Types of postoperative sutures and suture materials
Considering the technique of suturing, there are the following types:
| Name | Description |
| Continuous | When stitching a wound, one long piece of thread is used. |
| Nodal | During medical procedures, several pieces of thread are used, which are tied at a certain distance from each other. |
| Primary | They are used to stitch the edges of the wound for complete tissue healing. |
| Secondary | Threads are placed on top of the primary seam to strengthen it if the edges have separated. |
| Ligature | A method of suturing, in case of damage to blood vessels, to restore their integrity and circulation. |
The surgeon chooses the technique for connecting the edges of the wound, taking into account the severity of the surgical intervention and the patient’s condition.
For the production of suture material, high-quality raw materials are used, which makes the threads smooth and elastic with high strength. Their advantage is good glide and hypoallergenicity, and the threads do not swell when exposed to moisture.
The following types of suture materials exist:
- natural (silk, cotton);
- synthetic;
- absorbable (catgut, biopolymers);
- non-absorbable.
Threads for suturing a postoperative wound are made from one type of raw material or several at once, and may have different coatings. The doctor chooses the suture material, taking into account the type of operation and the patient’s condition.
How to remove stitches?
At home, sutures after abdominal operations are prohibited from being removed. Sutures can be removed when suturing skin defects on the upper and lower extremities.
Rules and techniques for removing postoperative sutures
- It is necessary to prepare sterile instruments and disinfect your hands up to the elbow. Provide access to the seam.
- Using an antiseptic, treat the suture area with a cotton swab.
- Then, taking tweezers in your hand, slightly lift the first knot.
- Taking the scissors in your hand, cut the suture thread.
- Do this with all nodes.
- Make sure that all suture material is removed.
- Treat the area of the removed suture with an antiseptic solution.
- Apply an aseptic bandage.
Stages of healing of surgical wounds, healing time
Complete healing of the postoperative suture requires careful wound care; this is the only way to minimize the likelihood of serious complications. It is important to strictly adhere to your doctor’s recommendations during the recovery period.
There are several stages of healing of a postoperative suture:
| Name | Description |
| Active phase | At this stage, collagen formation occurs. Tissue healing is facilitated by fibroblast, which moves to the site of damage. |
| Epithelialization | The surface of the wound is covered with epithelium. Over time, a protective layer is formed that prevents the penetration of infection. |
| Closing the wound | The area of damage is reduced due to the reduction of myofibroblasts. |
After 3 months, the epithelial tissue is completely rebuilt. A scar is formed, which is covered with an imperceptible light line. The wound finally heals 1 year after surgery.
Stages of suture healing after surgery
Healing of sutures after surgery is carried out in 3 stages.
At the first stage, the synthesis of connective tissue begins to increase from collagen fibers formed by fibroblasts.
At the second stage, epithelial cells change their localization, moving from the periphery to the center to the site of damage. These cells provide a barrier function, preventing microbes from entering the wound surface. The second stage ends by 4-6 days, if everything proceeds without complications.
At the third stage, complete closure of the wound defect occurs.
Important! Wounds should be treated only after cleaning the hands first with water and soap, then with alcohol. Tools must be disinfected before use.
Factors influencing the rate of wound healing
The healing process of a postoperative suture depends on numerous factors:
| Name | Description |
| Age | A young body copes faster compared to older people. |
| Body mass | Due to poor blood supply, fatty tissue is difficult to withstand various injuries, so stitching wounds in people with extra pounds is more difficult. |
| Nutrition | During the recovery period, the patient’s body requires more vitamins and microelements to regenerate damaged tissues. |
| Dehydration | Insufficient fluid levels in the body affect the functioning of internal organs and systems, on which the rate of healing of the postoperative suture depends. |
| Blood supply | In an area where there are a large number of blood vessels, wound healing occurs faster. |
| Immune status | Human immunity is necessary for protection. Various disorders slow down the process of regeneration of damaged tissues. |
| Chronic diseases | Concomitant pathologies not only slow down the healing of the postoperative suture, but also provoke numerous complications. |
| Medications | While taking certain medications, the postoperative wound heals slowly. |
| Insufficient oxygen supply | Epidermal cells need a large amount of oxygen in order for the postoperative suture to heal quickly. This process is disrupted by vascular insufficiency, tissue ischemia, or hypotension. The same applies to radiation therapy, when connective tissue grows and small blood vessels overlap. |
Secondary infection, when an infection gets into the wound, significantly worsens the condition of the suture and the regeneration process. After surgery, it is necessary to treat the incision area to completely eliminate the negative impact of provoking factors.
