Causes of sweating, hyperhidrosis of the palms and feet
- First, it’s worth understanding the reasons for the appearance of excessive sweating in order to understand how it can be worked with and prevented in the future.
- There are actually many reasons, but the most common reason (in 90% of cases) is a high concentration of sweat glands in the body. Note that this is congenital, and is most often passed on from generation to generation.
- From which we can draw a certain conclusion - you were born this way, and it is impossible to completely cut it off from yourself. But you can solve the problem, and also help your children solve the problem, because most likely, either they or their children will have it
Causes of sweating, hyperhidrosis of the palms and feet
Sweating also depends on the psychological reaction to stress and other external stimuli, adolescence, as well as hormonal imbalance.
And one more thing: if you have never experienced sweating and are now taking medication, hyperhidrosis may be a reaction to the concentration of the drug in the body.
Video: Excessive sweating - hyperhidrosis
There are two types of hyperhidrosis:
- General. The cause may be high temperature, active physical activity, or an unusual emotional situation that causes fear, panic, and even euphoria. The reason may also be the dryness of the room, and the body is trying to “moisturize” itself.
- Localized. These are most often the palms, feet and large folds. The reason here is most often emotional, as well as congenital (the concentration of sweat glands in this part of the body)
What is hyperhidrosis?
Hyperhidrosis
is severe profuse sweating in men, women and children. As a rule, it serves to cool the body when overheated. If more moisture is released than necessary, then increased sweating occurs.
There is secondary hyperhidrosis
which occurs as a result of any disease. These could be infectious problems. In particular, tuberculosis, a number of tumor and endocrine diseases. As a rule, sweating of the whole body occurs. Very often it appears at night.
There is also primary hyperhidrosis
- this is already a congenital pathology. That is, people are already born with such a disease.
According to localization, hyperhidrosis occurs:
- General
- severe sweating of the whole body - Local
- profuse sweating only in certain areas of the body (armpits, feet, palms, etc.)
The limit of normal sweating is where the sweat itself causes discomfort to a person. Therefore, you can’t say for sure here. For some, a little sweating may create discomfort. And someone can walk until all their clothes are wet.
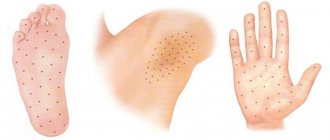
The sweat glands themselves are located throughout the surface of our body. The largest number of them are located in the forehead, armpits, palms, crotches and soles of the feet.
There are two types of sweat glands:
- Eccrine
- function from birth and are involved in thermoregulation of the body. - Apocrine
- develops during puberty. They do not take part in thermoregulation. They are activated only in a stressful situation and give sweat a characteristic odor.
Sweat glands of the armpits
Sweating centers are located in the hypothalamus, medulla oblongata and spinal cord. It is when they are irritated that a signal is sent to the sweat glands, which become activated, increasing sweating.
Hyperhidrosis is often localized in the armpit areas. About 2% of the population suffers from armpit sweating. Moreover, this is not the kind of sweating that regular antiperspirants help with. You can try hundreds of similar drugs, but still nothing will help.
In second place was sweating of the palms. After this comes hyperhidrosis of the legs. As a rule, these conditions are combined with each other.
How to deal with hyperhidrosis of the palms and feet?
How to deal with hyperhidrosis of the palms
We live in a society, and as soon as a child begins to attend a child care facility, until his very last breath in old age, he must say hello by shaking hands, hug when meeting, and also take off his shoes when visiting, etc.
Sweating of the feet and hands causes a lot of difficulties and even complexes. But we live in the age of nanotechnology, and we can certainly cope with such a difficulty!
When is hyperhidrosis treatment effective?
We currently have several treatment methods:
- Folk remedies
- Tablets and ointments
- Botox injections
- Surgical intervention
First of all, we would not recommend self-medication, especially if sweating began in adulthood.
- The doctor, unlike you, will analyze the situation in detail, take all the necessary tests and tell you how serious the situation is and what measures should be taken
- Many people perceive traditional methods as a panacea, and doctors as a species trying to prescribe chemistry. Don’t worry, if there are no significant reasons, the doctor himself will advise you on a folk remedy that has been proven over the years
- But if you look at a hormonal imbalance or other disorder of the body, despite the fact that it so actively “signaled” with the help of sweat, time may be irretrievably lost
Hyperhidrosis, which doctor should I consult?
Some may be concerned about this question, and if you have hyperhidrosis, which doctor should you contact? Usually people turn to their local doctor (general practitioner) for help. In principle, correct!
Moreover, he will immediately give directions for examinations. For example, take the necessary tests or x-rays. And this is also important!
So first of all, make an appointment with a therapist. And then you will look at the circumstances. Naturally, after research, the doctor can write out referrals for examination by other specialists.
Agree!
You need to understand that increased hyperhidrosis does not occur out of nowhere. Everything here is interconnected. Therefore, you will have to visit several specialists for examination. You won't be able to get by with just one therapist.
Next you will be asked to visit the following doctors:
- cardiologist
- narcologist
- endocrinologist
- phthisiatrician
- infectious disease specialist
- dermatologist
But nevertheless, there are 3 main specialists on this particular disease. This is a dermatologist, neurologist and surgeon. Therefore, be sure to undergo additional examination by these doctors.
Folk remedies for sweating and hyperhidrosis
This disease can be treated both by taking the medicine internally and externally. But the best way is to combine.
