Atopic dermatitis in adults is a chronic allergic-type disease that develops in people with a genetic predisposition to atopy. It is predominantly seasonal, non-contagious, and is characterized by dry skin, redness and severe itching. In severe forms, a small rash of watery blisters may form in areas of redness. Treatment in adults has many nuances. With the development of the chemical industry and the growth of production, the environment on the planet and the quality of nutrition are deteriorating. The food industry uses a huge amount of synthesized additives, which leads to an increase in people suffering from allergies. The most vulnerable part of the population - children - suffers especially. Among common allergic diseases, atopic dermatitis occupies a leading position.
This is a chronic allergic type disease
Atopic dermatitis - what is it and how does it manifest? As a rule, it begins to develop in early childhood (especially in children prone to allergies), but often manifests itself in adolescent children at the time of puberty and is observed throughout a person’s life.
The disease is also called atopic eczema or diffuse neurodermatitis.
According to the ICD-10 protocol, L20 is one of the most common skin diseases. But not everyone knows how to treat it. Doctors also call it atopic eczema or diffuse neurodermatitis. Its current cause is poor ecology, which is why the number of patients is constantly growing.
Causes of the disease
Today it is classified as a multifactorial disease. For example, if a patient has a hereditary predisposition, then it can be aggravated by the negative influence of the environment (harmful emissions, water, poor-quality food, etc.). The disease is based on various types of allergic reactions, so children are especially susceptible to the disease. Quite often, the disease manifests itself in connection with drinking cow's milk or choosing the wrong formula for the baby. In adults, the disease occurs during long-term treatment with antibiotics. In dermatology, it is considered an allergic non-contagious disease, predetermined by a hereditary factor, acquires a chronic form and is recurrent in nature. This disease is interconnected with the immune response to environmental factors and can develop with dysfunction of the digestive organs (enzyme deficiency, intestinal bacteriosis). May be accompanied by other types of allergic reactions.
People suffering from this disease are very anxious and depressed.
People suffering from the disease are very anxious and depressed, which is why they often acquire new diseases associated with damage to the autonomic system. Children who have been ill at least once are at risk of developing allergic rhinitis. Almost all allergic diseases are hereditary. If both parents had allergies, then the risk is 60-80%, if 1 parent - 45-50%, if parents do not have allergies - 10-20%. In infants, atopic dermatitis develops due to food allergies. This can happen if the body does not accept cow's milk, grains, or soy. Allergies are possible to sweets and citrus fruits. Over time, food allergies go away, and allergies to household dust, pollen of flowering plants, and fungal spores may develop. This form of atopic dermatitis is very difficult to control. In the development of an allergic reaction, staphylococcus plays an important role. It is because of staphylococcus that the chronic form of atopic dermatitis develops, developing in both adults and children. Often allergies suffered in childhood develop into bronchial asthma and allergies. Therefore, it is important to take timely measures. Atopic dermatitis - etiology: the disease is mainly hereditary. If both parents were sick, then the risk of developing the disease in the child is approximately 70-80%; if only the mother is sick, then the risk of getting sick is much lower - about 30-60%. More often than not, women suffer from this disease. The pathogenesis of atopic dermatitis is determined by the response of the human immune system to repeated introduction of the antigen. Factors that influence the disease:
The disease is mainly hereditary
- consumption of foods that provoke allergies (citrus fruits, chocolate, alcoholic drinks, drinks containing a large amount of dyes, red berries);
- poor nutrition;
- rare physical activity and sedentary lifestyle;
- taking certain medications.
- heredity;
- infections of fungal, viral or bacterial type;
- weak immunity;
- direct contact with the source of allergies (cosmetics, household chemicals, medications, dust, pollen);
- neglect of personal hygiene;
- use of cosmetics that cause dry skin;
- intestinal dysbiosis;
- sudden change of diet;
- dry microclimate indoors;
- constant severe stress, mental instability (psychosomatics).
