Red spots on the forehead: causes and treatment
The skin of the face constantly requires painstaking care. It is extremely common, especially in guys, to see reddish spots on the forehead - the causes and treatment for their occurrence are determined by a dermatologist.
It comes down to eliminating the burning sensation and severe itching that accompany the disease.
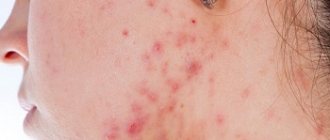
Most often, a rash on the forehead occurs with seborrheic dermatitis.
You can also find the popular name - seborrhea or seborrheic crown. Less common are other diseases that have identical symptoms:
– Sebopsoriasis is a combination of psoriasis and seborrhea.
Since seborrhea is the most common disease that causes reddish spots on the forehead, we will focus most carefully on the causes and treatment of this disease.
Red spots on the forehead: prerequisites and diagnosis of seborrhea
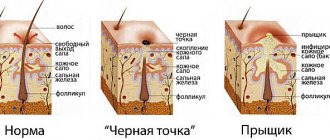
With seborrhea, the sebaceous glands are affected, so the literal translation of this disease sounds like sebum leakage. High-molecular alcohols, fatty acids, salicylic acid, iodine and other elements are excreted through the glands.
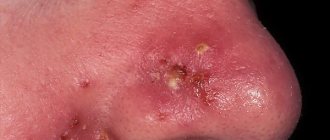
As a result, coin-shaped reddish spots appear on the forehead and other parts of the face. They peel and itch. The rashes can be located high on the forehead, reaching the hairline, which causes the appearance of scales - dandruff.
To establish a diagnosis, you need to consult a dermatologist. He will evaluate the clinical picture of burgundy spots on the forehead. The prerequisites and treatment will be determined based on the results of an in-person examination. This is enough to prescribe treatment.
The fungus Pityrosporum ovale causes burgundy spots on the forehead; this disease can also be caused by a lack of zinc or nicotinic acid in the body.
Exacerbation of seborrhea is observed more often in the cool season with a lack of ultraviolet radiation.
In the summer, you can occasionally meet those who have reddish spots on their foreheads.
Red spots on the forehead: healing seborrhea
The skin of the forehead, affected by reddish spots of seborrhea, requires special care and healing, which is local. The disease is acquired, so it is necessary to carefully follow the advice on caring for the skin of the forehead.
— To eliminate the symptoms of the disease, talkers containing zinc are used as therapy.
— To wash your hair, use special healing shampoos with ketoconazole, as well as zinc and tar.
While washing your hair with shampoo foam, you can wipe the skin on the forehead where there are reddish spots.
— In the morning, it is recommended to remove crusts on the spots with a cotton swab dipped in baby or medicinal shampoo, and wipe with 2% Ketoconazole cream.
If you consult a specialist in a timely manner, you can remove reddish spots on your forehead. The conditions and treatment must be determined by the doctor who prescribes the personal treatment.
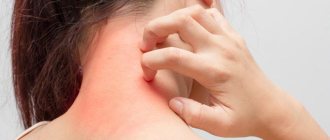
Allergy in the forehead area
The appearance of allergies on the forehead can be triggered by various factors, one of which is the body’s rejection of internal and external irritants.
To cure any allergy, it is necessary to identify the circumstances that provoke the development of the disease.
When acute symptoms develop, allergens may include food, clothing, the presence of animals, etc.
In children, the prerequisites for the occurrence of a rash in the forehead appear due to the lack of development of the immune system, when the baby’s body is not able to cope with the attack of allergens.
As a rule, a rash in the forehead reflects a malfunction of the patient’s internal systems, indicating a pathological process.
The rashes vary in appearance, number and severity.
Classification of rashes
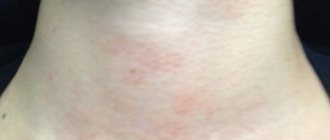
- A rash in the forehead area is most often accompanied by severe itching, but from time to time it can occur latently, without acute symptoms. It can be reddish, snow-white, purple or silver.
As a rule, the occurrence of rashes is accompanied by dermatitis and inflammatory diseases. - According to their structure, rashes on the forehead can be flat, embossed, scaly and uneven. In the form of spots, dots, spreading over various parts of the body. In addition, it can peel and flake off.
- In severe cases, an allergic rash on the skin of the forehead may be accompanied by swelling of the facial area and tongue, and difficulty breathing. This condition is extremely unsafe for the patient and is called anaphylaxis. If such symptoms occur, emergency treatment is required.
- If the rash on the forehead is characterized by purple spots, accompanied by fever and stiffness of the neck muscles, the development of bacterial meningitis must be excluded in the patient.
