Symptoms of atheroma
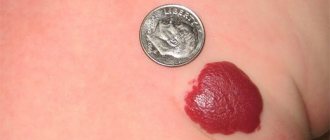
For a long time, the epidermal cyst may not appear visually. The formation under the skin grows slowly: the process can take a year or more. In this case, a tumor is formed under the skin, in which a secretion consisting of lipid, cholesterol and dead epithelial cells accumulates. The size of the capsule (wen) varies greatly - from a few millimeters to a 5-7 cm diameter.
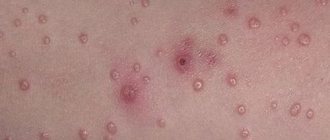
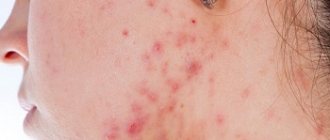
As a rule, a person notices visual symptoms of atheroma on any or several areas of the face. What does a subcutaneous pathological neoplasm look like? Facial atheroma is characterized by:
- dense structure, which is determined by palpation;
- mobility of the skin over the formation, inability to form a fold in this area;
- the cyst on the face under the skin has an even round shape (resembles a soft ball);
- the epidermis in the tumor area does not differ in color/structure;
- simple atheroma on the cheek or elsewhere on the face does not cause pain;
- the neoplasm is prone to suppuration and inflammation, and these processes are painful and stimulate an increase in skin temperature in the area of the wen;
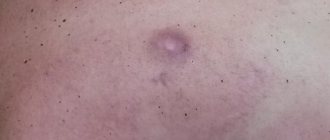
- a purulent sebaceous gland cyst on the face looks like an abscess (swollen neoplasm with white contents)
Origin of atheroma
The accumulation of detritus (secretion of the sebaceous glands) in combination with blockage of the excretory duct is the main reason for the formation of atheroma. Most often, a retention cyst is diagnosed in patients of both sexes from 16 to 60 years old. In rare cases, it is a congenital anomaly of intrauterine development of the fetus and is found in young children.
The skin of the human body is protected by about 90 thousand sebaceous glands. This allows it to retain moisture, maintain a constant body temperature and bactericidal properties. All these functions are carried out due to the fact that the sebaceous gland produces a specific secretion, simultaneously dividing its cells and partially destroying them. This cycle lasts 3-4 weeks, during which the contents of the gland are completely renewed.
Detritus is produced by three types of sebaceous glands:
- Large glands on the nose, cheeks, chin, and scalp;
- Medium glands in the vellus hair area;
- Small glands in the long hair follicles of the upper layer of the skin.
The excretory duct can open both into the hair follicle and onto the surface of the skin.
Causes of atheroma
The only cause of the disease is blockage of the sebaceous gland on the face due to increased density or impaired outflow of sebum. Different conditions can provoke this process. Such factors are divided into internal and external, the latter including:
- bad ecology;
- heat;
- work in highly polluted conditions;
- use of oil-based cosmetics.
Internal causes of atheroma are:
- oily seborrhea;
- bacterial growth on the face (insufficient skin hygiene);
- hyperhidrosis;
- heredity;
- acne;
- impaired metabolic processes;
- hormone imbalance.
In men, a factor provoking the disease may be an increased amount of testosterone produced and irregular shaving of the beard/mustache. In newborn babies, a cyst on the cheek, as a rule, indicates the presence of maternal hormones. Doctors often associate the appearance of oily warts with the effect of cosmetics with a thick texture on the skin (as a rule, these are oil-based products that clog pores).
Atheroma in a child
Benign formations on the face are more common during puberty, when adolescents begin puberty. However, experts sometimes diagnose a tumor in small children, including newborns. Atheroma in a child of this age is provoked by the accumulation of fatty secretions, as a result of which the gland duct is clogged. Possible causes of pathology in children may be:
- increased sweating;
- insufficient skin hygiene;
- wearing clothes that are too warm (overheating of the body) or things made of synthetic materials;
- changes at the hormonal level.