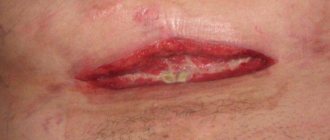
Why does the suture fester after surgery?
When dissecting the abdominal wall, be it a straight, transverse or oblique incision, it passes through the skin, subcutaneous fat, muscles, fascia or aponeurosis, preperitoneal tissue, and peritoneum. In some cases, the muscles are not cut, but moved apart, which subsequently speeds up healing. After abdominal surgery is performed, all layers of the abdomen are sutured. The technique of this manipulation will depend on where and how the access was performed. To make healing more likely to occur by primary intention, they try to sew each layer to a homogeneous tissue. Layer-by-layer suturing of a wound usually involves about 3-4 rows of sutures.
- After mid-upper laparatomy (access to the organs of the upper abdominal cavity), the parietal peritoneal layer, preperitoneal tissue and transverse fascia are picked up first. Catgut is used, which then dissolves on its own and does not require removal of suture material. Second row - separate interrupted sutures with silk, lavsan, nylon on the white line of the abdomen. This material does not dissolve and must be removed after the wound has healed. The third row of interrupted sutures is placed on the skin.
- Lower median laparatomy involves the first row to continuously suture the peritoneum and fascia with catgut, the second - separate sutures from catgut to the rectus abdominis muscles, the third - using synthetics with separate sutures to close the sheath of the rectus muscle, the fourth - to restore the skin and subcutaneous tissue with a discontinuous suture.
- Caesarean section usually involves a transverse approach along the suprapubic skin fold. The wound is sutured, starting from the parietal peritoneum in the longitudinal direction, with catgut continuously. The muscles are sewn continuously or with separate sutures using absorbable material. Aponeurosis - synthetics. Subcutaneous tissue - with catgut. The skin is sewn either with separate synthetic sutures, or with a continuous percutaneous self-absorbing suture, or fastened with metal staples.
To reduce the risks of postoperative inflammation even before surgery, in some cases, the patient is preventively prescribed cephalosporin antibiotics. The surgical field is treated with antiseptics before incision and after suturing. An aseptic bandage is applied to the area of the sutured wound. The sutures undergo specialized care until removal or complete healing - treatment with alcohol dyes and antiseptics (iodonate, chlorhexidine, ethyl alcohol, hydrogen peroxide) and change of dressings on the first, third, sixth and tenth days after surgery. The suture is carried out using the open method without signs of suppuration and treated with brilliant green.
note
The more carefully the sutures are cleaned, the lower the risk of suppuration and healing with the formation of a rough scar.
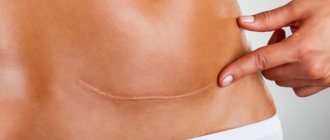
What does a scar look like in good, dry condition?
In the absence of complications, in most cases, after surgery, the patient develops a physiological scar. The seam is almost invisible and the color is close to the skin tone.
If the operation was performed on an area of the body where blood circulation is poor, a white or pink keloid scar will form. It rises slightly above the skin and is shiny. Such a scar also forms after deep surgery.
How to speed up the resorption of postoperative scars?
In the treatment of scars, agents that prevent the proliferation of connective tissue are in demand. Silicone gels and ointments without polyorganosiloxanes promote the natural resorption of scars after surgery. Among the latter, the creams “Contractubex” and “Kelofibraza” have proven themselves well. As consumers rightly note, these drugs are best used for small scars.
Silicone ointments and gels are used in the treatment regimen after removal of postoperative scars and scars, for the prevention of keloids and the resorption of other scars. Polyorganosiloxanes create a thin, almost invisible film that protects the cut surface from moisture loss and mechanical stress. In addition, itching and other unpleasant sensations are eliminated.
