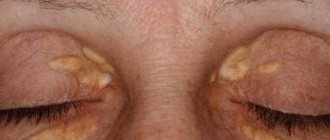
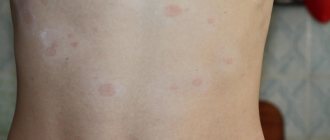
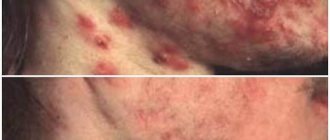
Xerosis , also known as xeroderma , is a symptom whose main symptoms are severe dryness of the skin, its roughness, and sometimes the presence of pityriasis-like scales on the skin.
The main reason for dry skin lies in the disruption of the sebaceous glands (hypofunction). The lack or absence of production of sebum (fat), which is actually the protective layer of the skin from the aggressive external environment, and also which maintains the water balance of the skin, leads to dry skin and its vulnerability to various infections. If there is a lack of sebum in the required amount, the skin not only dries out, it also tightens, peels, and wrinkles.
It has been noticed that if a person has dry and very dry skin, wrinkles appear much earlier, when other signs of aging are not even visible. Of course, not the last factor that leads to premature skin wrinkles is sun rays, which additionally dry out the skin.
Xerosis is dry skin that causes discomfort and unpleasant sensations. Another name is xeroderma. The disease has ICD-10 code L85. Drying out occurs due to a lack of moisture associated with age-related changes, diseases or side effects of medications. Skin xerosis negatively affects a person’s emotional state and creates difficulties in everyday matters. Dryness does not disappear when lubricated with creams and moisturizing oils.
The skin is called the largest and most vital human organ. Its structure includes:
- epidermis;
- dermis;
- subcutaneous tissue;
- adipose subcutaneous tissue.
The unique structure allows you to perform different functions, carry out metabolic, excretory, thermoregulatory vital processes. Defects on the body create cosmetic problems and also indicate the development of diseases in the body.
Causes of xerosis
Dry skin under the age of 25-30 is an inherited problem.
In the case of acquired xerosis of the skin, the reasons may be different and from the photo you can determine how the disease developed.
The problem comes gradually over the years. Contribute to this:
- Unfavorable climate. Excessive cold and heat are one of the main enemies of the skin. In cold weather, the air loses a lot of moisture, and in hot weather, sun radiation destroys collagen and elastin, which are responsible for the elasticity of the skin.
- Appliances. Heaters and air conditioners dry out the epidermis, the top layer of skin.
- Water. When a person comes out of the water, the latter remains on the body and begins to evaporate. As it evaporates, it takes away moisture from the layers of the skin. Therefore, you should not swim, shower or bath frequently.
- Hygiene products. Many of them contain aggressive substances. They destroy the skin's protective barrier - the water-lipid layer. Do not use cosmetics that contain sulfates and alcohol. Also, do not overuse peeling.
- Harmful working conditions. Working in production, for example, at a metallurgical plant, is unfavorable for the body as a whole. The skin reacts first.
- Violation of the regime. Irregular sleep and disordered eating cause premature aging of the skin. Due to dehydration and lack of vitamins. Thus, vitamins A and E are actively involved in the renewal of all layers of the skin.
- Metabolic problems. Promotes hormonal imbalance and improper absorption of nutrients.
- Unhealthy thyroid gland. It affects the activity of the sweat and sebaceous glands, as well as hormonal balance.
- Gastrointestinal diseases. As well as diabetes, hepatitis and cancer of any type.
- Taking glucocorticoid drugs. During a long time.
Separately, it is worth mentioning bad habits. Strong tea, coffee, alcohol and cigarettes are not your skin's best friends. They contain many toxic elements that contaminate blood vessels, burden the liver and interfere with the circulation of moisture in the body.
What is xeroderma pigmentosum: etiology of the disease
Lenticular melanosis is a genetic autosomal recessive DNA repair disease that causes extreme sensitivity of the skin epidermis to UV rays. The disease is very rare, in Europe and America it occurs on average one patient per million, in Japan and Asian countries more often - per hundred thousand. Most patients are in Brazil.