Diagnosis of atopic dermatitis
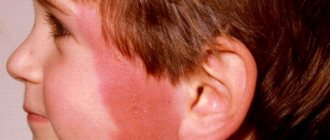
For diagnosis and treatment, the patient must visit a dermatologist or diagnostic center. Atopic dermatitis is characterized by skin rashes on the face, buttocks, and limbs. In adults, itchy rashes are possible on the elbows, legs, and neck. The skin becomes rough and thick with a sharply defined pattern. The rash may occur in patches or occupy large areas of the skin surface. The patient complains of itching, nervousness, and insomnia. As a disease, it does not have a specific clinical picture, but according to some signs (criteria) this disease can be recognized. Here are the main ones:
For diagnosis and treatment, the patient must visit a dermatologist.
- itching;
- change in skin color;
- occurrence in childhood.
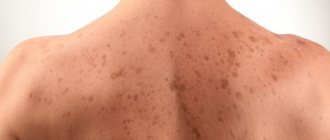
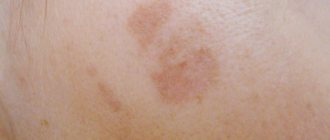
In addition to the basic ones, there are additional criteria for determining atopic dermatitis, which together can give a specific picture of the course of the disease. These include dry skin, inflamed skin on the hands, cracked lips, dark eyelids, and pale or red skin on the face. The disease manifests itself early: already at 1 year of life. Over the years, the disease may subside, however, the patient needs to take care of himself, even if the disease is in remission. Having determined the symptoms and treatment, the doctor must remind the patient about preventive measures.
Age-related features of the disease
The development of atopic dermatitis goes through three phases:
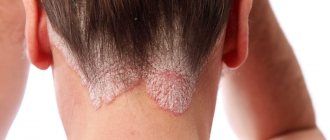
- Infancy develops up to 2 years, affecting the face and elbow bends, sometimes affecting the child’s torso. Erosion with a damp surface, crusts form, and the skin dries out. The first cases of the disease are observed during teething and with the start of complementary feeding.
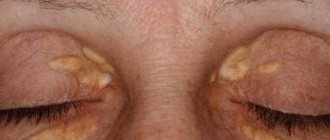
- Children under 12 years of age are localized under the knees and in the elbows, on the neck, and the back of the hand. The skin swells, turns red, the pattern becomes more obvious, blisters, pimples and erosions appear. The skin condition is complicated by cracks and itching, which results in scratches and scabs. A Denier-Morgan line appears above the lower eyelid in a child with allergies - an additional fold.
- Teenage - up to 18 years old. It may be accompanied by a subsidence of skin manifestations or their exacerbation with a significant increase in the affected area of the skin, including the face and neck, décolleté, arms up to the elbow.
- Adulthood is a continuation of a disease that developed in childhood. The rash is localized in folds of skin on the face, neck, hands, feet and fingers. With a bacterial infection that complicates the course of the rash, wet erosion appears. The skin of a person with dermatitis is dry, thickened, itchy and flaky.
Symptomatic picture
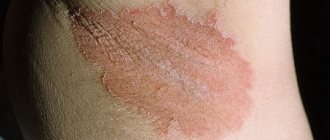
The main symptoms of the disease are severe itching and red rashes. The rash may appear as small, watery blisters that burst or form a thick crust. Dermatitis covers different areas of the skin, usually the face, neck and arms, sometimes in the groin and under the arms. What does atopic dermatitis look like? Symptoms can occur in either mild or severe forms. In a mild form, the rash encircles a small area of the skin, itching is observed, and with intensive hydration the symptoms disappear almost immediately. In the acute form, the rash begins over much larger areas of the skin, and the symptoms go away only after drug treatment. Atopic dermatitis has the following types:
- contact;
- allergic;
- perioral;
- seborrheic;
- diaper
In addition, it is divided into acute and chronic. Often the disease is psychosomatic in nature.
