A little bit of history
The first method of pain relief was used by Avicenna; he cooled the limbs until they lost sensitivity. Amroise Paré compressed blood vessels and nerves. In Ancient Egypt, they used sleepy tubes that were soaked in narcotic herbs.
The real anesthetic began to be used at the end of the nineteenth century, it was cocaine hydrochloride. But the drug was very toxic and led to high mortality; its use was abandoned.
They were made to faint by bleeding. This method was cruel and was not developed. During the period of hostilities, they even used alcohol until they were in a strong state of intoxication.
After operation
When to get up after surgery? The general rule is as early as possible! Don't linger! But of course, with the doctor's permission. Lying for a long time is fraught with the development of hypostatic pneumonia, acute thrombosis of the veins of the lower extremities, bedsores on the back, sacrum, and heels.
A case is described: a young patient, 23 years old, practically healthy, after a routine uncomplicated appendectomy, lay on his bed and did not want to get up (he was in pain, you see). On the third day I finally got up. Result: pulmonary embolism - instant death.
When can I return to normal work after anesthesia? After general anesthesia, after just two days, a person can perform normal work, work with complex mechanisms that require concentration, and drive a car! But the operating surgeons discharge the patient after 7-8 days, when the stitches are removed and the wound has healed. You can drink after anesthesia when your reflexes are restored and there is no nausea or vomiting.
We also recommend reading: Anesthesia without an injection - a real breakthrough in dentistry
You can eat it the next day, the diet is gentle: you can’t eat spicy, salty, fried, canned food, sausages, or alcohol. The Pevzner diet is usually followed.
Anesthesia and its effects
Anesthesia is a state of artificial memory loss that is reversible. It blocks the feeling of pain during surgical operations. Special anesthetics are used, which are selected by the anesthesiologist. He calculates the optimal dosage of the drug and combines it with other drugs. In this case, the individual characteristics of the patient are taken into account.
There are two types of anesthesia: general and local. General anesthesia is used to block pain. Such anesthesia leads to immobility, and the patient cannot control the body. Two methods are used: administering the drug through a vein and supplying gaseous anesthetic through a mask.
Local anesthesia involves injecting a painkiller into the area where surgery will be performed. For example, to remove a tooth, an injection is made in the oral cavity in the gum. This place begins to go numb and cannot be touched. Is local anesthetic dangerous? The patient is fully conscious, pain is blocked locally. Such manipulations do not cause any particular concern.
The effects of the common drug have been studied for a long time. But it is known that the anesthetic acts on the subcortical formation of the brain, which is supplied with energy. A common drug inhibits this function, it gradually fades away, the brain ceases to be active and falls asleep. We can say that the patient is in artificial sleep. During anesthesia, reflex functions to stimuli such as injections or touch may be preserved. Doctors consider this normal.
Is there such a thing as harmless anesthesia?
Any drug affects the functions of the brain and nervous system. Therefore, there are no absolutely safe compounds. But a large selection of medications in different forms allows doctors to choose the best option. The duration of the surgical intervention is taken into account.
For pain relief for women during childbirth, preference is given to Isoflurane and Sevoflurane , which are easily excreted from tissues by the kidneys. Increasingly, operations on the reproductive organs of young girls are performed using the laparoscopic method.
It allows the use of light anesthesia, in which the patient remains conscious without feeling pain. She is not bothered by severe nausea, dizziness and other unpleasant moments.
Why are people afraid of general anesthesia?
People are afraid not of the surgery itself, but of the effects of anesthesia, because each person reacts individually to the anesthetic.
History has many facts where the body did not succumb to the influence of drugs, and an additional dose led to death.
The famous Russian commander of the Red Army M.V. Frunze died under the influence of an anesthetic. But this is just one version. The legendary personality was given general anesthesia during the operation using ether; he could not sleep for a long time. Then the anesthesiologist added a dose of chloroform. After this, cardiac arrest occurred.
The second reason for fear of such drugs is the body's immunity. A person can receive an anesthetic but not be put into artificial sleep. So he can be immobilized, but feel physical pain. This can lead to death from pain or a feeling of terrible pain. Such cases are extremely rare and out of 1000 people there may be two such patients.
What drugs are used?
The following drugs are most often used for local anesthesia:
1. Lidocaine. It is one of the most common for conduction anesthesia. It has a longer and stronger effect when compared with novocaine. In significant concentrations it can be used to anesthetize mucous membranes through irrigation and lubrication.
