To determine how to treat seborrhea on the face, you need to correctly recognize its type and identify the cause of its appearance. Often it occurs due to disruption of internal organs and systems. Treatment of this disease is always carried out comprehensively. In addition to the underlying disease, they perform external treatment and relieve skin manifestations. Local treatment may include salon procedures, the use of medicinal ointments and creams. To reduce inflammation and itching, antihistamines are used, for example, Suprastin, Fenistil, Diazolin.
Reasons for the development of seborrhea on the face
The human body has a huge number of exocrine glands, which perform an important function: through the production of sebum (sebum), the glands nourish, moisturize, protect and soften the skin. Features of the localization of such glands, in particular on the face, provoke the progression of seborrhea:
- in the frontal region;
- on the eyebrows;
- nasolabial “triangle”;
- scalp.
When a malfunction occurs in the body, sebum is produced in excess and “works against a person” - it becomes a favorable environment for the development of fungal and infectious diseases. More often, facial seborrhea is accompanied by excessive activity of the secretion organs.
But in medical practice, there are cases of dry seborrhea of the face, when, under the influence of various factors, the function of the glands is inhibited. The third type of pathology is mixed, when both manifestations of seborrheic dermatitis occur.
In each case, the chemical composition of sebum changes, which disrupts the oxygen exchange of the skin, reduces the protective functions of the epithelium and provokes irritation.
The sebaceous glands in the body of a healthy person produce up to 20 g of sebum per day, in a patient - 1.5-2 times more.
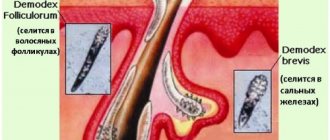
The main “provocateur” of the development of seborrhea is the opportunistic yeast-like fungus Pityrosporum (pityrosporum), which parasitizes the hair follicles, as well as the exocrine glands.
Normally, pityrosporum is found on the surface of the skin in 90% of people, but in the presence of a favorable environment, it begins to actively multiply and acquire pathogenic properties.
The reasons for the appearance of seborrhea on the face and the activation of the fungus are caused by the following factors:
- genetic predisposition;
- hypovitaminosis, weakening of the body's protective functions;
- pathologies of the endocrine system, including hormonal imbalance (increased testosterone), diabetes mellitus;
- stress, overwork, violation of work and rest schedules;
- disruption of the central nervous system;
- chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and liver;
- insufficient facial skin care, lack of proper hygiene.
Men are more susceptible to oily seborrhea of the facial skin. This fact is due to an excess of testosterone in the male population, the peak of which activity occurs during puberty (from 12 to 20 years). But in some cases, pathology manifests itself regardless of gender and age.
Specifics of drug use during pregnancy and lactation
During pregnancy, hormonal drugs are not used. The decision to prescribe antifungal and antibacterial medications is made by the doctor in each case individually. This is due to the fact that a small amount of active ingredients still penetrates into the blood and can cause complications.
The article discusses effective ointments for seborrheic dermatitis on the face.
During lactation, many products are approved for use, and when prescribing some ointments, it is necessary to stop feeding for a while. It is worth remembering that in any case, consultation with a doctor is required. During such periods, self-medication is dangerous.
Symptoms
The most common is oily seborrhea of the face, which is often accompanied by a secondary infection of infectious or fungal origin. Symptomatically, the pathology manifests itself as:
- increased sweating;
- enlarged pores on the face;
- inflammatory processes that provoke redness of the epithelium;
- foci of suppuration;
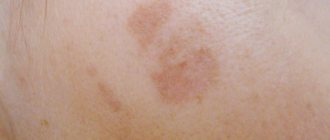
Dry seborrhea is characterized by:
- the appearance of dry, flaky skin;
- fine dandruff appears on the hair and face;
- hair loss occurs;
- changes in the skin are accompanied by itching and burning;
- Pinkish and red spots of thin epithelium appear on the skin.
The mixed type of disease combines the symptomatic manifestations of the two varieties described above.