Most often, xeroderma is diagnosed in children born from consanguineous relationships. Lentigo maligna is found in isolates of relatively small populations of people (up to 1000 people) with a low level of marriage immigration for subjective reasons or religious beliefs. Demes and isolates are characterized by relatively low natural population growth, but with a large number of genetic diseases.
The mechanism of development of the disease is a genetic failure of DNA synthesis, resulting in its destruction by short ultraviolet rays. In principle, the patient’s body does not produce enzymes that neutralize radiation.
Gradually, the genome is completely destroyed, which leads to oncogenic mutations. It is no coincidence that pigmented atrophoderma is called a precancerous condition of the skin, and every year the concentration of oncogene genes and tumor suppressors only increases.
Xerosis. Symptoms
Manifestations of skin xerosis are specific:
- Skin tightness;
- Increased sensitivity;
- Frequent irritation and rashes;
- Redness;
- Invisible pores;
- Coarsening of the skin surface;
- Peeling and cracks (especially in fold areas).
People with xerosis suffer from itching and constant skin tightness. Sometimes there is a burning sensation. The symptoms worsen after contact of the epidermis with water and dry air.
In general, this disease includes four stages of development. Based on their description, you can also determine the presence of xerosis and its development:
- Stage one. The main criterion is functional impairment. The skin loses its protective properties. There is dryness and tightness, which do not cause much discomfort. For now, the problem can be solved with moisturizing creams and that’s enough. Tightness is often felt during facial movements. No wrinkles appear. Sometimes peeling appears after contact with water, sun or dry air.
- Stage two. The appearance and development of hyperkeratosis. Dryness and tightness are always present. Even after the cream. Cause significant discomfort. Small wrinkles begin to appear. Peeling becomes noticeable. Skin sensitivity increases and makes itself felt even with minor influences: contact with warm water, being in a room with an air conditioner running. From time to time, itching and redness bother you. The upper skin layer (epidermis) becomes thinner, its integrity is compromised, and hyperkeratosis (unhealthy epidermal thickening) appears.
- Stage three. Dermal hypotrophy. The peeling is large. Wrinkles are more obvious. Especially on the face (expression wrinkles). The deformation has reached the dermal layer (deeper than the epidermis). Any creams do not work. The skin is inelastic and looks stretched. Hard and rough to the touch. It's cracking. Sensitivity increases several times, inflammation appears.
- Fourth stage. Atrophy of the epidermal and dermal layers. Trophic type ulcers may form on the skin. Signs of premature aging appear.
Read also Skin cancer, melanoma - symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, prognosis
Xerosis of the scalp
A particular manifestation of xeroderma is xerosis of the scalp, the causes and treatment of which are determined by the doctor.
In most cases, this is caused by hormonal imbalance. In second place is incorrectly selected skincare products.
Before going to the hospital, you should try to solve the problem yourself:
- Change the shampoo to a softer one - sulfate-free. Or resort to washing your hair with hair balm. The latter should not contain silicones.
- Skip the hairdryer. And other devices and instruments that injure the hair and scalp.
- Drink more water. To replenish the body's lack of moisture.
- Use moisturizing masks for the scalp. Sold in a pharmacy.
And also take into account general advice on the treatment of xerosis.
Types of xeroderma pigmentosa
There are 8 types of CP, depending on the genes affected, the mutation of which is associated with CP.
- KP A is a severe form with serious neurological impairment.
- KP B is a rare form with Cockayne syndrome. Characterized by insufficient growth, neurological disorders, and mental retardation.
- KP S is the most common form. Sensitivity to UV, problems with nails and hair.
- KP D – sensitivity to UV, neurological disorders, developmental delay.
- KP E is a rare form. Relatively mild symptoms without neurological disorders.
- KP F is a form affecting the Japanese population. The DNA repair system works, but very slowly.
- KP G is a very rare form. Characterized by neurological disorders and developmental delays.
