The appearance of a round swelling on the body, which increases in size over time, is an alarming sign. This disease is called atheroma. According to the international classification of diseases, atheroma is a type of follicular cyst of the skin.
The appearance of a round swelling on the body, which increases in size over time, is an alarming sign.
In this material, we will look at how to treat atheroma, why it appears, by what symptoms it can be recognized, and we will find out how to get rid of atheroma completely so that it does not appear again in the same place. We will also look into in what cases its removal is required, and whether there are ways to treat atheroma without surgery. Attention will also be paid to measures to prevent its occurrence.
Symptoms
With this disease, there may be a history of complaints about a subcutaneous formation, which easily moves when pressed. There is no pain at the initial stage of the disease. If the atheroma hurts, this indicates the progression of the disease. The skin cyst in the cavity is filled with horny masses and products of the sebaceous glands.
If the tumor hurts, this indicates progression of the disease.
If the patient does not receive proper treatment, the skin cyst progresses and severe pain appears. Pain indicates that the atheroma is inflamed. In this case, an abscess forms in the cavity of the cyst (accumulation of pus in the tissues with their melting).
A festering atheroma is a reason to see a doctor as soon as possible in order to remove it.
Common causes of inflammation are:
- violation of personal hygiene;
- excessive use of cosmetics and deodorants;
- presence of concomitant infectious diseases;
- regular trauma to the cyst with a comb, items of clothing, etc.
In some cases, inflammation of atheroma is associated with self-medication, so it is necessary to remember that conservative treatment, and especially removal of the cyst, should only be carried out by a doctor.
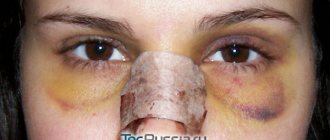
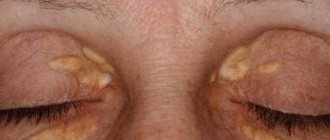
Removal of atheroma on the eyelid near the eye and suturing
Option three involves removing the contents of the cyst to reduce its total size and facilitate removal of the capsule. The method is used for large formations whose dimensions exceed the recommended minimum width of the skin incision. After cutting the skin and capsule, the detritus is squeezed out of the cyst cavity and the enucleated cyst is removed with a special clamp, like an empty “bag”.
The fourth option is similar to the third, but the detritus is not squeezed out, but scraped out with a special tool. They are used in the presence of very thick and dense contents in the cyst, as well as when removing formations in areas where pressing movements would be undesirable (for example, when removing atheroma on the eyelid or removing atheroma near the eye) and in areas rich in vascular network.
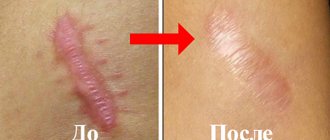
Actually, at this point the operation can be considered completed and the surgeon can only apply stitches after removing the atheroma on the wound using the usual or cosmetic method, or fix the edges of the wound with a special plaster, depending on the width of the wound, the expected cosmetic effect and the location of the intervention.
Causes
Skin atheroma appears due to blockage of the sebaceous gland ducts. The accumulated secretion of the sebaceous gland turns into a cyst. In the central part of the cyst, a pathologically enlarged excretory duct of the sebaceous gland can be seen.
Wen appears on the skin due to blockage of the ducts of the sebaceous gland.
In turn, disruption of the normal functioning of the sebaceous gland ducts can be caused by the following reasons:
- insufficiently careful observance of personal hygiene rules;
- genetic diseases (for example, cystic fibrosis);
- hormonal pathologies.
Classification and localization
This skin formation is considered a benign tumor; it can appear in a person on any part of the body, but predominantly the skin cyst is located in places where there are sebaceous glands:
- on the face;
- on the neck and back;
- on the scalp;
- on the genitals of men and women;
- on the chest, shoulders, forearms and abdomen.
This is what a tumor on the scalp looks like.
Less commonly, cysts can appear on the ears, arms and legs.
In science, atheroma is classified into the following types:
- sebaceous cyst;
- dermoid cyst;
- atheromatosis;
- steatoma.