Gels with silicones are used to resolve postoperative scars for at least 5–10 weeks.
A significant part of pharmaceutical products containing organosiloxanes is produced by European and American companies. Retail prices for waterproof gels and plates remain high. We offer to compare foreign-made scar correction preparations, which were evaluated by experts and consumers in the United States (table).
Possible complications in the suture area and their causes
Postoperative sutures require careful care and specialist supervision in order to heal properly.
In case of violation of medical recommendations, the patient faces various complications:
| Name | Description |
| Seroma | A common complication after surgery. Small capillaries grow together and a large amount of lymph accumulates in this area, which leads to tissue swelling. A serous fluid with a yellow tint and an unpleasant odor appears. |
| Suppuration | Purulent discharge from a wound occurs as a result of pathogenic microorganisms entering it. |
| Seal | The cause of compaction is often seroma, when a large amount of lymphoid fluid collects in the area of the surgical suture. |
| Redness | Inflammation indicates infection in the wound after surgery. |
You cannot treat yourself if complications arise. Consulting a surgeon and his recommendations will help you avoid more serious consequences, including even blood poisoning.
What to do if the suture festers after surgery
If preventive measures are ineffective, and the suture festers after surgery, there are a number of tactics that can reduce the risk of developing a septic complication and the formation of a rough scar.
Signs of inflammation can be detected during dressing by removing the bandage or peeling off the sticker. If the dressing material has dried, peel off the dressing with a ball soaked in peroxide or alcohol. Normally, even a properly healing suture may be slightly swollen in the first two days . But the edges of the sutured wound should not differ in color from the rest of the skin. The inflamed seam turns red, becomes tense and shiny. When palpated, pain appears.
The threads cut into the edges of the wound. Purulent discharge accumulates at the puncture sites. Inflammatory changes will require a special approach, including how to treat the postoperative wound.
- The skin near the wound is treated with a sterile ball moistened with 0.5% chlorhexidine and clamped with tweezers. Rubbing goes from the wound to the periphery.
- The edges of the suture are blotted with a sterile ball containing 1% iodonate, then with an alcohol ball.
- In the area of greatest swelling and redness, 1-2 stitches can be removed. The edges of the wound can be moved apart with a probe so that the pathological effusion drains away better.
- The wound is dried with gauze and a drainage outlet is inserted, through which lymph, blood or pus will be better separated. If there is little discharge, you can do without drainage by immediately applying an aseptic bandage.
- If the wound has become suppurated, the sutures are removed along its entire length. The edges of the wound have to be spread with Farabeuf hooks and washed with 3% hydrogen peroxide. Next, the wound is drained or a turunda with a hypertonic solution or levomekol is applied under a bandage.
- The bandage or sticker is made with sterile napkins and secured with an adhesive plaster or bandage.
- When the suppuration stops, the suture can be made openly, without applying bandages, treating it with brilliant green.
- Purulent discharge can stimulate the development of vegetations - excess scar tissue that complicates healing and makes the scar rougher and unaesthetic. The surgeon can cauterize them or excise them during the dressing process.
note
In the hospital, the treatment of sutures is carried out by a procedural nurse, at home - by a district nurse or a surgical nurse under the supervision of a surgeon.
Symptoms of poor seam condition
Healing of a postoperative suture does not always occur perfectly; in some situations, serious complications arise. An infection occurs, the human body reacts individually to surgery, and internal sutures are torn away.
Incorrectly performed surgery and the development of pathological processes are accompanied by poor clinical symptoms:
- the postoperative suture becomes inflamed, nearby tissues turn red;
- local temperature rises;
- the area around the suture swells;
- purulent or serous discharge appears from the wound;
- the edges of the seam diverge;
- the patient complains of severe painful sensations of a cramping or pulling nature;
- Small nodules form under the outer seam.
High body temperature indicates a serious inflammatory process. The patient needs to urgently go to the hospital and get medical help. Severe pain may be a sign of an adhesive process.
In most cases, nodules under the external suture resolve on their own. But you need to notify your doctor or surgeon about the appearance of pathological symptoms. If necessary, a specialist will select effective treatment.
