Types of fillers used in aesthetic medicine
Fillers can be defined as substances introduced into tissue to fill a defect, such as a wrinkle. Depending on their chemical composition, they can be divided into two groups:
- Biological fillers
. That is, completely natural substances that the body perceives as “its own” and, therefore, inert in relation to the body. Such fillers are characterized by faster or slower tissue resorption, depending on the preparation. Raw hyaluronic acid is a biological filler, but in this form it is practically not used. - Synthetic fillers
- partially or completely. Synthetic fillers are characterized by very slow absorption into tissues and they can also be permanent. Hyaluronic acid offered for aesthetic medicine contains a small percentage of synthetic impurities, which allows it to stay in tissues longer.
The ideal filler should be characterized by the highest possible filling results, long-term effects, minimal damage to the body during its implantation, availability and, above all, safety. Hyaluronic acid meets all the requirements, so it is close to ideal.
Unstabilized and stabilized types
Another classification of hyaluronic acid is also related to its molecules. Comes in two forms:
- Unstabilized.
- Stabilized.
Their main difference lies in the stability and adhesion of molecules. Thus, the first form of hyaluronic acid consists of particles that are not connected to each other by additional adhesions. Their behavior is unstable; they are not assembled into single chemical chains.
This fact suggests that, when it gets under the human skin, this form of hyaluronic acid is broken down into even smaller particles - polysaccharides, which randomly fill the gaps and increase the reserves of human hyaluronic acid.
Therefore, we can say that unstabilized hyaluronic acid is intended specifically to compensate for its own substance. The effect of its action is not as long-lasting as we would like, but it sufficiently moisturizes the skin, creates a protective film, makes it durable, and protects it from hypothermia and overheating.
Stabilized hyaluronic acid, on the contrary, is distinguished by the fact that it consists of molecules assembled into strong chains and adhesions. Thanks to this close interaction, they disintegrate very slowly, because they work together, as a united front. As a result, stabilized hyaluronic acid remains in the body for more than a year.
Therefore, its effect is of a different nature - it does not easily replenish hyaluronic acid reserves. The stabilized product restarts the processes of collecting human hyaluronic acid, accelerates cell function, and promotes the accumulation of collagen and elastin.
Both forms of medicine are used equally widely in cosmetology, but, nevertheless, their purpose is different and depends on the nature and extent of the problems.
What is hyaluronic acid obtained from?
The first hyaluronic acid-based products were created in the 1980s. Hyaluronic acid was originally obtained from cockscombs, so these fillers contained a mixture of poultry proteins. Currently, hyaluronic acid is obtained by biofermentation of Streptococcus equi and Bacillus Subtilis bacteria, strains that are non-pathogenic to humans.
Due to the fact that hyaluronic acid is the same substance for all organisms and species, its biocompatibility eliminates the need for preliminary testing, sensitivity testing and the body's response to its use. As medicine develops, we get an increasingly ideal product.
Properties and tasks of the Civil Code
In our body, hyaluronic acid is found in connective tissue, that is, lymph, blood, bones, cartilage, and also in the dermis. In addition to it, in the listed areas of our body there are compounds of proteins and amino acids, collagen and elastin fibers - that is, those components that are responsible for the condition of our skin and its appearance.
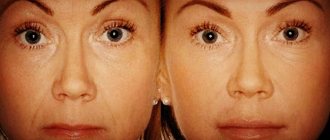
The absence of hyaluronic acid (or its active breakdown) increases dryness of the skin, slows down the synthesis of fibroblasts, leads to an increase in the number of wrinkles, pigmentation, and ptosis. Typically, a decrease in the production of HA in the body is associated with a person’s age, but external factors (sun rays, bad habits and poor diet, frequent stress) also have a detrimental effect.
The properties of artificially created hyaluronic acid provide natural processes, attracting water molecules and accelerating the production of fibroblasts.
Preparing hyaluronic acid: what is the difference between preparations with hyaluronic acid
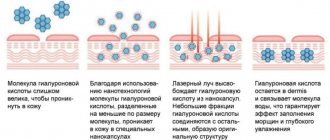
The half-life of hyaluronic acid in the skin is short and ranges from 12 to 24 hours, therefore, to prolong the effect of the drug in the tissues, it is necessary to properly process hyaluronic acid, which makes it stable and resistant to degradation factors. This process is called cross-linking of macromolecules and includes a corresponding transformation - cross-linking of hyaluronic acid chains, which gives it special physicochemical properties.
Hyaluronic acid preparations vary in the degree of cross-linking, giving the product different degrees of density and viscosity, as well as different binding abilities for water molecules. This variety allows you to choose the right drug for the type of treatment.
For example, drugs of different density are required to increase lip volume, correct facial contours, fill wrinkles and enlarge the labia. Thanks to the range of hyaluronic acid, we obtain a substance that, after implantation into the tissue, undergoes very slow degradation. Filling effects are visible depending on the drug and individual conditions for up to 18 months.
There are many drugs on the market, and new ones are registered every year. They differ from each other, among other things, in the concentration of hyaluronic acid, the degree of cross-linking and the morphology of the drug. These properties depend on the production technology and determine the viscosity, flexibility, ability to lift tissue, ability to bind water, and decomposition time in the tissues of the drug. The filler may be macroscopically homogeneous or molecular, resulting from a cross-linking technique.
Hyaluronic acid injection
How long does the effect last after the injection of hyaluronic acid?
As a result of processing hyaluronic acid, specialists obtain preparations with different densities. How long the acid will work depends on the crosslinking. The denser the drug, the slower it will dissolve.