Traditional methods of hyperhidrosis
For indoor use:
- Tea with lemon balm (not to be confused with mint) reduces sweating, especially in the palms of the hands.
- Another recipe: pour 2 tablespoons of sage into a glass (200 g) of boiling water in a thermos and let it brew for half an hour. Drink 60-70 grams of infusion 2-4 times a day. It is best to brew daily, but can be stored in the refrigerator for up to 3 days. Take no more than 2-3 weeks, as sage contains a substance - thujone, which, when accumulated, causes cancer
Video: Excessive Sweating of Hands, Feet and Armpits. How to fight hyperhidrosis? EXPERT Speaks
For external use:
- It is advisable to supplement the internal use of lemon balm with medicinal mint baths. Can also be combined with walnut, chamomile, sage, and beech leaves
- If you want to strengthen blood vessels, reduce sweating and improve skin health, take baths with oak bark. Pour a liter of boiling water over a pack (100 g) and cook over low heat for half an hour, then pour into the bath and take immediately. You can have a general bath, or you can have a local one
- Crushed oak bark is poured with boiling water until it just covers the bark and infused for 15 minutes. Pour into gloves and socks and wear throughout the night. In the morning, wash off with cool water. Please note that oak can stain clothing and bedding. Therefore, these days, do not make new bedding and do not wear clothes that you would be sorry to throw away.
- Potato starch can also be poured into gloves and socks at night. The advantage of this method is that it leaves no traces
- Baths with ammonia at the rate of 1 teaspoon per liter of water. Keep your hands in warm water for 10 minutes, then rinse everything off with cool water, blot dry with a paper towel and powder with talcum powder.
- Squeeze lemon juice into a spray bottle, twist tightly and spray your hands several times a day and whenever they start to sweat. Antiseptic bottles, which can be purchased in every supermarket, are well suited for this role.
- Lemon juice is an excellent substitute for wine or apple cider vinegar. But here you should be careful and dilute with water 1/1 or even 1/3 where 3 parts are water
- Another method: infusion of birch buds with vodka. Press the buds tightly into a glass bottle, fill to the top with vodka, and leave in a dark place. Wipe your palms and soles 1-2 times a day
- In summer, beer baths help with excessive sweating, but the beer must be live and not powder
Prevention and treatment
Diagnosis of excessive sweating begins with a visit to the pediatrician and dermatologist. The doctor writes out a referral for blood tests (general, sugar levels, hormones) and urine. If necessary, ultrasound, x-ray, ECG and additional consultation with specialists - endocrinologist, cardiologist, infectious disease specialist - are prescribed. To treat excessive sweating, sedatives, vitamin-mineral complexes, immunomodulators, and, if necessary, exercise therapy and electrophoresis are prescribed.
Compliance with preventive measures will help avoid or speed up the treatment process, these include:
- mandatory scheduled visits to the pediatrician;
- daily air baths;
- morning and evening water procedures;
- taking baths with chamomile, oak bark, string;
- wear loose-fitting clothes made of soft, natural materials;
- use of hypoallergenic laundry detergents;
- excluding fatty, spicy and salty foods from the diet, limiting sweets;
- maintaining temperature and humidity in rooms;
- maintaining a calm environment in the family, excluding nervous shocks.
Tablets and remedies for sweating, hyperhidrosis of the palms and feet
This chapter will focus on over-the-counter medications, but this does not mean that they can be purchased without consulting a doctor. Remember, in treatment it is important not only to get results, but also not to cause harm.
Foot wipes for hyperhidrosis
Formidron . The active ingredient is formaldehyde; in addition to it, the preparation contains alcohol and cologne. Our parents fell in love with this medicine in Soviet times; pharmaceuticals never offered a worthy alternative for price/quality. Using a tampon, it is necessary to apply to problem areas for 2-3 weeks at night, but you can extend the course if necessary.
Formidron
Formagel . Currently, doctors recommend this drug as the most highly effective and containing the maximum amount of formaldehyde. This is a colorless gel that can be used for a long time. According to clinical studies, it is worth using the drug for one day and sweating will decrease for 1-3 weeks. It is recommended for use on the palms, armpits and feet.
Formagel
Teymur's paste . The proven remedy, however, is very inconvenient. You need to use it 2 times a day, it stains clothes and bedding. As soon as other medications and ointments appeared, the paste immediately became less and less attractive.
Teymurova paste
Sedatives . If the cause of hyperhidrosis lies in the psychological state of a person, then first of all it is necessary to eliminate the cause, and in parallel with this, other medications can be prescribed. Tranquilizers are most often prescribed, but it is worth remembering that they are persistently addictive.
Sedatives in the treatment of hyperhidrosis
Herbal preparations . Preparations based on belladonna alkaloids are also very common in the treatment of excessive sweating. The most common of them are Belloid, Bellaspon and Bellataminal. Please note that herbal tablets are not addictive.
Herbal preparations for the treatment of hyperhidrosis
Diagnosis of hyperhidrosis
Diagnosing hyperhidrosis is not that difficult. However, she always requires medical supervision. As for local sweating, diagnostic criteria are highlighted.
The most important of them is the absence of sweating at night. Also, this is symmetrical sweating, a connection with anxiety, the presence of sweating in parents, and so on.
With the presence of such criteria, the doctor will clearly make a diagnosis. Plus, this is the duration of the illness. At least six months. And it mostly starts between the ages of 15 and 25.