- Transitional type - sensitivity to UV, the disease progresses slowly, and life expectancy is longer than in other cases.
Xerosis in children
The causes of skin xerosis in children are different, and treatment depends on their nature.
So, the causes of skin xerosis in children may be as follows:
- allergy;
- endocrinological disorders;
- weak immunity.
In most cases, all this is transmitted with genes. To identify the cause, it is worth visiting the appropriate specialists.
It is acceptable to use special children's cosmetics. For example, moisturizing and soothing creams. Sometimes the doctor may prescribe medications.
To combat the scourge on their own, parents can be recommended to use “improvised” measures. This will improve the condition of the child’s skin texture (examples of skin xerosis in children photos).
- start hardening (if there are no contraindications);
- instill a love of hygiene;
- improve nutrition (fresh natural foods, more vegetables, eating at the same time);
- establish a routine (wake up and go to bed at the same time every day);
- ensure healthy sleep (8-9 hours a day, in absolute darkness, in a pre-ventilated room);
- get interested in sports (for example, enroll in some sports section).
Regular spending time outdoors will also benefit your growing body. However, it is better to avoid active sun.
In general, skin xerosis in children is similar to that in adults, regardless of the cause, so the approach to therapy is similar.
Treatment of xerosis
When treating skin xerosis, it is worth taking into account all the factors that can cause this disease. Treatment should be combined: medications combined with a correct lifestyle and well-chosen cosmetics. You can also add traditional methods.
Drug therapy is recommended:
- Topical moisturizers (such as glycerin and hyaluronic acid). They retain moisture in the body and attract it from the outside. Promotes better cell division - skin renewal.
- Moisturizing and soothing creams, gels and ointments (usually they contain urea, salicylic and lactic acids). They soften the damaged area of the epidermis and remove dead scales.
- Products containing corticosteroids (indicated only for serious problems and prescribed by a dermatologist);
- Antibiotic medications (in case of infection through the skin).
A little about a healthy lifestyle:
Proper nutrition harmonizes water balance. Therefore, maximum attention should be paid to nutrition. It is worth giving up processed foods - they contain a lot of salt and preservatives.
The latter not only contribute to the rapid loss of moisture from the body, but also disrupt metabolic processes. In addition, there are few natural vitamins.
Features of xeroderma pigmentosum
Xeroderma pigmentosum is a disease characterized by a hereditary defect. The body of a healthy person contains enzymes that help neutralize the negative effects of ultraviolet radiation on the skin. A patient with xeroderma does not have it, or it hardly works.
With the help of certain proteins, tissues that have been damaged by ultraviolet rays are restored. But the patient begins to develop a mutation in them.
As a result, the number of pathological cells increases. Every year there are more of them, which can lead to skin cancer.
Xeroderma pigmentosum develops due to high sensitivity to ultraviolet radiation. But there is also a harmful factor that can provoke pathology. It can appear due to excessive sensitivity to radiation.
These negative factors provoke such changes:
- pigmentation is disturbed;
- atrophic changes occur in the skin;
- keratinization of the skin, cell atypia, connective tissue dystrophy are observed;
- the risk of developing cancer increases.
Often xeroderma pigmentosum is accompanied by a change in the healthy appearance of the limbs, since a person has a congenital fusion of fingers or toes.
In addition, dental health can suffer from the disease and baldness can occur. Growth is also delayed in many patients.
Xerosis. Diet
To make dry skin feel better, you should include these products in your menu:
- seafood (contains a lot of polyunsaturated fatty acids);
- vegetables and fruits rich in vitamin C (an antioxidant responsible for skin renewal);
- vegetables and fruits of red and green colors (contain beta-carotene, which is converted into vitamin A. This is a serious antioxidant that does not allow cells to be destroyed);
- clean, fresh water (daily intake for women - from 30 ml per kg of weight, for men - from 40 ml per kg of weight per day).
Traditional recipes:
- Glycerin bath. Restores the epidermal cover. Add 0.5 cups of natural glycerin (non-technical) to a bath of warm water. Take 10-15 minutes.