Atheroma can occur due to improper functioning of the endocrine system. In addition, children with excess weight, acne and acne are predisposed to pathology. The disease in a newborn indicates defects during the intrauterine formation of the epidermis. The reason for this anomaly is unknown, but some experts associate it with the diet and lifestyle of the woman bearing the fetus.
Symptoms and signs of atheroma
c The neoplasm does not hurt, does not become inflamed, does not change color, and does not change the structure of the skin. Doctors diagnose the disease based on external signs.
Main characteristics:
- Convexity with clear boundaries.
- Does not float or change shape when pressed.
- The neoplasm is mobile.
- Skin color is yellow.
- Liquid with a noticeable odor may be released from the small duct of the neoplasm.
A cyst of fluid formed by the sebaceous glands most often occurs on the face, forehead or near the eye. This location of the atheroma can interfere with the normal process of vision, especially if it concerns the eyelid or the lacrimal caruncle. Its rapid growth can be triggered by oily cosmetics. In rare cases, the wen appears on other parts of the body: on the back, ear, head, nose, cheek.
When an infection hits the atheroma, suppuration occurs. It changes color, the skin in its area becomes red, swelling and pain appear. Body temperature rises. In such cases, the wen must be treated immediately to prevent capsule rupture.
Can atheroma resolve on its own?
In rare cases, the neoplasm may disappear without surgical intervention, but you should not hope that the atheroma will resolve on its own. If your doctor advises you to remove the tumor, you should listen to him. A tumor under the skin can be removed in one of three ways: radio wave, surgical excision or laser. Getting rid of a tumor is easy: to reduce the risk of skin damage and scarring, it is better to choose a laser or radio wave method. Relapse after treatment is extremely unlikely - the tumor reoccurs in only 3% of cases.
Which method is better?
It is impossible to say exactly which method of getting rid of atheroma is better. This is determined by the attending doctor, based on the location of the tumor and its size. For example, it is better to remove large wen in difficult places using the radio wave method. Inflamed formations are eliminated exclusively through surgery. Doctors only agree that it is better to get rid of the wen in the early stages. Therefore, if you find a lump on your body, it is important not to self-medicate or use traditional medicine recipes, but to immediately contact a medical facility. This will allow you to get rid of the wen in the safest and most painless way and eliminate the risk of its reappearance.
Treatment of atheroma
Before starting treatment for the disease, atheroma is diagnosed, which consists of a visual examination of the patient and palpation of the tumor. To accurately determine the nature of the tumor, histology (analysis under a microscope) is done. This event makes it possible to establish the presence of atheroma under the skin even when visually it is practically indistinguishable. Gradually, the volume of contents in the cyst increases, which causes the growth of a tumor under the skin.
If you do not begin timely treatment of atheroma, the tumor will become large and can rupture, resulting in tissue infection. To avoid such consequences, it is important to resort to such a treatment measure as surgical removal of the atheroma. Conservative (use of drugs) and traditional methods of treating a tumor are powerless in this case, so cleansing the cyst cavity is carried out by resection, that is, the tumor is removed along with the capsule.
Treatment of atheroma without surgery
If you treat the disease without surgery, you should not expect a quick effect. In addition, only a few achieve positive results using traditional methods and the use of medications, while the condition of the tumor under the skin continues to worsen. If you try to open the capsule yourself, there is a high risk of developing sepsis, since it is impossible to thoroughly clean the cyst at home.
Treatment of atheroma without surgery is highly not recommended, however, if the tumor has ruptured on its own, you need to carefully wipe the wound with a sterile cotton pad, cover it with a bactericidal plaster and consult a doctor (dermatologist or surgeon). The specialist will clean the wound cavity, preventing suppuration or relapse of atheroma. Only surgery can guarantee with almost 100% probability that the tumor will not re-form under the skin.