2. Novocaine. Non-toxic product with broad therapeutic effects. Used for all types of local anesthesia in various concentrations, depending on the operation performed and indications.
3. Trimecaine. Used for conduction anesthesia. The drug has a fairly strong and long-lasting anesthetic effect. Local anesthesia with this type of drug is safe and completely painless for humans. Characterized by low toxicity.
4. Anecaine. A potent drug that has a long-lasting effect on the desired area of the body. Used for appropriate indications and during specific operations.
5. Dicaine. It is used, as a rule, for terminal pain relief by treating the mucous membrane with irrigation or lubrication. 10-20 times stronger than novocaine. Can be used for epidural pain relief. The use of the drug is limited due to its high toxicity compared to other anesthetics. In addition, the consequences after local anesthesia of this type can be dangerous.
6. Chlorethyl – liquid in ampoules. The local anesthetic effect of chlorethyl is based on the ability of the drug to quickly evaporate from the surface of the skin, causing sudden cooling and freezing of the surface layer with the onset of local anesthesia. Most often, anesthetics of this type are used when the patient refuses general anesthesia. It is believed that the human body tolerates these drugs better.
The effect of anesthetics on the body
The question of whether general anesthesia is harmful to humans will not be disputed by any physician. So why is general anesthesia dangerous?
The effect of anesthesia on the human body is primarily reflected in the activity of the brain. The most dangerous consequence is cognitive dysfunction leading to central nervous system disorders. Anesthesia has the following consequences for the body:
- loss of sleep or frequent awakenings at night,
- decreased ability to work and rapid fatigue,
- absent-mindedness and inability to concentrate,
- deterioration of memory and ability to memorize,
- disorientation in space,
- pain in the muscles and throat,
- slight clouding of consciousness,
- itching or irritation of the skin.
The causes of such symptoms are:
- A short-term loss of consciousness provokes a micro stroke due to a decrease in blood pressure.
- Death of brain neurons.
The following factors increase the risk of developing asthenic syndrome:
- chronic diseases,
- age category,
- high rate of anesthesia,
- low intellectual development.
The effects of anesthesia can manifest themselves for a long time in the form of:
- panic fear,
- local memory loss,
- changes in heart rate, increased blood pressure,
- changes in the functions of the liver gland and kidneys, the anesthetic is a strong toxin and has a negative effect on the body.
What are the dangers of general anesthesia for the cardiac and vascular system?
Heart parameters play a big role when using anesthesia.
If the patient suffers from ischemia, tachycardia, arrhythmia, then he is sent for diagnosis. Only then is it determined whether surgery with anesthetics is possible.
Very common and common adverse reactions and complications of anesthesia (consequences of anesthesia)
- Nausea
This is a very common consequence of anesthesia, occurring in approximately 30% of cases. Nausea is more common with general than with regional anesthesia. Here are some tips to help reduce your risk of nausea:
- you should not be active during the first hours after surgery - sitting down and getting out of bed;
- Avoid drinking water and food immediately after surgery;
- good pain relief is also important, as severe pain can cause nausea, so if pain occurs, inform the medical staff;
- deep breathing with slow inhalation of air can reduce the feeling of nausea.
- A sore throat
Its severity can vary from discomfort to severe constant pain that bothers you when talking or swallowing. You may also experience dry mouth. These symptoms may subside within a few hours after surgery, but may persist for two or more days. If the above symptoms do not go away within two days after surgery, contact your doctor. A sore throat is only a consequence, not a complication of anesthesia.
- Shiver
Trembling, which is another consequence of anesthesia, poses a certain problem for patients, as it causes them great discomfort, although most often it does not pose any danger to the body and lasts about 20-30 minutes. Trembling can occur either after general anesthesia or as a complication of epidural or spinal anesthesia. You may be able to reduce your risk of shivering somewhat by keeping your body warm before surgery. You need to take care of warm things in advance. Remember that the hospital may be cooler than your home.
- Dizziness and lightheadedness
The residual effect of anesthetics may manifest itself in the form of a slight decrease in blood pressure, in addition, dehydration, which is not so uncommon after surgery, can lead to the same effect. A decrease in pressure can cause dizziness, weakness, and faintness.