- Honey-oil bath. A liter of milk is heated without boiling. Add 200 g of natural honey (not store-bought, it is better to purchase it from beekeepers). Mix and gradually add 1 tablespoon of almond oil. The mixture is poured into a bath of warm water. Take - 10-15 minutes. Softens the skin.
- Olive mask. Mix 2 tablespoons each of olive oil and honey. Apply to damp skin after shower or bath. Keep for 20 minutes. Rinse off with warm water. Softens and moisturizes the skin.
Prevention of xerosis
To prevent xerosis, a number of conditions should be taken into account:
- Proper sleep is necessary for a person. It restores the body's resources and, accordingly, skin cells.
- Food is of utmost importance. These are the “building blocks” of the body. Skin is formed under the influence of many factors, but its main resource is what we consume. Convenience foods and sweets do not give the skin what it really needs.
- Overheating and hypothermia are harmful. This refers to aggressive environmental factors that cause the skin to “defend itself.”
- Bad habits destroy the body. Starting from smoking to the habit of staying late at the TV screen - all this is stress. And for the skin as well.
Manifestations of skin xerosis, causes and treatment are different (it’s worth looking at photos of different clinical cases). If you approach the problem thoroughly and create a treatment system, dryness can be both prevented and cured.
Causes of skin xerosis
Xerosis can have two main etiologies - congenital (atopic xerosis) or acquired.
If we talk about xerosis, which manifests itself in infants during the first months of life, then it can be a symptom of a mild form of ichthyosis. If we talk about acquired xerosis of the skin, then various unfavorable factors (reasons) can contribute to this.
Read also Trichomoniasis - symptoms, treatment, diagnosis
Of course, by the cause of xerosis it is fair to designate the cause of hypofunction of the sebaceous glands, which leads to insufficient production of sebum by them, which is manifested by dry skin. Let's look at them.
Causes of xerosis (dry skin):
- Features of the skin – thin skin;
- deficiency of vitamins in the body (hypovitaminosis), especially vitamin A;
- exposure of the skin to direct sunlight (ultraviolet radiation), incl. visiting a solarium, as well as cold, wind, rain, snow, frost;
- frequent bathing in hot water, daily hot showers;
- use of soap with surfactants (surfactants) for washing the body;
- use of household cleaners and detergents without protective equipment (gloves);
- use of alcohol-based cosmetics;
- hormonal changes in the body, age-related changes;
- long-term use of hormonal agents - systemic and external glucocorticoid drugs;
- metabolic disorders;
- violations of the daily routine - work/rest/sleep;
- diseases of the endocrine system, skin, gastrointestinal tract: psoriasis, eczema, ichthyosis, dermatitis, keratosis pilaris, diabetes, gastroduodenitis, hepatitis, liver cirrhosis, hypothyroidism, cancer.
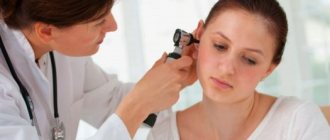
Which doctor should I consult for dry skin?
A dermatologist treats skin diseases. And if you put off visiting a specialist, trying to cope with dry skin on your own, then you need to immediately contact him for help if:
- The affected skin began to ooze.
- Exfoliation of large areas of skin occurs.
- Annular erythema (ring-shaped spots) appeared on the body.
- The skin condition does not improve for a long time (even after treatment).
Diagnostics
Before prescribing treatment for xeroderma, a dermatologist must differentiate the disease. In other words, clarify that this is xeroderma. After all, some skin pathologies, for example, eczema, have symptoms similar to it. This means that if you are diagnosed with eczema, the treatment plan will be different from the plan that is formed for a person with xerosis.
So, in order to diagnose xeroderma, you may be prescribed:
- Visual examination will help identify and compare symptoms.
- A skin biopsy will detect a fungal infection.
- Donating blood for biochemical analysis is necessary to assess the functioning of internal organs and identify deficiencies of microelements (potassium, magnesium, calcium, etc.) in order to replenish them.
