- Preoperative period
- Preparing for surgery
- Choice of anesthesia
- Carrying out the operation
- Video of the operation
- Recovery period
- Contraindications
- Possible complications
Otoplasty is the surgical elimination of congenital or acquired (traumatic) ear defects. This operation is one of the most common in plastic surgery and allows you to adjust the size of the ears, their shape and location relative to the face. The surgical intervention affects the cartilaginous as well as soft tissues of the ears. Otoplasty is often recommended for children and adolescents, since protruding ears, asymmetry of the ears and other congenital defects can cause psychological disorders.
Preoperative period
In addition to choosing a clinic with an impeccable reputation and qualified staff, an important part of the preoperative period is a detailed consultation with the surgeon who will perform the intervention.
Modeling the shape of the ear
!Before otoplasty surgery, it is important that the patient and the doctor reach full understanding regarding the aspects of the proposed correction and its final result. The doctor explains to the patient how otoplasty is performed, how long the procedure itself and the rehabilitation period take, and what effect should be expected.
Modern high-level clinics have the ability to simulate the result of an operation on a computer in a digital 3D format. However, the client needs to understand that otoplasty surgery, like any other plastic surgery operation, is associated with certain risks. Realistic expectations about the final result include the possibility of insufficient correction or the development of some complications.
Let's talk about the unpleasant: risks and complications
Any operation does not exclude risks and complications. Cosmetic surgery, be it laser otoplasty or any other operation, is usually resorted to by completely healthy people - hence the small percentage of complications.
Among the possible unpleasant manifestations during the recovery period, experts include:
- divergence of wound edges;
- development of infection;
- necrosis of ear tissue;
- volumetric hematomas.
An operation such as otoplasty shortens some of the nerves in the ear, so it may lose some of its sensitivity for up to 12 months.
The ear cartilage boasts a “memory”, under the influence of which the auricle constantly tries to take its original position. Therefore, any operation may be unsuccessful - the protruding ears will return to the patient over time. In such cases, repeat otoplasty is performed.
Preparing for surgery
Before undergoing plastic surgery, you must undergo a full medical examination. Direct preparation includes consultation with a therapist; if the patient has chronic diseases, a conversation with relevant specialists is also necessary. In addition, it is necessary to undergo a laboratory examination, as well as fluorography and electrocardiography.
Mandatory tests for otoplasty include:
- General blood analysis;
- Analysis of urine;
- Biochemical blood test (glucose, protein, electrolytes, urea, bilirubin);
- Testing for antigens and antibodies (tests for hepatitis and HIV);
- Test for syphilis.
Doctors need to find out whether the patient is prone to allergic reactions or the formation of keloid scars, and what operations they have undergone previously.
Before otoplasty it is necessary to undergo fluorography
Several weeks before the scheduled day of surgery, it is advisable to prepare the body. It is useful to take vitamins and follow a diet with sufficient amounts of protein, fruits and vegetables. Two weeks before surgery, the patient must stop taking medications that affect blood clotting. Smokers are advised to give up cigarettes at least temporarily. Moderation in alcohol consumption before and after surgery is also recommended.
On the appointed day, 4 hours before the procedure, it is advisable to refrain from drinking and eating. The day before surgery, you should thoroughly wash your hair and ears.
Before otoplasty, the surgeon also takes general and detailed photographs of the auricles, takes all necessary measurements of each ear, determines the relationship of the ears to the border of the scalp, takes into account the presence of asymmetry and the relative position of the concha, lobe, and helix.
When should you contact a surgeon?
If your ears hurt after otoplasty, you shouldn’t worry about it right away. Moderate pain is a companion for almost every patient during the recovery period. But if the pain lasts two weeks or longer, or gets worse over time, this is a good reason to visit your surgeon and consult about these symptoms.
Problems not related to pain include the following:
- persistently high body temperature for several days,
- bleeding at the suture site,
- suppuration,
- a sharp increase in the volume of the ears.
Such situations, like any other unusual conditions, should be a reason to immediately contact your doctor. In urgent cases, it is recommended to call emergency services immediately.
If your condition worsens rapidly, you should call emergency services immediately!
