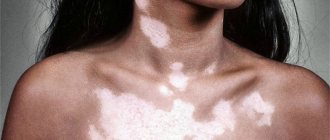
Chloasma - what is it?
The appearance of age spots on the face does not cause concern, itching or pain. Dark spots with clear boundaries behave like ordinary freckles - they fade in winter, become saturated with color by summer, require a thick foundation and do not create any problems other than aesthetic ones.
Having discovered chloasma on the face, a person strives to get rid of it; the appearance of unkempt aging skin does not decorate anyone. Expensive creams and whitening serums are used, but getting rid of chloasma is more difficult than whitening freckles.
Clinical manifestations and forms of pathology
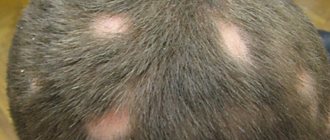
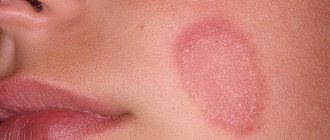
Melanosis, or in other words, skin hyperpigmentation, is characterized by the appearance of irregularly shaped brown spots that are flush with the skin surface and can merge with each other. They can affect both the face and body. On the face, such spots are most often localized in the forehead, cheeks, eyes, around the lips, and on the bridge of the nose.
These formations are not painful, do not peel, do not itch, do not cause a burning sensation and are not associated with inflammatory reactions.
There are 2 forms of melasma:
- solar, formed as a result of irradiation by sunlight;
- hepatic, associated with functional liver disorders.
According to the localization of pigment spots, there is the following classification:
- centrofacial, associated with the appearance of spots in the center of the forehead, on the nose, near the upper lip, in the chin area;
- molar, which is characterized by the formation of pigmentation on the cheeks and wings of the nose;
- mandibular (the second name is mandibular), with spots located in the area of the corners of the lower jaw (sometimes they can appear in the neck and chest).
Based on their level of prevalence, they are classified as:
- epidermal, having the appearance of surface formations of a dark brown color with clear boundaries. They respond well to treatment;
- dermal - light brown spots with unclear boundaries, usually difficult to remove;
- mixed (epidermal-dermal), representing heterogeneous pigmentation with more or less colored areas. In the case when the pigment is located in the epidermis, the treatment will be simple, if in the dermal layer it will be complex;
- asymptomatic (occur in dark-skinned races and are detected only with the help of a special medical lamp).
According to their clinical course they are divided into:
- passing (disappearing on its own without medical treatment);
- persistent (spots decrease during treatment, but the disease remains, slowing down in progression).
Only an experienced and qualified doctor is able to accurately determine the type of pigmentation and identify the true cause of its formation!
Types of age spots
Causes
The reasons for its appearance do not lie on the surface of the skin; it is caused by malfunctions in the body. Indicating serious internal problems, chloasma cannot be treated until the underlying fault in the system is corrected.
Excessive and uneven concentration of melanin can be caused by hormonal disorders, metabolic problems, and excessive exposure to the scorching sun or in a solarium. The appearance of chloasma is a signal of a disruption in the functioning of some organ or system associated with metabolism or the production of hormones.
This fact is confirmed by the fact that chloasma often “decorates” pregnant women, patients with a diseased liver, taking hormonal medications, and patients with inflammation in the reproductive system.
Another common cause of age spots is parasites in the body. If the spots are localized on the lips and near the mouth, an urgent visit to the doctor is necessary.
Causes of the disease
The main reason for the development of this pathology is disruption of the hormonal system. For this reason, the disease occurs most often in women during pregnancy, since at this time there is an increased level of estrogen hormones in the blood. Chloasma also develops in people with pathologies of the reproductive system and kidney diseases.
After pregnancy, hyperpigmentation most often disappears without a trace, but in rare cases it remains forever. Pregnancy is one of the causes of chloasma, but the mechanisms of chloasma development in other cases and with other systemic pathologies are not entirely clear.