General symptoms
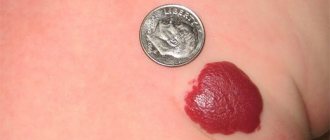
Angiomas are red spots on the body that look like droplets of blood, which only cause cosmetic discomfort to a person. Most often they are not accompanied by specific symptoms. But if these red dots on the chest, stomach or other part of the body are causing any problems, then urgent consultation with a specialist may be required.
Possible symptoms of such neoplasms include:
- Increased body temperature.
- Irritation.
- Cough and sore throat.
- Peeling of the skin.
- Heaviness and aching in the joints.
- Itching.
- Decreased appetite.
- Food allergies.
Causes of rash in adults
The main reason for the appearance of a rash on the forehead is an allergic reaction.
Sometimes such symptoms are not associated with allergies and may appear as a result of disturbances in the functioning of the pancreas and liver.
Often a rash occurs with rheumatoid diseases.
In this case, allergens can be food and animals, as well as clothing. Therefore, if a pinpoint hyperemic rash on the forehead is detected, an urgent consultation with an allergist is necessary.
Of no small importance is the genetic predisposition to allergies, both the social reaction of the body and increased sensitivity to a particular allergen.
In patients, rashes on the forehead are possible after contact with local antiseptics. In this case, it is necessary to eliminate the circumstances of the allergy. In addition, it is strictly not recommended to remove the rash on the forehead by physical means.
This can lead to infection and worsen the situation, especially in a child.
The causes of the disease may appear to be due to hormonal disorders, dysbacteriosis and malfunctions of the liver, pancreas and gall bladder.
In addition, errors in diet can provoke rashes. In this case, you need to reconsider your diet, excluding highly allergenic foods (coffee, tea, chocolate, sweets, etc.). It is preferable to choose a drink in the form of freshly squeezed juices, mineral or ordinary distilled water.
Causes of rashes in children
In infants, an allergy may appear at one moment and both external and internal causes can provoke a similar manifestation in the baby.
Any occurrence of a rash (especially in the forehead area) requires clarification of the reasons for the development of the disease in an infant.
In a newborn baby, an allergic rash may appear as a result of an allergy to mother's milk if the mother's nutrition is impaired. Food allergies are one of the most common causes of a rash on the forehead.
The skin of a newborn is extremely warm and susceptible to external influences, so a baby may be allergic to synthetic items from which clothing is made. In addition, allergies can occur upon contact with washing powders, baby detergents, animal hair, etc. In this case, you need to switch to hypoallergenic cosmetics, completely eliminating contact with allergens.
Quite often, pinpoint hyperemic rashes in a baby can appear due to prickly heat, when the surface layer of the baby’s skin comes into contact with wet underwear for a long time, resulting in skin irritation.
In case of infectious diseases, a hyperemic rash on the baby’s forehead may be accompanied by an increase in temperature, lethargy of the baby, refusal to eat, and excessive drowsiness.
The appearance of a rash in a baby should make parents think.
Reddish spots, flaky skin and irritation are quite easy to see in a baby. In addition, there may be the development of Quincke's edema (giant urticaria). This condition is a severe complication that occurs quite rarely, but is quite severe, especially for infants, and can lead to respiratory arrest due to the spread of swelling to the throat. If you suspect this burden, the baby should be hospitalized immediately.
Preventive measures
In order to prevent the appearance of red spots on the skin, the following preventive recommendations should be followed:
- compliance with hygiene requirements;
- use of detergents that do not contain aggressive surfactants;
- use of hypoallergenic cosmetics;
- use during cleaning, hand washing of masks and respirators that protect the skin of the face;
- rejection of bad habits;
- correction of sleep patterns, normalization of motor activity;
- enriching the diet with vitamin-rich plant foods;
- taking vitamins in the winter-spring period;
- taking walks in the fresh air;
- use of sunscreens;
- avoidance of stressful situations;
- normalization of intestinal function;
- avoiding sudden temperature changes.
Healthy well-groomed face
A red rash on the face causes a lot of discomfort. You can get rid of it with the help of salon procedures, medications and folk remedies. Following the rules of a healthy lifestyle will help normalize the condition of your facial skin.
Treatment
Any allergy requires specific treatment after urgent consultation with an allergist and dermatologist.
To obtain a positive result, the prerequisites for the disease are first determined.
In addition to limiting interaction with allergens, pharmaceutical therapy can be prescribed, which consists of prescribing the following pharmaceuticals:
First generation antihistamines (Tavegil, Suprastin, Diazolin) and more modern antiallergic drugs with prolonged action (Claritin, Zodak). Healing of a baby is carried out strictly under the supervision of the attending physician.
The symptoms of the disease in the baby must be neutralized with the help of a hypoallergenic diet, which is used in combination with the treatment of liver diseases, gall bladder and dysbiosis.
