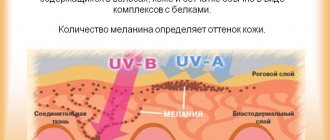
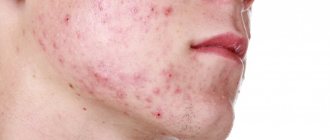
Types of purulent acne on the face
Depending on the presence of infection and the extent of its spread, there are 3 types of purulent acne. In addition to them, there is a primary form of acne - comedones. In some cases, they may precede the formation of ulcers, or remain in the same form for a long time.
Comedones are formed as a result of blockage of the mouth of the hair follicle with sebum and dead skin cells. Having no way out, the substance becomes denser, thereby expanding the pore.
From the outside, it looks like a black dot - this is the color that fat takes on during oxidation. This form of comedone is called open. The closed form is characterized by deeper localization and has the appearance of a dense white ball.
As a result of inflammation of the clogged mouth, the following types of ulcers can occur:
- Papule. Can be up to 1.3 cm in diameter. A convex or slightly raised head above the surface of the skin. It has a red or slightly bluish tint. It turns pale when pressed.
- Pustule. It may develop from a papule or occur primarily. Characterized by the presence of a visible purulent head.
- Cysts, nodules. A severe form of acne that affects a large area of the face. Pimples are interconnected by fistulous tracts, forming conglomerates. They are dense and quite painful.
By assessing the quantitative and qualitative composition of acne, you can determine the degree of skin damage (shown in the table below).
| Acne severity | Number of inflammatory units | Forms of acne | Damage area |
| I | To 10 | Comedones + single papules and/or pustules | No more than 1/3 of the face. It could be the chin or forehead. |
| II | from 10 to 40 | Comedones + inflamed acne. Possible scarring | More than 1/3 of the face. There are rashes on the body (back, chest). |
| III | more than 40 | Comedones (up to 100 units), or inflammatory elements with the presence of comedones. Characteristic scar formation | From 1/3 to 100% of the face. It also affects other areas of the body. |
| IV | from 5 | Nodular cystic acne, or 100 or more comedones. Can be present simultaneously in different proportions | From 50% to 100% of the face. May affect the back and chest. |
Degrees of acne - small purulent pimples on the face
Small purulent pimples on the face become a serious problem if their number continues to grow. However, the severity of the disease is expressed not only in this, but also in the ratio of the forms of inflammatory elements and the area of skin damage. Only by determining the severity of acne can you correctly select treatment methods.
What is the danger?
As soon as a patient develops pustular acne all over the body, it is necessary to contact a specialist and carry out the necessary treatment. Any attempts to independently cope with ulcers, which can provoke the spread of purulent fluid, are strictly prohibited. In severe cases, phlegmon may develop and damage internal organs. Often pus enters the bloodstream, which can lead to the death of the patient. Self-squeezing of ulcers is dangerous because the pathology becomes chronic. If similar actions are taken to eliminate purulent acne in the area of the nasolabial triangle, then the following complications are likely:
- inflammatory response in the brain;
- encephalitis;
- neuritis of the cranial nerves.
READ ALSO: Allergy to Viferon in a child, temperature and allergic reaction to the drug, treatment of allergy to Viferon
Return to contents
Causes of acne
Often the cause of acne is heredity or endocrine disorders in the body. They determine the likelihood of skin problems occurring at a given age.
However, there are many factors that trigger the mechanisms of acne formation.
Causes acting from outside
They can be either primary or a secondary factor in the appearance of pimples on the face.
The most common ones are:
- Cosmetical tools. Many of them contain comedogenic components - mineral, vegetable and animal oils, petroleum jelly, lanolin. They will moisturize skin prone to dryness, but for oily skin they will cause blockage of the follicular ostia. As a consequence, there is a disruption in the release of sebum and the risk of developing pathogenic microflora.
- Climate. Prolonged exposure to the scorching sun or wind has a drying effect on the skin. As a result, its protection against pathogen penetration is reduced.
- Stress. Often leads to a decrease in immunity, which is directly related not only to the health of the body, but also to the condition of the skin.
- Working with harmful substances (chlorine, petroleum products).
