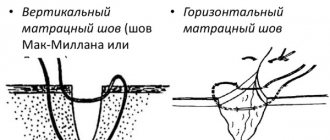
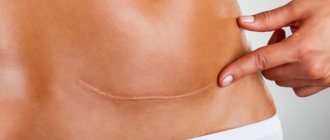
Colloidal scars (also called keloids) are thickening and changes in the skin that appear for various reasons.
A keloid can appear as a result of improper healing of a wound or cut, during the healing of various skin lesions and infectious infections. If stretch marks, atrophic and tight scars are at the same level as the rest of the skin, then keloids seem to rise above it.
This skin tumor is not at all dangerous, but many are trying to solve this problem because of the unesthetic appearance of the healed area of skin. How to remove colloidal scar? Let's look at this issue in more detail.
Why does a scar form?
Keloids are divided into two groups according to their formation:
Primary (spontaneous)
These scars appear on apparently healthy skin for no apparent reason.
The appearance of such keloids can result from:
- Hormonal imbalances;
- Internal injuries;
- Pregnancy;
- Chronic diseases.
Typically, scarring occurs on the neck, back, chin and jaw line, ears, especially the earlobes.
Secondary (false)
Such scars occur in areas of previously damaged skin due to any injuries, skin lesions and ulcers. Wound healing is often inhibited by infection, causing inflammation and scarring.
The reasons include the following:
- Unprofessional surgical intervention;
- Injuries, cuts and wounds healed without proper care and supervision of a specialist;
- Consequences of severe skin diseases, such as acne.
About the colloid node of the thyroid gland
In first place among diseases of the thyroid gland is a colloid node, which is a changed area of the thyroid gland visible during an ultrasound of this organ of the endocrine system or during a physical examination. The colloidal node of the thyroid gland is filled with colloid - the contents are completely consistent with the substance that fills physiologically normal follicles. That is why most of the identified clinical cases are not treated.
Only such a decoction will trigger REGENERATION of the thyroid gland
The goiter will disappear in 3 days! This remedy has become a sensation in the treatment of the thyroid gland!
- About the reasons
- Clinical manifestations
- Diagnostics
- Treatment
About the reasons
The reasons leading to the development of this pathology are quite diverse:
- Iodine deficiency provokes a compensatory increase in various parts of the gland in order to catch more iodine from the blood.
- Periods of physiological changes in the body associated with an increase in the load on the thyroid gland, such as puberty and the development of pregnancy.
- Impaired blood circulation in one of the lobes causes the accumulation of colloid in the tissues, which leads to the formation of a node.
- The presence of congenital anomalies, hemorrhages due to injury, impaired outflow of colloid leads to the formation of a cyst. Epithelial cells or connective tissue form its shell, which protects the contents of the cyst from healthy gland tissue. After all, its cavity may contain not only colloid, but also blood or pus.
- Frequent nervous overstrain and hypothermia of the body cause the development of local spasm of blood vessels, this leads to impaired nutrition of some parts of the gland and a decrease in local immunity. All this leads to disruption of the physiological mechanism of cell division.
- A negative environmental background ensures the entry of various free radicals and carcinogens into the human body. Their impact leads to disruption of the genome of the cells of the gland lobe and uncontrolled division begins, thus forming a formation that can become malignant.
- Previous infectious diseases cause the development of swelling of some parts of the thyroid gland, which can create favorable conditions for the development of a colloid node.
- In rare cases, there is a hereditary burden of development of the node.
The colloidal node can be single or multiple; the growth of these formations is slow. That's why they are detected by chance during preventive examinations using ultrasound.
Clinical manifestations
Mostly colloidal nodes are small in size, and due to their slow growth, they may not manifest themselves clinically for quite a long time. And the person is not aware of the existing pathology until there is an active growth of the formation in the lobe, which leads to the appearance of a cosmetic defect on the front surface of the neck and the appearance of subjective sensations:
- sore throat,
- difficulty swallowing,
- feeling of squeezing in the throat,
- lump in the throat.
When combined with toxic goiter, the existing node or nodes begin to actively secrete thyroid hormones, which causes the appearance of symptoms of thyrotoxicosis: weight loss, nervousness, hand tremors, symptoms of damage to the cardiovascular and digestive systems, which requires immediate treatment.
Since this gland pathology predominantly develops with iodine deficiency, it is worth paying attention to some clinical manifestations of this deficiency condition:
- poor appetite
- the appearance of problems with the health of teeth, skin and their derivatives (nails and hair),
- memory problems,
- headache,
- hearing problems.
If they are present, then you should contact a specialist who will prescribe appropriate treatment.
The clinical manifestations of the node directly depend on its size and the amount of hormones it produces. Some are detected by chance during an ultrasound of the right and left lobes of the gland and appear as areas that differ in color from the healthy tissue of the gland lobes. Using ultrasound, you can identify pathological formations from 5 mm.
Diagnostics
The examination of the patient begins with a visit to an endocrinologist, who begins to keep a history of the disease. During the examination, an increase or decrease in the size of the right and left lobes of the gland, its elasticity, and pain are determined; number of nodes and their density, mobility. It is important to note that the size of the right lobe of the thyroid gland is larger than the left - this is an anatomical feature of this organ. Then he proceeds to a survey and clarifies the existing symptoms and whether the node was treated by another doctor, if so, then it is specified with what drugs.
Then the patient is sent for a full examination - laboratory and instrumental diagnostic methods; only after receiving all the data will the doctor prescribe treatment.
When a node is detected, the patient must donate blood to determine the level of thyroid hormones: T3, T4, thyroid stimulating hormone, calcitonin.