The durability of HA is usually 6-12 months for denser acids and 3-6 for less dense ones. Pure hyaluronic acid lasts 1-2 days. Therefore, companies always indicate the density and retention period in the instructions.
It is necessary to explain what "retention period" means and differentiate between the retention of acid in the skin and the time at which the effects become visible. Hyaluronic acid, unlike other drugs, is immediately visible. Over time, it dissolves, so the effect seems to “melt away”. The process of HA degradation also depends on the personal predisposition of patients, age and lifestyle.
Consequences of use
After injections of hyaluronic acid, every second patient experiences temporary side effects. They manifest themselves in changes in skin sensitivity, bruising and swelling. This negative reaction of the body lasts up to 3 days and does not require special treatment.
Unfortunately, in some cases the consequences of injections can be more serious; we are talking about such a rare phenomenon as an allergy to hyaluronic acid. Symptoms of this phenomenon are often confused with common side effects. In the first hours they are expressed in redness and itching, then swelling forms. If it does not go away within a week, this is regarded as a clear sign of individual intolerance to hyaluronic acid. For the future, in such a situation, it is recommended to take allergy tests.
Allergic reaction to hyaluronic acid injections
There are more terrible consequences of injections than allergies. Thus, in rare cases, fibrosis (hardening of connective tissues) is observed at the injection site of the drug. In minimal quantities it is not dangerous, but it can grow and affect large areas of soft tissue, disfiguring a person’s appearance. Fibrosis occurs as a result of injecting too much hyaluronic acid or injecting it too deeply.
How safe is hyaluronic acid?
Pure hyaluronic acid is not used in aesthetic medicine. Only drugs with 20 mg of NA per 1 gram of drug, that is, a 2% solution, are recommended for use. The remainder is saline and excipients, including stabilizers and cross-linking agents.
Crosslinkers create bonds between chains, causing HA to dissolve more slowly. The advantage of crosslinking is that the acid will last longer. The disadvantage of the technique is that the base is cross-linked with chemicals. A high-quality product differs from natural acid by less than 1%, which ensures high safety of its use.
The most commonly used cross-linking process is 1,4-butanediol diglycidyl ether (BDDE), which breaks down in the human body. Independent studies to determine the unwanted effects of BDDE have proven that it is a completely safe product. The second substance used for these purposes is 1,1′-sulfonylbisetene or vinyl sulfate, but it is now used much less frequently. Together with additional substances, hyaluronic acid decomposes and is eliminated from the body naturally, without causing the formation of any metabolites dangerous to humans.
The safety of hyaluronic acid filler is guaranteed by the following certificates:
- ISO - a guarantee that the product is not toxic or mutagenic and should not cause hypersensitivity reactions;
- FDA is the American Food and Drug Administration, which is responsible for regulating foods, dietary supplements, drugs, cosmetics, medical devices, biological materials, and blood products in the United States. Its positive opinion, viewed worldwide, is an indicator of quality and confirmation of the absence of negative health effects of the product.
For these reasons, it is worth using drugs from well-known companies: only they guarantee the use of the best product in terms of quality and safety.
Hyaluronic acid formula
Essenthyal subtil Hyaluronic acid + Colloidal silver or Colloidal gold
Hyaluronic acid from Bacillis Subtilis, 20 mg/ml in composition with nanoelements of colloidal gold and colloidal silver. Colloidal gold nanoelements are an active inducer of collagen synthesis and have a noticeable tightening effect, smoothing the skin. Perfectly corrects facial contours, making them clearer and more prominent. Colloidal silver nanoelements have a positive effect on skin restoration mechanisms and actively prevent the formation of inflammatory processes. The HA in this preparation is a natural matrix of gold and silver particles and has a significant effect of rejuvenating the deep layers of the skin, which is especially important for the fine-wrinkled type of aging.
Hyaluronic acid - how to choose?
When choosing hyaluronic acid, the rule usually works: the more expensive the product, the better it is. Of course, this is a simplified approach, but it can certainly be assumed that more expensive acids have a better purification and cross-linking process.
It is worth explaining that the division of hyaluronic acid into non-cross-linked, slightly cross-linked and highly cross-linked acid is sufficient for choosing a drug. Any other options, for example, HA for the area around the eyes or for filling wrinkles, are a marketing ploy. The doctor chooses the remedy precisely according to the density’s compliance with the goals set.
The drug must be certified because it is a medical item, just like a dental implant, a knee implant, or a breast implant. If there is no certificate, then it is not hyaluronic acid, but who knows what.
An important indicator of the quality of hyaluronic acid are parameters indicating the degree of its purification, that is, the degree of removal of the cell walls of acid-forming bacteria. This is important because excess elements can cause allergic reactions. Parameters indicating how much bacterial debris remains in the acid should be found in the instructions or on the manufacturers’ website. Preparations can vary in degree of purification by up to ten times. The general rule is to choose drugs with bacterial residue levels below 10 U.
It is important to know how much cross-linking agent is in the preparation. This information is difficult to find, but it can determine the presence of complications. Doctors who practice procedures with hyaluronic acid already know in practice what to expect from a particular brand. For example, a drug may contain up to 9% BDDE, while other acids contain much less of this substance. More chemical products work longer, but using them in very visible areas is risky.
Finally, it should be remembered that since HA, despite its biocompatibility, is a foreign body, therefore not everyone can use it. To avoid complications, you need to choose the right drug, prepare for the procedure and take into account all contraindications and restrictions.
Continuation of the article
- Part 1. Hyaluronic acid. Properties you don't know about
- Part 2. Hyaluronic acid: how to choose a drug. What manufacturers and cosmetologists are hiding