To get a complete picture of your skin problem, the doctor will take a medical history (ask questions about current and previous diseases, ask whether there have been surgical interventions on the body, etc.).
Based on the data obtained, he will draw up a suitable treatment regimen using medications.
Symptoms of xerosis
The main symptoms of xerosis (xeroderma) are:
- severe dryness, tightness and irritation of the skin;
- the presence of easily detachable scales on the skin, roughness;
- the appearance of cracks in the skin, especially in places of bends/folds - fingers, elbows, knees;
- coarsening of the upper layer of the epidermis;
- almost invisible pores;
- the presence of wrinkles at an early age;
- a feeling of itching of the skin, sometimes severe, as well as a burning sensation.
Exacerbation of symptoms often occurs after skin contact with cold, water, and soap.
Development of xerosis
The development of xerosis (xeroderma) occurs during 3 stages.
Xerosis 1st degree. Structural changes and wrinkles on the skin are not visible. After skin contact with an unfavorable environment or substances harmful to it, some burning, itching occurs, the skin becomes dry and tightens. Symptoms disappear after treating the skin with a moisturizer.
Xerosis 2 degrees. The structure of the skin is disrupted; in addition to dryness and tightness, peeling, red itchy spots, and wrinkles appear. Symptoms cannot be completely relieved by moisturizing cream alone.
Xerosis 3 degrees. Clear signs of xeroderma appeared on the skin - dryness, tightness, scaly scales, red spots, itching, cracks and wrinkles, especially in the folds. Sometimes swelling appears on the skin. The skin becomes thinner. Frequent skin diseases appear - eczema, dermatitis, infection - staphylococci. Premature aging of the skin occurs. At this stage, serious complex treatment is necessary.
Diagnosis of xerosis
To confirm the pathology, the following activities are carried out:
- conversation with the patient to collect information (complaints, family and genetic history, living and working conditions, diet, presence of concomitant diseases);
- visual inspection of affected skin areas;
- tests to exclude other dermatological problems (detection of fungus, bacterial and other lesions);
- biochemical blood test to determine hormonal status.
If necessary, additional laboratory and instrumental tests may be required, as well as consultation with specialists (endocrinologist, allergist).
It includes the collection of anamnestic data to establish the root cause of dryness; the affected areas of the skin are examined and have a characteristic appearance: dry, rough, in the form of pityriasis scales, mainly on the extensor surfaces of the extremities. If necessary, a set of laboratory and instrumental diagnostic measures is carried out, determined individually in each case.
Diagnosis of skin xerosis includes the following examination methods:
- Visual examination of the patient;
- Taking anamnesis;
- Blood chemistry.
Treatment of skin xerosis (dry skin)
Treatment of dry skin (xeroderma) includes the following points of therapy:
1. Elimination of the root cause of dry skin; 2. Nourish and moisturize the skin; 3. Local treatment of dry skin areas; 4. Diet; 5. Compliance with preventive measures to prevent dry skin.
Addressing the root cause of dry skin
Treatment of skin xerosis is carried out based on the diagnosis of a dermatologist, who must determine the cause of this pathology.
If the cause of xeroderma lies in diseases of the endocrine, nervous, immune, gastrointestinal tract and other systems, then therapy is aimed at their treatment, and with the right actions, after getting rid of those diseases, the functioning of the sebaceous glands will be restored automatically.
Nourishes and moisturizes the skin. Skin care
Due to the fact that dry skin means there is no protective layer on it, the skin needs to be moisturized and nourished. This must be done to prevent pathogenic microflora, for example, staphylococcus, streptococcus and other bacteria, from entering the body, or the skin layer itself, through micro-traumas of the epidermis. If this is not done, then a secondary infection with its own complications may join the dryness.
Moisturizing and nourishing the skin also gives the skin elasticity, which helps prevent the appearance of cracks, stretch marks, and wrinkles on the skin. Moisturizing also relieves itchy skin.