Recurrence of atheroma
Recurrence of atheroma is mainly observed in cases where the capsule of the cone is not completely excised during surgery. Since it remains in the skin, the wen grows again in the same place, sometimes reaching an even larger size than before. Reappearance of the tumor is also observed during self-medication. People decide to squeeze out the atheroma themselves, which in most cases leads either to infection of the wound and subsequent inflammatory process, or to incomplete removal of the capsule.
The optimal method for removing atheroma is selected depending on the size and location of the tumor.
Surgical methods
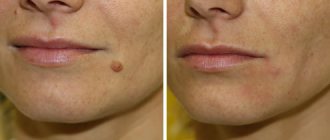
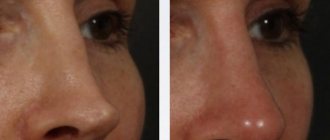
If atheroma has formed on the face of a small child (under 7 years old), then the only suitable treatment method is to remove the capsule with a scalpel, laser or radio waves under general anesthesia. In adults, this procedure is performed under local anesthesia. Unlike classic excision with a scalpel, other methods of surgical intervention do not leave visible marks on the skin and minimally injure blood vessels. In addition, laser and radio wave procedures eliminate the need for postoperative measures.
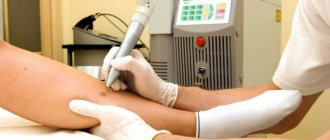
Removal of atheroma on the face with laser
The method is indicated for small tumors without tissue inflammation. Removing atheroma on the face with a laser leaves virtually no scars or scars and does not disturb the subcutaneous microflora. The technique belongs to the bloodless category, and the wounds left after the operation heal quickly. The average duration of the procedure is 20 minutes. If atheroma is removed from the scalp, the patient does not need to pre-shave. The laser treatment method almost completely eliminates the likelihood of relapses.
Atheroma after removal
After excision of a large tumor, the wounds are sutured, and the sutures are removed after about a week (with normal healing process). After removal, atheroma should be treated daily with an antiseptic solution such as Betadine. In addition, in the first few days the wound site should not be wetted. Dressings after surgery are carried out if the source of the disease is in the area of clothing friction. Until the wound is completely healed, it is recommended to treat the skin with Levomekol and Vishnevsky balm.
Treatment methods
Atheroma in a newborn is dangerous because it cannot be removed surgically. Since the operation is performed under anesthesia, and subsequently antibacterial therapy is used, there is a risk of harming the baby’s health. This is why doctors rarely prescribe surgery.
In most cases, a wait-and-see approach is used. If the cystic formation increases slightly in size, there is no risk of complications, and the child feels well, then nothing is done for a long time. Surgical intervention is postponed until 2 years.
After reaching this age, the decision to perform surgery is made based on the patient's condition. The danger comes from the seals that are located on the head. In this situation, with the development of the inflammatory process, there is a risk of brain infection. This is fraught not only with developmental disorders, but also with death.
Medications are ineffective because they cannot remove the capsule. Therefore, drugs are prescribed only during infection or during the recovery period after a surgical procedure. Complex treatment involves the use of antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs. Any medications or ointments are used only as prescribed by the attending physician.
Methods for removing epidermal cysts
Since the only way to eliminate the wen is to remove the capsule along with its contents, doctors prescribe surgery. This happens in cases where atheroma poses a danger. There are several main ways to eliminate a benign tumor. A classic surgical operation is prescribed, the procedure is performed using a laser or radio wave method. Each of these types of manipulation has its own characteristics and advantages.
Surgical
The walls of the capsule are excised under anesthesia.
This is the most common way to eliminate a tumor. In this case, the walls of the capsule are excised under anesthesia. A surgical scalpel is used to open the membrane. Then not only the liquid contents are removed, but also the cavity itself. This helps prevent re-clogging of the duct.
