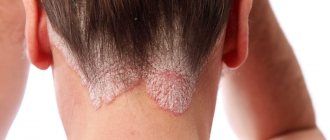
If your head of beautiful hair gradually begins to lose its shine and fall out, and your skin is unbearably itchy and flaky, you should pay special attention to it. There is a possibility of developing a fungal infection on the scalp. The causative agents of this disease are various types of fungus. The disease brings a lot of unpleasant sensations and threatens with dangerous consequences. But do not despair, modern medicine can cope with this disease.
Causes of fungus on the head
The occurrence of a fungal infection on the head can be caused by various reasons.
Mycosis of the skin is provoked by:
- contact with an infected person or animal;
- failure in the body's hormonal system;
- nutritional disorders that contribute to a decrease in the amount of vitamins and proteins - if there is a lack of them in the body, fungi develop very quickly;
- failure of the endocrine system;
- cancer;
- increased sweating;
- blood diseases.
External factors can also trigger the appearance of fungus on the head:
- overheating and dehydration of the body;
- bad ecology;
- failure to comply with basic rules of personal hygiene;
- abuse of ultraviolet radiation;
- frequent stress and depression.
What causes hair loss
The skin, like any human organ, is exposed to internal and external factors throughout life. It requires a normal supply of nutrients and protection from bacterial and fungal infections.
If your hair looks bad, it often falls out or even in clumps, your scalp is flaky, there may be an infection and treatment is needed.
The cause may not only be an infection. Sometimes hair loss is caused by hormonal imbalance, parasites, perm or coloring.
The main diseases of the scalp and hair that occur due to fungal infection:
- seborrheic dermatitis caused by the yeast Malassezia;
- lichen;
- white and black piedra (tricosporia);
- sporotrichosis;
- dermatomycosis.
The appearance of rashes on the scalp may be associated with exposure to external factors. A lesion such as eczema, a bacterial infection, is accompanied by the appearance of ulcers and requires complex treatment.
Classification of fungal infections and their symptoms
Mycoses (skin lesions) are divided into three groups:
- Trichophytosis (ringworm).
- Microsporia.
- Favus (Scab).
Trichophytosis
Belongs to a group of serious diseases caused by the fungus Trichophyton. A patient with this disease is at risk of extensive hair loss with the formation of large bald patches. Such a patient is very contagious, and upon contact with him, the likelihood of infection is very high.
Superficial form of trichophytosis
Ringworm has three forms of development: superficial, chronic and infiltrative-suppurative (deep).
- The superficial form of trichophytosis is expressed by the manifestation of symptoms on the 5-8th day of infection. Spots no larger than 2 cm in size are visible on the scalp. The hair in these places begins to thin and the lesions become covered with a gray crust. The affected areas cause severe itching, and when scratched, red sores appear. Over time, redness and swelling increase, ulcers and crusts appear. In focal areas, hair changes its color, shine and elasticity.
- Chronic trichophytosis develops in an unnoticeable form for the patient. It begins mainly on the head, from where the inflammation spreads to the smooth skin. Chronic trichophytosis is localized on the temples and back of the head in the form of small, fuzzy, scaly spots. Basically, it is a consequence of untreated superficial trichophytosis. Chronic trichophytosis is usually called “black dot”, since black dots can be one of the distinctive signs of the disease.
- Infiltrative-suppurative (deep) form of ringworm. The manifestation of the disease begins with small spots of a pinkish tint, along the edges of which there are clearly defined boundaries. Over time, the affected areas of the skin increase in size and rise significantly above the skin level, and a strong inflammatory process begins. When connected to each other, the spots form figures of unusual shape, covered with ulcers and flaky crusts. The hairs begin to partially fall out. A characteristic feature of this form is inflamed hair follicles filled with pus, which, when pressed, release copious fluid. With inflammation, the lymph nodes become enlarged, and malaise is noted, accompanied by fever and headache.