Description and reasons for appearance
Oral dermatitis is an inflammatory process of the skin and mucous membranes. Signs of pathology can appear on the lips, skin around the mouth, inside the oral cavity, and on the mucous membrane lining the lips from the inside. The cheek may also be affected by the pathology.
Perioral dermatitis is a fairly common, life-threatening pathology. It can act as a self-developing disease or be a consequence of any disease.
The pathology manifests itself in the form of small papules, which subsequently merge to form a large plaque.
Women under thirty years of age are more susceptible to this disease. In children and men, this form is extremely rare. Among the main and most common factors contributing to the development of dermatitis on the lips are:
- Negative effects of external factors - cold, wind, ultraviolet radiation. As a result, the lips become chapped and dry, which leads to the development of the disease.
- Allergic reactions and dermatoses, the provoking cause of which is contact of the lips with harmful chemicals.
- Ringworm, psoriasis.
- Disorders of the thyroid gland.
- Decreased immune system, congenital or acquired.
- Clogged pores with lanolin as a result of using lipstick.
- Ecological situation.
- Pathologies of internal organs, for example, the liver and gastrointestinal tract.
- Use of topical steroids such as Prednisolone or Hydrocortisone.
- Features of hormonal levels. In some cases, premenstrual syndrome contributes to the increased appearance of the rash.
Oral dermatitis in children, as a rule, develops as a result of improper breathing or vitamin deficiency.
Age classification of atopic dermatitis:
- infant (children under two years old);
- children's (children from 2 to 12 years old);
- adult (persons over 12 years old).
Often the disease is psychosomatic in nature
Thus, in infancy, skin rashes form in the form of small watery pimples, which, when breaking through, form a dense, dry crust on the body. In mild forms, the rash covers the skin of the face, arms and legs, and in more severe forms it appears on the folds of the arms and legs, in the neck and wrists. Dysbacteriosis and atopic dermatitis are 2 diseases that often accompany each other. In children from 2 to 12 years of age, it forms in the form of irritation and peeling with characteristic cracking of the skin; the affected areas have clear boundaries with a clearly visible skin pattern. Atopic dermatitis is characterized by the appearance of pigmented spots on the body after the peeling disappears. In adulthood, rashes can affect almost the entire upper body, forming large lesions. With improper treatment or lack thereof, there is a possibility of complications such as swelling of the soles (peeling and cracks appear on the feet), hair loss, and the formation of folds in the lower eyelid. Between exacerbations, especially after minor contact with an irritant, the disease can manifest itself in the form of minor redness of a small size and the formation of microcracks in the area of the lobes. After 12 years, it may be accompanied by symptoms such as: white coating on the mucous membrane of the tongue, swelling of the nasopharynx, conjunctivitis, ARVI, constipation, diarrhea. Bronchial asthma and atopic dermatitis often occur already in adolescence. Often the disease affects such areas of the skin as: elbows, knees, neck, folds, outer integuments of the feet and hands, forehead, temples. Psychosomatics often influences the manifestation of the disease. People who have suffered severe stress, depression or other nervous system disorders often suffer. Therefore, if it is not possible to find the cause that provokes the development of the disease, then, most likely, psychosomatics will help to reveal it.
Classification
Most often, dermatitis on the lips occurs in women, one of the most obvious causes of which is the frequent use of lipstick.
Depending on the course of development of the pathology, acute and chronic forms are distinguished. In addition, perioral dermatitis has several types:
Contact allergic
It usually appears in adolescence after 14 years. The skin around the lips begins to peel off, and wounds form on the mucous membrane. Often the cause of this type of dermatitis is an allergy to chemicals contained in toothpaste, water, cosmetics, food and dentures.
Atopic dermatitis
The symptoms resemble diffuse neurodermatitis and atopic dermatosis. It occurs to a greater extent in people with pathologies of the digestive system or as a result of poor nutrition. During the cold season, the risk of exacerbation of the disease increases.
Exfoliative
It appears against the background of frequent stress and depression, with endocrine system disorders, reduced immunity, as a result of hereditary predisposition. Accompanied by redness, cracks and peeling of the lip edging.