If sweating develops after 45 years, then doctors usually ask themselves a question, since this is not typical for hyperhidrosis.
But fortunately there are specialized centers
who study this disease in depth. I recommend contacting them.
Treatment of hyperhidrosis of the palms and feet with Botox
In the event that doctors have tried all medicinal and traditional methods of treatment with the patient and have not achieved the desired result, the doctor may offer another treatment option - Botox or Dysport.
The mechanism of action is intradermal administration of a drug that blocks the transmission of impulses from nerve endings to the sweat glands, thus fundamentally combating the problem of sweating.
Treatment of hyperhidrosis of the palms and feet with Botox
The method is truly effective, and 100% effective, but the method has a lot of contraindications and complications. Therefore, it is necessary to agree to it only in extreme cases. Also, the method is not permanent and will have to be repeated every 6 months.
Video: Botox for sweaty hands
Diagnostics
To determine hyperhidrosis, perform the Minor test . In case of severe sweating of the hands, problem areas are treated with iodine and the product is left until it is completely dry. Then the palms should be treated with starch and left for some time.
The interaction of these substances under the influence of moisture leads to the appearance of a darker shade. Depending on the severity and area of hand staining, a specialist will be able to determine the degree of hyperhidrosis.
Hyperhidrosis of the palms and feet in a child
Local hyperhidrosis of the palms and feet in children does not appear often and has not been fully studied by medicine. Until now, no doctor can say for sure the reasons for the appearance.
But this does not mean at all that you should not treat this with the utmost care and expect that it will go away on its own. As soon as you notice regularly wet palms or wet socks on your child, while the child is dressed for the weather and the temperature outside is comfortable for the body (not hot summer), you can immediately consult a doctor.
Hyperhidrosis of the palms and feet in a child
A doctor, usually a dermatologist, must order a series of tests to rule out disorders in the body, and then prescribe appropriate treatment.
If the problem appeared in childhood and was not resolved, there is no point in relying on successful treatment in adulthood. Love your children and treat them as soon as you notice the disease.
Video: Hyperhidrosis in a child
Botulinum toxin for hyperhidrosis
Botox is a widely known means of preserving youth. Another way to use it is to reduce excessive sweating.
Correction with botulinum toxin involves injecting the substance into the problem area. The action of the drug blocks impulses and eliminates the effect of hyperhidrosis. The duration of exposure is up to 10 months.
Features of the effects and benefits of Botox injections
Medications for the treatment of excessive sweating of the armpits include botulinum toxin type A, which is a strong poison of organic origin. In small doses it is safe for the body - it is used to block nerve and muscle impulses.
When Botox is injected under the skin, impulses from sweating fibers are not transmitted to the glands - hyperhidrosis stops. At the same time, heat and water exchange of the skin is not disturbed.
Treatment with this method is effective in the second and third stages of the disease, when severe sweating is observed due to nervous tension, discomfort in communication, or a person has constant sweating and wet clothes under the arms. During the first stage, it is recommended to use aluminum chloride antiperspirants that block the sweat glands for a period of 3 to 4 days.
Among the advantages:
- long-lasting effect, lasting up to 10-12 months;
- safety of injections provided the correct injection technique is used;
- short recovery period.
Treatment technique with botulinum toxin
No preparation is required for the procedure. To eliminate pain, a local anesthetic is applied to the skin. The composition is injected to a depth of 2 to 3 mm. Together with Minor's test, the procedure takes from 40 to 60 minutes.
Post-procedure care
After the session, slight swelling, redness and nodules are observed in the armpit area, which disappear after 3-4 days. Botulinum toxin begins to act on the 4th day, the final result will be visible after 2 weeks and lasts for 10-12 months, it depends on the characteristics of the body. Then the treatment must be repeated. Each time the amount of the drug decreases, and the duration of exposure increases.
Recommendations for care after the procedure:
- for three days, massage, which reduces the effectiveness of the product, and the use of antiperspirants are contraindicated;
- For seven days it is not recommended to visit the bathhouse, swimming pool, actively engage in sports or drink alcohol.
Hyperhidrosis of the palms and feet: View reviews
Kirill: For as long as I can remember, I hated the “man’s handshake” because my hands were wet and sticky. My parents complained, but my grandmothers convinced them that it was temporary and would go away as soon as I grew up. It’s gone because I inject Botox every six months. Other methods are not effective, because the disease is advanced. My advice is if your body is sweaty for more than a week, see a doctor. It is better to hear that you are an abnormal parent than to start the disease.
Natalya: after giving birth I started sweating a lot, nothing helped. I went to the hospital and was diagnosed with a hormonal imbalance with hyperhidrosis. They prescribed pills and baths with oak bark decoctions, tea with lemon balm, and so on. It all happened in 2 months. Here, the sooner you apply, the more gentle the treatment will be.
Hyperhidrosis in children
Young children are no less susceptible to hyperhidrosis than adults. It should be taken into account that before reaching the age of 6 years, the sweating system is just being formed. Afterwards, the sweat glands begin to work stably, and are more similar to the system of an adult. A child’s sweat glands begin to function from 3-4 weeks of life; their work is unstable and may respond inadequately to temperature changes. At the age of three, children sweat a lot during sleep and while eating, which is the norm - the body removes excess heat outside, protecting itself from overheating.