Infiltrative suppurative form of ringworm
Microsporia
The second group of varieties of mycosis. Most often, this disease occurs in children, so all family members are at risk. Microsporia leads among fungal infections in terms of speed of spread. The symptoms of microsporia are similar to other infectious diseases of the head, so the type of fungal disease can be recognized only after examination.
Symptoms of microsporia include:
- The affected areas are concentrated mainly on the crown, temporal and parietal parts of the head.
- Foci of microsporia are approximately 2 to 6 cm in size, round in shape and clearly defined.
- At the beginning of inflammation, the fungus is located at the root of the hair follicle. As the disease progresses, you can see a white ring surrounding the hair in the form of a cuff.
- After a week, the fungus spreads throughout the hair, causing it to become brittle.
- Stumps remain in this place, which, when stroked, tilt to one side.
With advanced microsporia, lesions appear on the head in the form of tumors with red edges.
Favus Scab
Favus
The third group of fungus is on the head. A characteristic feature of Scab is the presence of crusts on the head, within which hair can grow. If treatment is not started in time, the fungus quickly spreads throughout the entire scalp. After the disease, the skin atrophies, and complete baldness occurs in those places where the inflammatory process lasted for a long time. Patients with Scab are constantly bothered by itching, heaviness due to the accumulation of keratinized crusts and unpleasant sensations from hair sticking together.
Major diseases of the hair and scalp. Their treatment
Dandruff (Seborrhea)
Dandruff is by far the most common disease
A scalp disease that is accompanied by dandruff is called seborrheic dermatitis. In most cases, it occurs due to disruption of the sebaceous glands. There are two types of seborrhea of the scalp: oily and dry. With oily seborrheic dermatitis, yellowish sebaceous scales are present on the surface; they stick to the skin and hair and cannot be shaken off. Dry dandruff is white, easily separates from the skin and falls off. White scatterings are especially noticeable on dark clothes.
Dandruff treatment
- The use of medicinal shampoos (Keto plus, Nizoral, Perhotal, Friederm zinc).
- Following a diet, limiting sweets, fatty, flour, salty, fried foods.
- Sulsena paste. Quickly eliminates itching of the scalp, eliminates dandruff and normalizes the functioning of the sebaceous glands.
- Tar soap. A proven folk remedy.
- Cryomassage with liquid nitrogen or darsonvalization. Salon procedures.
- The use of folk remedies, herbal infusions and masks is also an effective treatment for dandruff on the scalp.
Hair loss (Alopecia)
Alopecia is one of the most serious diseases, especially hard for women.
At this time, in addition to treatment, psychological support is needed. One of the most serious problems is baldness. The concept of Alopecia is quite capacious and under it all diseases that cause hair loss are combined. They differ in the cause of origin, the course of the disease, the rate of loss of vegetation, the localization of bald spots and bald patches. Alopecia can be androgenic, seborrheic, diffuse, focal. There is also a distinction between scarring and non-scarring baldness. There are forms that can be treated, but in some cases only hair transplantation can get rid of the problem. Treatment for baldness is always long-term and the sooner it is started, the more hair you can save. When treating Alopecia in women, psychological support is very important.
Treatment of alopecia
- Eliminating the cause of hair loss.
- The use of agents that stimulate the awakening and functioning of follicles.
- Taking vitamins, strengthening the body.
- Head massage.
Psoriasis (scaly lichen)
A disease of the scalp and body, representing several types of scaly lichens. Formations can be in the form of large spots or a scattering of small plaques. In most cases, psoriasis on the scalp is the beginning of the spread of the disease throughout the body. 85% of sick people most often have a simple form of psoriasis, which sometimes develops against the background of untreated seborrhea. In the remaining 15% of patients, a complicated form of the disease that affects the entire head and body is called pustular psoriasis. Photo of scalp disease (common psoriasis):
Treatment of psoriasis is always complex
- Detoxification of the body using sorbents.
- Taking antihistamines.
- Ultraviolet radiation.
- The use of medicated shampoos and tar soap.
- Applying medicinal ointments, for example, salicylic 2%.
