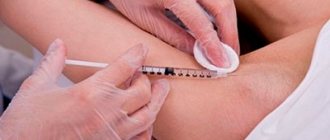
Where do allergies come from?
Is there an allergy to Botox? Unfortunately, the answer to this question is yes. Despite the fact that people encounter this problem quite often, this complication is still poorly understood.
A reaction occurs for certain reasons:
- dermatitis, inflammation of the skin;
- various immune problems;
- tendency to develop allergies;
- taking strong medications;
- chronic infectious diseases (especially the period of exacerbation).
Can Botox cause allergies if you have recently had surgery? Yes maybe. In addition, chronic pathologies of internal organs can provoke an undesirable reaction.
Many people are interested in whether there can be an allergy to the drug Botox while breastfeeding or carrying a child. Please note that during such periods the body produces special hormones, so it becomes more vulnerable to various influences. During lactation and pregnancy, the consequences of botulinum toxin administration are often unpredictable.
Ingredients of Botox
The main active ingredient of Botox is botulinum toxin. Usually the body is sensitive to this substance.
Sometimes allergies occur to other components that manufacturers include in products based on botulinum toxin:
- sucrose - in Refinex, Xeomin, Lantox;
- lactose and albumin - in Dysport;
- albumin (human protein) - in Botulax, Relatox, directly in Botox.
An allergic reaction to additional elements is most often not very serious. Usually it has an effect on general well-being and appearance.
Lidocaine
To achieve the required concentration of the active substance, specialists dilute botulinum toxin with sodium chloride (0.9%). However, some cosmetologists who want to experiment (or simply due to inexperience) use lidocaine for this.
This component is not always positively perceived by the human body. It can cause a very severe allergic reaction.
What makes the situation worse is that there is quite a lot of lidocaine in painkillers. They are almost always used before Botox injections to minimize discomfort.
Allergy to Botox: myth or reality?
For more than 25 years of active use in cosmetology, preparations based on botulinum toxin have established themselves as an effective and safe way to eliminate facial wrinkles. However, they may well cause serious problems for the patient.
Allergy to Botox is an extremely rare and little-studied complication. Nevertheless, such a reaction is indeed possible, although most often it is caused not by the toxin itself, but by stabilizer proteins and other substances with which the patient somehow comes into contact during the procedure. What symptoms should you pay attention to during and after injections? What should the treatment be? Do I need to take any tests in advance? Is there reliable prevention? TecRussia.ru answers the most pressing questions:
↑ Let's analyze the composition of drugs: which components are safe and which ones should be wary of?
The main active substance of Botox and all its analogues is botulinum toxin type A. As medical statistics show, a small number of patients have an increased susceptibility to this component. It manifests itself in the fact that even a small dosage leads to severe muscle paralysis in the injection area. This feature can complicate the injections and negatively affect their results, however, there is currently no confirmed scientific evidence that the toxin can also cause an immune response in the form of an allergy. But such troubles can be caused by excipients that are included in cosmetic preparations for botulinum therapy:
- the original Botox, as well as Relatox and Botulax, contain the human protein albumin;
- in Dysport - albumin and lactose;
- in Lantox, Xeomin and Refinex - sucrose, etc.
These components are able to cause a full-fledged allergic reaction in those patients whose body was initially hypersensitive to them. As a rule, it proceeds relatively easily and does not directly threaten life or health, but it can still spoil the appearance and also negatively affect overall well-being.
In addition, all modern botulinum toxins must be diluted to a lower concentration before use. According to the protocol, only saline solution – 0.9% sodium chloride – can be used for this. But some cosmetologists, due to their inexperience or desire to experiment, add lidocaine to the resulting “cocktail” - and, as you know, it is extremely ambiguously perceived by our immune system and can cause very serious problems, even anaphylactic shock. Also, a fairly large amount of lidocaine may be contained in the anesthetic cream, which is almost always applied to the skin before injections to make them more comfortable.
Thus, allergies to Botox do happen. At the same time, botulinum toxin itself in small medical dosages can be considered safe, but the real cause of unwanted reactions in the body are the auxiliary components of the drug, as well as the anesthesia used in preparation for injections.
↑ Is it possible to identify the problem in advance? What tests should I take?
The most effective way to determine your body’s sensitivity to an injection product is a skin test, which any cosmetologist can perform:
- A small cut or scratch is made on the patient’s wrist, into which a small amount of the test substance is then injected, in our case several units of Botox or another botulinum toxin-based product.
- If you have an allergy, clearly visible symptoms will appear in this area within 1 hour: redness, swelling, etc.
If the test is positive, it will need to be repeated several more times using different drugs to understand which component is causing the problem - most often it is a stabilizing protein or sugars.