A child's body is well adapted to environmental temperature conditions; a temperature of 18-22 degrees is comfortable for walking in a regular T-shirt. An adult at the same temperature can feel cool and dress a child according to his feelings. When overheated, the body sweats to compensate for excess clothing.
A large number of natural factors can explain a child’s severe sweating, but if signs of hyperhidrosis occur frequently, it is worth consulting with a specialist.
Types and reasons for the development of this condition
Hyperhidrosis of the extremities is divided into primary and secondary. The latter is said if increased sweating is caused by a disease or pathological condition of the patient. The reasons for the appearance of secondary are as follows:
- infectious diseases (tuberculosis, malaria);
- taking certain medications;
- pregnancy;
- genetic disorders (cystic fibrosis, etc.);
- menopause;
- hormonal imbalances;
- Hodgkin's disease;
- diseases associated with metabolic disorders (thyrotoxicosis, diabetes mellitus, hypoglycemia, pheochromocytoma);
- neurological disorders (Parkinson's disease, neurosyphilis), etc.
Excessive sweating is often associated with a psycho-emotional state, nervous tension, and constant stress.
As for primary hyperhidrosis, its appearance is caused by high activity of the sympathetic nervous system. There are other classifications of this disease. The disease is divided into:
- diffuse (or generalized), in which increased sweating is a symptom of another disease;
- limited (or local), in which certain areas of the body suffer (hyperhidrosis of the face, feet, palms, armpits, etc.).
Fact! It has been proven that about 2% of people worldwide suffer from excessive sweating.
Excessive hand sweating may be associated with certain diseases
reading information
Causes
Doctors have not yet established the exact causes of the pathology. Heavy sweating occurs with increased activity of the sympathetic system. Factors that provoke improper functioning of the sweat glands have been identified.
Most often, excess sweat is caused by:
- disruptions in water-salt metabolism;
- endocrine diseases;
- heavy physical activity;
- excitement, stress;
- pathologies of the nervous system;
- spicy, hot food;
- obesity, diabetes;
- diseases of the kidneys, heart, blood vessels;
- improper functioning of the thyroid gland.
Note! Night sweats are one of the signs of tuberculosis.
Types of hyperhidrosis:
- primary. About 1% of the population suffers from the pathology. The main category of patients is people 15–35 years old;
- secondary. Appears after a neurological disease.
Treatment
If you experience excessive sweating of your feet and hands, you should consult a doctor.
Remember. Today there are many ways to combat this condition. The doctor will help identify the root cause of the pathological process and prescribe an appropriate course of treatment.
Different doctors treat foot hyperhidrosis. To exclude fungal diseases and anatomical defects of the legs, consultation with a dermatologist is necessary. If excessive sweating of the feet is associated with a psycho-emotional state, you should contact a neurologist. To exclude pathological disorders of the endocrine glands, you will need the help of an endocrinologist. Each case is individual.
Often, increased sweating of the feet occurs in men and women due to wearing tight or poor-quality shoes
To treat hyperhidrosis of the legs and arms, the following means and methods are used:
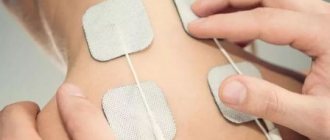
- Iontophoresis. This physiotherapeutic procedure is performed by exposing the limbs to an electric current with an ionizing substance. The patient places his feet or palms in special containers of water, and the device generates a weak electric current. The procedure lasts no more than 40 minutes. The course of treatment is 7-10 days. The duration of the effect can be up to six months.
Fact! Iontophoresis is the most effective treatment for hyperhidrosis of the feet and palms. According to medical statistics, physiotherapy helps in 80% of cases.
- Ointments, antiperspirants. These drugs reduce sweating and eliminate unpleasant odor by blocking the excretory ducts of the sweat glands. The most effective are those that contain aluminum chloride.
- Botulinum toxin, or botulinum toxin type A (Botox). Botox subcutaneous injections are used to treat hyperhidrosis of the legs and armpits. The drug disrupts the functioning of the glands responsible for sweating by blocking their nerve endings. The patient's sweating decreases after a few weeks. The blocking effect can last up to a year.
If none of the listed methods for treating limb hyperhidrosis help, patients may be prescribed surgery to block nerve pathways or remove sweat glands (endoscopic sympathectomy, curettage, etc.).
On pharmacy shelves you can find many products to reduce sweating and eliminate odor. However, the effectiveness of such drugs is very low.
How to reduce sweaty feet
Let's talk about how to reduce sweaty feet. In general, hyperhidrosis of the feet is an indication for iontophoresis.
Moreover, when sweating palms, treatment with Botox and sympathectomy is widely used. However, with hyperhidrosis of the legs, sympathectomy is difficult. Especially for obese people. And the use of bolotoxins requires a lot of money.
In this case, iontophoresis is the main treatment method. It is done in the same way as for excessive sweating of the palms. The difference is that the current level here will be much higher. Approximately 20% higher.
Foot hyperhidrosis is not so obvious to the patient and those around him. Unlike the palms, a person’s feet are closed and are not publicly displayed.
But still, for the patient, all this poses significant problems. This includes damage to shoes, smell, various abrasions, and so on.
Unfortunately, the iontophoresis method does not guarantee a 100% result. However, with moderate or moderate sweating, the likelihood of results will be high. About 70 - 80%.