- Cryotherapy. Exposure to cold causes the death of pathogenic cells.
Pediculosis (Lice)
Pediculosis (Lice) is the most unpleasant disease.
During this time, the patient should have minimal contact with others, especially children. Pediculosis is caused by blood-sucking parasites - lice. Not a single person is safe from it. The main symptom is severe itching and scratching of the scalp, which can lead to various rashes and boils. Blood-sucking lice lay eggs - nits, which complicate treatment and require repeated treatment. As a result of head lice, a person often suffers from insomnia and loss of appetite. Long-term illness leads to deterioration of the general condition and exhaustion of the body.
Treatment of pediculosis
It involves exterminating lice. Previously, folk remedies were used for this: kerosene, vinegar, oil. Today you can buy drugs that are sold in pharmacies: shampoos, sprays and creams. Not so long ago, to get rid of lice it was necessary to cut or even shave off the hair; modern means for etching do not require such radical measures. The only point you need to remember is nits. They lead to the reappearance of lice, so you need to carry out the etching several times until it is completely cured.
Favus (Scab)
A disease of fungal origin. It is characterized by the presence of dry yellow crusts on the scalp. They are thick at the edges and sink toward the center. In the middle there are emerging hairs. Scab is accompanied by an unpleasant odor from the crusts and itching. When trying to separate the plaques, the skin is injured and the wounds bleed. Hair becomes dull, brittle and easily torn out. Favus is transmitted through contact with a sick person or using his personal belongings. Pets and birds can also get scab. Treatment of the scalp with favus is carried out in a hospital setting, depending on the severity, it can take 2-3 months.
Scab treatment
- Antibacterial therapy.
- Use of antifungal drugs.
- Taking vitamins and immunomodulators.
- The hair is cut, the crusts are softened with oils and removed.
- The affected areas are lubricated with iodine and sulfur-salicylic ointment.
Furunculosis of the scalp
Inflammatory disease of the hair follicles. Most often caused by staphylococcus. Entering the scalp through damage, the microorganism develops and inflames the hair follicle and nearby sebaceous glands. Inflamed bumps form, inside which pus accumulates. When the boil matures and ruptures, its contents spread over the skin and cause numerous rashes.
Treatment of furunculosis
- The patient is prescribed a course of antibiotics.
- If the boil does not open on its own, then this is done surgically.
- An unopened abscess is not treated externally; it can only stimulate the acceleration of maturation.
- Hair is removed around the formation and the wound is regularly treated with bactericidal and anti-inflammatory ointments.
Early graying of hair
The “friends” of premature graying are stress and poor ecology
Hair turns gray when it loses pigment. Recently, this is happening much earlier and in 70% of people the first signs appear at the age of 35. Moreover, it has been noticed that brunettes turn gray earlier than blondes. In 2% of people, graying begins at age 25. What causes early graying? Scientists have concluded that unfavorable environmental conditions, stress, overwork, iron deficiency anemia and insufficient intake of vitamins have an effect. It is impossible to cure early gray hair, but at the first signs of it, you can slow down the process.
Treatment of early gray hair
- Taking vitamins, iron supplements, monitoring hemoglobin levels in the blood.
- Rejection of bad habits.
- Taking sedatives, avoiding stress.
- Get proper rest, sleep at least 8 hours a day.
Differential diagnosis of fungus on the head
After the initial examination of the patient, the attending physician determines the degree of damage to the scalp. The most effective way to ensure correct results is to scrape the scalp to check for fungal infection. However, there may be some obstacles to making an accurate diagnosis.
The method of differential diagnosis is necessary in order to exclude diseases that are not suitable for some symptoms or signs and to find the only possible disease.
Head fungus should be distinguished from the following pathologies:
- Alopecia areata is a disease characterized by hair loss and the formation of round bald patches of varying sizes on the skin. With complications, it can be total and spread throughout the body. At the initial stage, the blood vessels supplying the hair follicles close due to the proliferation of tissue, most often connective tissue. The hair growth cycle is disrupted and the hair shafts break off. The localization of areas of skin not covered with hairs depends on the form of alopecia: in some cases, only the area of the back of the head and temples can go bald, in others - eyebrows, eyelashes and even the entire scalp.