Experts name a large number of factors that can provoke the appearance of chloasma:
- pregnancy (most often);
- period of hormonal changes in the body (menopause, puberty, etc.)
- gynecological diseases;
- systemic pathological conditions;
- diseases of the liver and biliary tract;
- prolonged exposure to the sun and exposure to UV rays;
- long-term use of hormonal drugs;
- some infectious diseases (tuberculosis, malaria);
- exposure to chemicals on the skin when using household chemicals;
- the effect on the skin of essential oils and other ingredients contained in a cosmetic composition.
How it manifests itself
The medical description of this phenomenon is an area of skin with clear contours, on which there is increased pigmentation. The pigment melanin, which is responsible for skin color and tanning, begins to be produced in increased quantities, and a dark-colored spot of round or irregular shape appears on a specific area of the skin.
It does not protrude above the surface, does not sink, and does not remind of itself in anything other than color. The color of the spots resembles a dark tan, numerous spots are often connected by edges, the face looks uneven and unkempt.
Places where chloasma may appear:
- forehead;
- skin above the upper lip;
- cheeks;
- bridge of the nose;
- facial contour.
Another area stands out, typical only for girls: spots appear symmetrically around the mouth, including the nasolabial folds.
This also includes the pigment line, which runs through the forehead, cheek and goes to the side of the neck. This type of chloasma is an important early symptom of serious brain damage, in particular it is used to recognize Parkinson's disease.
The concept of chloasma
Every year the number of patients with melasma and chloasma increases.
Every year the number of patients seeking help from cosmetologists and dermatologists regarding the appearance of pigmentation on the face is increasing.
Experts pay special attention to this defect for the following reasons:
- skin cells called melanocytes, which produce the pigment melanin, can degenerate into an insidious malignant tumor;
- Benign hyperpigmentation does not affect health, but serves as a strong irritant that can lead to serious psychological personality disorders.
There is no precisely formulated concept of what chloasma is. It is one of the types of melanosis acquired during life, characterized by excessive pigmentation of limited areas of the skin due to excessive production of melanin pigment by cells.
The number of women suffering from this pathology is much higher than men. The age range of patients is 20 – 50 years.
Diagnostics
Dermatologists quickly diagnose chloasma. Inspecting the stain is enough. Having clarified the situation and time of appearance, the doctor rules out moles and darkening of the skin after injuries, abrasions, and burns.
Chloasma must be differentiated from other types of pigmentation:
- Mongolian spot;
- secondary hyperpigmentation;
- occupational melasma;
- borderline and giant pigmented nevi.
When identifying chloasma, examinations are divided into two directions:
- Siascopy (examination of spots with a scanner in detail, allows you to notice malignant changes at the earliest stages) and dermatoscopy (examination using high magnification). These studies allow us to understand the degree of pigmentation, depth and prescribe appropriate treatment for this cosmetic defect.
- Chloasma is a symptom of hidden diseases, so patients are given a referral for examination of internal organs. Without their recovery, chloasma will return.
Diagnosis of chloasma
The task of a dermatologist is to differentiate the disease from other skin diseases associated with excess melanin in the cells of the epidermis and dermis. These include:
- lentigo;
- Becker's nevus;
- pseudoleukoderma;
- pityriasis versicolor;
- cutaneous lymphoma;
- drug-induced melasma;
- pellagra;
- melanoma skin cancer;
- pigmentation associated with injuries and burns.
To make a clear diagnosis, a dermatologist examines pigmented spots under a Wood's filter. This is a diagnostic device that emits ultraviolet rays in the long spectrum. The examination allows you to determine the histological type of the disease:
- Epidermal type. Foci of pigmentation are located in the upper layer - the epidermis, and under fluorescent lighting they give a sharp contrast.
- Dermal type. Under the lamp, the foci of pigmentation do not contrast, as they are covered by areas of healthy skin. This type occurs when melanin is captured by blood macrophages and transported to the deeper layers of the skin.
- Mixed type. In the filter field, the doctor detects contrasting and non-contrasting areas; melanin is located both in the epidermis and in the dermal layer of the skin.