The impact of external factors on skin health at different ages is not the same:
| Causes | After 25 | After 30-35 | After 40-45 |
| Cosmetics | Often | Often | Rarely |
| Solar radiation, other climatic factors | Often | Often | Rarely |
| Stress | Often | Often | Rarely |
| Contact with toxins and ionizing radiation | Rarely | Rarely | Rarely |
If there are no more serious underlying causes of acne, acne goes away soon after the irritating factor stops.
Internal reasons
Very often, it is the occurrence of acne that indicates the presence of physiological changes or disorders in the body. In some cases, they go away on their own, and sometimes they remain until the provoking factor is eliminated.
Small purulent pimples on the face can appear for a number of reasons:
- Genetic predisposition. Most people with acne likely had one or both parents with the condition.
- Hormonal changes. Most often, the appearance of acne is provoked by a jump in the level of sex hormones - androgens. This may be as a result of dysfunction of the adrenal glands or ovaries during puberty - puberty.
- Hyperkeratosis. A prerequisite for the formation of acne may be the increased production of cells of the stratum corneum of the epithelium. At such a rate of cell division, the horny scales do not have time to peel off and make it difficult for sebum to come out. The result is an excellent environment for the development of bacteria.
- Gastrointestinal disorders. Associated, for the most part, with weakened immunity.
The role of internal factors in the occurrence of acne is different for each age category:
| Causes | After 25 | After 30-35 | After 40-45 |
| Heredity | Often | Often | Often |
| Hormonal changes | Often, it can be associated with both pregnancy and disorders in the endocrine system. | Often, reasons:
| Often, reasons:
|
| Hyperkeratosis | Average frequency | Average frequency | Rarely |
| Gastrointestinal diseases | Rarely | Rarely | Rarely |
Among the most common internal causes of acne are heredity and hormonal changes. They are the ones that lead to the manifestation of the disease in 70% of cases.
Why does it appear during pregnancy?
During pregnancy, there is a sharp jump in female sex hormones - estrogen and progesterone. Their relationship with androgens, the so-called male hormones, changes dramatically, and the usual balance is disrupted. The production of sebum increases significantly, which is the cause of acne. Normally, it goes away after the first trimester.
Pustule on the skin: photo, causes of formation
There are quite a few reasons for the appearance of pustules. It is impossible to determine exactly why ulcers began to appear on the body on your own. Therefore, you should definitely visit a dermatologist.
The main reasons for the formation of purulent pustules include:
- Bacterial infections, in which weak immunity can cause the appearance of numerous pustules.
- Irritations and injuries to the skin, for example, scratching with severe itching during allergies, burns, violations of the integrity of the skin due to small wounds, scratches and abrasions.
- Reduced immune defense, when any microbe or virus can become a real danger and cause disease, including pustules.
Pustules with pus also appear in such unpleasant diseases as acne, scabies, excessive sweating, hormonal imbalances, candidiasis, syphilis and many, many others.
Signs characteristic of a pustule (abscess)
A pustule (abscess) on the surface of the skin can have a very different appearance. Most often it is an inflated ball or cone and sometimes a flat plaque. The purulent contents inside the pustule can also have a variety of colors - white (most often), gray, green or yellow.
Only a doctor can understand by the color of the pus what caused the appearance of these rashes.
The sizes of pustules can also be very different - from a couple of millimeters to several centimeters. There must be a white head, or abscess, at the top of the pustule. Also, the pustule is always surrounded by red, inflamed tissue.
You can see what a pustule looks like in the photo below.
The process of development of an abscess occurs in several stages.
- The first stage is the appearance of redness.
- The second stage is the formation of a compaction (infiltrate) in the very center of the red spot.
- The third stage – the process of decay begins, which causes the appearance of pus, which means the pustule begins to increase in size, that is, it actively grows.
- The fourth stage is the maturation process.
- Fifth - the opening of the abscess begins, its contents burst out.
- The sixth stage is the appearance of a wound after the opening of the pustule. The wound gradually tightens and a scar appears on the surface of the skin.
Classification also involves dividing pustules according to their type. They can be:
- Follicular . In this case, a pustule (abscess) develops inside the hair follicle.
- Non-follicular . In this case, the abscess develops outside the hair follicle, for example, in the sebaceous gland, which happens with acne with pustules.
There is also a classification based on the depth of the lesion. If the abscess has formed in the epidermis, then it is considered superficial.
If the pustule appears in the dermis, it means it is deep. The formation of a pustule takes from several hours to a couple of days.
What not to do for acne, can you squeeze it?