Folk recipes
Excessive sweating of the feet and palms in men and women can be combated at home. Traditional healers recommend:
- make medicinal baths for limbs based on lemon juice, oak bark or apple cider vinegar;
- for general hyperhidrosis, take warm baths with mint, chamomile infusion and sage;
- for foot hyperhidrosis, wear socks filled with crushed oak bark at night;
- wipe your palms and feet with lemon juice several times a day, etc.
Hyperhidrosis of the extremities cannot be cured using folk methods alone. Baths, herbal applications, decoctions and compresses are effective only in combination with traditional treatment.
reading information
What is hyperhidrosis of the head, limbs, armpits
To correctly answer the question “What is hyperhidrosis,” you need to familiarize yourself in detail with the localization of the disease. If the area of the scalp and facial area suffers (cranial-facial hyperhidrosis), then you probably have several wet handkerchiefs in your pocket, a sweaty face, damp hair, and streams running down your neck. Sensitive skin on the face, under the influence of irritating secretions, quickly becomes covered with unpresentable-looking and itchy red spots.
At the end of the day, do you feel an unpleasant “squelching” in your shoes, an unpleasant odor emanates from your feet, your socks become wet in the evening, the skin of your lower extremities itches and traces of fungal activity are visible? Most likely, the doctor will diagnose “Hyperhidrosis of the feet.” What palmar hyperhidrosis is is known for certain by those people who are reluctant to extend their hand for a handshake, leave stains on the paper when leafing through documents, and drop writing instruments due to wet, slippery fingers and palms.
Ugly stains on clothes in the armpit area can ruin even a perfectly chosen look. What can we say about the terrible smell, discomfort and emotional instability caused by such a cosmetic defect? All these are signs of axillary hyperhidrosis.
Preventive measures to reduce excessive sweating
To reduce the manifestation of hyperhidrosis, doctors recommend following simple rules:
- observe the rules of personal hygiene;
- eat right, exclude coffee, alcohol, fast food, etc. from your daily diet;
- wear comfortable clothes and shoes made of natural fabrics and materials (linen, cotton, silk, etc.).
There are many ways to treat hyperhidrosis of the extremities, the main thing is to identify the root cause of the pathology, and then deal with unpleasant symptoms.
Source
Is hyperhidrosis dangerous, how to treat it with medications, ointments and traditional medicine.
Secondary causes of hyperhidrosis
Fever and chronic infection
Malaria, tuberculosis, brucellosis, subacute bacterial endocarditis can manifest as fever and generalized hyperhidrosis. Under the influence of bacterial substances, cytotoxins are released, which act not only as hormones, but also as internal modulators in the brain. This raises the set-point temperature (causing fever) and simultaneously stimulates the mechanisms that cause episodes of heavy sweating.
Metabolic and systemic diseases
Severe sweating has been reported in diabetes mellitus, hypoglycemia, congestive heart failure, hyperpituitarism, dumping syndrome, carcinoid syndrome, and drug withdrawal. Sweating increases (especially in men) with acromegaly, because... the size of the sweat glands, their innervation is more pronounced than in the control group.
Hyperhidrosis and malignant diseases
Hodgkin's disease is characterized by a triad of symptoms: fever, sweating and weight loss. Night sweats may be the only symptom, and 31 out of 100 patients may have symptoms of B-cell disease (fever, weight loss, sweating). The pathogenesis of the disease consists in the release of a huge amount of prostaglandins by interleukins, which act on the anterior part of the hypothalamus, causing an increase in the “set” temperature.
The symptomatic triad includes excessive and inadequate paroxysmal sweating, tachycardia, pulsating headaches associated with increased blood pressure.
Alba- and beta-antiadrenergic therapy is the mainstay of treatment for this disease; in very rare cases, sweat gland necrosis develops as a result of preoperative therapy.
Generalized hyperhidrosis caused by drugs/toxins
Hyperhidrosis is often associated with inhibition of serotonin reuptake by prostaglandin inhibitors. Serotonin syndrome and neuroleptic malignant syndrome include increased body temperature, fluctuations in blood pressure, hyperhidrosis, a state of nervous agitation and confusion.
Hyperhidrosis, which often occurs with acute or chronic use of opioids, develops as a result of the release (degranulation) of histamine by mast cells.
Modern statistics say that 45% of patients experience profuse sweating when using methadone.
Sweating in combination with high blood pressure, nausea, mydriasis (dilated pupils) is characteristic of alcohol withdrawal (a sharp decrease or complete cessation of alcohol).
Some drugs that can cause hyperhidrosis
| Drug class | Examples | Probable mechanisms |
| Anticholinesterase drugs | Pyrodostigmine | Cholinesterase inhibition |
| Antiglaucoma drugs | Physostigmine, pilocarpine | Inhibition of cholinesterase by physostigmine, stimulation of muscarinic cholinergic receptors by pilocarpine |
| Bladder contractile stimulants | Bethanechol | Stimulation of muscarinic cholinergic receptors. |
| Opioids | Fentanyl, hydrocodone, methadone, morphine, oxycodone | Release of histamine, disturbance of central thermoregulation |
| Serotonergic antidepressants | Citalopram, duloxetine, escitalopram, fluoxetine, fluvoxamine, mirtazamine, paroxetine, trazodone, venlafaxine | Effects on serotonin receptors in the hypothalamus and spinal cord |
| Salivary stimulants | Cevimelene, pilocarpine | Simulation of muscarinic cholinergic receptors |
| Amitriptyline, desipramine, doxepin, imipramine, nortriptyline, protriptyline | Inhibition of norepinephrine reuptake with stimulation of peripheral adrenergic receptors |
Polyneuropathy
Damage to peripheral nerves, manifested by impaired sensitivity, motor and autonomic dysfunction. The clinical picture includes a huge number of signs (weakness or atrophy of muscles, numbness and tingling in the fingers, changes in sensitivity - decreased, increased, perverted), the main thing in violation of autonomic function is severe sweating, often in combination with increased blood pressure and tachycardia. When the underlying disease is treated, hyperhidrosis also disappears without a trace.