The choice of treatment tactics depends on the type of chloasma. The epidermal type is most amenable to correction.
For a more accurate diagnosis, patients undergo additional studies that show the condition of the liver, gastrointestinal tract organs, identify inflammatory diseases of the reproductive organs in women and assess the state of hormonal levels. Treatment of chloasma sometimes requires the efforts of several specialists: a dermatologist, gynecologist, gastroenterologist and endocrinologist.
How to remove chloasma on the face
Successful treatment of chloasma is possible after an accurate diagnosis of the diseases that caused it. Once metabolism and hormonal balance are restored, pigmentation of areas of the skin becomes a cosmetic problem that can be easily corrected. For successful recovery you need to follow several rules:
- avoid being in bright sun;
- use sunscreen;
- take vitamins prescribed by the doctor: aevit, folic acid, methionine, riboflavin, injections of B vitamins.
- stop visiting the solarium;
- Avoid using essential oils in cosmetics; they increase sensitivity to the sun and cause pigmentation.
Methods of cosmetic facial correction
A visit to a cosmetologist gives lasting results in the treatment of hyperpigmentation on the face. The work of a cosmetologist on chloasma comes down to the following actions:
- Protection from direct sun exposure. For this purpose, suitable protective equipment is selected for the patient.
- Removing the layer of dead cells. Thus, some of the dark cells are mechanically removed and the spots become lighter. The skin begins to renew itself more actively, and the stain gradually disappears.
- Suppression of melanin production in certain areas. For this, whitening cosmetics with traditional and modern components are used: acids, plant extracts, omega-3 and others.
In addition to cosmetics, hardware procedures are used for correction: dermabrasion, laser corrections, massages, injections.
Medicines
Drugs prescribed for the treatment of chloasma require careful adherence to instructions, dosages and specialist supervision. Overdosing or increasing the time of procedures can lead to the opposite effect: the skin in the affected area will be excessively whitened, and this area will also stand out on the face. In addition, in some cases, actively targeting melasma can cause increased melanin production, causing the spot to darken even more.
To control the production of melanin, doctors prescribe vitamins that affect its production and excretion:
- The essential amino acid methionine effectively lightens chloasma. It is prescribed three times a day, 0.5 g.
- Ascorbic acid, when applied to the skin, easily penetrates the external barrier, stops the formation of melanin, promotes active collagen production and whitens the skin. To enhance the effect, ascorbic acid is prescribed for oral administration.
- Folic acid (vitamin B9) has a beneficial effect on the skin. Among its many beneficial properties is the ability to create invisible protection against UV radiation. Take 0.1 g per day.
- Skinoren cream not only solves the problem of excess pigmentation, it cleanses the skin of inflammation and helps remove traces of acne. The active ingredient of the cream is azelaic acid. It suppresses the development of excess melanocytes, making them non-viable. To get rid of pigmentation, a course of about three months is required. A 2.5 cm strip of cream is enough to apply to the entire face.
Which doctors should I contact for this problem?
Skin problems are dealt with by specialists - dermatologists. You can also start treatment by making an appointment with a therapist, who will write a referral to a dermatologist and specialists in major chronic diseases. Based on the test results and taking into account your medical history, you can receive a referral to a gastroenterologist, gynecologist, oncologist, neurologist and other specialized specialists.
Prevention of chloasma
Prevention of the disease consists of identifying the causes of chloasma and adopting subsequent treatment tactics. During the course of treatment, some restrictions should be observed:
- do not sunbathe in the sun or in a solarium;
- do not allow direct sunlight to hit the spots;
- use natural sun protection: hats, glasses, umbrellas;
- use sunscreen with a high SPF of at least 50;
- protect the skin from overheating and temperature changes;
- Take a break from cosmetic and other procedures during the course of treatment.
Treatment at home
Considerable experience in the treatment of chloasma has been accumulated in folk medicine. Various methods of topical whitening are often quite effective in combating blemishes on the face. Lotions and poultices, that is, masks and compresses, are made in courses for several days in a row, observing the changes.