This classification is devoid of practical significance, because from a clinical point of view, all these types manifest themselves and proceed in the same way. Practicing doctors, depending on the cause of this disease, distinguish such types as congenital and acquired sebaceous cyst.
Surgical removal of large atheroma (with video)
The second option is similar to the first in terms of intactness in relation to the formation and is suitable for larger formations located in visually invaluable surrounding areas of the body (not on the face) or in areas densely covered with hair. To provide surgical access, incisions are made bordering the formation or its outlet, the edges of the wound are moved apart and fixed. After complete removal of the atheroma, the wound is sutured with preservation of all skin flaps.
This video shows the surgical removal of atheroma from a patient with diabetes mellitus and provides explanations from the operating surgeon:
Treatment
Understanding why a tumor is dangerous requires a doctor to make a decision about its removal. The cyst does not pose an immediate danger to human life. However, if an inflammatory process begins inside the cyst, its consequence is a deterioration in the person’s general condition: increased temperature, pathological enlargement of the lymph nodes. Possible introduction of a purulent infection under the surface of the skin threatens general blood poisoning.
It is possible to establish that in a particular case a purulent atheroma has formed by a number of signs:
- the occurrence of pain when pressing on the cyst;
- general unsatisfactory health of the patient, lethargy;
- fever;
- redness, swelling at the location of the formation.
Treatment of suppurating atheroma is a rather complex task, which is usually resolved as planned, but sometimes, for health reasons, urgent removal of the cyst is necessary. Its planned removal occurs in two stages:
- Gradual relief of inflammation.
- Direct removal of the cyst.
The main rule for the patient when treating this disease is to consult a doctor without delay. Many patients do not consider atheroma as a serious problem and delay seeking medical help until the moment when the formation already causes noticeable pain or if the wen is located in places that are always visible to others.
This attitude towards this disease is wrong, because... It is easiest to remove atheroma in the initial stages of the disease. The development of a purulent-inflammatory process in the cyst leads to its increase in size. In this case, its removal becomes problematic.
General principles of treatment
Medicine gives an affirmative answer to the question of whether atheroma needs to be removed. If the patient does not receive adequate treatment (that is, if the pathological formation is not removed), then negative dynamics of his condition are observed. Cases of spontaneous disappearance of atheroma are unknown to medicine. It is believed that in no case can it resolve itself, and if removal of the cyst is delayed, this can only lead to various complications.
It is possible to completely recover from this formation only by removing it in different ways. However, it will not be possible to remove (completely squeeze out) the cyst without consulting a doctor. If some skin diseases (for example, a pimple), due to their small size, are in principle amenable to such self-treatment, then the atheroma is too large. Therefore, attempts to squeeze it out rarely end in success.
In some cases, self-squeezing of the atheroma leads to a large amount of an unpleasant-smelling mass of pasty consistency coming to the surface. However, this does not mean that a cure has occurred, because Only removal of the pathological formation by a doctor can eliminate the root cause of the disease.
By independently squeezing out the pathological formation, it is impossible to remove the atheroma capsule.
If you simply pierce the capsule, for example, with a needle, and remove the mass located in the capsule through the resulting hole, the duct of the sebaceous gland will remain clogged. This will lead to relapse of the disease, that is, to re-filling of the cavity with the formation of a cyst.
The literature describes cases in which the atheroma burst (opened) on its own. In such a situation, there is no need to panic, because... In itself, the fact that the cyst is opened does not pose a great danger. The only thing you need to worry about is the possible penetration of infection.
The following measures must be taken:
- As soon as the atheroma has opened, you need to carefully squeeze out the mass in the cavity.
- Cut off a piece of sterile bandage and remove the resulting liquid.
- Treat the wound with an antiseptic.
- Apply any ointment that has a wound healing effect.
- Apply a sterile bandage or adhesive tape on top.
These measures need to be taken only in one case: if the atheroma has broken through without intervention from the patient. Unauthorized opening of a pathological formation is strictly not recommended under any circumstances.