Small purulent pimples on the face do not always go away on their own and require long-term treatment. Despite the aesthetic side of the problem, there are a number of contraindications that should be followed to avoid worsening the condition:
- Squeezing pimples. Mechanical removal of comedones or pustules is fraught with further spread of infection. This can provoke not only the appearance of new acne, but also blood poisoning. If the cause of acne is hormonal changes or heredity (hypersecretion of sebum), then only comprehensive treatment will help.
- Scrubbing in the presence of inflamed elements. At first glance, the surest way to solve the problem is cleansing the skin. However, in this case, the scrub further injures the skin, provoking an inflammatory process.
- Foundations and concealers. The occurrence of acne is provoked by blockage of the sebaceous glands. Applying thick cosmetics further blocks the outflow of sebum and the supply of oxygen, worsening the condition.
Sometimes women hesitate to treat their skin, preferring to squeeze out or mask pimples. However, the positive result quickly passes, and the problem remains unresolved.
Photos before and after
See methods for cleaning your face from acne at home. How to get rid of the causes of whiteheads on the face. Find out further.
How to choose an effective treatment with tablets for juvenile acne with pustules?
The answer is here. Treatment with ointments and oral tablets should be prescribed by a qualified dermatologist after a thorough examination.
How to get rid of acne
Acne can be a consequence of serious health problems, and then recovery can only be achieved through comprehensive treatment. This may require consultation with both a dermatologist and an endocrinologist or gynecologist. Only a specialist will determine the cause of acne and prescribe competent drug treatment.
After 25
Acne is often associated with puberty, which usually ends by the age of 18-20. However, in some cases it may return after a short or long absence. Depending on the cause of acne, the doctor may prescribe both local and systemic medications (presented in the table below).
| Pharmacological group | Drugs | Description | In what cases is it prescribed |
| Antiseptics | Streptocide; Effezel; Ichthyol ointment; Benzoyl peroxide | They have an antimicrobial effect, disinfecting the skin and preventing the formation of pus. | In the presence of inflammatory elements, with comedones, they are not advisable. |
| External antibiotics | Zenerite; Metrogil; Klenzit S; Levomikol | They affect pathogenic microflora localized in/on the skin. | With II, III and IV degrees of acne. |
| Systemic antibiotics | Tetracycline; Erythromycin; Lincosamides | Suppress the growth and development of a pathogen that has already penetrated into the internal environment of the body. | For III and IV degrees of acne severity. |
| Hormonal drugs (oral contraceptives) | Diana-35; Jess; Janine | They normalize hormonal levels by increasing or decreasing the level of androgens. | With III and IV degrees of acne, less often - II. |
| Retinoids | Roaccutane; Retinol palmitate (vitamin A); Retinoic ointment | Capable of influencing all parts of the pathological process: sebum production, hyperkeratosis and pathogenic microflora. | For stages III and IV acne, when other methods of therapy have not yielded positive results. |
| Combination drugs | Klenzit-S; Epiduo; Isotrexin | Contains retinoids and antibiotics. | At stages II and III. |
Small and large purulent pimples on the face are more effectively eliminated with the help of retinoids and hormonal drugs. In advanced stages, when the infection has penetrated and spread throughout the body, systemic antibiotics cannot be avoided.
After 30-35
Less than 10% of women over the age of 30-35 suffer from acne. This could be a progressive form of “teenage” acne or signs of diseases such as polycystic disease or impaired glucose tolerance.
If the acne is mainly comedones, then topical treatment will be sufficient.
For this purpose drugs are used:
- With salicylic acid. These can be lotions or creams. Helps exfoliate dead skin cells and dissolve acne plugs.
- With antibacterial effect. In the form of gels and creams. They may contain antibiotics or have a bacteriostatic effect (azelaic acid, benzoyl peroxide, other antiseptics).
- Based on hormones. Hydrocortisone ointment and analogues.
For more serious stages of acne, topical medications rarely have a positive result. Therapy is supplemented with hormonal contraceptives (in case of suspected polycystic disease or hyperprolactemia), or systemic antibiotics and retinoids (in case of infection in the blood).
After 40-45
With age, sebum production gradually decreases, but this does not mean that dry skin is less susceptible to acne. If you do not provide the epidermis with additional moisture, the protective barrier against the penetration of pathogens will be damaged.
Pharmaceutical preparations that not only moisturize, but have bacteriostatic and cleansing effects:
- Salicylic acid;
- Metrogyl gel;
- Effezel;
- Ichthyol ointment;
- Hydrocortisone ointment.