However, remember that you cannot moisturize your skin with many cheap moisturizers, because... they draw out the remaining moisture from already dry skin. It is best to moisturize the skin with products containing substances such as: vegetable oils (olive, flaxseed, almond), animal fat (bear, greyhound), vitamins, etc.
The best way to moisturize your skin is to drink plenty of liquid – up to 3-4 liters per day. Shouldn't lemonade be the dominant drink?
For your washing, use products without surfactants (surfactants), which disrupt normal sebum secretion, remove the protective film from the skin, thereby increasing dryness of the skin.
Shower gels with a skin moisturizing effect, which contain various oils, incl. ethereal. There is also soap with a moisturizing effect. Yes, these products are usually more expensive, but your health is worth it.
An air humidifier also has a beneficial effect on the skin, especially in winter, when the air in residential areas becomes dry due to heating.
Local treatment of xeroderma
To relieve skin itching, you can take an antihistamine: Suprastin, Claritin, Diprazine.
To relieve itching locally, you can apply a bandage soaked in novocaine to the itchy skin.
For severe itching, you can apply a bandage of weak hormonal ointment - 1% hydrocortisone.
In case of microcracks, in order to prevent infection from entering the body, it is advisable to disinfect the skin by treating it with ointments and creams based on tar and naphthalan.
In case of microbial damage to the skin: if various crusts of a greenish-yellow hue begin to form on the skin, these areas can be treated with antimicrobial lotions: 0.25-0.5% silver nitrate, Brilliantgrun, Rivanol, 0.5 -1% “Resorcinol”, copper sulfate solution. But at the first such symptoms, immediately see a dermatologist!
Read also Cutaneous leishmaniasis - symptoms, diagnosis, treatment
To remove the top layer of scaly epidermis, keratolytic therapy is performed, which is based on treating the skin with creams and ointments with components such as salicylic or lactic acid, urea. These creams soften the skin, remove sebaceous plugs and dead scales, and help normalize the breathing of the epidermis.
Diet for xeroderma
Diet is an integral part of the treatment of many diseases. This is due to the quality of modern food. The fact is that from year to year, less and less healthy food is sold on store shelves. More and more food products are inventions of the chemical industry, artificial products from greenhouses, etc. This food does not contain the necessary vitamins and substances that, when sufficiently supplied to the body, contribute to normal growth, development and human health. Thus, often, diet alone is able to concentrate the body on any failures that have occurred in it, and solve them on its own.
A diet for xeroderma implies the exclusion from the diet of fatty, fried, spicy and smoked foods, fast food, alcoholic beverages, various store-bought chips, crackers, etc.
What can you eat with xeroderma: firstly, drink more fluid, up to 3-4 l/day, secondly, eat foods rich in vitamins and microelements - raw vegetables, fruits, berries, nuts, cereals, fish.
It is worth noting that the least loss of vitamins and other useful substances in food occurs when steaming, so a steamer is an integral household appliance recommended by many nutritionists.
For dry skin, special emphasis should be placed on additional oral intake of vitamins A (retinol) and E (tocopherol). B vitamins are also indicated because most of them, if not all, directly affect the normalization of the cardiovascular system. It’s no secret that low-health food leaves in the human body, especially in blood vessels, remnants of “bad cholesterol”, which over the years disrupts normal blood circulation in many organs, clogging blood vessels, especially disturbances appear in blood vessels with a small lumen (veins, capillaries) . B vitamins help cleanse and quickly remove “bad” cholesterol from blood vessels, blood nourishes all human organs and systems, normal metabolism occurs, and the body begins to function with maximum efficiency.
Additional treatment for dry skin
Beneficial to the surface of the skin, i.e. When treating dry skin (xeroderma), the following procedures are used:
- ozone therapy;
- mesotherapy;
- skin treatment with microcurrents (darsonvalization).