- A bacterial abscess is a purulent inflammation, which is accompanied by the appearance of cavities filled with purulent exudate. Superficial symptoms include redness of the affected areas of the skin, increased sensitivity and soreness, as well as swelling. All this is accompanied by general malaise, weakness and fatigue. When the abscess spreads to the brain, intracranial pressure increases, coordination of movements is impaired, and hallucinations are possible.
- Trichotillomania is a disease that occurs due to stress or disorders of the nervous system. Manifests itself in the pulling out of hair on the head or other parts of the body. May occur in conjunction with compulsive hair eating (trichophagia). The skin at the site of baldness is healthy without itching or discomfort. Pulling out hair brings pleasure and relief to the patient.
- Seborrheic dermatitis is a disease caused by a disorder of sebum production. With pathology, the secretion of sebum by the holocrine glands increases and the chemical composition of the fatty secretion changes. Most often occurs in the occipital-parietal region of the head. The affected areas experience peeling, redness and itching. May spread to the bridge of the nose, eyebrows and nasolabial folds. The causes of the development of the disease are often associated with hormonal, genetic or nervous disorders, as well as improper use of personal hygiene products. Baldness does not usually occur.
- Folliculitis is a lesion of the hair follicle of an infectious nature, which leads to purulent formations. In places where hair grows, pustules appear, after opening which ulcers form. After healing, the skin becomes scarred, and deep damage to the scalp tissue negatively affects the condition of the hair.
Head fungus in children
Both children and adults are equally susceptible to fungal diseases. In the initial stages, a single focus of infection appears. After suppuration, the disease intensifies and the number of formations on the skin increases.
Very often, the cause of fungus on the head in children can be interaction with infected animals. Parasitic fungi can also enter the body through contact with children or playing outside. Any personal hygiene item, clothing and underwear are potential sources of fungus. Infection is especially dangerous in a hairdressing salon where untreated and undisinfected tools are used.
One of the hallmark symptoms of fungal infection in children is enlargement of regional lymph nodes. Each of these groups serves as a kind of protection for a certain part of the human body. Biological poisons of mushrooms, after entering the body, significantly affect it and worsen the general state of health. Rashes may appear, as in allergic reactions or viral diseases. After the patient’s condition improves and is cured, scar tissue appears at the site of the fungal lesions.
Young children with weakened immune systems are most susceptible to harmful microorganisms entering the body, the most common of which are dermatophytes. Children complain of rash, burning and itching of the skin.
Drug therapy
Systemic medications with antifungal properties are most effective. Unlike local remedies, they are active throughout the body. An important disadvantage of such drugs is their high level of toxicity, which can affect the functioning of various organs and systems. They should not be taken by people with kidney disease, cancer, anemia, metabolic disorders, or pathologies of the cardiovascular system.
When treating fungus on the head, the following are popular:
- Miconazole is a drug in the form of an ointment that is used to treat both fungus and dermatophytes, external forms of candidiasis.
- Clotrimazole is a synthetic drug with an antifungal effect; used for various mycoses.
- Griseofulvin - antifungal tablets for systemic use; the drug stops the division of fungal cells;
- Keratolytic ointments and tablets - soften and reject the hypertrophied layer of the epidermis;
- balms and antifungal shampoos.
This treatment lasts more than a month. In case of complications or severe cases, hormonal therapy and antibiotics may be prescribed.
Treatment principle
You can choose remedies for scalp fungus only after a detailed diagnosis. For treatment use:
- special shampoos;
- antifungal ointments and sprays;
- folk remedies.
Medicines and remedies for scalp fungus must be used regularly. When using sprays and ointments, skin treatment should be carried out daily. Shampoos for scalp fungus are used every other day or 2-3 times a week.
