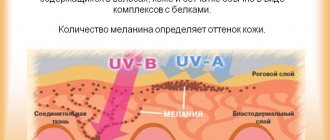
Medical terminology
Most often, acne vulgaris (acne, acne vulgaris) is one of the types of acne that occurs against the background of seborrhea.
Seborrhea is a common dermatological disease, which is expressed in increased greasiness of the skin, large fat content of the epidermis of the back, face, shoulders and décolleté, which leads to inflammatory processes in these places.
Why do acne most often appear on the upper torso and face? The thing is that an increased number of sebaceous glands per 1 square centimeter is concentrated here. And if in other areas of the skin this figure is 100, then here it will be 900.
Thus, acne vulgaris is characterized by the following features:
- Frequent relapses. If the disease manifested itself in adolescence or young adulthood, it may occur again at 30 or 40 years of age.
- It often manifests itself between the ages of 11 and 20 years, but may have a later or, conversely, earlier onset.
- Rashes mainly appear in areas where there are many sebaceous glands.
- In addition to acne and pimples, redness, flaking and itching may occur.
Since acne is a disease that is treated by a dermatologist, it has its own ICD code and it looks like this - L70.0.
What acne vulgaris is is now clear. It remains to find out what causes the disease and how to get rid of it.
Why do acne vulgaris appear?
Before starting treatment, you need to find out what is the cause of the disease. Without this, the use of even modern drugs may be ineffective and useless.
The main cause of acne vulgaris in adolescents is considered to be the onset of puberty.
At this time, the level of androgen hormones in the blood increases, and this happens not only in boys, but also in girls.
This hormone leads to increased secretion of the sebaceous glands, as a result of which sebum becomes thick and viscous, clogs the skin ducts, and pathogenic microorganisms begin to multiply here, which causes redness, inflammation, peeling and itching of the skin.
However, adolescence is not the only reason for the appearance of pimples and blackheads on the face. No less common provoking factors include:
- Diseases of the digestive system in the acute stage, for example, gastritis.
- Genetic predisposition.
- Taking certain medications.
- Constant consumption of sweets, soda, chips.
- Diseases of the endocrine system.
- Excessive sweating.
- Hormonal disorders that occur in the female body during pregnancy, as well as after childbirth and when feeding a newborn with breast milk.
- Gynecological diseases.
- Weakened immunity.
- Smoking.
- Frequent consumption of alcoholic beverages.
- Prolonged exposure to the sun.
- Work in dusty conditions and at elevated ambient temperatures.
- Emotional stress.
- Improper body hygiene or its complete absence.
- Excessive application of cosmetics to the face.
As you can see, there are many reasons for the appearance of common acne. It is difficult to understand exactly why you have acne. Here you simply cannot do without consulting a doctor. and only after identifying the cause can we begin to eliminate it and subsequent treatment.
What do acne symptoms look like?
The appearance of acne vulgaris is characterized by a whole list of symptoms, which are extremely difficult to confuse. The first signs of acne formation on the skin look like this:
- a small red spot appears, which has a swollen appearance with obvious signs of swelling;
- the inflamed neoplasm begins to itch and becomes painful upon palpation;
- on the 2nd day from the moment of appearance, the affected area of the skin becomes elastic and increasingly takes on the shape of an acne;
- biological fluid in the form of lymph and blood begins to accumulate inside the pimple;
- As the inflammatory process develops, the pimple fills with purulent contents, swells, turns red and becomes very painful.
To prevent the transformation of acne at any stage of its development, it is necessary to use drug therapy. Properly selected medications will help not only eliminate unpleasant symptoms, but also speed up the process of completely cleansing the skin of a dermatological disease.
How does acne vulgaris form?
The entire process of formation of acne vulgaris on the skin can be divided into several stages. And every pimple that appears on the face, shoulders or back will definitely go away.
The first step is to begin to increase sebum production. This secret not only becomes abundant, but it changes its structure. And if earlier sebum easily passed from the sebaceous gland to the skin and performed its protective function, now it is not able to leave the gland because it is too thick.