Choice of anesthesia
The choice of type of anesthesia for otoplasty depends on many factors:
- Patient's age;
- Difficulties of the operation;
- Estimated duration of the surgical procedure;
- Presence of concomitant diseases;
- Psychological state of the patient.
In children and adolescents, the intervention is performed under general anesthesia (drugs are administered intravenously). In healthy adult patients, surgery is often performed under local anesthesia. Sometimes sedative and analgesic medications are administered intravenously.
Rehabilitation in the late postoperative period
The postoperative period following the early period involves the implementation of measures and recommendations that help reduce the negative impact of the external environment on the ears and stimulate the healing process.
These recommendations include:
- Following a diet aimed at consuming foods with plenty of protein and vitamins. Here you can highlight lean meat and vegetables that are easily digestible by the body.
- Reducing the amount of junk food, including smoked meats, fatty and spicy foods.
- Avoiding alcohol and other bad habits, as they are considered toxic and interfere with cell renewal and scar resorption.
- A complete ban on certain sports and activities, as well as a partial limitation of physical activity, is necessary to prevent tissue displacement and opening of postoperative sutures.
- Maintaining an optimal temperature - favorable for a good regeneration process, so that it happens faster. This optimal temperature is 18-20 degrees Celsius. Limiting visits to baths and saunas, since high temperature and high humidity contribute to the divergence of the edges of the postoperative wound.
- Avoid exposure to ultraviolet rays, because solar radiation promotes protein denaturation, which gradually leads to poor healing of the postoperative suture.
- washing with extreme caution, avoiding contact of detergents with the wound, so that chemical irritation of the epithelial cells at the site of the formed scar does not occur.
This rehabilitation period lasts one month, it is worth following all the proposed recommendations.
During the rehabilitation period, you should pay attention to some subtleties of its course, which affect the quality of scar healing and the effectiveness of the entire operation.
Such subtleties include:
- Bleeding – occurs due to damage to a large vessel during rehabilitation procedures, and is often observed at the beginning of the entire postoperative period. To prevent this from happening, tight bandages are made. Sometimes napkins impregnated with a hemostatic agent are used to promote the formation of a blood clot and stop the release of blood.
- Bandage - made from a characteristic cotton-gauze napkin. The blank is placed on the operated ear. Such a bandage protects against mechanical injury to the wound and infection, and gives shape to the auricle. The bandage is fixed with a special mesh bandage, shaped like a stocking or adhesive plaster.
- hygiene - within 3 days after surgery, this procedure is not allowed at all; for up to 10 days, you should wash your hair with warm water without using detergents. Until the end of the rehabilitation period, it is allowed to wash your hair using baby shampoo; they do not have an irritating effect on the skin.
This will avoid complications that arise in the early postoperative period. In addition, the skin of the ears may lose sensitivity, but you should not be afraid of this - everything will return to normal very quickly.
The return of sensitivity is accompanied by “goose bumps” - this is a rather unpleasant, but not painful sensation that does not last long. Patients' fears about hearing loss or decrease after otoplasty are unjustified.
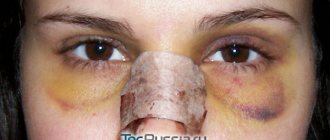
The operation does not affect the inside of the ears. Often after surgery, bruises appear on the face - this is natural, since the tissues not only of the ear are affected, but also the neighboring ones. There is no need to be afraid of them, because within two weeks all the bruises and swelling will disappear and not a trace will remain of them.
Carrying out the operation
Otoplasty cannot be classified as a difficult operation for a qualified specialist: it is performed on an outpatient basis (the patient does not need to be hospitalized).
Prominent ears can be corrected with otoplasty
If correction of protruding ears in children is carried out, then the ideal time for otoplasty is 5-8 years. By this time, the child has not yet had time to form a critical attitude towards his appearance, and in the future, young patients simply forget that they were once “lop-eared.”
Otoplasty options depend on the anatomical features and the technique chosen by the surgeon based on his professional experience. ! Modern aesthetic surgery includes more than 150 methods for correcting protruding ears and other ear defects. The general goal of protruding ear surgery is to bring the ears closer to the head: this is achieved by plastic surgery of the cartilage that forms the basis of the outer ear.