During premenopause, hormone replacement therapy is often prescribed. It helps relieve unpleasant symptoms and prevent possible complications.
In adulthood
Over the past decades, the age of acne has increased markedly. If previously young people under 18-20 years of age were susceptible to it, today the age limit has risen to 45 and above. This may be a relapse of a long-existing disease, or a disorder in the endocrine system.
It is recommended to eliminate small purulent pimples on the face using gentle medications that do not have serious side effects.
It can be:
- ointments and creams with antiseptic and antibacterial effects;
- preparations with azelaic acid;
- retinoids.
The use of systemic antibiotics and hormonal drugs by women in adulthood can be associated with health risks.
What it is?
Several main factors provoke the occurrence of purulent rashes. Most often, the reason lies in the proliferation of pathogenic flora. The culprits are viruses, bacteria, and fungi.
With such ailments, purulent acne can form on the entire body or individual areas:
- acne;
- streptococcal infection;
- staphylococcus;
- seborrhea;
- dermatomycosis;
- allergic dermatitis;
- demodicosis;
- childhood skin infections;
- hormonal imbalance in the body.
Among other things, this type of rash is caused by failure to comply with basic hygiene rules, the use of low-quality cosmetics, and poor nutrition due to a lack of certain vitamins and microelements.
Treatment of acne with traditional methods
Nature has many plants in its arsenal, whose medicinal properties have long been used in cosmetology and medicine. Green tea and aloe vera are often included in facial cleansers, and jojoba oil is often included in moisturizing mousses and creams.
You can make your own acne remedy. Below are recipes that are used both to eliminate comedones and to treat inflammatory elements.
Oils
They moisturize well and serve as an excellent preventative, preventing the skin from drying out and reducing its protective properties.
The most effective are:
- Tea tree oil. It also has a healing, antiseptic effect. Apply 2-3 drops of oil to a cotton swab and apply to the problem area for 5-10 minutes.
- Jojoba oil. Due to its chemical composition similar to sebum, it does not clog pores and perfectly moisturizes. Apply 5-6 drops to a cotton pad and apply to the pimple. Keep it like this for a few minutes.
- Juniper oil. It is used not only for acne, but also for various dermatitis and eczema. Apply 1-2 drops of oil to gauze or a piece of cotton wool and apply to the problem area for 5-10 minutes.
Before using oils, you should test them on a small area of skin as they may cause an allergic reaction.
Aloe vera
Has antibacterial and healing properties.
It is used both unchanged and as tinctures:
- Rubbing with juice. Pour boiling water over the cut aloe leaf and place it in the refrigerator in the vegetable storage section for 1.5 weeks. Remove the skin from one side and wipe your face with the pulp 2 times a day.
- Alcohol tincture. Pour aloe juice with alcohol in a ratio of 4:1. Wipe the skin 1-2 times a day. Keep refrigerated.
- Egg white mask. Beat one egg white and combine with 1 teaspoon of aloe juice. Add a few drops of lemon juice. Apply to face and leave for 15-20 minutes. Then wash off.
You can buy aloe vera gel in pharmacies. It is used as an independent remedy or infusions are prepared.
Calendula
This plant not only promotes the healing of inflamed elements, but also helps fight minor scars.
Here are several ways to prepare the infusion:
- Pour 2 tsp of crushed raw materials into 100 ml of boiled water. Leave for 7-10 minutes. After cooling, moisten a cotton pad or napkin and apply to the problem area for 25 minutes. Course – 20-45 days, 1-2 times.
- 2 tbsp. l. Finely chopped flowers pour 100-150 ml of vodka or alcohol. Infuse the product for a week in a dark place. Keep refrigerated. Wipe your face with it 1-2 times a day.
- Dilute 2 tsp of calendula alcohol tincture in 200 ml of water, add 2 tsp of honey. Wipe your face with the product 1-2 times a day. Store the composition in the refrigerator.
Calendula solution can be used as a lotion to treat purulent formations and as a wound healing agent.
Treatment with medications
The list of medications for the treatment of purulent skin acne is quite extensive, its use depends on the etiology of the disease.
Antibacterial ointments:
- zinc ointment 10%, applied locally, has an antimicrobial and good drying effect;
- tetracycline ointment 3%, contains a broad-spectrum antibiotic against microorganisms, applied topically;
- levomekol, consists of active components (methyluracil with chloramphenicol), softens the pimple core, draws out its contents, promotes rapid tissue regeneration.