Raynaud's phenomenon
Disturbance in the extremities (usually the arms) of peripheral circulation due to vasoconstriction (vasospasm). The main pathogenetic mechanisms are: changes in vascular tone and blood rheology, the release of substances (mediators) by nerve endings. The mediators released by nerve endings are calcitonin peptide and neuropeptides. With any change in blood vessels, a response to cold temperature and emotional stress appears. Raynaud's phenomenon has a specific clinical picture that is difficult to confuse (changes in the color of the limbs, a three-stage process, the area of changed color has clear boundaries with normal skin), but the presence of a rare symptom of hyperhidrosis misleads the doctor, because more often characterized by decreased sweating and dry skin.
Syringomyelia
A serious disease of the central nervous system in which a cavity forms inside the spinal cord. The causes of the development of this disease are: trauma, infection, congenital malformations. Clinic: impaired pain and temperature sensitivity, muscle weakness (most often the muscles of the extremities). Swelling, cracks appear on the skin, color changes (marble or white) and sweating increases.
Erythromelalgia
A rare disease manifested by acute and unbearable skin pain (most often the feet are affected). In addition to irritation, itching, redness, patients complain of severe sweating, in which things on the affected surface are constantly wet.
Cord tympani syndrome
Increased sweating in the chin area, which occurs in response to spicy, salty, hot, and sour foods. This syndrome is acquired (after surgery, facial trauma), and unilateral hyperhidrosis may occur.
A modern method of treating string tympani syndrome is injections of botulinum toxin A into the chin area.
Erythrophobia
A disorder that occurs in people who are poorly adapted to speaking in public. The main clinical symptom: the appearance of red spots (most often on the face), additional: the heart rate, respiratory rate, blood pressure increase, gastrointestinal motility slows down, sweating increases.
How does it arise
Hyperhidrosis can be idiopathic or secondary. In the first case, sweating occurs for no specific reason. In this case, your armpits, palms and feet sweat a lot. In the second case, the pathology is associated with diseases of the internal organs, when sweat is secreted over the entire surface of the skin in large quantities.
Basically, hyperhidrosis occurs when there is a disruption in the functioning of the autonomic nervous system. This can be frequent stress, tension, various diseases, changes in hormonal levels, etc.
In addition to stress, hyperhidrosis occurs against the background of poor nutrition, environmental conditions, and bad habits. Sweaty palms may occur when taking certain types of medications.
Video: how hyperhidrosis is treated
Features of hyperhidrosis
Many people experience seasonal increased sweating in the spring and summer. Constant manifestations are rare - sweating occurs regardless of the weather and is not associated with activity or stress. Relapses may occur when, after hyperhidrosis, the work of the sweat glands returns to normal, and then increased sweating returns. This is usually due to hormone surges and disruptions in the functioning of the autonomic nervous system.
How can you treat hyperhidrosis of the palms, feet or hands?
To get rid of severe sweating, it is necessary to maintain personal hygiene, as well as strengthen the nervous system. The easiest way to get rid of the disease is to use antiperspirant deodorants. They block the sweat glands, which reduces the amount of sweat produced.
If the patient has secondary hyperhidrosis, the underlying disease is first cured. To do this, you will need to undergo an examination and obtain a doctor's prescription.
Ultraviolet light has a good effect, which helps to overcome severe sweating of the hands. You can try an ionization session, which is performed by a dermatologist.
It is better to use special powders for the palms and feet
Medicines
To reduce sweating, sedatives are prescribed to help reduce stress and tension. If this does not produce results, drugs with belladonna and belladonna, which are not addictive, are prescribed:
- Bellaspon - the drug helps reduce sweating and also has a calming and sedative effect.
- Belloid – helps overcome irritability and nervousness.
To reduce nervous excitability, drugs with bromine (Propintheline) are prescribed. It reduces the amount of sweat produced.
In advanced forms of hyperhidrosis, tranquilizers can be prescribed to improve a person’s mental state. For excessive sweating, Diazepam, Oxazepam, etc. can be prescribed.
Tranquilizers are prohibited for use by pregnant women and those with severe depression.
Ointments and creams
To combat severe sweating, ointments and creams can be prescribed:
- Cream “5 days” - this drug has an antiseptic, drying, deodorizing effect, and also relieves inflammation on the skin.
- Cream "Nepotoff" - helps to overcome the unpleasant odor of sweat.
- Formagel - the drug helps relieve the unpleasant symptoms of severe sweating, as well as reduce sweating.
- Teymurov's paste - has an antiseptic, antimicrobial effect. Dries the skin and fights the unpleasant odor of sweat.
- Lassara paste - helps eliminate heavy sweating, fights its symptoms and helps to quickly get rid of the disease.
Folk recipes: list
To quickly get rid of unpleasant sweating on the palms, folk remedies are used:
- Baths with potassium permanganate - for this you will need to prepare warm water, to which you add a couple of grams of potassium permanganate so that the water turns pink. After this, hold your hands in it until the condition eases, dry and lubricate with powder or deodorant.