For these purposes, an area of skin behind the ear is excised, and the cartilage is partially removed (or it is shaped in such a way as to give the shell the most aesthetic appearance). This way, the incisions and future scars remain on the back of the ear, making them invisible. Over time, the scars become completely invisible.
Bandage after otoplasty surgery
The ideal angle between the concha of the ear and the head is 30°, while the distance between the head and the edge of the ear should not exceed 2 cm. The deformation can be observed in both ears or one, and the types and degrees of protruding ears and other ear defects are so diverse that there is no single medical tactic there is simply no fix.
! The duration of the operation depends, of course, on its complexity and course. Usually the procedure takes from half an hour to 2 hours. The patient remains in the clinic for several hours (sometimes until the next morning). The next day he can do his normal activities. Children can start school in a week.
Immediately after the treatment, medical napkins and a special bandage after otoplasty are applied to the correction areas. A special tampon soaked in plant oils and antiseptic components is inserted into the ear canal. The tampon should be changed every three days. A day after surgery, the first dressing is performed. A photo of the postoperative period of otoplasty clearly demonstrates the condition of the patient’s ears after the procedure.
Evaluation of results
7 days after surgery, specialists are able to evaluate the initial aesthetic improvement in the shape and location of the ears. Once the bandage is removed, the patient can immediately notice improvements. In a favorable situation, the result progresses every day. This will continue for an average of 6 weeks. At this same stage, the doctor may decide that otoplasty was unsuccessful.
Doctors come to a final conclusion a year after the procedure. Most patients are satisfied with the result. However, almost always the operated ears differ minimally from each other - a slight asymmetry remains. This does not mean that revision otoplasty is inevitable. This can be caused by the course of the procedure itself, or, most likely, by the initial asymmetry of the ears.
As you can see, the rehabilitation period after this type of cosmetic surgery plays a key role in ensuring the proper result and achieving a positive cosmetic effect. The lion's share of successful ear correction is hidden in painstaking adherence to the entire list of doctor's recommendations.
0 0 vote
Article Rating
Recovery period
Immediately after surgery, the doctor prescribes painkillers (analgesics), which should be taken again after 2-3 hours and before bedtime. Pain after otoplasty usually does not last longer than a day or may be quite mild for several days. To eliminate pain symptoms, pharmaceutical analgesic drugs are quite suitable. Hematomas can be severe for a week, after which they gradually disappear. Swelling after otoplasty persists for 1.5 months.
Suture line after otoplasty
For a week, you should definitely wear a bandage made of several layers, which fixes the ears in a certain position and provides protection from mechanical stress (see photo of the bandage after otoplasty). Patients should also protect their ears from water getting into them. Sutures after otoplasty are removed after about 7 days.
! Complete rehabilitation after otoplasty lasts approximately six months. For 5-8 weeks, the patient is recommended to sleep in a special fixing bandage that prevents the displacement of cartilage. The bandage is put on after the stitches are removed. You should also protect your ears after otoplasty from insolation (solar radiation) and exposure to cold wind.
You can wash your hair 2 weeks after surgery. You can't go to the sauna or swimming pool for a month and a half. After 3 and 6 months, the patient should visit the surgeon for examination and consultation regarding the course of the recovery period.
During the rehabilitation period after otoplasty, patients are not recommended to engage in contact sports, diving, or weightlifting, since there is a high probability of injury and deformation of the operated cartilage.
Reviews from patients after otoplasty surgery are mostly positive - after recovery, people quickly get used to their new appearance and get rid of all complexes and psychological problems associated with ear defects, if any.
What is the bandage for?
The main purpose of the bandage is to protect the ears from various types of damage and the influence of external factors. In addition, it helps to fix the ears in the desired position after surgery.
The purpose of wearing a bandage is primarily to reduce the risk of inflammation. In addition, it allows you to relieve swelling, speed up the process of restoration of soft tissues damaged after surgery, eliminate bruises and prevent the entry of pathogenic microorganisms that can cause inflammation and infection.
Possible complications
Otoplasty, rehabilitation after which requires a serious approach, can also cause complications. Negative consequences are rare and almost always occur as a result of patients’ non-compliance with medical recommendations. Complications after otoplasty due to medical error are also possible.