Prevention of xeroderma (dry skin)
- For skin care, use detergents without surfactants;
- Swim in warm water, not hot;
- When using household chemicals, use protective gloves;
- Try to eat more raw vegetables and fruits, foods enriched with vitamins and microelements;
- Avoid alcoholic beverages and smoking;
- Move more;
- Avoid exposure to sunlight in summer, during daytime active sun;
- When sunbathing on the beach, use sunscreen;
- Try to apply less cosmetics to your facial skin; if possible, avoid them altogether, especially if the cosmetics are alcohol-based;
- Don’t let chronic illnesses take their course;
- Avoid stress;
- Wear clothes made from natural fabrics - cotton, silk, but wool can irritate the surface of the skin.
Who is at risk
Elderly people are susceptible to developing excessive dryness when body cells die. The type of dehydration is called senile. Xerosis also develops in those who often come into contact with water or live in cold climates or places with insufficient air humidity.
The disease is classified into two groups:
- Drying with good tone - the epidermis retains smoothness, elasticity and a pleasant color. There are no wrinkles on the surface. But under the influence of irritants, the skin becomes dry and inelastic. This type of dryness is common among young people. This type of epidermis requires constant care.
- Dryness with low tone - the skin is thin, forming early wrinkles around the mouth and eyes. This type of epidermis requires increased care using special cosmetics. Standard methods and creams will not bring visible results.
Having a predisposition to early aging and excessive drying of the body surface, you should carefully care for it using specially developed products. This will help restore elasticity and pleasant sensations.
What to remember:
- Xeroderma is a mild type of ichthyosis; it is characterized by constantly dry skin.
- The disease is not contagious and appears in individuals with reduced sebum production from the skin.
- Abnormal dryness of the skin can be caused not only by xerosis, but also by other diseases, such as eczema. Therefore, skin treatment cannot begin until an accurate diagnosis is made.
- Proper nutrition plays an important role in the treatment of xeroderma.
- The most important thing is to drink plenty of fluids.
- Allergy on the skin in the form of red spots. Treatment on the arms, legs, neck in adults and children if they itch
- Hand skin fungus effective treatment
- Dermatitis on the legs (wet, dry, venous) - causes, treatment
- Allergy from skin patch treatment - Allergy and me
Xerosis in infants
Dry skin in newborns is not a pathological sign. This is explained by the fact that the baby’s sebaceous epidermal layer does not function for the first time after birth. The discomfort will go away on its own, without the use of additional means, after the body adapts to the changed environment. Also, dehydration in children can be associated with artificial nutrition, early complementary feeding, or a woman’s improper diet during pregnancy and breastfeeding. Increased water hardness and frequent bathing affect the elasticity of the skin.
Dryness of the body often signals problems and diseases of the intestinal tract. Having ruled out possible diseases, it is necessary to combat dehydration of the child’s epidermis. In the first days of life, the skin is very sensitive, easily forms cracks, peeling, redness and itching. This causes discomfort to the baby and interferes with restful sleep.
Dry feet and soles of an infant can cause various infections and bacteria to enter the body and develop inflammatory processes. Insufficiently careful care of a child’s feet leads to the formation of dermatitis and urticaria. Therefore, after each bath, you need to apply a special moisturizer to the baby’s body and massage the legs.
Symptoms and signs
The clinical picture of scleroderma is expressed:
- in calcinosis - deposition of excess calcium on the walls of blood vessels, in soft and hard tissues;
- in damage to peripheral vessels (Raynaud's syndrome), when spasmodic capillaries are poorly supplied with blood and are very sensitive to the effects of cold;
- change in the appearance of the fingers (thickening, deformation, shortening);
- decreased peristalsis of the stomach, intestines and bile ducts, weakness of the sphincters;
- dilatation of small vessels (telangiectasia);
- pain in the limbs;
- hypersensitivity of hands to cold;
- formation of subcutaneous nodules, ulcerations, and areas of necrosis on the body;
- development of joint contractures (violation of their flexion-extension function and joint shape);
- tachycardia, arrhythmias, bradycardia, extrasystoles.
With extensive damage to the kidneys, liver, heart bags, lungs, the disease becomes life-threatening, severe pathologies develop: acute cardiac, pulmonary, liver or renal failure - patients with scleroderma can die from such complications.