The advantage of this type of intervention is that there is no risk of relapse. However, the recovery is long, and a cosmetic scar may remain.
Laser
During the intervention, a laser is used to make small pinpoint incisions.
Using a laser, you can remove atheroma that has not yet reached a large size. Large thickenings are usually removed using the classical method. During the intervention, a laser is used to make small pinpoint incisions. Through them, the cavity is cauterized along with its contents.
The advantages of the procedure are that there is virtually no pain during the recovery period, the rehabilitation itself does not last long, there are no scars left, and healthy tissues are not affected. Disadvantage: laser is not used if the wen has reached a large size.
Radio wave excision
This method is also used for small thickening diameters. The manipulation is similar to that performed with a laser scalpel. The difference is in the use of radio wave radiation.
The child recovers quickly and feels virtually no pain.
During the operation, bleeding is eliminated, since the vessels are simultaneously cauterized. Healthy tissues are also not affected.
After the procedure, the patient recovers quickly and feels virtually no pain. The mark will be barely noticeable, which is important when localizing atheroma on the face.
Treatment of atheroma with folk remedies
Therapy of a neoplasm using non-traditional methods can be carried out only if the symptoms of the disease are not pronounced. At the same time, the most effective are considered to be rubbings, compresses and ointments that are prepared independently at home. Treatment of atheroma with folk remedies may include:
- Ointment for swelling on the skin of the face with burdock. Mix the plant, ground using a meat grinder, with pork fat, leave the mixture in the dark for 3 days. Lubricate the atheroma with the resulting product 1-3 times daily.
- Onions against neoplasms (wen) of skin water. You can reduce the swelling like this: mix the same amount of baked onions with laundry soap, after grinding the ingredients. Apply the mixture to the atheroma, covering the skin with a sterile bandage on top. Change the compress twice a day.
- Lamb fat for adipose tumor. Melt the product and rub it into the affected area of the skin until completely absorbed. Continue using fat until the symptoms of the skin disease decrease.
Symptoms
With this disease, there may be a history of complaints about a subcutaneous formation, which easily moves when pressed. There is no pain at the initial stage of the disease. If the atheroma hurts, this indicates the progression of the disease. The skin cyst in the cavity is filled with horny masses and products of the sebaceous glands.
If the tumor hurts, this indicates progression of the disease.
If the patient does not receive proper treatment, the skin cyst progresses and severe pain appears. Pain indicates that the atheroma is inflamed. In this case, an abscess forms in the cavity of the cyst (accumulation of pus in the tissues with their melting).
A festering atheroma is a reason to see a doctor as soon as possible in order to remove it.
Common causes of inflammation are:
- violation of personal hygiene;
- excessive use of cosmetics and deodorants;
- presence of concomitant infectious diseases;
- regular trauma to the cyst with a comb, items of clothing, etc.
In some cases, inflammation of atheroma is associated with self-medication, so it is necessary to remember that conservative treatment, and especially removal of the cyst, should only be carried out by a doctor.
Prevention of atheroma on the face
Neoplasms arise due to a violation of the outflow of sebum, which occurs due to blockage of pores, therefore the prevention of atheroma on the face should be based on regular cosmetic procedures for cleansing the skin. These include:
- visiting the sauna;
- steam baths;
- cleansing masks;
- massages.
To reduce facial skin oiliness, you should use special tonics and cleansers. In addition, preventing the development of tumors on the skin of the face should include proper, balanced nutrition. So, with high fat content of the skin, you need to exclude fatty and carbohydrate-rich foods from your diet. If the tumor recurs after removal of the tumor, you should definitely contact an endocrinologist who will help determine the causes of the disease.
Prevention methods
To enhance the cleansing process, you can use the following methods:
- steam baths for the face, they help open pores and deep cleanse dirt;
- the diet should be balanced, complete with fats, proteins and carbohydrates;
- For women, it is very important to remove makeup with high-quality products before going to bed;
- take vitamin complexes once a year;
- limit sun exposure.