Antimicrobial solutions:
- zindol, a liquid suspension based on zinc, has a cleansing, disinfecting, pain and swelling agent. After using it, acne dries out;
- dimexide, a solution based on dimethyl sulfoxide, is used only diluted with water or mixed with cream, applied locally to problem areas of the skin. Has antimicrobial, drying, healing properties;
- salicylic acid, used for antiseptic treatment and drying of purulent acne, has an exfoliating and anti-inflammatory effect.
Biologically active drugs:
- Ichthyol ointment, a product of oil shale processing, treats deep purulent pimples, softens and draws out the internal contents of the abscess well, has a disinfecting, regenerating effect;
- Vishnevsky ointment, consists of castor oil, xeroform and tar. The product has a softening, pulling effect, with its help purulent foci are well cleaned;
- Heparin ointment contains sodium heparin. Relieves redness, reduces swelling and inflammation, resolves hematomas. Used to treat pustular skin diseases and their consequences - scars and spots.
Pharmaceuticals have wide possibilities for treating acne on the hands, but the choice of the drug needed for each specific case is best done after consultation with a doctor.
Nutrition and lifestyle
Treatment of acne and acne comes down not only to medications and cleansing the skin. It is also necessary to reconsider the diet and the presence of bad habits, which can become a decisive factor in the progression of the disease.
For effective treatment and prevention of acne, you must follow a few simple rules:
- Daily skin care. Use cleansing lotions and tonics based on your skin type. For combination and dry skin types, do not use products for oily skin. Regularly apply disinfectant facial lotions.
- Eliminate sweets, flour and high-fat foods from your diet. Acne is often caused by foods with a high glycemic index. The exception is durum wheat.
- To give up smoking. Nicotine destroys collagen fibers, reducing skin elasticity and its protective properties.
- Touch your face with your hands as little as possible.
- Drink 1.5-2 liters of water per day.
A healthy and active lifestyle will not cure acne on its own, but with proper treatment it can speed up the healing process at minimal cost to your health.
Acne or inflammatory skin disease affects women of all age groups. However, most often it first appears during puberty and can recur throughout life.
Small purulent pimples appear both on the face and other parts of the body, and then a severe stage of skin damage is diagnosed. Acne treatment is effective after determining the cause of its occurrence and the severity of the condition.
Prevention
Observing the rules of personal hygiene, physical activity, regular exercise, and swimming in the pool helps prevent purulent acne on the skin. Evening foods in the fresh air are beneficial.
Proper nutrition plays an important role. Fatty, salty, smoked foods, mayonnaise, fast food, carbonated drinks, and chips should be excluded. It is necessary to enrich the diet with fruits, herbs, vegetables, grains, and dairy products.
Localization on the body
Superficial pustules, however, like deep ones, can be located on different parts of the body. Based on the location, a preliminary diagnosis can be made.
On the face
External signs : resemble small rings with erosions. Most often, pustules in this area are located on the chin, nose or forehead.
Nature of the lesion : mostly always follicular.
Causes : acne, which happens most often, candidiasis, allergies to medications, aseptic skin lesions called pustulosis.
On the back
External signs : resembles a small ball, in the middle there is a white head. The swelling is small, the redness around is barely noticeable.
Nature of the lesion : most often located under the stratum corneum and are called superficial. Sometimes there may be deep abscesses.
Causes : acne, impetigo, bacterial damage, infections, pustular psoriasis.
On the arms and hands
External signs: rashes of various sizes with purulent contents inside. Most often appear in women.
Nature of the lesion : can be either follicular or non-follicular, deep or superficial, but more often the middle layer of the epidermis is affected.
Causes : insect bites, bacterial infection, use of household chemicals, vaccinations and vaccinations.
On the legs and buttocks
External signs : can have very different sizes. Inside there is purulent contents.
Nature of the lesion : located in the middle layer of the epidermis.
Causes: insect bites, bacterial damage, increased sweating, neglect of hygiene rules, psoriasis, allergies.
On the shoulders and neck
External signs : similar to small balls. In the center there is a white purulent head. There is a red rim of inflammation around the circumference.
Nature of the lesion : most often superficial, in rare cases it can be deep.
Causes : acne, skin infection, bacterial infection, impetigo.