Face masks
- Hydrogen peroxide is mixed with brewer's yeast and ammonia in a ratio of 2:1:1, applied pointwise to the stains, and left for no more than a quarter of an hour.
- Add half a teaspoon of honey and lemon juice to a tablespoon of mashed parsley. Apply to the entire face for 20 minutes. This mixture whitens, nourishes and tones the skin, and has a pronounced effect on aged and tired skin.
- Kefir, yogurt, sour cream, and acidophilus have excellent skin whitening properties. For ease of application and protection from rapid drying, the fermented milk product can be mixed with oatmeal, which will gently exfoliate the top layer.
Lotions, Compresses
If the mask is prepared for one time, the whitening lotion can be prepared for several days in a row. Wipe the skin with a cotton pad with lotion twice a day.
For intensive use, take a cotton pad or gauze, fold it several times, soak it with a useful composition and apply it to problem areas. Cover the top with a film and a dry cloth to retain heat and have an effective effect.
- a mixture of apple cider vinegar and water 1:1;
- cucumber lotion: the juice of one cucumber is mixed with the juice of half a lemon.
Melasma treatment
Cozy site about healthSkin rash 20 photos and reasons
If it has been possible to establish what factors provoked the appearance of melasma, then it is necessary to exclude them to prevent further spread and worsening of hyperpigmentation.
External means
With a mild degree of the disease, when the spots on the skin are single and light, sometimes even barely noticeable, and small in size, external remedies help get rid of them. Peels and scrubs with acids are used, as well as creams and masks containing whitening components (arbutin, thymol, kojic acid, etc.). Many women faced with this problem also use traditional whitening remedies: milk, kefir and other fermented milk products, masks with parsley, citrus, and cucumber juice.
More severe pigmentation requires a more serious approach to treatment, since cosmetic products will not be enough to get rid of melasma. Dermatologists prescribe external preparations that contain substances that inhibit the formation of melanin; they contain azelaic acid (skinoren, Azix-derm, Azelik, etc.) and hydroquinone. Treatment of melasma with such means is carried out for 2-3 months, in parallel, additional methods described above are used.
Hardware cosmetology
With dermal melasma, when pigment production is disrupted in the deeper layers of the skin, the use of external agents is usually ineffective. In such cases, laser therapy is recommended. Under the influence of laser radiation, selective destruction of cells containing an excess amount of pigment occurs. In addition, the procedure stimulates metabolism and regeneration of healthy tissue, which is why such manipulation is often called photorejuvenation. The number of procedures required depends on the depth of the skin lesion and the extent of the process.
Any procedures aimed at getting rid of melasma are recommended to be done in the autumn-winter period, when the activity of sunlight is minimal, since in this case the likelihood of secondary hyperpigmentation is lower.
Prevention
All people who are prone to the appearance of melasma are recommended to use cosmetics containing SPF of at least 30 (Sun Protect Filter - a filter to protect the skin from solar radiation). In summer, you should avoid exposure to the open sun during the period of maximum activity of UV rays; your face should be covered with a visor or hat brim. You will also have to refuse to visit the solarium.
Chloasma during pregnancy
Pigmentation increases during pregnancy; this is a normal phenomenon that should not be dealt with. The areolas and the line at the bottom of the abdomen darken, and freckles become more noticeable. Hormonal changes in the body working with double load provoke the appearance of melasma.
It is advisable for pregnant women to protect themselves from the sun, take vitamins on time, and consider a diet rich in sea fish, herbs, vegetables and fruits.
If spots do appear, they will disappear on their own 3-5 months after birth. If they do not go away, you should consult a doctor. Pigmentation can signal internal problems in the body; after pregnancy, it is especially important to check the proper functioning of the ovaries and thyroid gland; the functioning of these organs may change during pregnancy.