Ear swelling is one of the complications
Complications after ear correction include:
- The occurrence of allergies (epidermal blisters) - this may be a reaction to anesthetics and other medications;
- Complications due to anesthesia (more often occur in children);
- Inflammation of soft tissues (prolonged swelling and redness of the ears);
- Inflammation of cartilage tissue (perichondritis);
- Formation of keloid scars;
- Deterioration of the aesthetic result due to spontaneous deformation of the ears.
Some of these complications can be prevented if you strictly follow your doctor's instructions. If negative reactions develop, repeated correction of the ears may be required, which can be carried out no earlier than 6 months after the first procedure.
If the patient follows all the recommendations for the rehabilitation period after otoplasty, no re-correction will be required. The result will be sustainable and will remain with the person for life.
Swelling after otoplasty
It increases on the second or third day after the procedure and is considered as a natural physiological phenomenon. Lymphatic and blood vessels and cells were injured along the cut line. Liquid accumulates in the intercellular space and remains until tissue repair.
The following will help speed up the process:
- sleeping on a high headboard;
- diet without spicy, salty foods, smoked foods:
- refusal to drink beer, strong alcohol;
- moderate physical activity - walks, measured walking for 20-40 minutes.
Swelling after otoplasty lasts up to 5-7 days. Hidden forms can remain up to 10-14 days. After the tissues and capillaries heal, they too will go away.
Still have questions? You can ask them to a practicing surgeon, Candidate of Medical Sciences Guzal Melisovna Isamutdinova at a free initial consultation.
Types of ear surgeries
Tympanoplasty
- an operation that involves restoration of the chain of auditory ossicles in case of their complete or partial loss during the inflammatory process with simultaneous closure of defects and restoration of the eardrum. Indications for surgery may be the following diseases: chronic purulent otitis media (outside the period of exacerbation), adhesive otitis media, dry perforated otitis media, fibrosing otitis media, tympanosclerosis, atelectasis of the tympanic cavity, as well as conditions after traumatic injuries to the middle ear, anomalies of the middle ear . Tympanoplasty involves the restoration of a defect in the chain of auditory ossicles, i.e. ossiculoplasty, and restoration of the integrity of the eardrum, i.e. myringoplasty. Currently, ready-made prostheses of the auditory ossicles made of biocompatible materials (titanium) are used. In addition to ready-made prostheses, otosurgeons use autografts (autoincus, auricular cartilage, cortical bone). The most commonly used tympanic membrane grafts are tragus cartilage and temporalis muscle fascia. After this operation, the patient may have improved hearing and possibly an improved quality of life due to the fact that there is no discharge from the ear and the patient can allow water to get into the ear.
Tympanoplasty for a total defect of the tympanic membrane
Ear surgery is performed under general anesthesia.
Endoural sanitizing surgery
- performed for chronic purulent otitis media (epitympanitis). Using a burr and cutters, the altered bone part of the mastoid process is removed with maximum preservation of the ear structures. It can be performed with simultaneous tympanoplasty.
Attico-adito-antrotomy with reconstruction of paratympanic spaces and tympanoplasty for chronic otitis media with cholesteatoma endaural approach
Stapedoplasty
- an operation performed for otosclerosis. The clinic performs piston stapedoplasty. This technique is characterized by less trauma during surgery, so the postoperative period is shorter and less noticeable for the patient. A titanium prosthesis (from KURZ) instead of the auditory ossicle (stirrup) is installed for life and does not need to be replaced. It is recommended to operate on one ear first—the worse-hearing ear. Then, as the otosclerotic process progresses, after 1-2 years the second ear can be operated on. The operation is predominantly performed under general anesthesia. The operation under local anesthesia is decided individually.
Removal of exostoses of the external auditory canal
- sometimes bone growths, called exostoses, form in the ear canal. They can close the lumen of the external auditory canal, cause recurrent external otitis media and hearing loss. Using a burr and cutters, the growths are removed, and the external auditory canal and hearing are restored. The operation is performed under anesthesia.
Resection of parotid fistula
- sometimes people at birth are left with a hole above the ear, which was previously a gill slit. This fistulous tract is tortuous and can reach a length of several centimeters in depth. An incision is made above the hole, the entire fistula tract is isolated and removed. However, relapses of the disease may occur, since the fistulous tract can have many branches.