The second step - the sebaceous gland begins to stretch and noticeably increase in size, as more and more sebum accumulates here. This leads to the formation of closed comedones, which are located under the skin.
The third step is the addition of infection. Propionibacterium acnes, which is present on the skin of all people and is completely harmless under normal conditions, becomes dangerous when inflammation begins to develop. It is this microbe that leads to inflammation, which occurs in the stretched sebaceous gland with a large content of sebum, which cannot flow out of it.
The fourth step is the appearance of acne vulgaris on the skin. Gradually, there are more and more pimples, and it is no longer possible to get rid of them using the usual skin care products, for example, gel or foam for washing.
What are they?
Acne vulgaris is one disease with different manifestations. Pimples and blackheads can look different in this condition.
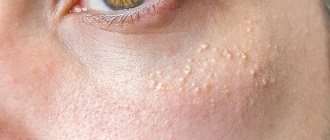
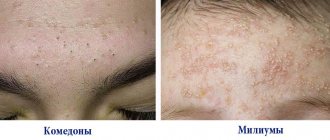
Closed comedones or whiteheads
The most common manifestation of acne vulgaris should be considered closed comedones or whiteheads. These are small papules measuring 1 or 2 mm that may not be noticeable under normal conditions, but become visible when the skin is stretched.
When pressing on such a comedone, its contents come out with great difficulty. they often become inflamed and form a real pimple.
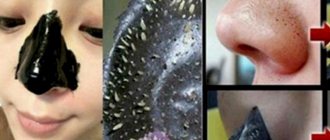
Open comedones or blackheads
Open comedones are so-called blackheads. They appear when oxygen penetrates into the site of the stretched sebaceous gland and the oxidation process begins. The gland itself and the hair follicle are clogged with a sebaceous plug. When pressed, the contents easily appear on the surface of the skin.
Open comedones rarely become inflamed. A natural scrub made from ground oatmeal helps get rid of them.
Pimples
A pimple is an inflamed comedon. They can be represented by papules, pustules, cysts and nodules. This is a real inflammatory process, which is difficult to fight on your own.
Acne comes in many forms, but there are some that pose a real health threat.
Conglobate acne - tends to merge, spreads over a large area of the body, is large in size and literally disfigures the appearance.
Indurative acne is hard to the touch, leaving behind deep scars and scars that are not so easy to fight.
Phlegmonous acne - filled with pus, can increase in size, cause general symptoms of intoxication (fever, headache) and cause blood poisoning if left untreated.
All rashes on the face that occur with acne vulgaris can be divided into inflammatory and non-inflammatory.
Non-inflammatory elements are comedones, both open and closed. All others are called inflammatory.
Traditional methods
Acne vulgaris is often treated with traditional methods. If the form of the disease is severe, they are usually not enough. But in mild and moderate stages, especially at the beginning of the disease, traditional medicine will really help cope with the disease, subject to systematic treatment:
- Masks. They can be very different, depending on the skin type and rashes. Clay masks help a lot; they tighten pores, mattify, and cleanse the skin. You can add calendula tincture or a few drops of essential oil of tea tree, rosemary, lemon, mint to this mask. Good reviews about masks made from raw potatoes and grated carrots and cranberries.
- Lotions based on herbal infusions, with and without alcohol. Aloe juice, lemon juice, and chamomile infusion help well.
Before using any essential oil for the first time, be sure to conduct a sensitivity test. Mix a couple of drops in vegetable or olive oil, apply the mixture to the area under the elbow or next to the palm.
Acne vulgaris can and should be treated. The main thing is to carry out treatment under the supervision of a specialist and regularly cleanse the skin.
Acne vulgaris belongs to a group of dermatological diseases characterized by a chronic course with inflammation of the hair follicle. In all cases, without exception, damage to the skin occurs exclusively in parts of the body where a large number of sebaceous glands are concentrated. The disease manifests itself in the form of seborrhea with the formation of inflamed pimples, comedones and profuse acne. Much less often, purulent abscesses and deep nodular formations can be found in a patient with this diagnosis.