Hypovitaminosis
It is characterized by inflammation at the corners of the lips, in the border area and on the tongue. As a result of non-compliance with hygienic rules for oral care, and existing bad habits, such as biting or licking lips, cracks form. This type of oral dermatitis usually occurs as a result of a deficiency of B vitamins, retinol and thiamine.
Glandular
It is characterized by an increase and development of a chronic inflammatory process in the area of the minor salivary glands. The situation is aggravated by periodontal disease, caries and other pathologies of the oral cavity. In most cases, this type of disease occurs in adolescents. Among the main provoking factors are infections, genetic predisposition, hypovitaminosis, and impaired mineral metabolism.
Meteorological
Provoking factors are weather conditions and radiation. Hyperemia and infiltration of the lips appear. In the absence of therapy, severe forms that are difficult to treat may develop.
Melkerson-Rosenthal syndrome
Among the main reasons are the presence of infection in the body and heredity. The course of the pathology occurs in a very severe form.
Prevention of atopic dermatitis
If you are diagnosed with atopic dermatitis, what should you do? First of all, you should start treatment after the examination, try to eliminate the causes that provoke the development of the disease. To overcome the disease, it is important to learn everything about atopic dermatitis and constantly engage in prevention. There are the following types of prevention - primary (aimed at eliminating symptoms and avoiding its occurrence) and secondary (aimed at eliminating relapse). Clinical recommendations: atopic dermatitis should be strictly controlled already in the first year of a child’s life. You should follow a diet intended for children of this age and avoid excessive use of medications. A woman who is breastfeeding must follow a diet and remove spicy foods, red fruits and vegetables, citrus fruits, chocolate, drinks containing large amounts of preservatives and dyes, and alcoholic beverages from her diet. Secondary prevention is aimed at eliminating exacerbations, and, if any, mitigating their course. Includes preventing exacerbation of existing chronic diseases. Serious attention should be paid to skin care and the choice of underwear. When bathing every day, it is common to use mild soaps and rinse the skin with warm water; you should avoid taking a hot shower with a washcloth to avoid damage to the epidermis.
Serious attention should be paid to skin care and the choice of underwear
The skin with atopic dermatitis becomes dry. This is due to a violation of its barrier function, so only skin moisturizing (hydration, saturation with water) does not restore the lipid layer. Atopic dermatitis is a serious skin disease that becomes chronic and seasonal. With inappropriate treatment and non-compliance with personal hygiene rules, it can cause complications through the addition of bacterial, fungal and infectious skin diseases. You should be careful when choosing hygiene products, underwear and clothing. Any contact, even minor, with an allergen or irritant can trigger a relapse of the disease or aggravate the current condition at the time of exacerbation. Atopic dermatitis rashes can cause wounds and ulcers.
Local treatment
What to do if atopy worsens? Skin symptoms are mainly treated with topical remedies that help relieve swelling and itching, eliminate flaking and dry skin, and also prevent fungal and bacterial infections.
In the acute form of the disease, lotions with a 1% tannin solution, Burov's liquid, rivanol, as well as strong tea and oak bark are used.
The products have an astringent and anti-inflammatory effect, therefore they reduce all symptoms of the rash. Solutions of methylene blue and Fukortsin are used as antiseptics, which are applied locally with cotton swabs.
For chronic cases, ointments with cortisone are prescribed. Moisturize the skin with water-based Betnovate oil cream, Beloderm or Celestoderm ointment. For inflammatory processes, Sinaflan and Advantan are used, and for extensive processes, Dermovate is used.
Infants are allowed to smear the rash with Advantan from the age of six months, as well as Elok from the age of two.
Treatment and prevention of atopic dermatitis
Treatment of atopic dermatitis in adults, no matter how severe it may be, is always the same. During an exacerbation of the disease, you must follow a strict diet and take all medications prescribed by your doctor. Lifestyle plays a big role in alleviating the patient’s condition. You must pay attention to the following rules:
- Strictly follow the daily routine.
