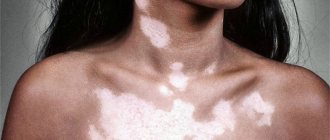
Do you suspect you have lichen? Don’t know what its symptoms, types, treatment methods are? Would you like to know the causes of this disease, possible complications, as well as existing preventive measures? We will tell you all the most interesting things about this insidious disease!
Clinical symptoms of lichen depend entirely on the type of virus or fungus
General signs of the disease and symptoms
Clinical symptoms of lichen completely depend on the type of virus or fungus that caused it, and therefore can manifest as:
- increased body temperature;
- malaise and general weakness associated with intoxication of the body;
- enlarged lymph nodes;
- skin rashes with the presence of papules or spots with uneven outlines;
- peeling, itching and even pain in the affected areas.
If you find yourself with several of the symptoms listed above, immediately consult a dermatologist for an accurate diagnosis and timely drug treatment to quickly get rid of this disease without serious consequences and complications!
How to treat lichen at home
There are several ways you can try to combat the symptoms of ringworm at home.
A mixture of sulfur and Vaseline
To do this, you will need to take 33 g of sulfur and 67 g of petroleum jelly, and mix everything thoroughly. This will help relieve itching and redness.
Sulfur, tar soap and salicylic alcohol
Sulfur will help get rid of bacteria and viruses, salicylic alcohol will relieve inflammation, and tar will eliminate unpleasant itching.
The course of such treatment should be no more than 10 days. Apply to the affected area morning and evening. But if the lichen does not go away within two weeks, then it is better to consult a doctor.
Iodine
This remedy is effective only in the early stages of the disease. To do this, you need to lubricate the lichen lesions for three days, then stop using it for 5 days.
Iodine + brilliant green
These remedies need to be alternated every other day. The course of such treatment is no more than 10 days.
Causes
The most common causes of lichen on the face are:
- direct contact with viruses/fungi found on animal fur;
- household contact with a person who is a carrier of lichen;
- reduced immune defense of the body;
- tendency to allergic diseases;
- prolonged stress conditions and diseases of the nervous system;
- vitamin deficiencies;
- hereditary factors;
- frequent colds;
- bites of certain insect carriers;
- improper or insufficient skin care;
- non-compliance with hygiene measures - mandatory hand washing after contact with animals and visiting public places;
- damage by helminthic infestations;
- problems with the gastrointestinal tract;
- oncological diseases.
Treatment methods
For lichen on the face, treatment is selected depending on the type of disease. The first time you encounter a problem, you need to consult a doctor. After examining and analyzing scrapings of the affected epidermis, the doctor will tell you how to treat lichen on the face in order to get rid of the problem as quickly and effectively as possible.
To treat the pink form of skin lesions, use:
- antiviral drugs;
- antihistamine tablets;
- ointments for skin treatment.
Antiviral tablets are selected depending on the pathogen. Treatment often includes taking the medication Acyclovir. Allergy medications are prescribed to relieve skin swelling and itching. Antiseptic treatment and acceleration of skin regeneration are ensured by the use of salicylic or zinc ointment. Ointments and creams containing tar also help speed up recovery.
The herpes virus, girdling the skin, causes not only a rash, but also pain. Treatment of this form of the disease should be aimed at suppressing the virus. To do this, take special tablets. The danger of this shingles lies in the development of neuralgic pain, for the relief of which non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs can be used. During treatment, you should avoid exposure to sunlight and do not use cosmetics.
Pityriasis versicolor is caused by a fungal infection, so treatment is carried out with the help of antimycotic drugs. For extensive skin lesions, antifungal tablets are indicated. To treat stains, use broad-spectrum antifungal ointments, for example, Clotrimazole. Patients are advised to sunbathe to reduce the severity of symptoms.
Lichen planus is a recurrent disease and is therefore difficult to treat. Therapy for this form of the disease includes treating the skin with hormonal ointments. For treatment, medications containing corticosteroids are recommended. Allergy pills help relieve unpleasant symptoms. For extensive skin lesions, antibiotics may be prescribed. If the affected skin is infected, additionally use antibacterial ointments and antiseptic solutions to regularly treat the spot.
Existing types of lichen
- Pityriasis rosea is considered the most common type of infectious lesion of the skin of the face, very difficult to diagnose, since its manifestations are similar to allergic reactions, accompanied by itching, peeling, burning, pale pink lesions with unclear and blurred boundaries. Additional symptoms are a slight increase in body temperature and general weakness. The duration of the disease, subject to treatment, is from 1 to 2 months.
- Lichen planus , as a rule, affects the mucous membranes of the lips and mouth, but can also appear on the surface of the face in the form of tubercles of a pale pink or purple hue, turning into ulcers under the influence of various irritation factors. The shape of such spots is ring-shaped, erythematous, and resembles warts.
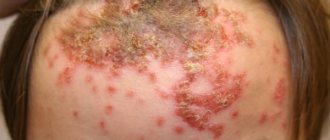
- Ringworm affects the areas of the face bordering the hair, as well as the chin. It looks like pink spots with uneven outlines and a white edge. In the center of such formations, yellow or gray crusts appear over time. This type of lichen is characterized by mild itching and lesions of varying sizes (from 1 to 3 centimeters). The first symptoms may appear as early as 5-10 days after contact with the carrier.