Possible complications
If a person after abdominal surgery (caesarean section, removal of tumors for cancer or benign formations) is in pain for a long time, the body temperature rises, suppuration appears, the suture is diagnosed as infected. This is the most common complication after surgery. The wound may become wet and inflamed if not treated correctly. A similar complication develops when unsuitable materials are used to form sutures. Wound infection also occurs when the immune system is weakened, when the patient’s body is unable to fight the pathogenic bacteria surrounding it.
Dehiscence of sutures often occurs in elderly or weakened patients, if the recovery regime after the intervention is not followed. In such cases, repeated suturing is practiced. The edges of the wound are cut and new threads are applied to prevent infection. If the sutures come apart after the injured tissue has healed, there is no need to reapply them. The wound requires routine care and observation by doctors.
How to speed up healing at home?
Complex therapy of a postoperative suture involves the use of antiseptic agents that reduce the inflammatory process. Wound healing creams and gels are also used, which accelerate the regeneration of damaged tissues.
In the absence of serious contraindications, you can use folk remedies, but strictly consult with your doctor to avoid complications.
Local remedies
The postoperative suture often does not heal due to problems in the circulatory system.
In this case, it is recommended to treat it with the following external means:
| Name | Application | Contraindications |
| Levomekol | The gel has a bactericidal and antimicrobial effect, promotes rapid healing of the postoperative suture. The medicine is applied directly to the wound or the open cavity is filled with well-soaked sterile wipes. The daily dosage is 3 g. |
|
| Contractubex | The ointment is applied to the area of the postoperative suture 2 times a day in the morning and evening in a small amount, rubbing in with light massage movements. The standard course of treatment lasts 30 days. | Individual sensitivity |
Before applying the cream, the postoperative suture should be treated with an antiseptic (brilliant, iodine, chlorhexidine, potassium permanganate, fucorcin). Procedures are carried out at least 2 times a day. Before processing the seam, wash your hands thoroughly.
Folk remedies
Recipes from witch doctors and healers help the postoperative scar to heal quickly if you choose the right remedy in consultation with your doctor.
| Name | Recipe | Application |
| Tea tree oil | Add to 1 tbsp. water 3-5 drops of essential oil. Mix all ingredients well. | It is recommended to apply the product to the seam using a gauze swab. Tea tree oil can be used in its pure form to lubricate a postoperative wound. |
| Onion | Peel, wash and chop a small onion using a grater. | Onion pulp should be applied to the seam 1-2 times a day. The juice kills pathogenic microorganisms, promoting the process of regeneration of damaged tissues. |
| St. John's wort | Mix dry leaves of the plant (4 tbsp) with hot water (500 ml). Leave and strain. | It is recommended to wash the wound with the prepared solution |
A properly selected folk remedy will help the stitch heal quickly, relieve pain and reduce the inflammatory process. It is important to choose a treatment method with a doctor, since an allergic reaction or worsening of the condition can be provoked.
Rating of the best ointments for healing sutures after surgery in 2020
Cicatrix
This cream reduces hypertrophic scars, fresh and old scars, the effects of burns, frostbite, stretch marks and keloids. The drug increases the healing rate, guarantees proper epithelization of the skin and regenerates it.
Among the active elements of the product:
- Centella asiatica.
- Pinus sylvestris.
The first increases the speed of healing. This component affects collagen with 2 amino acids:
- Alanine.
- Proline.
These are the 2 main structural proteins for biological synthesis that stimulate granular tissue. On the other hand, Centella asiatica facilitates proper epithelialization of scars by stimulating the biological synthesis of glycosaminoglycans and regenerating the amorphous matrix.
The mixed effect of the 2 above-mentioned components, which are natural and enhanced through molecular activation, makes the drug we are considering highly effective, which allows us to observe a positive result after 3 weeks.
Cost – 2,000 Russian rubles.
Cicatrix cream
Advantages:
- unique composition;
- normalization of skin tone in the scar area;
- increasing the elasticity of scar tissue;
- enhanced moisturizing effect and relief from discomfort in the scar area (relief from tightness, dryness and irritation);
- There is no need to prepare the skin in advance before use.
Flaws:
- difficult to find on sale, but available in online stores and online pharmacies.