- Night work during illness is unacceptable.
- Business trips are undesirable, especially those accompanied by a change in time zones (flying on an airplane is not recommended).
- There should be no irritants in the patient’s room: pillows with feathers, animals, carpets.
- Wet cleaning should be done as often as possible and you should not forget to ventilate the room.
- You can take non-hot baths; clothes should be rinsed thoroughly after washing.
How to treat this insidious disease? Hormonal (Lokoid), antiallergic drugs, Calcium and Elidel are prescribed as the main treatment. Sometimes a group of psychotropic medications is prescribed to calm the patient’s psyche, since itching during illness is very debilitating. It is difficult to treat atopic dermatitis in adults, since the disease does not have a clear pattern of progression due to the fact that the causes of its occurrence are steadily growing every year, however, with the help of a doctor’s advice, you can forget about it for a long time. In cases of illness, especially those associated with food allergies, diet plays an important role. It is necessary to find and eliminate the allergen. You need to exclude certain foods from your diet and conduct skin tests.
In case of illness, especially associated with food allergies, diet plays an important role.
The patient needs to stop eating citrus fruits, sweets, fatty and fried foods. Patients should include fermented milk products, cereals and vegetable dishes in their diet. When breastfeeding, the mother must follow a strict diet. Sometimes it is necessary to transfer the child to artificial feeding. Doctors recommend a hypoallergenic mixture. How to treat atopic dermatitis with medications? To treat atopic dermatitis, the attending physician prescribes antihistamines. Hormonal drugs - glucocorticosteroids - are also prescribed. Hormonal medications should be prescribed only by a pediatrician or allergist and taken under control to avoid side effects. In complex treatment, drugs are used to treat the gastrointestinal tract. External treatment of atopic dermatitis is carried out using special ointments. It is more difficult to treat allergies to household dust and seasonal allergies. To do this, there should be no carpets or rugs in the apartment that collect dust. The bed must be constantly ventilated. At home, you need to carry out wet cleaning regularly and ventilate the room more often.
In case of acute illness, vaccinations should not be given.
Many people are interested in whether it is possible to get vaccinated for dermatitis? In acute cases of the disease, this is not possible. Vaccinations for atopic dermatitis can cause serious complications. During the period of illness, the body is already greatly weakened; vaccinations for atopic dermatitis will further undermine the body’s defenses. Vaccination is possible only after the acute phase of the disease has passed and the symptoms of the disease have almost disappeared. But even in this case, the patient should be under strict medical supervision for some time after vaccination. Atopic dermatitis and vaccinations are compatible things, but not always. For example, a vaccination such as the Mantoux reaction often gives an incorrect result, so there will be no benefit from the vaccination. Make it better after eliminating the symptoms of the disease.
Diagnosis and treatment of dermatitis on the lips
In medicine, dermatitis on the lips is a fairly common pathology, but there are still some difficulties in diagnosing it. This is due to the fact that the symptoms are in many ways similar to some infectious skin diseases.
To make an accurate diagnosis and confirm that it is oral dermatitis that is occurring, special studies are carried out: a patch test of the skin and mucous membranes.
Results can be obtained within 1-2 days.
After blood tests and skin tests, it becomes clear what substances or products caused the allergy.
After the diagnosis is confirmed, the doctor prescribes treatment. Basically, drug therapy is used.
Drug therapy
At the first stage of treatment, it is necessary to discontinue hormonal drugs. Therapy should be aimed at relieving the negative manifestations of withdrawal syndrome. It is also important to give up cosmetics and facial hygiene products. This stage is called zero. The patient's general condition worsens for a while, but then he gets better.
The following medications are prescribed:
- Metronidazole - should be used up to two times a day.
- Protopic 0.3% in the form of milk - has an anti-inflammatory effect and is non-toxic.
- Sken-Cap - the zinc contained in the composition dries and relieves itching.
- Adapalene has camelolytic and anti-inflammatory effects.
- Rozamet is highly effective.