Stages (severity) of acne vulgaris
Acne vulgaris, like many other diseases, occurs in 4 stages of its development. Each of them has its own characteristics and symptoms.
Stage 1 (severity)
On the body, and most often this is the face, there are small amounts of open comedones (blackheads). Papules may also appear in the form of small elevations above the skin, but without pus. There is slight redness.
The disease apparently has the minimal possible symptoms and can be cured without the use of medications.
Stage 2 (severity)
There are more pimples on the skin, and now they are not only comedones, but also noticeable ulcers. New elements of acne appear almost every day. The skin becomes noticeably painful, itching and peeling appear.
It is important to remember that in the second stage you can still get rid of acne without any consequences and using drugs only for external use - ointments, creams, gels, lotions.
Stage 3 (severity)
At this stage, there are about 50 pimples and ulcers on the skin. they all look like inflamed, ugly formations that can give rise to many inferiority complexes.
In addition to ulcers, cysts filled with pus also appear on the skin. The skin is constantly inflamed, painful to the touch and there is severe redness. Inflammation affects not only the upper layer of the epidermis, but also deeper layers.
Stage 4 (severity)
The whole face is covered with ulcers. The papules become large and any touch to the skin causes severe pain. Despite the fact that the pustules are very large, they can also increase in size due to the pus that accumulates in them.
Even full treatment cannot eliminate the formation of scars and cicatrices. Therefore, you should not bring your skin condition to stage 4 of acne vulgaris. Not only are the inflammations themselves very difficult to treat, but getting rid of post-acne can be extremely difficult.
How acne appears
Pimples on the skin of the face, chest and back appear in areas where a large number of sebaceous glands are located. In common forms, acne appears on the skin of the shoulders and forearms. The disease can be mild (open comedones), moderate in severity (closed comedones and papules), and severe (pustules).
Stage I: comedones formation
When the processes of exfoliation of the stratum corneum of the skin are disrupted, retention hyperkeratosis develops (delayed exfoliation). The mouth of the follicle becomes clogged with horny scales, as a result of which sebum accumulates in the cavity of the follicle. A microcomedone (milium) is formed, obstructing (closing) the excretory duct of the sebaceous gland. Over time, open and closed comedones are formed - non-inflammatory elements in acne.
Rice. 3. Microcomedones are formed when sebum accumulates in the ducts of the sebaceous glands and the mouths of the follicles. They look like small hemispherical nodules of milky color.
Rice. 4. In the photo, comedones are open in the area of the external auditory canal. With open comedones, the openings of the follicles are open. Under the influence of environmental oxygen, the fats that make up sebum oxidize, which gives comedones a black color.
Rice. 5. The photo shows open comedones on the face.
Rice. 6. In the photo, the comedones on the face are closed. With closed comedones, the openings of the follicles are closed. Horny scales and sebum, having no way out, remain under the epithelium layer.
Rice. 7. The photo shows elements of acne. Mild - mild degree of severity. Modtrant - moderate severity. Severe - severe course - abundant papules and pustules, abscess formation and the formation of fistulous tracts.
Stage II: development of inflammation
Lack of oxygen, dead horny scales and sebum create conditions for the proliferation of propionobacteria acne - permanent representatives of the skin microflora.
- Acne propionobacteria have the ability to break down sebum and cause inflammation of surrounding tissues, which leads to the development of papules. With the formation of large inflammatory infiltrates, an indurative form of acne develops.
- When a staphylococcal infection is attached, pustules (ulcers) and microabscesses develop - pustular, abscessing, necrotic and phlegmonous acne. These forms of acne are severe.
- With necrotic acne, inflammation develops deep in the follicles. Most often, acne appears on the skin of the forehead and temporal area. Pustules with hemorrhagic contents appear on their tops. After opening them, a scab forms. The disease ends with the development of a smallpox scar.
- With phlegmonous acne, the inflammatory process penetrates and develops in the subcutaneous fatty tissue. When a purulent lesion is opened, thick, creamy pus is released. The course of the disease is long. Deep scars remain in place of acne.