Atheroma requires immediate medical intervention, despite the fact that it is benign. Delaying a visit to the doctor can lead to suppuration of the capsule, which leads to serious consequences. Timely assistance eliminates relapse and guarantees a full recovery.
Possible complications of atheroma
Often people tend to ignore the manifestations of atheroma, believing that if the tumor does not cause pain, then it is not dangerous, and, therefore, there is no need to treat it. And if people think about treating atheroma, they prefer to postpone its treatment until later due to various circumstances.
Indeed, atheroma is painless and asymptomatic - just a small round-shaped wen that is noticeable under the skin.
And people usually pay attention to such formation only when it begins to hurt and cause concern. But despite its so-called external harmlessness, atheroma still has its negative consequences. Fortunately, the likelihood of their occurrence is not very high, but still such a possibility exists and should not be ignored.
There are several types of possible consequences of skin atheroma: Inflammation of atheroma is the most common and dangerous type of complications of a wen. This complication occurs when the patient delays treatment of atheroma without consulting a doctor on time.
Sebum and epithelium, which has exfoliated, which is located inside the atheroma, are an extremely favorable environment for the formation and development of pathogenic bacteria. Unfortunately, it is now unknown what exactly causes inflammation of a previously stable atheroma, but it has been proven that this can occur at almost any time during the development of atheroma.
After the atheroma begins to become inflamed, you must immediately consult a doctor who can clean the wen from the pus that has accumulated inside it, treat it with an antiseptic, and then install drainage - it will help protect the wound from accumulations of pus in it.
Only after such procedures can you rest assured that everything will be fine with the atheroma. It should be remembered that atheroma can be removed only if inflammation from the atheroma is completely removed. Relapse is another complication of atheroma, which manifests itself in the repeated formation of atheroma in the same area of skin.
This happens if, when cleaning out the atheroma, some of its parts were not completely removed. If even a small piece of wen remains under the skin, it can very easily recur into a new atheroma. Cellulitis is a consequence of atheroma, which is considered the most serious complication of this disease.
With phlegmon, purulent melting of the atheroma capsule occurs, after which pus spills into the subcutaneous layer and deeper. The result of this can be widespread inflammation of the subcutaneous tissues. If treatment for this complication is not started in a timely manner, it can lead to very serious complications, including inflammation of the tissues and organs that are located next to the atheroma.
In addition, penetration of pus into the circulatory system and sepsis is possible. Inflammation of the scar that remains after surgery is a complication that usually occurs after the procedure for removing atheroma.
With this complication, the postoperative scar begins to become inflamed and rot. As a rule, such consequences occur when the operation was performed without observing the rules of personal hygiene, or when after the operation the patient himself did not adhere to the rules of personal hygiene.
Taking these factors into account, it is important to remember that the larger the atheroma, the larger the scar after it, and, consequently, the risk of scar inflammation is higher. Malignant degeneration of atheroma is the development of low-quality tumors from particles of atheroma that remain after removal.
Fortunately, the likelihood of such a development is minimal, but still it should not be completely excluded. That is why the remains of atheroma are often sent for histological examination to a special laboratory. As you can see, even such an innocent disease as skin atheroma can have a number of rather serious and unpleasant consequences.
The patient must strictly adhere to the rules and recommendations that the doctor will give him after the operation. Often, in addition to recommendations for wound care after removal of atheroma, the doctor prescribes the patient to take certain medications - often painkillers, as well as antibiotics.
After the operation, a small scar remains at the site of the atheroma, which tends to resolve over time. The time for complete healing of the surgical site depends on the individual characteristics of the body. After the patient has had the atheroma removed, the occurrence of various complications is quite rare.
However, it should be remembered that any intervention in the human body cannot pass without leaving a trace. Sometimes after surgery there is bleeding from the wound. It is also quite possible that there will be a slight increase in overall body temperature on the first day after the operation.