Symptoms
Chloasma on the face is expressed by increased pigmentation in a specific area. She has rather uneven contours
It is important to note that if this is really chloasma, it is flush with the skin and has no bulges. The color is different from natural, it becomes darker, each person has their own degree of coloring
In medical practice, there are 4 main types of color pathology:
- yellow;
- brown-brown;
- light brown;
- dark brown.
The exact size has not been established. In some cases, the diameter of pigmentation can reach 1 – 1.5 cm, and sometimes it can occupy more than half the face.
Pathology most often manifests itself in such areas of the face as:
- upper lip;
- forehead;
- bridge of the nose;
- cheeks.
In the area of the chin and eyelids, the disease occurs extremely rarely. It is also very rare to see age spots on the stomach, inner thighs and chest area. In most cases, their location is single, but there are times when several spots of different diameters appear in one area at once.
There are no special symptoms when a problem appears. This disease does not have such unpleasant sensations as itching or pain. Only psychological and aesthetic discomfort arises.
Scientists have identified a separate type of chloasma, which is called perioral. The question arises, what is it? These are pigment formations that are formed only in girls and women. They are located in the mouth area and have a dark brown tint. If the spots do not go away for a long time, they can affect the area of the nasolabial triangle.
In this pathology, there is also another phenomenon called “pigment line”. It appears on the face in the form of a stripe. Its width can range from a few millimeters to 1 cm. It passes, as a rule, across the entire surface of the forehead, sometimes it covers the cheek area and can go down to the neck. Why does such a line appear? The fact is that this may be a sign of problems with the central nervous system.
Typically this could be:
- meningovascular syphilis;
- a brain tumor;
- syringomyelia;
- Parkinson's disease.
Residents of countries in the Asian region quite often suffer from a disease called bronze chloasma. Its name comes from its appearance, as it has a bronze tint. Most often, this disease is observed in the indigenous population, but it is worth noting that the rest of the country’s inhabitants are not immune from the disease. In this territory, the disease appears in people randomly and disappears in the same way.
Causes and predisposing factors of melanosis
Melanin synthesis occurs in melanocytes (epidermal cells). I distinguish three types of pigment, the combination of which or the predominance of one of them is decisive in the color of hair and skin:
- eumelanin, which is brown and black in color;
- pheomelanin - red color;
- Leukomelanin is colorless.
Although melasma/chloasma is predominantly dark in color, its color and shades depend on the combination of certain types of melanin.
The processes of pigment synthesis and regulation of melanocyte function remain not entirely clear. However, it is assumed that the basis of the disorders is a genetic predisposition, which manifests itself in the presence of certain factors. It has been established that the genetic factor is triggered indirectly under the influence of ultraviolet radiation, contributing to an increase in the formation of free radicals. The latter increase the oxidation of fats, which can lead to damage to the DNA of melanocytes and accelerated redistribution of pigment along their processes into epidermal cells. In addition, UV rays themselves can also damage the DNA of cells.
The main predisposing factors include:
- Excessive UV exposure - 50-60%.
- Acute or chronic inflammatory processes and hormonal disorders that are not associated with pregnancy, including hormone-producing tumors and hormonal contraceptives (except for their use as replacement therapy during the menopausal period) -25-30%.
- Pregnancy - 18-25%.
In the second and third cases, hormonal dysfunctions are in one way or another associated with changes in the content of estrogen and progesterone in the body. Less significant factors are metabolic disorders in the body, disorders of the liver and pancreas, stomach and intestines, insufficient intake of vitamins and minerals, and improper use of cosmetics and procedures.
Chloasma
- pigment spots that occur during pregnancy and some diseases of the female genital area, helminthic infestations, etc. Chloasma can appear both on the face (forehead, cheeks, lips) and on the body (back, chest, legs, neck, etc.). The appearance of chloasma is associated with a disruption in the production of melanin pigment in the body.
According to etiology, there are chloasma of pregnant women, chloasma in gynecological diseases, hepatic chloasma, traumatic, etc. Chloasma of pregnant women
As a rule, it disappears on its own some time after birth and does not require special treatment.