- With the development of multiple abscesses, an infiltrate with several fistulous tracts is formed (nodular cystic acne). Extensive infiltrates after healing leave cyst-like formations.
- The fulminant form of acne is more often recorded in boys aged 14–17 years and women. The disease is extremely severe and has a malignant course. Symptoms of intoxication are significantly expressed, symptoms of arthralgia are noted, and the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract is disrupted.
Initially, areas of the skin turn red and swelling develops. After a few days, boil-like rashes appear on the skin. Pustules can reach enormous sizes. Foci of necrosis form. After healing, rough scars remain.
Rice. 8. The photo shows acne on the face (papular acne).
Rice. 9. The photo shows acne on the face. When a staphylococcal infection is attached, pustules (ulcers) and microabscesses develop - pustular and abscessing acne.
Rice. 10. The photo shows pustular acne.
Rice. 11. The photo shows an indurative form of acne. The inflammatory process affects neighboring areas and penetrates deep into the tissue. Pustules are located on a dense base. Infiltrates are often extensive, their surface is bumpy. The disease leaves rough, disfiguring scars.
Rice. 12. The photo shows nodular cystic acne. Nodes more than 1 cm in diameter, always painful, protrude deep into the dermis, often merge, forming extensive infiltrates with fistulous tracts. When healing occurs, cyst-like formations remain. The skin of the face is most often affected.
Rice. 13. The photo shows cystic acne.
Rice. 14. In the photo, the acne on the back and chest is conglobate (spherical). Nodules, ulcerations, cysts and abscesses are the main elements of inflammation. The diameter of the nodes reaches 1 - 4 cm. Merging, the nodes form sharply painful conglomerates. Long-term non-healing abscesses often form. Healing occurs with the formation of rough bridge-shaped scars. The skin of the torso and chest is affected, much less often - the face. Acne conglobates occur in men with an additional Y chromosome, less often in women suffering from polycystic ovary syndrome.
Rice. 15. The photo shows excoriated acne. The disease occurs when pimples are scratched and squeezed out. Sometimes this condition develops into neurosis, which is characterized by behavior deviating from the norm.
Stage III: acne healing
All types of juvenile acne leave scars. When the pustules heal, small atrophic (smallpox-like) scars remain, sometimes pigmented.
When spherical, abscessive and phlegmonous acne heals, hypertrophic and, less commonly, keloid scars remain, disfiguring the skin.
Rice. 16. Atrophic scars form after healing of pustular acne.
Rice. 17. The chronic course of the disease often ends with the formation of scar tissue.
Rice. 18. The photo shows acne keloid (keloid acne). In the back of the head, dense pink rashes are visible, which are inflammation of the follicles located at the border of smooth skin and scalp. The disease is long-lasting and torpid. The affected areas become sclerotic over time.
Diagnostics
Acne vulgaris, which in medicine is coded according to the ICD as L70.0. is a disease. Therefore, the first thing to do is to consult a dermatologist and get a referral for those tests that the doctor considers necessary to make an accurate diagnosis.
Most often, the doctor writes out directions for:
- Determination of testosterone levels in the blood.
- Determination of prolactin levels in the body.
- Determination of dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate, as well as dehydroepiandrosterone, is mandatory.
- Determination of the amount of globulins.
- For girls and women - lutein-stimulating hormone, as well as follicular-type hormone.
A dermatologist may also advise you to visit a gynecologist and get a referral from him to analyze alpha-hydroxyprogesterone and cortisol in the blood. this is necessary in order to exclude such a dangerous disease as polycystic ovary syndrome.
A dermatologist can also rinse or scrape the skin to determine which microbe is causing this inflammation.
If necessary, the doctor may prescribe other tests - ultrasound, general blood test, general urine test.
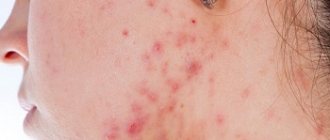
Photo of acne
Read here! Gastritis - types, description of the disease, treatment with proven modern and traditional methods (110 photos)
Please repost
0
2
Treatment
Acne vulgaris or acne vulgaris is a disease that requires a mandatory visit to the doctor. the course of treatment, the set of medications and the duration of treatment will depend on the stage of the disease.