- Vinegar baths - for this you need to take 3 tsp. vinegar and a liter of warm water. Such baths should be done for 2 weeks three times a day.
- A mixture of vinegar, soda and borax - this will require 100 grams of vinegar, 1 tsp. soda, mix everything thoroughly. After the mixture has stopped fizzing, 4 grams of borax and 300 grams are added to it. glycerin. Pre-dissolve borax in half a glass of warm water. Wipe your hands with the resulting mixture every 2 hours.
- Herbal baths - you will need half a liter of hot water and 1 tbsp. horsetail and calendula. All ingredients are mixed and infused for half an hour. After this, strain the broth and dip your fingers in it for 15 minutes. This procedure should be done every day until sweating decreases.
- Baths with salt – 1 tsp. salt 1 liter of warm water. You should immerse your hands in the resulting liquid for half an hour. You need to do this procedure 3 times a day.
How to get rid of sweaty hands
Let's talk about how to get rid of sweaty hands. Very often, in the treatment of such a disease, the method of iontophoresis is used.
Ordinary tap water is poured into the baths with electrodes.
In some regions it can be very soft without mineral salts. In this case, it makes sense to add half a teaspoon of baking soda. If the water is already mineralized, then nothing needs to be added.
Next, the current level is selected, which will be sufficient to produce a therapeutic effect. In most cases, on certain instruments these levels are already known in advance. The patient only needs to set the desired mode.
The method itself is accompanied by a slight tingling sensation. During the treatment process, you need to change the polarity once, since the current is directed.
To obtain the effect, 8 - 12 sessions of 20 - 30 minutes a day or 5 - 6 times a week are generally required.
There are two ways to save the effect:
- Or the patient waits how long the dry effect lasts and then repeats the treatment cycle again
- Or maintenance treatment is carried out - as a rule, this is once every 5 days
Using the iontophoresis method allows many patients to achieve very good results. Moreover, it is worth noting that this is a safe method that is not subject to serious changes on the human body.
However, it has some limitations. For example, it should not be done by those who have contraindications to physiotherapeutic methods. This also applies to those who have massive metal structures. For example, artificial joints.
How long does it take to treat hand hyperhidrosis?
The duration of treatment depends on the duration of the disease, as well as its stage. On average, it takes 2-3 weeks to treat hyperhidrosis. But already from the first days of treatment, the patient observes relief and less sweat.
With hyperhidrosis, the most important thing is to follow the rules of hygiene. It is necessary to treat the skin of your palms daily with antiseptics and deodorants, make herbal baths, etc. If there is a smell of sweat, then cosmetic deodorants are suitable.
Classifications of hyperhidrosis
- Primary, secondary.
- Generalized, local.
Primary focal hyperhidrosis
- Palmoplantar.
- Axillary.
- Craniofacial.
- Generalized.
Secondary causes of localized hyperhidrosis
| Cerebral infarction |
|
| Spinal cord injury |
|
| Other diseases of the central nervous system |
|
| Diseases of the peripheral nervous system |
|
| Local skin diseases |
|
Secondary causes of generalized hyperhidrosis
| Diseases of the central nervous system |
|
| Fever and chronic infection |
|
| Metabolic and systemic diseases |
|
| Malignant tumors |
|
| Taking medications |
|
| Toxic syndromes |
|
| Diseases of the peripheral and central nervous system |
|
Primary focal (essential) hyperhidrosis is one of the most common sweating diseases. This condition is defined as visible excessive focal sweating without an obvious cause with a minimum duration of 6 months, which has at least two of the following characteristics:
- Symmetrical sweating.
- Excessive sweating interferes with daily activities.
- The frequency reaches at least one episode per week.
- Age of onset before 25 years (most often begins in childhood or prepuberty).
- Positive family history.
- Stopping sweating during sleep.
This disease occurs equally in both sexes and continues for years, sometimes with spontaneous improvement after 35 years.
Primary focal hyperhidrosis does not manifest itself in patients under general anesthesia and often worsens when exposed to thermal stimuli and physical activity. Sweating can be episodic or continuous (especially difficult to tolerate in the summer).
Hyperhidrosis of the palms
Can occur at any time regardless of ambient temperature, stress or pleasure. The severity of hyperhidrosis varies from occasional, slight wetness of the palms to a daily huge amount of discharge - profuse sweat, requiring constant use of towels.
Plantar hyperhidrosis
It is one of the most unpleasant for the patient. In addition to discomfort when wearing shoes, playing sports, or simply walking, a secondary infection often occurs - the development of mycosis of the feet. Early diagnosis and treatment of plantar hyperhidrosis is necessary to prevent the development of mycosis. Treatment limits the process (in the absence of therapy, not only the foot is affected, but the entire leg, including destructive processes in the nail plate).
Prevention of plantar hyperhidrosis:
- Short foot baths (up to 3 minutes).
- Using socks made from natural fibers.
- Deodorants, powders and antiperspirants for feet (an important condition is for a clean body).
The difference between deodorants and antiperspirants for feet lies in the intention of use: deodorants - odor elimination (perfume ingredients), antiperspirants - a therapeutic option (because they contain substances that reduce hyperhidrosis, and also envelop the walls of the sweat gland duct, thereby suppressing sweat secretion) .