Removal operations
To get rid of atheroma completely, you need to not only open it, but also completely remove it along with the capsule. Indications for immediate surgery are as follows:
- complaints about a cosmetic defect caused by the appearance of a cyst in a visible place;
- increased risk of injury to the cyst due to its location;
- disruption of the normal functioning of adjacent organs.
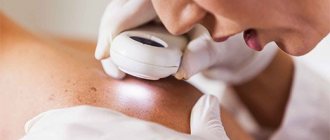
It is possible to separate the walls of the cyst from the surrounding tissues and remove it only with surgical removal of the atheroma. The operation is performed under local anesthesia. The use of general anesthesia is considered excessive for such an operation.
A tissue defect forms in the place where the cyst was located. The prognosis for the patient is favorable: in the future, a new cyst will not form, because the cause of its appearance is eliminated - blockage of the sebaceous gland duct.
To get rid of the pathology completely, you need to remove it along with the capsule.
If for any reason (the cyst is located in an inconspicuous place, failure to see a doctor in a timely manner, etc.) the cyst has reached a large size, it still needs to be removed. In such a situation, stitches cannot be avoided.
Surgery to remove the cyst is not indicated if inflammation of the atheroma is diagnosed. In such a situation, anti-inflammatory therapy is recommended before surgery to remove the painful formation. If this stage of treatment is omitted, there will be a high risk of relapse of the disease. Only the attending physician can tell you how to relieve inflammation of atheroma. Self-medication in such cases is unacceptable.
If inflammation is combined with the formation of pus, then opening the atheroma with the release of pus is indicated. Next, you should leave a hole for the drainage of pus and take measures to treat the inflammation. Only after this is it recommended to remove the atheroma.
Treatment of atheroma without surgery is impossible; the only question is which method of intervention will be used to remove it. The decision on how to remove atheroma in a particular case is made in consultation with the attending physician. In any case, with proper treatment under the supervision of a physician, the atheroma does not reappear in the same place after removal.
After removal of the pathological formation, it is necessary to continue monitoring with the attending physician. You will need to go to him for dressings after removal of the atheroma. However, dressing is not used if the formation is located on the face or neck. This is due to the fact that in this case the risk of regular injury to the vulnerable area after the operation is not too high. If the removal of the formation was performed in a place where the skin is constantly in contact with clothing, then dressings are necessary. Sutures (if they were applied) are usually removed 7 days after surgery.
Laser removal
Laser removal of atheroma is usually carried out in cases where it is located in places visible to others (for example, on the face). The specialist performing the operation acts on the patient's skin using a laser emitter. The advantage of removing the formation using this method is that it is possible to avoid the appearance of obvious cosmetic defects (scars, etc.) on the skin.
Laser removal is usually carried out in cases where it is located in places visible to others (for example, on the face).
However, this effect can only be achieved if treatment is started in a timely manner. This method of treatment is indicated if it is necessary to remove cysts in areas of the skin that are always visible to others.
The minimum cost of an operation to remove a cyst using a laser is approximately 6,000 rubles.
If the cyst is large enough (exceeds 10 mm in size), then the atheroma is first excised using a laser, then the area where the operation is performed is treated.
Radio wave removal
This method of removing skin lesions, like the previous one, is gentle. It allows for selective action on pathological formations while preserving adjacent tissues. Like laser treatment, removal of pathological formations using radio waves gives the patient a chance to avoid the appearance of obvious cosmetic blemishes on the face and other important areas.
In this case, the operation is bloodless. Unlike the traditional method of removing atheroma surgically, when using radio waves, its removal is carried out without sutures.
The minimum cost of removing atheroma using the radio wave method is about 2000 rubles.
Radio wave method
Removal of atheroma using the radio wave method is highly effective and safe. Radio waves are converted into high-frequency radiation energy, which is directed to the abnormal contents of the cystic formation, but does not affect healthy tissue. During the manipulation, the patient does not feel pain, since when the wen is removed, there is no effect on the nerve endings.
We recommend reading Hemangioma on the skin: causes, treatment, what is dangerous
Radio wave removal of atheroma requires no more than twenty-five minutes; the patient is not given anesthesia, the skin is not cut, and the hair at the site of the wen is not shaved. High-frequency radiation leads to sealing of subcutaneous blood vessels, so there is no bleeding during the procedure, as with surgical excision.