To carry out scintigraphy, the patient is first given preparations with radioactive iodine, the isotopes of which are absorbed by the tissues of the gland, and with the help of a special gamma camera the areas of its accumulation are determined. When the concentration increases in the area where the node is located, it indicates the active absorption of iodine and the production of hormones. When the concentration decreases, there are no cells actively producing hormones in the control. This study is contraindicated during pregnancy.
The main diagnostic method is ultrasound of the organ.
Ultrasound is prescribed for all patients in whom nodes are identified during physical examination. It makes it possible not only to determine the exact location of the formation, but to accurately determine its size and examine intact gland tissue. On the ultrasound machine screen, the nodes are defined as anechoic formations, since they cannot reflect ultrasound waves. The gland itself has uneven contours and a heterogeneous structure.
FNA of the thyroid gland is a modern diagnostic method that allows us to speak with high accuracy about the nature of the formation. With this method, a small area of the node is taken for microscopic examination under ultrasound guidance, so as not to injure nearby organs.
Treatment
For small colloid nodes, drug treatment is not carried out; patients are recommended to introduce iodine-rich foods into their diet. And they are monitored by endocrinologists, who must be visited twice a year; before the appointment, an ultrasound must be done to monitor the dynamics of the growth of the node.
If rapid growth of the node is detected and signs of compression of nearby anatomical formations appear, surgical treatment is indicated. It can be performed under local or general anesthesia; in some cases, another ultrasound of the gland is performed before the operation. It lasts no more than an hour; at the end, a cosmetic suture is applied. Surgical treatment requires short-term hospitalization, after which the patient is discharged and is under the supervision of the treating endocrinologist for a certain period of time.
The appearance of a keloid
There are three stages before the complete formation of a keloid:
- During the first 7-10 days, a thin epithelial layer appears on the affected area of the skin, which may be accompanied by painful sensations;
- Next, scarring occurs within 25-30 days, scar tissue protrudes above the main skin;
- After the formation of a scar in the affected area, the percentage of connective tissue increases, blood vessels disappear over time, and the scar becomes denser.
Diagnostics
For an accurate diagnosis, gland tissue is needed. To obtain them, a biopsy is used. The material is taken where there is an accumulation of colloid in the thyroid gland, under ultrasound control, using disposable syringes with thin needles. The puncture does not require additional anesthesia, because the procedure for collecting material takes place within a few seconds. The study of biological material allows us to exclude a malignant tumor. A laboratory blood test ordered to determine hormone levels will indicate the functionality of the gland.
Read more about thyroid puncture in the following article >>
Colloid formations in the thyroid gland are determined by external examination.
Colloid formations in the thyroid gland are determined by external examination. It allows you to determine the dimensions and contours of the node. To obtain a more accurate picture of the disease, an ultrasound is performed, which allows one to determine the structure of the tumor. This type of examination reveals the exact size of the colloid nodules of the thyroid gland. If there is a suspicion of cancer, a computed tomography scan is prescribed.
Having undergone such a diagnosis of the disease, the patient receives from the doctor an accurate diagnosis and recommendations on how to correct the dysfunction of the internal secretion organ discovered during the examination.
Home treatment
Time-tested folk remedies can be quite effective in preventing relapses and tumors.
Some folk remedies against keloids:
- Compresses and infusions of chamomile, geranium, St. John's wort, mint, yarrow, marshmallow root or larkspur, individually and in mixtures;
- Oils and extracts rich in vitamins, acids and antioxidants, for example, sea buckthorn, camphor, olive or melaleuca oil, known for its healing and healing properties;
- The well-known cabbage, in particular, crushed leaves of the plant with honey give a positive effect against colloidal scars.
Prevention
By following simple rules, you will not only protect yourself from the growth of operated or treated scars, but also prevent the appearance of new keloids on the body.
To protect against colloidal scars you must:
Allergic dermatitis - causes of appearance, first symptoms and treatment in children and adults (video + 130 photos)Treatment of dermatitis - professional methods for effectively getting rid of the disease in different areas of the skin (105 photos)
Treatment of varicose veins - which specialist to contact and how the treatment procedure occurs. Stages of recovery and description of treatment (140 photos + video)
- Do not allow tissue tension around the keloid;
- Do not take risks by trying to cure a scar on your own;
- It is forbidden to massage or put pressure on the damaged area;
- Do not expose the colloid to direct sunlight and avoid high temperatures;
- Let treatment take its course, ignoring and neglecting the advice of a specialist.
With proper care and timely treatment, this problem will not cause you much trouble and worry.
Conservative methods of relieving itching
There are many conservative ways to relieve the discomfort caused by itching of a scar or scar on the skin. You can resort to them if the methods described above did not help. For example, old scars can be removed using non-surgical and conservative methods. Specialists in clinics use hormonal drugs administered by injection. The dosage and the product itself are determined taking into account individual factors.
If the scar after a cesarean section is very itchy, Contractubex and corticosteroid-based ointments can be applied after healing. The main thing is to choose the right moment, when the scar has not yet hardened, but has healed sufficiently. The scar should still be a little soft and elastic, and the suture fibers should not be stretched.
When scars itch after surgery, doctors may prescribe electrophoresis or physical therapy to patients. This could be laser scar removal - the procedure involves cutting off the blood flow to the suture, as a result of which it evens out and takes on the color of the surrounding skin. The laser can also evaporate fluid from scars and scars, clearing the surgical site.
As for phonophoresis, which is based on ultrasound exposure and the use of medications, it also helps fight the problem of itching a scar or scar. Microcurrent therapy evens out the skin with weak current pulses, ensuring effectiveness and absolute safety of the procedure.