Quite often, such diseases can become a prerequisite for an allergic rash on the forehead.
Enterosorbents have a positive effect in the treatment of allergic symptoms in adult patients and children. They are prescribed to remove toxic substances from the body that are formed as a result of the action of the allergen. These include Enterosgel. Polysorb, activated carbon, etc.
In addition to antihistamines and enterosorbents, pharmaceuticals in the form of ointments and gels can be prescribed. These include Fluorocort ointment, Fenistil.
In addition, glucocorticosteroids (hydrocortisone, prednisolone, etc.) may be prescribed. But it should be noted that the dose is selected individually for adult patients and children.
Effectively relieves allergy symptoms with a remedy for external use - La-Cri. This gel neutralizes itching, skin hyperemia, swelling, flaking, promoting healing and restoration of damaged skin.
Its advantage is its neutral effect on the skin of infants.
Prevention
To prevent rashes on the forehead and face, as well as to prevent its spread and the development of various complications, the following actions should be avoided:
- allergies on the face require urgent consultation with an allergist;
- In no case should you wipe the rash with an alcohol-containing substance, especially if the rash occurs in a child;
- you cannot take pharmaceuticals without the help of others without a preparatory examination by a specialist;
- It is not recommended to smear the forehead with greasy ointments and creams;
- when a rash appears, you can take baths with a decoction of chamomile and string. These herbs have good disinfectant and anti-inflammatory properties, disinfecting the site of the rash. You can dip a clean napkin into the freshly prepared solution, wring it out and wipe the area of the rash;
- It is necessary to monitor the temperature and humidity in the room, especially if the baby has an allergy. To avoid scratching and infection, you need to trim your baby’s nails on time.
It is necessary to keep in mind that an allergy on the forehead, with all its manifestations, can be complicated by secondary diseases, accompanied by serious complications, therefore independent healing is strictly prohibited!
It is important to take into account that allergies in the facial area occur quite often, especially in children, therefore it is necessary to identify all the prerequisites for the disease and carry out the necessary medical treatment.
In the case when the rashes are not accompanied by complications and provided that all the advice of the treating doctor is followed, the rash on the forehead quickly disappears, leaving no consequences.
Before starting any intervention in the body, you need to consult a specialist who will perform a series of laboratory tests to identify the etiology of the disease and prescribe adequate treatment.
Pathological redness of the face.
- Rapid occurrence after the onset of the irritating factor;
- Rapid disappearance after the cessation of the irritating factor;
- The severity of redness traditionally does not increase over time, reaching a maximum soon after appearance;
- After the redness disappears, the skin takes on its normal appearance and no changes remain;
- The redness goes away without the help of others and does not require any special therapy;
- The severity of redness is reduced with constant training to increase endurance to the action of an irritating factor;
- Redness does not cause any negative consequences.
That is, physiological redness of the face is a normal response of the body to the action of some factor unfavorable for the skin or blood vessels.
It should be remembered that physiological redness of the face is never accompanied or mixed with itching, flaking or dryness. A burning sensation may accompany physiological redness of the face. Among the reasons:
- Low ambient temperatures that come into contact with the skin of the face (for example, washing with ice water, being in the cold, etc.);
- High ambient temperatures (heat, stuffiness, washing with hot water, taking long hot baths or showers, steaming the face, etc.);
- Redness of the face when eating hot, hot or spicy foods, as well as tea, coffee;
- Consumption of alcoholic beverages;
- Rubbing the skin with a cloth;
- Very energetic facial skin massage;
- Very vigorous rubbing of cosmetics into the skin of the face;
- Performing physical exercises or heavy work;
- Lack of sleep;
- Applying irritating cosmetics to the skin of the face (masks, creams, scrubs and other products that increase blood flow to the skin);
- Nervous tension or mental agitation;
Mental complexes.
- Relatively slow onset of redness with increasing severity over time;
- Long-term redness;
- Redness does not go away without the help of others, and to eliminate it you need to eliminate the provoking factor;
- After eliminating the provoking factor, the redness may not completely go away, and traces may remain on the skin that will have to be removed using different methods;
- The severity of redness remains approximately unchanged for a long time, increasing only when the provoking factor intensifies;
- Redness can cause various bad consequences.
With prolonged presence of redness of the skin of the face, as a rule, it is pathological.
Therefore, if for any reason a person’s face often and forever turns red, you need to consult a doctor for an examination to find out which specific diseases can cause redness of the skin among the existing pathologies.
Preventive measures
A mandatory point of treatment is a balanced diet. It is especially important for people suffering from allergies or congenital vascular weakness. Fatty and sweet dishes, hot seasonings, canned food, smoked meats and sausages are removed from the menu. It is necessary to completely eliminate alcohol and smoking; nicotine, tobacco tar and ethyl alcohol destroy the weak walls of blood vessels. The diet includes fresh vegetables and fruits, dairy products, animal proteins (fish, poultry). These products strengthen capillaries and stimulate the production of natural collagen.