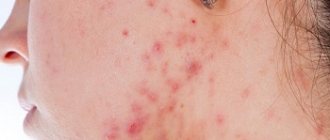
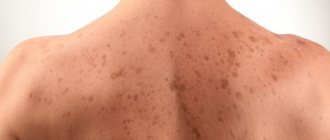
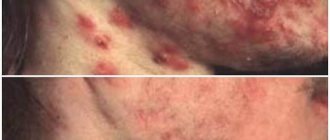
Appearance from photo
Externally, oily facial seborrhea is characterized by the following manifestations:
- acne;
- comedones;
- milia;
- scars on the skin as a result of acne;
- increased oiliness of hair and skin.
With the dry type of the disease, dry skin, cracks, peeling and scales appear. The hair of patients with dry seborrhea is brittle, and the head is covered with fine dandruff. Dry seborrhea is more common in children.
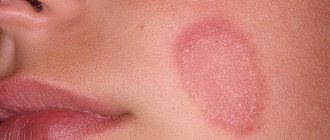
Mixed seborrheic dermatitis is easily confused with the manifestation of atopic dermatitis, psoriasis, and lichen. Therefore, to clarify the diagnosis, a doctor’s examination is necessary.
Symptoms
Symptoms and manifestations of seborrheic dermatitis can be confused with the following diseases:
- psoriasis;
- contact dermatitis;
- atopic dermatitis;
- lichen;
- rosacea on the face.
Seborrheic dermatitis on the face symptoms and treatment
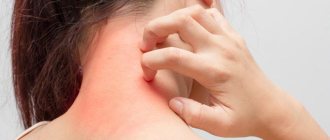
Symptoms of seborrheic dermatitis are:
- redness of the skin, increased sensitivity to soap, cosmetics;
- itching;
- peeling;
- coarsening of the affected areas;
- the appearance of white and then yellow scales and papules on the face.
Note! It is difficult to make a diagnosis on your own without laboratory testing. At the first signs of skin irritation, you should consult a doctor.
The development of the disease occurs stepwise, increasing. Symptoms get worse over time. The areas affected by the fungus increase, the inflammatory process is added, and a complication arises in the form of acne on the face.
Redness of the skin on the face is accompanied by itching and swelling. In places where the skin naturally folds (behind the ears, near the nose, nasolabial folds), creases and cracks form, which can burst and bleed.
Exfoliated skin accumulates and becomes saturated with sebum, acquiring a yellow color and the appearance of solid crusts. If seborrheic dermatitis is not treated adequately, inflammatory processes will develop.
Inflammation is expressed in the appearance of a polymorphic rash. In the center of the scales, papules are formed - bubbles with liquid contents.
At the last stage of development of seborrheic dermatitis on the face, complete blockage of the sebaceous and fatty ducts and inflammation of the hair follicles are added. This is expressed in the appearance of persistent acne.
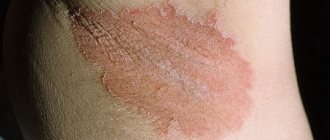
Seborrheic dermatitis on the face photos and types
The above symptoms and manifestations of seborrheic dermatitis on the face cause moral suffering to patients and greatly worsen the patient’s quality of life. However, with adequate and timely treatment, stable remission of the disease can be achieved. Maintenance therapy will prevent exacerbations from occurring.
Treatment of seborrhea on the face
The standard therapeutic regimen for the treatment of seborrheic dermatitis includes:
- means to enhance the body's immune function;
- multivitamin complexes;
- external agents (creams and ointments);
- sedatives;
- physiotherapy (ozone therapy, cryotherapy, Darsonval microcurrents, UV and gamma radiation).
If secondary infection develops, the doctor prescribes antibiotics and NSAIDs. Also, in the treatment of dry and oily seborrhea on the face, external agents (usually corticosteroid ointments) are actively used to relieve foci of inflammation.
Use of external preparations
Among the variety of external remedies for the treatment of oily and dry seborrhea on the face, the following creams and ointments are popular:
- Flucinar is an antiseptic that relieves itching and redness of the skin;
- Advantan is an effective hormonal remedy against itching and inflammation;
- Skin cap. The ointment is based on zinc, which eliminates allergic rashes, reduces itching and irritation;
- Belosalik (Russian analogue of Akriderm). Effective in the treatment of dry seborrheic dermatitis.
Ketoconazole, Lamisil, sulfur-salicylic and naphthalene ointments are also used for medicinal purposes.