Chloasma symptoms
Chloasma predominantly occurs on the forehead, near the mouth, upper lip, cheeks and nose. With hormonal problems, during pregnancy, age spots appear as stripes on the stomach, near the nipples on the chest, in the anus or on the inner thighs.
Education data:
- Have a brown or brownish color
- Do not rise above the skin
- Not accompanied by pain or itching
- Can be multiple
- Sometimes they disappear on their own after the root cause disappears
- Borders are clear but uneven
Treatment complex: how to get rid of chloasma?
Chloasma therapy is a common task for dermatologists and cosmetologists. The goals of the main treatment tactics are to reduce melanin synthesis and remove accumulated pigment.
In cases where chloasma is provoked by a somatic disease, primary treatment is aimed at eliminating it. Lightening pigment spots against the background of progressive pathology is useless and can lead to complications.
UV protection
Patients with chloasma need to regularly use photoprotective agents SPF 25-30, even on non-sunny days.
In cases where UV irradiation is the direct cause of chloasma, photodesensitizing drugs are used:
- Plaquenil;
- Delagil;
- Rezokhin;
- Hingamin.
The use of conventional cosmetics containing essential oils that increase sensitivity to solar radiation is excluded.
Reduced melanin production
This line of treatment uses external depigmenting agents in the form of ointments, creams and serums.
The active substances of these drugs are tyrosinase inhibitors and melanin synthesis inhibitors. Also the enzyme lignin peroxidase, which eliminates the formed pigment, but does not affect the production of melanin.
Active substances:
- kojic acid;
- salicylic acid;
- arbutin;
- azelaic acid;
- hydroquinone up to 2%;
- ions of copper, zinc, iron;
- retinoic acid 0.05%-0.1%;
- gentisic acid esters;
- N-acetylcysteine;
- 1-aminoethylphosphinic acid.
These components are mainly found in cosmeceutical products designed for pigmented skin.
The best results are achieved with a combination of bleaching agents. In this case, a synergistic effect is noted - mutual enhancement of the action of active substances. Therefore, creams for the treatment of chloasma rarely contain only one depigmenting component.
Creams based on extracts of bearberry, aloe, cucumber, lemon, mulberry roots and licorice work well to lighten shallow pigments.
The effectiveness of the product does not depend at all on the cost. The basis for effectiveness is the components they contain, correct and regular use. It is difficult to understand the huge number of offers on your own, so you need to select a product together with a dermatologist.
To treat age spots, medicinal ointments and pastes are used:
- zinc;
- salicylic;
- retinoic;
- sulfur.
Despite their effectiveness, the use of these products is somewhat inferior to dermatocosmetics creams. They are formulated for treatment purposes only and do not contain the moisturizing and photoprotective ingredients needed daily for pigmented skin.
Vitamins
A course of treatment with vitamins helps regulate the production and metabolism of melanin in the skin structures.
Appointed:
- folic acid;
- riboflavin;
- B vitamins;
- ascorbic acid.
Vitamins are used in the form of injection solutions.
Removing pigment from skin
It is possible to completely get rid of hyperpigmentation only after a course of professional cosmetic procedures.
Chemical peeling
This is a dermatologist-controlled method of burning the facial skin with acids in order to renew the damaged layer, along with which pigment spots are eliminated.
Acids are used to treat chloasma:
- glycolic;
- retinoic;
- carbolic acid;
- trichloroacetic acid (TCA);
- alpha hydroxy acids (AHA): phytic, mandelic;
- salicylic;
- pyruvic.
The number of procedures depends on the depth of the pigment spot and the characteristics of the skin. This can be one procedure or a course of 4-5 sessions with intervals between them of 1 month.
Cryotherapy
Cryotherapy is recommended for epidermal chloasma. This is a local effect on age spots with liquid nitrogen. Exposure to low temperatures leads to necrosis of pigmented cells and their subsequent exfoliation.