Due to the overall low number of allergic complications associated with Botox, many doctors consider it necessary to perform a skin test only on patients who have already encountered any problematic consequences of injections. However, those who are generally prone to hypersensitivity reactions or doubt that the body will react normally to all components of the chosen drug should also insist on carrying out this simple, quick and very informative analysis.
↑ Alarming symptoms: what to pay special attention to?
The administration of botulinum toxin can be accompanied by both local and general allergic manifestations. In the first case, one or more of the following symptoms occur:
- redness of the skin in the injection area;
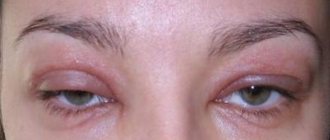
- severe increasing swelling of the treated area, sometimes painful (see more in the article about the types of swelling after Botox);
- local or general increase in temperature;
- difficulty moving the eyelids, eyebrows or lips, swallowing, etc. - depending on where exactly the injections were given;
- itching in the injection area or dispersed throughout the body;
- peeling of the skin;
- dysarthria.
Such deviations may appear within 5-10 minutes after administration of the drug, but more often the patient notices unpleasant changes several hours, and sometimes even days after the session. They do not always indicate exactly an intolerance reaction: for example, redness and swelling are considered a normal consequence of injuries from injections, and difficulty swallowing and other problems with muscle activity may indicate the presence of another complication - strong diffusion of the drug. Therefore, it is advisable that the final conclusion about their character be made by a cosmetologist during an in-person examination (for more details, see also the article “Complications after Botox”).
The second group - general allergic reactions - includes Quincke's edema and anaphylactic shock. These conditions are much more dangerous, and their signs appear instantly, literally “at the tip of the needle”:
- severe, rapidly increasing swelling of the face;
- feeling of lack of air;
- tremor of the limbs and whole body;
- a sharp drop in blood pressure;
- tachycardia (increased heart rate);
- the appearance of cold sticky sweat;
- depression of consciousness.
Typically, such problems arise already during the injections, but if they appear and increase in the early post-procedure period, you should immediately contact any available doctor to accurately determine their cause and begin treatment.
↑ What to do if signs of allergies appear after Botox?
Minor local symptoms of hypersensitivity, as a rule, do not require special treatment: the main task here is to make sure that we are not talking about any more serious complication. Further therapy comes down to taking tableted antihistamines: Eden, Claritin, Loratadine, Suprastin, Tavegil, etc.
- Why does my head hurt after Botox: causes and solutions to the problem
- Allergy to hyaluronic acid: fact or fiction?
More serious malfunctions of the body - Quincke's edema and anaphylactic shock - require immediate medical attention. Fortunately, they happen extremely rarely, and in most cases - as a reaction to lidocaine used for injections (and patients usually find out about this intolerance long before visiting a cosmetologist). However, everyone should know the general principles of first aid for these pathologies:
- if an allergic reaction develops directly during the procedure, ask the specialist to stop administering Botox;
- take an antihistamine;
- apply cold to the treated area - this will constrict the blood vessels and reduce swelling;
- provide fresh air access to the room;
- call an ambulance;
- in especially severe cases, it is necessary to administer hormonal drugs that suppress the immune response, such as Prednisolone or Dexamethasone.
↑ Preventive measures: is it possible to insure against unpleasant consequences?
Despite the fact that the main effects of Botox and its analogues have been well studied, serious scientific studies that would determine the incidence and characteristics of allergies to these drugs have not yet been conducted. At present, it is possible to give only those recommendations that are based on the practical experience of doctors and patients:
- The total number of cases of individual hypersensitivity to botulinum toxin and auxiliary components is extremely small, and their manifestations do not threaten life or health. Therefore, for people who are generally not prone to allergic reactions, no special prophylaxis is required before the session.
- At the same time, it is extremely important to make sure in advance that your body normally accepts lidocaine - it is this that most often causes Quincke's edema and anaphylaxis. To completely secure the procedure, you must ask the cosmetologist to use other types of anesthetics.
- Those who have already experienced Botox intolerance, even in the mildest form, should avoid further injections until the allergen is accurately identified. It is known that with each subsequent session the hypersensitivity reaction intensifies: what looked like insignificant redness or swelling the first time can take on a much more dangerous form already in the second.
- To determine which component our body reacts so acutely to, it is necessary to conduct several skin tests. As a rule, based on their results, you can choose your own safe brand of drug for each patient: for example, for those who are lactose intolerant, any brand except Dysport is suitable, and for those who “do not work” with albumin, you can use Lantox or Xeomin.
- In those extremely rare cases when the problem is caused precisely by individual intolerance to botulinum toxin type A, you will have to completely abandon injections and choose one of the alternative wrinkle correction methods - for example, hardware skin tightening or fillers based on hyaluronic acid.
