. With such removal, there is a high probability of a new mole appearing.
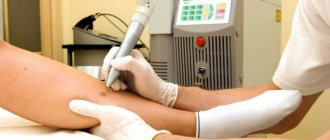
- Laser removal is an effective method for pink mole removal.
- Infrared or light coagulation is also used.
It is easier and faster to remove flat moles. When removing a dangerous or unwanted formation, various anesthetic creams are used, since the procedure is not particularly pleasant. Depending on the size and type of lesion, removal may leave a small red spot that will go away over time. In the first month after removal, it is not recommended to visit a solarium or be in the open sun.
Traditional therapy
If the formation is small in size and benign, then you can try to remove it using folk remedies. Since such therapy can be harmful, you should consult a specialist before using it. Common folk methods for getting rid of pink moles:
- Using vinegar to smear the nevus before bed.
- Mix garlic, vinegar and honey, apply the resulting mixture to the mole and leave for 4 hours. The treatment lasts a month, and the procedure is carried out every day.
- Celandine juice, which is applied to the damaged area of the skin 2 times a day, is considered effective.
- An ointment consisting of dandelion roots and butter. The medicine is applied to the pink mole three times a day.
- To remove a raised nevus, use pineapple juice.
What types of moles are there?
One person may discover very different tumors. Types of moles are classified according to several criteria. This helps in correct diagnosis in case of changes. They differ in:
- origin – congenital, newly acquired;
- structure – pigmented, vascular;
- place of formation - in depth, on the surface, in the boundary layer;
- raised above the skin - flat - even, protruding as a hemisphere, pedunculated, larger birthmarks;
- potential threats - dangerous, degenerating into melanoma, non-dangerous.
Prevention and prognosis
It is extremely rare for a pink mole to degenerate into a malignant tumor. If modifications or active growth of the formation are noticed, you should consult a doctor and undergo diagnostics. To prevent such formations and their degeneration into malignant tumors, preventive measures should be followed. It is not recommended to stay in the sun for a long time and visit solariums. If you cannot avoid exposure to ultraviolet rays, then you should cover exposed areas of your body and wear a hat.
Consequences of surgical removal
The most unpleasant consequence of this type of treatment is the postoperative scar. The main thing is that the surgeon makes it less noticeable. It is possible to form a keloid scar, which is a connective tissue tumor. It is formed when a suture is placed on a large wound.
A relapse is also possible if the mole was not completely removed, or serious violations of its technique were made during the operation.
After the operation, consequences such as itching, redness of the skin, and slight discomfort may also be observed. Usually these symptoms go away quickly, otherwise it is better to consult a specialist.
Did you know that papillomas, warts and moles can be caused by parasites in the body?
According to the latest WHO data, it is the numerous parasites that live in the human body that are the cause of almost all fatal human diseases, including the formation of cancerous tumors.
Statistics tell us that every 9 people get cancer with similar rashes:
- Papillomas..
- Unusual moles.
- Warts.
- Pimples.
- Unknown spots.
- Redness for no reason...
All this is possible due to weakened immunity, due to the fact that parasites have appeared in the body!
.
But there is a medicine, and medicine is in no hurry to advertise the CORRECT methods of treatment, since it is not profitable for them. This is what the girl who coped with this illness says
Watch before the site is blocked. Find out here >>>
Video
There are several main types of raised moles, which can vary in size, structure, and etiological factors. Most often, formations of this kind are localized in the back and neck, but other options are quite possible. The main types of raised moles are:
- Papillomatous growths. They are thread-like formations, most often localized in the area of the eyelids and neck. They can have different shades from pink to brown.
- Intraepidermal. They have a high risk of malignant transformation. Such growths have a dark color and a rough surface. At the initial stages of appearance, moles are not convex; their increase is a sign of cell transformation. Such a convex mole appears especially often on the back.
- Fibroepithelial. They have a shade similar to the color of the skin, and are also significant in size. More often, such formations appear as a result of the development of liver pathologies.
- Hemangiomas. They have a pronounced red color and are the result of the proliferation of small blood vessels.
Especially often, large convex moles appear due to the development of diseases of the digestive tract, liver, as well as hormonal imbalances.
Here's what a simple girl who solved this problem says: Even pretty moles are dangerous: yes, my dears, it's a virus. More than 80% of the population is infected with it, not to mention warts and papillomas, the first thing you need to do is this. Read more.
How quickly does melanoma develop from a mole?
The transformation of a nevus into a cancerous formation can occur in different ways. The process depends on the stage of the disease and the type of tumor. Instant metastases are dangerous. Begins:
- growth of cancer (oncological) cells in the deep layers of the epidermis;
- their entry into the blood and lymph;
- penetration into the lungs, liver, kidneys;
- growth in these organs;
- complete damage to the body;
- death.
The growth phases of pigment cells are observed, along which melanoma develops from a mole. There are varieties:
- horizontal - damage to the upper layers of the skin occurs, lasting up to 10 years, but metastases do not appear;
- vertical – accompanied by the spread of cancer cells throughout the organs, can last two years, has an unfavorable prognosis;
- nodular - especially dangerous - characterized by deep spread within two months.
The first signs of melanoma
The patient can be assisted only when suspicious changes begin to be identified. The diagnosis, research, and referral for surgical treatment save a person’s life. The first signs of melanoma:
- increase in the height of the tumor;
- bleeding;
- the appearance of discharge;
- redness;
- burning, itching;
- swelling of tissues;
- softening of the nevus;
- the appearance of a crust;
- thickening;
- hair loss;
- expansion of pigmentation around the lesion.
With the further development of dangerous melanoma, the following are observed:
- significant change in size;
- the appearance of pain;
- enlarged lymph nodes;
- surface ulceration;
- formation of new foci;
- bleeding from places of pigmentation;
- liquid separation;
- skin thickening;
- the appearance of an earthy tint;
- signs of metastases are chronic cough, weight loss, cramps, headaches.
Is color change dangerous?
Nevi come in various shapes - flat or convex. Pink spots vary in size - from a small spot to a dark red spot located on the entire arm. Capillary formations become pale if you press on them. You can see a red dot in the center of the growth, from which a vascular network extends. The surface of the mole is rough or smooth.
A mole may turn red due to regular injury, frequent visits to the solarium, or diagnosis of diseases of the internal organs. An altered mole causes discomfort and pain. If the color of the nevus has changed, it is not recommended to treat or remove the formation yourself. This increases the risk of infection, the development of an inflammatory process with further transformation of the spot into a malignant tumor. Consultation with a dermatologist or oncologist is necessary.
If symptoms begin that indicate degeneration or inflammation of the spot, the spot should be examined. These symptoms include:
- Disappearance of symmetry.
- The formation itches, itches, and hurts when pressed.
- The size of the nevus has changed (it has become more than seven millimeters).
- The color changed to dark red or black.
- The hairs that were previously on the mole and indicate good quality have fallen out.
- The surface of the growth peels off.
- The occurrence of bleeding or clear fluid from the nevus.
- A compaction has appeared.
The above signs are a dangerous sign that requires an immediate visit to a dermatologist. When examined by a doctor, it will be determined whether the cause is cancer cells or external factors (sun, household chemicals, injuries). A changed shade may indicate the acquisition of a permanent color or the development of cancer.