- Microsporia is a type of ringworm that affects the epidermis in the area of the forehead, temples, and neck, which are in contact with the scalp. The spots that form on the skin are characterized by a pale pink tint with a darker edging around the edges and peeling in the center. Their shape can be varied. This type of lichen is rarely accompanied by itching.
- The pityriasis versicolor type is characterized by pinkish-brown spots with uneven and not clearly defined boundaries, itching and flaking after scratching.
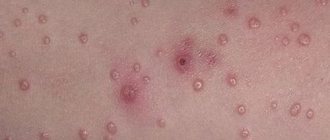
- Weeping lichen is characterized by multiple small blisters that, after opening, form erosions containing oozing serous fluid. As they dry, they turn into crusts, causing severe itching and burning, preventing normal rest at night.
- The first signs of shingles on the face are pain on the skin, aggravated by touch, a significant increase in body temperature, and a general deterioration in well-being. External manifestations have the form of edematous spots of light red color, covered with blisters with liquid contents. After the blisters burst, dense crusts form on the skin.
How to recognize the disease
What lichen looks like depends on the type of disease. The following symptoms are typical for pityriasis rosea:
- formation of round or oval spots on the skin;
- inflammation of the epidermis in the affected area;
- dryness and flaking;
- itching;
- discomfort when touched.
Despite the infectious nature of the disease, the symptoms of this form of lichen can be aggravated by exposure to cosmetics, household chemicals and other skin irritants.
The shingles type of the disease is characterized by the formation of pink spots of inflamed skin covered with a blistering rash. In this case, the herpes virus first affects the nervous system, only then do symptoms of a skin disease appear. This pathology may be accompanied by increased body temperature, loss of strength, itching and discomfort. Often patients feel neuralgic pain spreading in the area of the affected nerve.
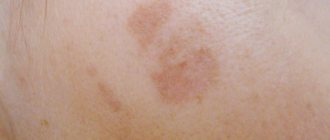
The pityriasis form of the disease is often mistaken for hyperpigmentation of the skin due to the fact that the spots on the body and face are colored in all shades of brown. The disease begins with the appearance of a small light spot, which darkens and grows over time. Around the mother spot, daughter spots may appear, which are characterized by a smaller diameter. The skin in the affected area becomes thinner and peels, and wrinkles may form. This makes it possible to distinguish pityriasis fungal skin lesions from age spots.
Lichen planus appears as round spots that are colored red, purple or light pink. The affected area swells and is very itchy, but in most cases there is no peeling. The skin becomes inflamed and may become wet; when scratching, erosions often form, which is dangerous due to the risk of infection.
The ringworm form of the disease is characterized by the formation of regularly shaped spots. The skin in the affected area is light pink; in some patients, the spot may be lighter than healthy skin. A small pustular rash often forms at the borders between the affected and healthy epidermis. The spot itches, patients note a feeling of tightness and discomfort when touched. A characteristic feature of this fungal disease is the easy separation of dense skin flakes. The spot quickly increases in size. Over time, hair in the affected area may break off and thin out.
What treatment methods are there?
It is necessary to begin complex treatment of lichen only after diagnosing its type by a dermatologist. General therapeutic treatment methods include the use of the following drugs and equipment:
- antifungals for internal use (for example, acyclovir, valacyclovir, griseofulvin);
- antifungal ointments for external, local use (exoderil, clotrimazole, mycoseptin, micoconazole);
- immunomodulators to increase the body's defenses;
- vitamin ointments, iodine solution, sulfur-salicylic composition;
- cryotherapy using liquid nitrogen, ultraviolet irradiation, diathermocoagulation;
- anti-itch formulations (with menthol, anesthesin, sulfur, tar);
- ointments with corticosteroid hormones (prednisolone, sinaflan, flucinar, fluorocort).
Possible complications
In the absence of proper treatment prescribed by a dermatologist, consequences may occur in the form of:
- gangrenous condition;
- spread of purulent infection in the body;
- lesions of the central nervous system;
- bacterial infection of the epidermis, leading to scar formation;
- hemorrhagic complications;
- damage to the mucous membrane of the eyes up to blindness;
- transition of the disease to a chronic form with constant relapses;
- the appearance of psoriatic erythoderma, generalized pustular psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis, facial paralysis.
Traditional methods
If the disease has not spread much on the skin, you can use recipes from your grandmother’s stash.
How to treat lichen on the face using traditional methods:
- raisins: you will need 200 g of dark, seedless raisins, grind 10 g of dried grapes daily and apply the pulp to problem areas, keep for 15 minutes, the course of therapy lasts 10-12 days;
- apple cider vinegar: this remedy should be used twice a day in the form of lotions;
- juice from cranberries: juice is squeezed out of fresh berries, you need to lubricate lichen rashes 3-4 times a day.
Prevention measures
In view of the severity of the disease, the long and difficult treatment period, and the possibility of a number of serious complications, it is best to take the following preventive measures to avoid this dangerous infection:
- increasing the body's immune defense;
- avoiding contact with stray animals, as well as mandatory hand washing after playing with pets;
- monitor the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract;
- try to eat as many foods high in vitamins as possible;
- be checked for parasites;
- undergo an examination of the body for oncological formations;
- fight long-term and protracted stress;
- monitor the health of the nervous system;
- try to have less contact with aggressive allergens;
- strengthen the body to avoid colds;
- Be sure to treat insect bites with antiseptic compounds.