Treatment of acute inflammatory response
An acute inflammatory reaction with seborrhea on the face requires rapid relief of unpleasant symptoms, so the course of treatment includes:
- antiallergic drugs, such as Loratadine;
- NSAIDs, such as Indomethacin;
- corticosteroids such as Dexamethasone and Akriderm;
- in some cases - antibiotics.
Complete elimination of the disease is possible only with comprehensive treatment and adherence to a gentle diet. At the discretion and with the permission of the attending physician, therapy is supplemented with traditional medicine and physiotherapy (after the symptoms have subsided).
Traditional recipes for seborrhea on the face
Traditional recipes for the treatment of seborrhea on the face and scalp are designed to normalize the secretory function of the sebaceous glands and restore the epithelium. The main components are often the following herbs:
- series;
- plantain;
- chamomile;
- St. John's wort;
- nettle;
- burdock;
- sea buckthorn;
- viburnum.
Also used in home remedies are sea salt, castor oil, kefir, whey, and apple cider vinegar. Here are a few recipes:
- Gauze wipes are moistened in whey and applied to the affected areas for 1 hour twice a day. After the procedure, the face is thoroughly washed. Kefir is used in the same way;
- Every morning, wipe the skin with the following mixture: add 150 g of vermouth and 100 g of crushed horseradish root to 300 g of vinegar. The infusion is kept for a week and stored in a cool place;
- Based on the above herbs, infusions are made at the rate of one tablespoon per glass of boiling water. Rinse hair with infusion or use it as a tonic and facial compress;
- Make a mask from one fresh cucumber and a tablespoon of honey. The mixture is kept on the face for 10-15 minutes, after which it is washed off;
- Sea salt is used as a scrub, which is used to massage the scalp and face. In this way, it is possible to gently exfoliate dead skin and “dry” excess sebum.
Home remedies cannot replace basic treatment, and independent “therapy” provokes the development of complications. Therefore, the use of traditional recipes must be agreed with a doctor.
What are the ointments and creams for seborrheic dermatitis?
External remedies for eliminating the symptoms of the disease differ depending on the composition, principle of action and effectiveness. The most popular are medications based on zinc and salicylic acid, but they are not prescribed for advanced forms of the disease.
There are also hormonal and non-hormonal creams and ointments. The former are considered the most effective and are used for chronic forms of pathology with severe symptoms and regular relapses.
In addition, products with antibacterial and antifungal effects are produced, as well as medications with restorative and preventive properties. Many drugs are used to treat lesions not only on the face, but also on the scalp.
It is worth noting that each group of drugs is selected taking into account the degree and prevalence of the disease, associated disorders and the characteristics of the patient’s body.
Diet
The condition of the skin directly depends on the diet. Therefore, another step on the path to recovery is to follow a diet plan that includes:
- refusal of “fast” carbohydrates;
- minimizing salted, smoked, fried foods in the diet;
- refusal of spices, spices, alcohol.
In the treatment of skin diseases, including seborrhea on the face, it is important to normalize digestive function, as well as daily bowel movements to effectively cleanse the body of toxins.
For seborrheic dermatitis, emphasis is placed on the use of:
- dairy and fermented milk products;
- soups;
- vegetables;
- steamed fish, lean meat;
- foods rich in fiber;
- rye bread.
Doctors also recommend eating small meals and having “fasting” days once a week. "Fasting" does not mean fasting. As an alternative, mono-diets, “unloading” on kefir, fruits or vegetables, are recommended.
It is very important to follow a hypoallergenic diet even after facial seborrhea has been cured.
Pros and cons of surface preparations
External use products have their advantages and disadvantages, which should be taken into account before starting a therapeutic course.
| Advantages | Flaws |
|
|
Despite the disadvantages, the products are actively used in the treatment of seborrheic dermatitis.
Prevention
Compliance with simple rules prevents the primary development of pathology and also reduces the possibility of relapse to a minimum:
- first of all, eliminate the factors that provoked the disease (treat pathologies of internal organs, avoid stressful situations);
- strictly follow a hypoallergenic diet;
- pay attention to skin care cosmetics;
- carefully observe the hygiene of the face and other “seborrheic” areas;
- observe a work and rest schedule in which walks and sea air are recommended.
The main thing in the treatment of facial seborrhea is to identify the primary source of the pathology. Only in this case will the doctor be able to draw up the correct therapeutic regimen to effectively solve the problem in a relatively short time.