It is important to protect your face from aggressive sun rays. Before going outside, apply a cream, gel or spray with a high SPF to your face. Properly selected decorative cosmetics can also hide redness. A foundation without mineral oils covers imperfections well and does not cause irritation. It is important to avoid contrasting procedures: steam baths, ice compresses. They have a destructive effect on fragile capillaries and increase the risk of their rupture.
Medicine has not yet fully studied the reasons for the formation of red dots on the skin, which look like moles. However, we can say with confidence that these growths are benign. Small spots of ruby or dark red color cause only cosmetic discomfort, but do not pose any danger to the body. Many people do not know whether they need to undergo treatment if blood spots form.
Causes of facial redness
1.
Physical (external) reasons;
2. Pathological (internal) causes.
Physical reasons
- Wind;
- Temperature effects (heat, cold, burning or ice water, etc.);
- Mechanical friction of the skin (rubbing, intense massage, vigorous rubbing of cosmetics, etc.);
- Sun rays (sunburn on the skin);
- Dust (dust getting on the face and staying on the skin for a long time);
- Physical stress (work or active training);
- Staying in an inclined position for a long time when the face is below lumbar level (for example, bending, weeding a garden, etc.);
- Burns and injuries.
Since physical preconditions cause physiological redness of the face, which quickly passes, then, as a rule, their identification and elimination or minimization of the influence does not pose any problems.
Therefore, we will most carefully dwell on the pathological causes of facial redness, which are caused by various disorders of the functioning of the body, and therefore are of even greater importance as probable signs, including serious diseases.
Pathological causes
- Allergic reasons;
- Infectious causes;
- Inflammatory processes;
- Vascular diseases;
- Diseases of internal organs;
- Mental reasons.
Allergic facial redness
- The redness is bright;
- All facial skin is reddish to one degree or another, but more pronounced redness is observed on the cheeks in the area of mustache growth, on the chin, between the lips and nose;
- Reddened skin is swollen;
- Itching in the red area.
In addition, itching and swelling with allergic redness of the face can lead to the formation of wounds, scratches and cracks on the skin, in the area of which infection and the development of an inflammatory process can occur.
Redness of the skin due to diseases of internal organs
- Increased body temperature due to any disease or condition;
- Diabetes;
- Menopause in women (“hot flashes”);
- Atherosclerosis;
- Avitaminosis;
- Hypertonic disease;
- Heart failure;
- Reduced acidity of gastric juice;
- Chronic constipation;
- Damage to the trigeminal nerve;
- Taking antibiotics;
- Sinusitis, rhinitis and other acquired diseases of the ENT organs;
- Worms;
- Gynecological diseases;
- Digestive disorders and diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (for example, gastritis, cholecystitis, etc.);
- Taking atropine;
- Poisoning with alcohol or hallucinogenic drugs;
- Autoimmune diseases (systemic lupus erythematosus, in which a butterfly-shaped redness appears on the face);
- Kidney failure;
- Erythrocytosis (blood tumor);
- Liver cirrhosis (clearly visible spider veins on different parts of the face).
Seborrheic dermatitis
Signs characterizing seborrheic dematitis are the appearance of flaking and dandruff with a yellowish tint. It is also found on the eyebrows, mustache and beard. Red spots appear on the scalp.
The disease develops due to a malfunction of the exocrine glands. They produce an excess of secretion called sebum. The second cause of pathology is the uncontrolled proliferation of bacteria, which are normally found on the skin of most people. They concentrate around the ducts. The source of their vital activity is the secreted secretion. But its production is not carried out to “maintain the strength” of bacteria; it helps maintain the skin in normal condition, moisturizes and softens it.
Hyperactivation of pathogenic microflora occurs due to changes in the composition of sebum. In this case, the protective functions of the epidermis are disrupted. The main causes of these failures are changes in genetic, hormonal, neurogenic or immune factors.
Seborrhea develops in one of three types:
- In the dry form of the disease, the ducts produce a reduced amount of secretion. In this case, the emerging symptoms are cracked, dry skin, brittle and dry hair, and the presence of a large amount of small dandruff. Seboreids appear on the affected areas of the skin - reddish spots.
- The oily type of the disease is marked by increased activity of the sebaceous glands. The skin becomes oily and shiny. There is a lot of dandruff, it is large in size. You have to wash your hair often. This happens because the hair quickly becomes oily and sticks together.
- The mixed form is characterized by the simultaneous manifestation of two types of seborrhea. For example, there is a dry variety on the face, and an oily one at the top of the head.