Levomekol
When thinking about which company is better to buy ointment, pay attention to the Nizhpharm brand and their well-known wound healing agent Levomekol. The drug has an antimicrobial and bactericidal effect, helps accelerate cell regeneration. The functionality of the product is that it is an antibiotic and a reparant. Thanks to its effective healing properties, the ointment has the laudable status of “the surgeon’s favorite assistant.” Levomekol has the ability to penetrate deeply into cells, creating a healing, therapeutic effect. In this case, cell membranes are not damaged and retain functional activity.
The product is classified as a low-hazard substance for humans. The ointment is used for both treatment and preventive purposes. The main indication for the drug is the treatment of purulent wounds; the drug is also used for burns of 2 and 3 degrees, for the occurrence of trophic ulcers and for the treatment of boils. For prevention, the product is applied to a bandage or cotton wool and applied to sutures, as a result of which healing is accelerated and infection is prevented. The ointment is used externally, applied once or twice a day, the treatment process lasts from 5 to 10 days.
Cost: about 150 rubles.
Levomekol
Advantages:
- Accelerates the process of cell regeneration;
- Accelerates cell renewal;
- An effective remedy for deep wounds prone to suppuration;
- Anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial;
- Suitable for healing postoperative sutures;
- Itching and irritation of the dermis are eliminated;
- Budget.
Flaws:
- Over time, bacteria develop resistance to the active substance of the drug;
- Allergic reactions are possible.
Mederma
An excellent hypoallergenic gel is Mederma, which helps smooth out scars. Its amazing functionality includes improving blood circulation, antibacterial effects and accelerating skin cell renewal. The product is not a hormonal substance and can be purchased without a prescription. Available in tubes in the form of a transparent gel, it has a herbal aroma.
Many buyers praise Mederma for smoothing out scars and scars and returning the skin to its original state. Mederma is prescribed for post-operative scars, marks from tattoo removal, consequences of skin peelings and to combat stretch marks of various origins. But you need to remember that it helps only with fresh scars, and will not cope with old ones. Apply the product externally, rub until completely absorbed; treatment of problem areas of the skin is needed about 4 times.
You can buy it for about 700 rubles.
Mederma
Advantages:
- Anti-inflammatory ointment;
- Accelerates the process of cell regeneration;
- Suitable for removing fresh scars;
- Helps with acne scars;
- Hypoallergenic.
Flaws:
- Expensive;
- There are complaints that it rolls into lumps.
Solcoseryl
The Swiss drug Solcoseryl is very popular among the Russian population, and all thanks to its effectiveness and versatility. The product is used for many different purposes, even as a rejuvenating elixir, but we are concerned about its use for the healing of postoperative sutures. The functionality of Solcoseryl is such that it helps to increase collagen production and perfectly activates the process of tissue metabolism. The drug is available in different formats: gel, ointment, dental adhesive paste and solution.
This medical product belongs to the group of products that stimulate tissue regeneration. Allowed to be applied to a wet seam. A thin and even layer is carefully applied to the washed and disinfected wound. The course of use is a month. For a fresh wound, it is advisable to use a gel; if the wound has already crusted over, then you need to purchase an ointment. Numerous surveys regarding the drug revealed that thanks to Solcoseryl it was possible to avoid scars and cicatrices.
Cost: about 330 rubles and above.
Solcoseryl
Advantages:
- Affordable price;
- Smoothes scars;
- Activates the metabolic process;
- Accelerates the process of cell regeneration;
- Accelerates cell renewal;
- Suitable for healing postoperative sutures.
Flaws:
- The product is prohibited for sale in other countries due to little research.
Ichthyol ointment
Ichthyol ointment is used for antiseptic and anti-inflammatory effects. The drug has a dark brown color and a specific aroma, is available in dark-colored jars, the volume can be 80, 800 and 1800 grams. The ointment is popular among consumers, all thanks to its wide range of therapeutic effects. The product improves skin microcirculation, dries tissue, accelerates wound healing and prevents the process of decay. Thanks to the use of ichthyol ointment, tissue regeneration is accelerated and its functions and structure are rapidly restored.