↑ Briefly about the most important
Botox and its analogues can cause allergies, but in the vast majority of cases it is caused not by the main active substance, but by the auxiliary components of the drugs or the anesthetic used. Symptoms, as a rule, are not life-threatening or health-threatening, but tend to intensify with each subsequent session.
| What should the patient do: | |
| Before the procedure |
|
| If allergy symptoms appear during the procedure |
|
| If symptoms occur at home |
|
In general, for any atypical manifestations after botulinum toxin injections, it is advisable not to self-medicate and consult a doctor immediately. The fact is that people often tend to attribute any newly emerging symptoms to the consequences of “beauty injections,” which in fact can be caused by completely different reasons. Only a complete diagnosis will allow you to accurately determine the source of trouble and choose the best way to eliminate it.
Symptoms
Symptoms of an allergic reaction to botulinum toxin can occur not only a few hours after the procedure. It happens that they appear almost during the injection.
If symptoms of hypersensitivity are mild, treatment is usually not required. To make them disappear, most often it is enough just to take antihistamines: Cetrina, Tavegil, Suprastin and the like.
If symptoms are severe, you should seek medical help as soon as possible. After all, some of them can be life-threatening.
Let's look at what an allergy to Botox is. In particular, local and general manifestations of the reaction.
Local
Local symptoms can appear either immediately or several days after the injection. Some of them do not always indicate an allergy. Sometimes such symptoms are simply a normal reaction to bruises, injuries, or injections.
The most common local manifestations of allergies:
- dysarthria;
- difficulty swallowing, moving facial muscles;
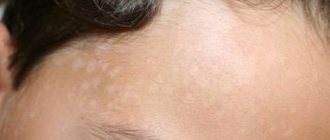
- skin redness;
- peeling, itching;
- heat;
- pain;
- severe swelling in the place where the cosmetologist gave the injection.
Are common
Common manifestations of allergies include anaphylactic shock and Quincke's edema. Typically, such reactions occur during the procedure. These are very dangerous conditions.
The following general manifestations of an allergic reaction can be distinguished:
- confusion;
- very rapid decrease in blood pressure;
- swelling of the face (severe and quickly occurring);
- increased sweating;
- increased heart rate (tachycardia);
- tremor of the whole body, arms and legs;
- feeling of lack of air.
Causes
An allergic reaction to Botox is rare. However, if the rules for using the drug were violated, then the likelihood of such a side effect increases several times.
In addition, experts identify another equally significant factor that can provoke such a negative reaction - this is the implementation of the procedure in the presence of characteristic contraindications.
Botox injections are prohibited if you are allergic to protein, have dermatological pathologies of the skin, or have chronic diseases. The limitation is the weakening of the immune system and the use of potent medications, with which botulinum toxin may be incompatible.
If we talk about Botox for hair, then the cause of an allergic reaction may be the substances present in the composition. These are, as a rule, elastin, keratin amino acids, fragrances, lactic acid and cosmetic oils.
Treatment
If the symptoms are local, there is no need to worry. However, you need to make sure that the complication is really not very serious.
To recover from the onset of local symptoms, it is usually sufficient to use suitable medications for a while. In more complex cases, you should immediately consult a doctor.
First aid is as follows:
- Apply something cold to the injection site. After this, the vessels will narrow, as a result of which the swelling will significantly decrease.
- Take an antihistamine.
- Ventilate the room. Fresh air can improve the condition of a person who has an allergic reaction.
- Call a doctor as soon as possible.
- If the case is very severe, use a hormonal agent that suppresses the immune response. This is, for example, Dexamethasone or Prednisolone.
Consequences
Undesirable results may occur if the dosage of the drug is violated or the administration technique is incorrect. Among them:
- asymmetry of facial contours;
- loss of muscle sensitivity;
- deterioration of visual acuity;
- seals in the form of bumps and tubercles;
- spasm of the eyelids;
- impaired mobility of the upper lip;
- subcutaneous hemorrhages;
- drooping eyebrows;
- loss of natural facial expression.
Prevention
It is much easier not to fight allergies, but to prevent their occurrence. Prevention involves the following actions:
- Do not drink alcohol before receiving botulinum toxin.
- Postpone injections if you have skin diseases.
- Tell the specialist about your illnesses, as well as what medications you are taking.
- Do not take “beauty injections” if you are feeling generally unwell.
- Report any susceptibility to allergic reactions.
Before injecting botulinum toxin into the forehead or any other area, an allergy test should be done. This will allow you to gain confidence in your safety before the procedure and avoid unnecessary risks.
Advantages and disadvantages
Botox injections, like other cosmetic procedures, have their positive and negative sides. Advantages:
- growing effect;
- restoration of skin in the fold area;
- elimination of facial wrinkles;
- unnoticed drastic changes;
- minimum contraindications;
- does not provoke addiction;
- lack of rehabilitation period;
- affordable price;
- combination with all cosmetic procedures.