Complications of the disease
In severe cases of the disease, the cyst festers. Suppuration of atheroma in dermatological practice occurs quite often. If, under such circumstances, the atheroma is not removed in a timely manner, then there is a risk of pus spreading inside the body, first within the soft tissues, and then throughout the internal organs.
In severe cases of the disease, the cyst festers.
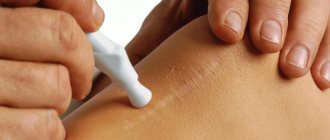
A tumor after surgery to remove it can lead to unpleasant complications. Excessive tissue fluid increases the risk of infection. To prevent infection, it is necessary to prevent the accumulation of excess fluid in the place where the pathological formation was located. You can use a pressure bandage for this.
If there is a suspicion that an infection has been introduced into the wound after surgery, you must immediately make an appointment with a doctor about this problem. An alarming sign is an increase in body temperature to 38 degrees or higher.
Care after removal and possible complications
It is believed that after laser removal of atheroma there is no postoperative period. But this does not mean that the wound does not need to be looked after. Care is necessary to avoid complications.
A crust forms on the wound. Later, when it falls off, there are no scars left. The patient’s task is to maintain the integrity of this crust for as long as possible in order to avoid infection of the wound. To do this, he needs to follow the following recommendations:
- do not wet the wound for 3-4 days;
- regularly change dressings using sterile bandages, plaster, and other dressings;
- Wash your hands thoroughly before dressing;
- refuse to visit the sauna, bathhouse, solarium for the entire wound healing period;
- Use only medications recommended by your doctor to treat the wound.
Complications after laser removal of a trichodermal cyst are possible in the following cases:
- If an infection occurs during suturing. In this case, the seams become inflamed, itching and redness of the skin occurs at the site of the atheroma. Temperature may rise to 37.5°C or higher. This condition must be treated with antibiotics in the form of ointments and systemically.
- Usually, when a tumor is removed with a laser, bleeding does not occur, since the vessels are sealed. But if the drainage is not installed correctly, and bloody and serous discharge accumulates in the wound, this can lead to secondary inflammation. The complication can be eliminated by installing drainage.
Prevention
To prevent the appearance of sebaceous cysts, it is advisable to use the following preventive measures:
- minimizing the amount of trans fats in the diet;
- regular hygienic treatment of the body (showering, etc.);
- timely treatment of skin diseases, fight against dandruff;
- taking measures to eliminate increased sweating;
- minimizing the use of hygiene products that clog skin pores;
- taking measures to normalize skin oiliness.
Removal of atheroma of the scalp in a child and an adult (with video)
Children usually have congenital atheromas, since, as a rule, they do not have any factors contributing to the formation of acquired epidermal cysts. When removing atheroma from a child under 7 years of age, general anesthesia is also used, but the mechanism of the operation itself remains the same as for adults and depends solely on the chosen surgical method. In very young children, a small atheroma without rapid growth and mechanical pressure on surrounding tissues can be observed until the age of 3 years, when the formation can be safely removed. In emergency cases, with complicated atheroma or for other medical reasons, atheroma is urgently removed even in children, without delay.
If the tumor is located on skin densely covered with hair, for example, when removing atheroma of the scalp, you will need to first trim and shave a small area of skin over the tumor to provide unobstructed surgical access.
Watch the video of removing atheroma on the head, which shows the preliminary preparation of the surgical field and the process of the operation itself:
All operations begin with a minimally short surgical incision of the skin, which is made in a certain direction (along the lines of force of the skin) and is performed with a quick and clear movement. The minimum possible incision width is 3-4mm.
Classic surgery to remove an uncomplicated sebaceous cyst can be performed in 4 different ways.
Option one, without affecting the contents of the atheroma and without damaging its capsule. Suitable for small lesions that can be easily removed through a minimal skin incision. The skin is pushed back and the cyst is peeled out like a pea from a pod.