When applied to the skin, the drug has the ability to be absorbed locally into the local bloodstream, avoiding the systemic bloodstream. There are many indications for use, including burns, boils, eczema, dermatitis and wounds. The drug is used externally, it is applied 2-3 times a day to the damaged tissue in a thin layer. You should not rub it in; you must cover the top with a sterile napkin. The course of treatment is determined by the doctor.
Cost: from 100 rubles and above.
Ichthyol ointment
Advantages:
- Budget;
- Anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial;
- Accelerates the process of cell regeneration;
- Suitable after surgery;
- Has a bactericidal effect;
- Relieves redness;
- Resolves hematomas.
Flaws:
- Specific smell;
- Skin coloring brown.
Heparin ointment
If you need an analgesic and anti-inflammatory medication, then pay attention to heparin ointment. It has anticoagulant properties and prevents the formation of blood clots. Most often, this ointment is needed after hemorrhoid surgery to remove stitches. The functionality of heparin is such that it indirectly improves microcirculation, and thanks to this, hematomas and blood clots resolve much better. There is a significant reduction in tissue swelling. The ointment also contains the substance benzocaine, which is aimed at blocking nerve impulses, that is, a good anesthetic effect occurs.
Pain impulses do not arise at the endings of the sensory nerves. For external use, apply a thin layer of the product to the damaged area. The course of treatment is usually a week. There are contraindications, which include children under 2 years of age, ulcerative-necrotic processes, hypersensitivity and damage to tissue integrity. If there are purulent processes, then it should not be applied to open wounds.
Cost of the drug: from 62 rubles and above.
Heparin ointment
Advantages:
- Budget;
- Excellent at resolving hematomas;
- Reduces tissue swelling;
- Prevents the formation of blood clots;
- Anti-inflammatory.
Flaws:
- May cause burning and redness of the skin;
- May cause allergic reactions.
Contractubex
Contractubex received a lot of positive feedback. This combination drug has anti-inflammatory, antithrombotic, keratolytic and fibrinolytic properties. It is prescribed in the presence of hypertrophic and keloid scars, and is also used as a prophylaxis for the formation of pathological scars. They can remove fresh stretch marks. Apply 2-3 times a day, rubbing gently into damaged skin.
If the scars are fresh, then the approximate course of treatment will be one month. You will have to deal with old scars; you will need to apply a bandage with the product for 3-6 months before going to bed. There are special instructions, for example, for greater effectiveness of the medication, it is applied to steamed skin. If you are going to care for fresh scars, then try to avoid extreme cold, harsh massage and ultraviolet radiation. The instructions give the go-ahead for using the product in children.
Cost: from 550 rubles and above.
Contractubex
Advantages:
- Accelerates the process of cell regeneration;
- Smoothes scars;
- Suitable for removing fresh scars;
- Can remove facial scars;
- Used for prevention.
Flaws:
- The price may seem high;
- Not very effective on old scars.
Bepanten
Bepanten is probably known to every second resident of our country. The drug remarkably accelerates tissue regeneration, healing occurs faster and more efficiently. Its main characteristics include anti-inflammatory and regenerating properties, as well as normalization of cellular metabolism. Indications for use include the treatment of dry tissue and prevention of damage to the integrity of the skin, healing of minor injuries, care for the delicate skin of babies, and use as a caring agent during breastfeeding. Application is quite simple, the product is applied externally, smeared on the damaged area of the skin 1 or 2 times a day, and rubbed in a little. Unfortunately, side effects do occur, and these include allergic reactions.
The cost varies from 400 rubles to 1100 rubles.
Bepanten
Advantages:
- Suitable for any age category;
- Relieves irritation;
- Accelerates cell renewal;
- Healing for minor injuries;
- Normalizes cell metabolism;
- Helps with dry skin;
- Aimed at maintaining skin health.
Flaws:
- Prices for the drug are often inflated;
- Allergic reactions may occur.
Vishnevsky ointment
Any rating of high-quality ointments for healing sutures includes the famous Vishnevsky ointment. It has a wide range of beneficial effects for the body, including anti-inflammatory, bactericidal, immunomodulatory and antiseptic effects. In addition, due to the local irritating effect on tissue, microcirculation improves. The list of indications for use is quite impressive, but if a person suffers from impaired renal function, then the ointment should not be used. It should be smeared on the seam itself or applied to a sterile bandage three times a day, after which the bandage is fixed. In case of overdose, allergic reactions may occur. Use the drug until the wound is completely healed.