As already mentioned, Botox is a poison, but it is contained in an ampoule in a very small dose. Although clinical studies in many countries have proven that it is safe, it is advisable to weigh the pros and cons before deciding to undergo the procedure. The main disadvantage of this injection technique is the limited effect of the injection.
- low effectiveness for injections into the chin and cheeks;
- inability to get rid of deep wrinkles;
- likelihood of complications.
How to do an allergy test
The skin test is a very effective method for determining whether you are allergic to Botox. The specialist conducts it as follows:
- First you need to lightly scratch the patient's hand. Then the specialist injects a small amount of a product into this wound, which includes botulinum toxin.
- If an allergic reaction occurs, swelling and redness will be noticeable on the skin within 60 minutes.
In cases where the test result is positive, it is performed several more times, using different drugs based on botulinum toxin. So, in the end, it turns out to find out which element a person is allergic to.
Allergens in preparations for botulinum therapy
There are several drugs for botulinum therapy on the cosmetology medicine market: Botox, Dysport, Lantox, Xeomin. They differ not only in name and manufacturer, but also in the amount of the fundamental component and the content of excipients.
The main component of all injection medications is botulinum toxin type A. As mentioned above, in large quantities it is extremely toxic. However, clients of aesthetic medicine clinics should not worry: a very small dose is injected into the body.
Botulinum toxin is a neurotoxin produced by the bacteria Clostridium botulinum. It is protein in nature, so we can say with confidence that people with hypersensitivity to proteins will be at risk of allergies.
About 2% of patients are not susceptible to botulinum toxin type A at all (for example, those who have had botulism)
| Allergy to components of botulinum therapy drugs | ||||
| Botox | Dysport | Xeomin | ||
| Botulinum toxin | + | + | + | |
| Human plasma albumin | Fever, chills, shortness of breath, tachycardia, low blood pressure, urticaria, itching, vomiting, nausea | |||
| Auxiliary components | Sodium chloride: does not cause allergies | Lactose:
| Sucrose: pseudoallergic reactions - gastrointestinal disorders, skin rash, itching, cough, nasal discharge | |
The drugs “Botox”, “Dysport”, “Xeomin”, in addition to botulinum toxin, include human plasma albumin. Could it be an allergen? Maybe. Possible allergic reactions are described in the table above. We must not forget that the component is produced from blood plasma, which is taken from different donors. What does it mean? This means that, although minimal, there is a danger of transmitting dangerous viruses
The third ingredient is:
- Botox has sodium chloride;
- Dysport has lactose;
- Xeomin has sucrose.
Sodium chloride is used as a detoxifying agent. It does not cause allergies.
Lactose acts as an excipient - a filler. It is obtained from whey. There is virtually no allergy to lactose, but there are a large number of people with lactose intolerance. Allergy and intolerance are different concepts: the second is associated with the lack of an enzyme in the body for breaking down lactose - lactase. Lactose intolerance can cause diarrhea, nausea, stomach pain, and flatulence.
Sucrose, like lactose, is a filler. Sucrose causes “pseudoallergic reactions.” They are expressed in disorders of the gastrointestinal tract, skin rashes, itching, cough, and nasal discharge.
Lantox is slightly different from the above medications. Its components:
- botulinum toxin;
- gelatin;
- sucrose;
- dextran.
Gelatin here plays the role of a neurotoxin stabilizer. Practically not allergic.
Dextran is a detoxifying agent. May provoke anaphylactic and anaphylactoid reactions.
When choosing a drug for Botox injections, you must carefully study its composition to exclude allergic reactions.
In conclusion
When Botox injections are performed by a professional cosmetologist in a salon or clinic with an impeccable reputation, the “beauty injections” will be effective and safe.
However, no one is immune from complications and allergic reactions. To minimize the risk of complications, you need to take your choice of salon as seriously as possible. For example, you can read customer reviews. You should also undergo a medical examination first. Doctors will identify possible contraindications to the use of Botox and give you appropriate recommendations.
The principle of action of the drug
Every woman dreams of remaining forever young and beautiful. Botox injections are one of the most commonly used, popular and fairly safe methods of rejuvenation. Its effectiveness has been confirmed by almost thirty years of active use in cosmetology. What is Botox and how does it work?
The main component of this popular drug is an organic protein poison - botulinum toxin or botulinum toxin.
But don't be afraid of the scary name. In microscopic doses administered subcutaneously or intramuscularly, it acts as a relaxant. Once in the tissue, botulinum toxin blocks nerve impulses, preventing the desired muscle from contracting. In this way, facial wrinkles are corrected.
The second ingredient in Botox is another protein called albumin, which is produced from human blood. Its purpose is to transport the active substance to a specific place in need of action.
Another excipient in Botox is a solution of sodium hypochloride, which is necessary for the physiological functioning of the body.