These symptoms are quite normal for a person after surgery to remove atheroma. However, if the body temperature tends to rise and persist for some time, then the patient needs to urgently seek help from a doctor.
Source: lady-all.ru
Surgical removal of atheroma: features and reviews
A sebaceous cyst (atheroma or, in common parlance, a wen) is a benign formation consisting of a capsule with sebum inside. Atheroma can be located anywhere on the body. Very often it becomes infected. But in the absence of inflammation, the formation is usually asymptomatic.
This formation is the result of blockage of the ducts of the sebaceous glands. Atheromas are very rare in children, but quite common in adults.
The formations are mobile, grow slowly, have a round shape, are painless and are located in the subcutaneous tissues. Atheromas consist of a thin white capsule filled with keratinized material.
Their size can vary from a few millimeters to 5 centimeters.
Sebaceous cysts are more properly called epidermal inclusion cysts. They are benign skin lesions. Lesions rarely require intervention due to medical necessity, so they are most often removed for cosmetic reasons. If cysts become inflamed, reappear, or become so large that they interfere with the patient’s normal life, it is recommended that they be removed.
Atheromas do not go away on their own. Their size may increase or decrease over time. But to completely get rid of such formation, you need to contact a specialist.
Biopsy
This method is carried out in conjunction with laser excision. In this case, the laser makes a small hole through which the contents are removed. Removal of the outer walls of the cyst occurs after about 4 weeks. With this method of removing atheroma, fairly rapid healing occurs.
Regardless of the method chosen, the contents of the wen capsule are poisoned for laboratory research.
Rehabilitation
After surgical removal of the atheroma, the doctor prescribes the use of antibacterial ointment to prevent infection of the postoperative wound.
It must be used until the incision is completely healed. Your doctor may also prescribe a cream to reduce the risk of scars and keloids.
It must be used immediately after the sutures have healed and until complete resorption and the disappearance of the cosmetic defect.
In some cases, slight swelling may occur after removal of the atheroma. After some time it should go away on its own. If the swelling does not go away, but on the contrary increases, and other symptoms appear, such as:
- redness of the area around the incision,
- discharge of pus after drainage is removed,
- temperature increase,
- the appearance or intensification of painful sensations,
It is recommended to seek qualified medical help immediately.
Complications
There are minimal risks after any surgery. The same is the case with surgical removal of atheroma. Here are some complications that may occur during and after the procedure:
- cyst rupture,
- abscess,
- incomplete removal of the contents of the atheroma or the capsule itself,
- blood clot formation,
- degeneration into oncological education.
A sebaceous cyst is considered unusual and may have signs of malignancy if the following characteristics appear:
- diameter is more than five centimeters,
- rapid relapse after opening,
- signs of infection, such as redness, pain, or pus.
Features of atheroma
The fatty deposit is formed due to blockage of the entrance channel of the sebaceous gland, which occurs against the background of disturbances associated with the proper outflow of sebum. As a result, the fat accumulates, becomes thicker, and eventually forms a benign tumor. Modern medicine knows many reasons why atheromas can occur, especially on the face. Depending on the provoking factors, they can be of two types:
- Congenital - the problem is associated with intrauterine disorders of the development of the epidermis. For example, these could be improperly formed sebaceous ducts that are either too narrow or crooked. People with a similar problem very often experience an ailment such as atheromatosis - this is multiple formation of small fatty deposits, usually localized in the head and groin area.
- Acquired - they are also called retention cysts. They appear as a result of pathologies associated with impaired functionality of the sebaceous glands.