The cost starts from 48 rubles.
Vishnevsky ointment
Advantages:
- Multifunctional ointment;
- Budget;
- Anti-inflammatory;
- Until the scar is completely eliminated;
- Activates the metabolic process;
- Improves blood circulation.
Flaws:
- Specific smell;
- Will not cope with old scars.
Methyluracil ointment
Another useful ointment for treating sutures after surgery is methyluracil ointment. It is characterized by regenerating, anti-inflammatory and anabolic properties. In addition, the provision of repair processes, the presence of photoprotective qualities, and the fact that the active substance is an immunomodulator were noted. The medication is used to speed up regeneration processes on long-healing wounds or burns.
It is also often prescribed after fractures for use during the recovery period. The product can be used for both adults and children. The list of indications for use includes the treatment of wounds and burns, photodermatosis, bedsores, furunculosis and other skin problems. There are contraindications, these include leukemia, open wounds and individual reactions to one or another component. Apply up to 4 times a day, first the ointment is squeezed onto a sterile bandage, and then applied to the damaged area.
You can purchase from 125 rubles and above.
Methyluracil ointment
Advantages:
- Budget;
- Suitable for treating various skin problems;
- Can be used for children;
- Used to accelerate regeneration;
- Has an anti-inflammatory effect;
- Has a bactericidal effect.
Flaws:
- There are complaints about the greasy consistency.
What to do if the seam is red?
The postoperative suture often does not heal if an inflammatory process occurs. It is necessary to constantly treat the wound with antiseptics (2-4 times a day). Its redness indicates a possible wound infection, improperly installed drainage, or a surgical error.
After treatment with an antiseptic, a gauze bandage with anti-inflammatory ointment should be applied to the seam, following the instructions or doctor’s prescriptions.
What to do if you have seroma?
In most cases, seroma goes away on its own within 1-3 weeks. If after the specified period it is still present, you need to go to the hospital, the doctor will prescribe treatment.
Seroma is the reason why the postoperative suture does not heal
The main goal of therapy is to remove accumulated fluid. For this purpose, drainage or vacuum aspiration is used. In each case, special devices are used to pump out liquid.
A variety of products for the treatment of stitches and scars
- Cream - such products have a lighter consistency, they quickly penetrate into the deep layers of tissue, do not stain clothes and do not leave greasy marks or a sticky feeling.
- Ointment has a thicker texture; after application you will feel a greasy feeling, so the product should be absorbed. In most cases, these remedies are most effective. In order for the drug to have the maximum possible effect, ointment dressings made of cotton-gauze material should be used.
- Gel is the least effective remedy; it is suitable for complex therapy or for working with fresh sutures. The texture of the product is light, quickly penetrates into the layers of fabric, but not deep enough.
What to do if a fistula forms?
A fistula is a kind of channel that connects cavities. Purulent discharge comes out through it. If they are absent, an inflammatory process develops.
The cause of a fistula is an infection that has entered the wound. The same applies to a chronic inflammatory process, a foreign body. A fistula also forms if the infection has not been completely cured or the threads have been rejected.
For treatment, the patient is prescribed anti-inflammatory and antibacterial drugs. It is necessary to wash the wound with antiseptic agents and also drink vitamins.
What to do if the seam diverges?
There are numerous reasons for seam divergence:
- infection in the wound;
- concomitant diseases in the human body;
- high blood pressure;
- tight stitches;
- overweight;
- bad habits;
- seam damage.
In this situation, the patient urgently needs consultation with a surgeon, additional treatment and strict supervision of a specialist. If the suture diverges, patients are also recommended to wear a special postoperative bandage.
Possible complications that slow down the healing of sutures
After suturing, complications with its healing may arise for various reasons. As a rule, this is an infection, due to which suppuration of the suture develops, preventing its healing. There may be several reasons for infection:
- poorly processed materials during surgery;
- the appearance of hematoma and the development of tissue necrosis;
- poor quality of materials used for suture;
- weak immunity and general health.