Also, if necessary, prescribe:
- antiallergic drugs (Suprastin, Zyrtec, Claritin);
- diuretics – in case of edema development (Furoemide, Veroshpiron);
- sedatives (Valerian, Novo-Passit).
The second stage of therapeutic treatment is aimed at combating pathogenic microorganisms that provoke skin inflammation. It is advisable to use the following antibacterial drugs:
- Azelloic acid;
- Metronidazole;
- Doxycycline and others.
To achieve a more effective result, your doctor may prescribe inhibitors. They are recommended to be taken together with Monocycline.
Dermatitis on the lips, like any other disease, should be treated only as prescribed by a doctor. Self-medication is extremely dangerous!
Folk remedies
Additionally, you can use traditional medicine aimed at reducing the symptoms of pathology and giving no less positive results.
- Lotions based on calendula and sage. 2-3 tablespoons of the collection are mixed with 0.5 liters of boiled water, put on fire and boil for 10 minutes. After this, filter. The use of the decoction is allowed every 30 minutes.
- Aloe juice. To obtain juice, the leaves are washed and crushed. Then the resulting consistency is mixed with vegetable oil in a ratio of 1:3. It is recommended to smear lips up to three times a day.
It is important to remember that using only traditional methods will not cure the disease, you can only reduce the symptoms.
Dermatitis on the lips is a fairly serious disease. If diagnosis and treatment are not timely, there is a high risk of complications. Therefore, at the first suspicion of pathology, it is necessary to seek medical help as soon as possible.
Use of homeopathic remedies for treatment
How to cure atopic dermatitis with homeopathic remedies? Depending on the shape and nature of the rash, the following is prescribed:
- Spots - Belladonna, Calcarea carbonica, Lycopodium, Pulsatilla, Sepia.
- Papules - Calcarea carbonica, Kali iodine, Silicea, Mercurius solubilis, Petroleum.
- Vesicles - Rhus toxicodendron, Causticum, Natrium muriaticum, Ranunculus bulbosus, Sulfur, Urtica urens, Sepia, Euphorbium.
- Bubbles - Cantharis.
- Blisters - Apis, Dulcamara, Sulfur, Antimonium crudum, Arsenicum album, Natrium muriaticum.
- Pustules - Mercurius solubilis, Silicea, Hepar sulfur, Arsenicum album, Calcarea carbonica, Psorinum, Clematis, Anacardium.
- Corki - Calcarea carbonica, Graphites, Mercurius solubilis, Petroleum.
- Cracks - Acidum nitricum, Calcarea carbonica, Graphites, Lycopodium, Sepia, Silicea, Argentum nitricum.
- Cracks in the mucous membranes - Natrium muriaticum, Graphites.
- Scaly peeling - Arsenicum album, Calcarea carbonica, Arsenicum iodatum, Sulfur.
- Scars - Acidum fluoricum, Lachesis, Silicea.
Treatment of atopic dermatitis with homeopathy should begin after the first sign of the disease appears and continue after all external manifestations of the disease on the skin have been eliminated. With proper homeopathic therapy, the elimination of all symptoms of the disease occurs within 3 weeks (with a mild form of the disease). In advanced cases, treatment with homeopathy for atopic dermatitis can take about a year.
Complications caused by atopic dermatitis
Incorrect or untimely treatment, as well as failure to comply with personal hygiene rules at the time of exacerbation, can cause a bacterial infection (pyoderma) and atrophy of the skin.
Incorrect or untimely treatment can cause a bacterial infection
Pyoderma causes white pustules to appear on the skin of the arms, legs, and even on the head. May be accompanied by general weakness and fever. And also an important complication of this disease is the addition of infections of various etiologies, often herpes. Herpes rashes can appear both around the affected areas of the skin and on healthy ones. Basically, herpes rashes affect the mucous membranes of the mouth and nose. Another complication of atopic eczema is a fungal complication. In adults, the nail plates, scalp, feet, and hands are affected; in children, this complication manifests itself in the form of thrush on the tongue.