Depending on the severity of the pigment, several treatments may be needed to remove pigmentation at intervals of 3 weeks. This procedure is combined with the use of cosmetics that block tyrosinase or mesotherapy.
Microdermabrasion - hardware peeling
This is hardware resurfacing of the skin with microcrystals, which is considered one of the most gentle methods of mechanical peeling. The use of this method is recommended for hyperpigmentation of aging skin or in cases of combination with hyperkeratosis.
During the procedure, the stratum corneum of the skin is exfoliated, and accumulated melanin is eliminated along with it. To achieve the desired result, you will need 3-5 procedures.
Laser therapy
The effectiveness of this method in the treatment of chloasma is due to the ability of melanin cells to absorb the energy of a laser beam, which leads to their destruction.
Depending on the characteristics of pigment formations, the following methods can be used:
- laser resurfacing;
- fractional photothermolysis;
- exposure to short pulsed bursts.
To completely remove age spots, 1-3 procedures will be needed. The recovery period lasts up to 2 weeks.
Mesotherapy
This method of injection cosmetology is used to treat excessive melanin production and lighten already accumulated pigment. During the procedure, individually composed vitamin cocktails are administered intradermally.
Ingredients for the treatment of chloasma:
- vitamin C;
- emoxipin;
- placenta extract;
- linoleic, glycolic acids;
- multivitamin complexes.
The course of treatment is from 3 to 8 procedures at intervals of 7 days.
The choice of a specific procedure depends on individual contraindications, the depth of the pigment spot and the age characteristics of the skin.
How does the treatment work?
Patients who have had registered chloasma should try to spend as little time as possible in direct sunlight, and it is advisable to avoid solariums altogether for a while. It is necessary to carry out corrections in those systems where violations occurred.
First of all, it may be the hormonal system and metabolism of internal substances. In order to stabilize the functioning of the systems and the entire body as a whole, it is necessary to conduct a course of therapy. In this case, doctors most often prescribe vitamin therapy.
It includes:
- B vitamins;
- ascorbic acid;
- riboflavin;
- folic acid.
Hospital treatment with such drugs is not mandatory. You can undergo a course of treatment at home, but you just need to periodically visit your doctor so that he can see the dynamics of improvements.
It is worth noting that precise treatment methods have not yet been found. The treatment is based on cosmetic techniques. With their help, craftsmen lighten problem areas to the desired color. Also, using special tools, they help reduce the level of production of melanin cells in the body. And the exfoliation method removes dead skin in problem areas.
In order to reduce the formation of melanin in the body, you must take the following substances:
- inhibitors of pigment synthesis in melanocytes (including: hydroquinone, azelaic acid);
- tyrsinase inhibitors - arbutin, kojic acid;
- foods that contain vitamin C.
Almost all of the above products are toxic. But, despite this, when using them, the result becomes noticeable after a short amount of time. The above substances are components of many ointments and creams that have a whitening effect.
Often during pathology a number of peelings are used:
- phenylic;
- ANA;
- glycolic;
- TCA.
The following procedures are very effective:
- laser peeling;
- dermabrasion;
- cryotherapy.
The following can combat chloasma and many other pigmentary diseases:
- laser cosmetology;
- mesotherapy;
- photorejuvenation;
- cryo massage.
Each method must be repeated in order to achieve a good result. During pregnancy, treatment of this disease is prohibited. Since most substances are toxic, this can cause irreparable harm to the fetus.
After the birth of a child, as a rule, age spots disappear on their own. If this does not happen, then you should contact a specialist. If your baby is breastfed, be prepared for the fact that he will have to be switched to artificial nutrition.
Causes
The causes of chloasma can be quite varied. These are age spots that are acquired over time due to excess melanin deposition as a result of certain factors. Most often this is:
- Exposure to ultraviolet rays
- Pregnancy
- Climax
- Acne
- Liver dysfunction
- Tuberculosis
- Use of oral contraceptives
- Poor quality cosmetics
- Gynecological pathologies
- Age-related changes
- Hormonal imbalance