These reasons significantly complicate the patient’s recovery. If the surgeon’s work was not sufficiently qualified, and complications arose after the operation, then in this case it remains to deal with the consequences. But you can try to eliminate the cause of weakened immunity in advance. You just need to eat right, take vitamins and exercise. Such active people have much greater body reserves, and at critical moments they will cope with inflammation and illness. In addition, their internal reactions proceed faster, and these include the processes of recovery, metabolism, oxygen transport and the formation of new tissues. Therefore, people who lead an active lifestyle usually recover faster and tolerate various diseases more easily.
Why does the postoperative suture itch, how to eliminate the itching?
The postoperative suture does not heal and itches if dirt gets into the wound. Itching is the body's reaction to the action of pathogenic microorganisms. The same thing happens when a wound heals, when it tightens and the skin dries out.
Itching may also appear as a reaction to the fastening threads. In this situation, it is not recommended to scratch the wound; you must continue to treat it with antiseptics, as prescribed by the doctor, and strictly adhere to the specialist’s recommendations.
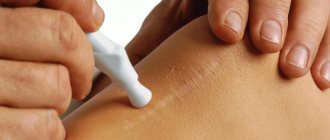
Processing rules
In order for the healing of sutures to take place as quickly as possible without the development of complications, it is necessary to adhere to the following rules:
- before starting the procedure, it is necessary to disinfect hands and instruments that may be needed to carry it out;
- You should carefully remove the applied bandage, and if it is stuck to the skin, pour peroxide on it;
- you need to smear the seam with an antiseptic using a cotton swab or gauze swab;
- the bandage must be carefully applied.
It is important to remember that seams should be treated twice a day, but if necessary, the amount can be increased. In addition, it is necessary to carefully examine the wound each time for the presence of any inflammation. It is not recommended to remove dry crusts and scabs from the wound, as this can lead to the appearance of scars on the skin. You should shower with care and do not rub the seam with a sponge that is too hard. If the sutures on the abdomen turn red or purulent exudate begins to ooze from them, you should see a doctor as soon as possible.
Only a doctor can decide when sutures are removed after abdominal surgery. This procedure is carried out under sterile conditions using special instruments and usually 5-10 days after surgery.
Dry scar care
In some situations, the postoperative suture becomes covered with a dry crust, which absolutely cannot be removed independently. It is also important to protect it from water, for example, in the bathroom while showering. Moisture promotes the proliferation of pathogenic flora and the development of the inflammatory process.
The dry crust should fall off on its own; to do this, it is enough to use special products prescribed by your doctor or folk recipes, if there are no medical contraindications.
In most cases, the wound heals quickly after surgery. However, sometimes certain characteristics of the patient’s body slow down this process. Don't panic. If the postoperative suture does not heal, it is necessary to consult a surgeon to exclude possible complications.
Scar classification
Scars have several varieties, which are determined by different criteria. Regarding the surface of the skin, scars are classified according to the volume of connective tissue.
Normotrophic scars
Such defects are the most favorable outcome of operations or injuries. Most often, they do not bother the patient either aesthetically, cosmetically, or functionally. Also, such scars do not cause pain after full recovery after surgery.
Atrophic scars
Most often, such a defect is formed if the wound surface or postoperative suture has been subjected to inflammation. The inflammatory process occurs when the damage is not properly cared for.
What do atrophic scars look like? This is a small depression in the skin, devoid of pigmentation. This problem does not cause discomfort to the patient in most cases. However, in the case of facial scarring, many people may experience complexes.
Hypertrophic scars
They look like brown bumps on the surface of the skin, streaked with cracks and brightly pigmented. Often the hypertrophic process is combined with the presence of atrophic scars.
Keloid scars
The most severe case, practically untreatable. This defect occurs after unsuccessful suturing: the surgeon’s rough work is combined with suppuration and infection of the suture. The scar stands out noticeably and rises above the surface of the skin; the defect has a glossy appearance and a pale tint. Keloid scars can spread to healthy tissue.
Advice! The choice of ointment for scar healing and suture care should be accompanied by consultation with a specialist. You must take into account concomitant treatments, as some medications reduce the effectiveness of others. Also, do not forget about individual intolerance and allergic reactions.