Parotid temporal hyperhidrosis
Localized sweating on the lips, forehead, scalp and nose, while taking a hot bath and spicy food, occurs physiologically in many people and is caused by the trigeminovascular reflex.
This type of hyperhidrosis is characterized by two subtypes: asymmetric and intense. The cause is the abnormal regeneration of damaged and undamaged parasympathetic nerves in the face, which are intended to innervate the salivary glands, but instead innervate the sweat glands of the face, which lack sympathetic innervation. Most often this occurs with Frey's syndrome, when sweating occurs along the innervation of the auriculotemporal nerve after injury, abscess or surgery in the parotid gland. Frey's syndrome can occur in infants and children, often following the birth trauma of forceps delivery.
Diagnostics: to accurately localize areas of sweating, indicator powder is applied to the face, neck, upper body while the patient is chewing, and the result is photographed.
Axillary hyperhidrosis
Axillary hyperhidrosis is the most common form of excessive sweating for which people consult a doctor. This type of hyperhidrosis is more difficult to tolerate from a psychological point of view than from clinical manifestations.
Complaints:
- Continuous wet skin, and as a result - wet clothes in the armpit area.
- An unpleasant odor that is felt not only by the patient, but also by others.
- Later (due to infection), itching, burning, swelling, and redness occur.
- Limitation in professional activity: most often - dentist, musician, workers in the field of electrical engineering and electricity.
- Restrictions in sports activities: most often sports that require contact with objects or players (volleyball, handball, basketball, rugby, boxing).
- The main complaint is lack of self-confidence, personal discomfort, possible development of depression, fear of intimacy.
The United States of America has added axillary hyperhidrosis to the basic list of insurance diseases, the treatment of which is paid for if necessary.
Preventive measures to prevent axillary hyperhidrosis do not guarantee protection against occurrence; rather, they are an option for stabilizing the process.
- Proper nutrition: avoiding coffee, tea, limiting the consumption of simple carbohydrates (baked goods, sweets, sweet carbonated drinks).
- To prevent infection, a daily shower with detergents that do not contain aggressive substances is necessary.
- Clothes should be made of natural fabric, not tight-fitting, and be loose (prevents the development of dermatitis with complaints of itching and burning).
- Using over-the-counter antiperspirants with aluminum zirconium tetrachlorhydroxyglycine 20% anhydride. A pronounced clinical effect has been proven. Apply topically after a shower to the armpit area. Side effects: itching, expensive.
Psychological aspect of primary hyperhidrosis
Severe primary hyperhidrosis interferes with many daily activities, and patients report a deterioration in quality of life. Avoiding a handshake can lead to awkward professional situations, and avoiding touch leads to social and interpersonal withdrawal and other symptoms of social anxiety disorder.
Hyperhidrosis: symptoms of the disease
Sweating is a normal physiological process that is necessary for humans to ensure thermoregulation. But when should you talk about the disease? The following symptoms indicate disturbances in this process:
- Sweating occurs even in a state of physical and emotional rest.
- The volume of sweat is significantly increased, which leads to physical discomfort. Clothes become wet, and rivulets of sweat can be seen on the back and face.
- Hygiene procedures and the use of deodorants do not bring relief.
- Strong foul odor - bromidrosis. Normally, sweat fluid has virtually no odor if hygiene procedures are followed.
- The appearance of colored sweat (chromidrosis). This occurs due to slagging in the body or due to severe intoxication.
- Formation of abrasions and redness in areas of increased sweating and skin folds.
In addition, a person’s behavior and character changes. He develops a sweat anticipation neurosis. This is a panicky fear when a person is constantly expecting that at the most important moment he will become wet and disgrace himself. Such tension leads to worsening of the disease. Headaches, attacks of lack of air (hyperventilation syndrome), and hypertension also occur.
Symptoms and characteristic signs of the disease
Symptoms depend on gender:
- in women - during pregnancy, menopause and changes in endocrine function;
- in men - with stress, hypertension and diseases of the cardiovascular system, excessive physical activity.
Reasons to see a doctor:
- Strong separation of fluid during sleep (at this moment all body functions slow down, so a person without pathologies sweats only at high temperatures or when sick);
- pungent odor of discharged liquid;
- change in physical parameters: stickiness, viscosity;
- excessive glandular function (any time of day);
- constant manifestation of general symptoms of diseases: weakness, fatigue, nausea, drowsiness. All this happens without fever.
Important! Unpleasant sweat odor is caused by the presence of infectious agents or toxins.
Symptoms boil down to hydration of individual areas or the entire body. The skin becomes sticky, damp, cool. Acrocyanosis (blueness of the toes and hands) is detected.
Surgical methods of treatment
Surgeries are performed on the sympathetic nerve or problem areas. Types of sympathectomy:
- Traditional, performed during the opening of the thoracic or cervical spine. New, less invasive methods have been discovered, so this method has become rarely used. The nerve is inactivated by applying current, chemicals, or compressing it. When opening a patient, the surgeon assesses his condition, selects a method and decides whether to remove the nerve or temporarily block its action.
- Endoscopy. The nerve is found by inserting an endoscope through the skin. An incision is made in the armpit. A camera is inserted there, the required area is clamped or removed. The patient goes home an hour after the intervention.
- Local option. Excess fat tissue or skin is excised. In the first case, hydration decreases when fat is removed, which affects the secretion of liquid secretions; in the second, sweat glands are removed along with the skin (large scars remain).