- Headache
There are many reasons that can cause a headache. These are medications used for anesthesia, the operation itself, dehydration and simply unnecessary anxiety for the patient. Most often, the headache goes away a few hours after anesthesia on its own or after taking painkillers. Severe headache can be a complication of both spinal anesthesia and epidural analgesia. The features of its treatment are described in detail in the article “Headache after spinal anesthesia.”
- Itching
Itching is usually a side reaction to anesthesia medications (particularly morphine), but itching can also be a manifestation of an allergic reaction, so if it occurs, be sure to tell your doctor.
- Back and lower back pain
During surgery, the patient remains in one constant position on a hard operating table for quite a long time, which can lead to “tired” back and, ultimately, to lower back pain after surgery.
- Muscle pain
Most often, muscle pain after anesthesia occurs in young males, most often their occurrence is associated with the use of a drug called ditilin during anesthesia, usually used in emergency surgery, as well as situations when the patient’s stomach is not free from food. Muscle pain is a consequence of anesthesia (general anesthesia), it is symmetrical, most often localized in the neck, shoulders, upper abdomen and lasts approximately 2-3 days after surgery.
- Confusion
Some patients, most often elderly, experience confusion after surgery and anesthesia. Their memory may deteriorate, and their behavior may differ from their usual state. This can be very worrying for you, your family, friends and loved ones. However, all these phenomena should disappear along with recovery from the operation.
The following recommendations can reduce the likelihood of postoperative impairment of consciousness:
- before hospitalization, try to be as healthy as possible, eat healthy food, do exercise;
— talk to your anesthesiologist about the possibility of performing the operation under regional anesthesia;
— if your operation is not large in scope and you do not live alone at home, then discuss with your attending surgeon the possibility of returning home as early as possible after the operation;
— make sure that you do not forget to take your contact lenses and hearing aids to the hospital;
- unless your doctor says otherwise, continue to take your usual home medications in the hospital;
- if you drink alcohol, you should consult with a narcologist about how to safely reduce it and then completely stop taking it. In the hospital, you should also tell your doctors how much alcohol you drink.
Effect of anesthetic on women
The female body is special; it goes through several stages of development. The effect of anesthesia on a woman’s body depends on the periods of life: puberty, pregnancy, menopause and menstruation.
General anesthesia is harmful for pregnant women, as it will have negative consequences on the health of the unborn child.
Artificial birth or caesarean section using anesthetics has the following consequences for a woman:
- headache,
- disgust,
- vomit,
- impaired concentration,
- back muscle spasms.
Effect of anesthesia on children
Is anesthesia harmful for children? The effect of anesthesia on the child’s body is reflected in brain activity. Doctors believe that anesthesia for a child under two years of age affects his development. At such an early age, the child’s brain is in the formative stage and has the greatest likelihood of consequences such as neuronal destruction. As a result , children experience difficulties: their memory deteriorates, they find it difficult to concentrate, their activity decreases, and their ability to memorize decreases.
Anesthetics definitely have a negative effect on the body. But if you think about how many human lives have been saved by anesthesia, the risk is completely justified. The narcotic state makes it possible to perform complex operations that last for several hours. Science does not stand still, and anesthetics are being improved. The risk of dying from drugs exists, but it is much lower than being in a car accident.
Contraindications for use
Without pain relief, it is impossible to perform even the simplest operation; the slightest surgical intervention causes unbearable pain. Therefore, from time immemorial, before anything was removed or corrected, people were rendered unconscious by stunning them with a blow to the head. Over time, drugs began to be used, which caused side effects.
The consequences of anesthetics may appear during surgery or much later; they are determined by the method of administration and composition. There are often side effects and complications that occur very rarely, but are critical, even fatal, which is why general anesthesia is dangerous.
Undesirable consequences after surgery can develop due to the presence of many contraindications in anesthetics. These include:
- pathologies of the cardiovascular system;
- diseased kidneys and liver;
- nervous system disorders;
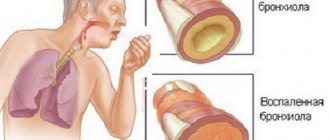
- diseases of the respiratory system: pneumonia, emphysema, atelectasis, obstructive bronchitis, exacerbation of bronchial asthma;
- diathesis;
- blood poisoning.
There are characteristic contraindications for children: recent surgery, rickets, any diseases caused by infection, recent vaccination.