If in the first case everything is clear enough, then in the second there must be a certain reason. Today there are a significant number of provoking factors:
- sudden changes in hormonal levels. A similar phenomenon is very often observed in adolescents;
- hereditary predisposition;
- failure to comply with personal hygiene rules;
- poor ecology and unfavorable climate, provoking increased work of the sweat and sebaceous glands;
- increased sweating (hyperhidrosis);
- use of low-quality cosmetics and hygiene products;
- long-term acne;
- keratinization of the upper layer of the epidermis, which prevents proper cleansing of the skin;
- mechanical removal of large pimples and boils at home;
- metabolic disorders.
The disease can progress in different ways. In most cases, the cyst remains small in size, has a round shape and average density. If the provoking factors persist, the atheroma grows to the size of a classic wen - this is a fairly large and soft formation.
The tumor is usually localized in the cheeks, ears or chin.
Contrary to popular belief, wen does not always remain safe for humans. Sometimes the neoplasm can become inflamed, which will lead to its suppuration. Over time, a small channel will open, from which purulent contents will be released, consisting of exudate, dead epidermal cells and secretion of the sebaceous glands. This is already an obvious pathological process, which can lead to the spread of infection to healthy tissues and the occurrence of atheromatosis.
As for the nature of the neoplasm, in most cases it remains unchanged. But there is still a possibility that the tumor can transform into a malignant one, that is, it will become malignant.
Considering all of the above, treatment of atheroma is relevant for all people who have this pathology. Here it is imperative to take into account all the risks associated with the further development of the tumor, as well as the presence of a pronounced cosmetic defect. Lack of proper treatment can result in extremely serious problems for the patient.
Diagnostic methods
To diagnose the pathology, you need to contact a surgeon. The first stage of the examination will be to interview the patient and identify the probable cause of the tumor. Next, the doctor examines the atheroma, identifies the degree of inflammation, and determines a proposed treatment regimen.
A mandatory stage of diagnosis is a general blood and urine test and a biochemical blood test. Sometimes the doctor prescribes an ultrasound examination of the tumor, especially if it is large. It is important to differentiate the diagnosis from other pathologies with similar manifestations. In addition, the doctor always identifies chronic diseases of the internal organs, which can affect the course of the process and recovery.
Atheroma is often confused with lipoma. But these are completely different pathologies. When pressed, the subcutaneous atheroma remains in place, but the lipoma slips out, so it is impossible to press it with one finger. In addition, it is worth paying attention to the consistency of education. A lipoma is softer and more flexible, while a cyst is hard.
Thanks to simple manipulations, the specialist makes a final diagnosis and prescribes appropriate treatment.
Symptoms. How to diagnose?
- Subcutaneous thickening from 0.5 to 5 cm or more
- Soldered to skin
- Movable
- There is an opening of the excretory duct (not always clearly visible)
- Consistency from soft-elastic to dense
- Painless (in the absence of inflammation)
If left untreated, the cyst can reach significant sizes.
Most often, the diagnosis is made based on examination. If in doubt, an ultrasound is performed.
Types of atheroma and what it looks like
In medical practice, the following types of formations are distinguished: true - arising due to genetic predisposition, and false - the appearance of which is associated with other factors.
Despite the identity of symptoms and treatment tactics, different types of atheromas differ in their microscopic structure, which allows them to be classified into epidermoid or epidermal, dermoid, tricholemmal and multiple steatocystoma.
This systematization is important exclusively for scientific research and is not used by specialists.
In addition, wen can occur as single formations (in 30% of patients) or multiple formations (in 70% of patients). It is possible that there are more than ten bumps of various sizes on the skin, located throughout the body or grouped in a small area.
Symptoms of blockage
- The appearance of a dense formation that can be easily felt by palpation of the skin. It can be small or reach the size of a large nut.
- Your temperature may rise.
- The skin around the blockage will turn red.
- Painful sensations occur.
- If the disease is advanced, the blockage becomes bluish in color.
- An unpleasant odor occurs if the cyst begins to fester.
The blockage looks like a small tumor. It is soft to the touch, its diameter is most often 5 cm. If inflammatory processes begin, the skin may acquire a light brown or red tint.