Drug treatment
Fungal infections of the scalp must be treated not with cosmetics, but with medications. To treat the affected areas, ointments and sprays containing an antimycotic are prescribed. The choice of drug depends on the causative agent of the disease, but in most cases preference is given to drugs with broad antifungal activity. In therapy they use:
- Lamisil;
- Exoderil;
- Clotrimazole;
- Candide;
- Tinedol;
- Griseofulvin.
All of these products are available in the form of ointments or gels. This form of release provides a long-term therapeutic effect, but is not convenient enough to use. The ointment must be applied to previously cleansed skin. Treatment is carried out 1-2 times a day. The main disadvantage of ointments is that they make the hair greasy, making the appearance rather untidy. However, with timely treatment, you will only have to endure the inconvenience for two weeks - this is enough time to successfully cure the disease.
All of these drugs are intended for the treatment of various mycoses, including foot fungus. This is due to the fact that all fungal skin lesions are sensitive to the same medicinal components.
In severe cases, the use of systemic antifungals may be required. In addition to topical medications, your doctor may prescribe Fluconazole, Nystatin, or Itraconazole tablets.
In addition to ointments, you can use antifungal solutions - Bifon Skin, Mikospor, Stop-Active.
Shampoos for fungus
Nizoral is one of the most popular drugs
Balms, creams and ointments against scalp fungus are quite effective, but require the simultaneous use of special shampoos with an antifungal component in the composition.
The choice of antifungal shampoos for scalp fungus is made by a doctor. Pharmacies offer many products in this form, so if necessary, choosing a broad-spectrum shampoo will not be difficult.
The most popular drugs:
- Nizoral;
- Sebozol;
- Keto Plus;
- Mycozoral.
To successfully treat fungal scalp infections, shampoo must be used correctly. The required amount of product is first applied to the skin, foamed and immediately washed off. Then the skin is re-treated. A small amount of the product is mixed with water, applied to the skin and left for 5 minutes, after which the hair is washed as usual.
Shampoos and other products for external use are quite safe and do not cause side effects. The use of tablets for systemic action should be discussed with your doctor.
Traditional medicine recipes
In some cases, traditional medicine recipes also produce a positive effect. In the initial stages of fungus or mild forms, eucalyptus oil will help. A small amount should be applied to hair using a comb, without touching damaged areas.
Garlic has proven itself as a means of combating fungal infections. To prepare the mixture you need garlic juice, almond or olive oil. If desired, you can add citrus juice (lemon). Rub the resulting product into the scalp with gentle movements, and after an hour, wash well. Do this procedure before every shampoo. Blood circulation improves and hair becomes stronger. The only thing that bothers me is the specific smell of garlic.
To get rid of scales, you need to pour 1 tablespoon of tansy with boiling water (0.5 l) and leave for two hours. Wash for 4 weeks. For the same purpose, use a decoction of lemon peel (cook for 15 minutes over low heat).
Diagnostics
To identify the disease and determine the type of fungus, conduct a visual inspection of the scalp.
Only a dermatologist can identify a fungal infection of the scalp.
If a fungus is suspected, microscopic examination of the hairs is used. A small amount of flaky skin is also sampled.
When performing microscopy, the doctor takes a crust, scale or hair from the affected area. Studying them under a microscope reveals the presence of fungal mycelium.
Diagnosis of trichophytosis
Human hair under a microscope
To identify trichophytosis (ringworm), a hair is taken for analysis. It is examined under a microscope.
If there is a disease, fungal spores are found in its inner part in the form of a chain that covers the entire hair, like a clutch.
Diagnosis of microsporia
Glow of microsporia under UV
When microsporia is detected, fungal spores are found on the surface of the hair, which are located pointwise around the preserved hair shaft.
A fluorescent lamp is also used when making a diagnosis. Using it, you can identify microsporia in a person. Under the influence of the lamp, hair acquires a special greenish-blue glow.
To determine the type of fungus, a culture test is carried out on a tank by inoculating spores in a special medium.