Treatment of mild acne vulgaris
At the initial stage of development, the doctor will advise the use of cosmetics based on salicylic acid, sulfur or other antiseptics.
Typically, on the prescription sheet, the doctor may write:
- Any product from the Klerasil line that is perfect for cleansing the skin and getting rid of the initial stage of inflammation and redness.
- Oxy-5 lotion based on benzoyl peroxide. This is one of the most popular remedies for treating mild acne. It is easy to use, has a minimum of contraindications, is not an antibiotic and can be used until complete recovery.
- Avone Clearskin is one of the popular series of cosmetic medicinal products for relieving teenagers of acne and pimples at the initial stage. It fights well against comedones.
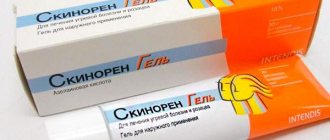
- Skinoren cream is an affordable and popular remedy for the treatment of early stage acne. It contains azelaic acid, which destroys microorganisms that cause inflammation and reduces the formation of sebum.
Other popular drugs for treating the initial stage of acne include cindol mash, infusion of calendula or celandine for washing, and a solution of salicylic acid for topical application only to areas of inflammation.
Treatment of moderate acne vulgaris
In addition to antibiotic-based medications, patients are recommended to use retinoic acid-based medications. For example, an excellent drug from this group of mild action can be called retin-a.
Among antibiotics, doctors recommend choosing ointments and gels based on:
- Doxycycline.
- Tetracycline.
- Erythromycin.
- Clindamycin.
- Lincomycin.
We cannot refuse the methods of traditional medicine. But still, the first place should no longer be cosmetics and not herbal infusions and decoctions. Namely medicines from the pharmacy.
Salicylic ointment can be applied to the area, but do not touch healthy skin.
For large pimples, it is recommended to apply compresses from Vishnevsky ointment.
Another proven cure for moderate acne vulgaris is rozamet.
A month after the start of treatment, it is necessary to evaluate the condition of the skin and, if necessary, replace medications that turned out to be useless. Under no circumstances should you self-medicate, as it will only worsen the skin condition, which will cause scars to appear.
Treatment of severe acne vulgaris
Severe acne vulgaris is a dangerous disease that sometimes has to be treated even in a hospital. In this case, not only preparations for application to the skin are used. But also those that need to be taken orally (capsules, tablets).
Girls may be offered a course of oral contraceptives, for example, this may be the drug Jess.
One of the most powerful drugs for the treatment of acne at this stage is isotretinoin, which is called abroad as roaccutane. However, the drug has many contraindications, so it should be used only under the strict supervision of a doctor.
General therapy for acne
In cases where the use of external therapy for 3 months has not produced results, as well as in severe forms of acne, general (systemic) treatment is used, which includes the use of antibiotics, synthetic derivatives of vitamin A, specific immunotherapy and antiandrogens.
Antibiotic therapy
For acne, the use of macrolide and tetracycline antibiotics for 2 to 3 weeks is indicated. Antibiotics of the cephalosporin group and gentamicin are indicated for phlegmonous acne.
Synthetic vitamin A derivatives
The substance isotretinoin is a synthetic derivative of vitamin A. The retinoid isotretinoin (the drug Roaccutane) is a dermatoprotector. The drug has anti-inflammatory, anti-acne and antiseborrheic effects. When used, terminal differentiation of cells is normalized, proliferation of the epithelium of the sebaceous gland ducts is inhibited, the formation of detritus is reduced and its evacuation is facilitated, the production of sebum is reduced and the outflow of sebum is facilitated.
Rice. 26. The photo shows the results of acne treatment with Roaccutane.
Antiandrogens
Drugs in this group (Andokur, Diane-35, Zhanin, Cyproterone, Spironolactone) reduce sebum production. Antiandrogens are prescribed to women in case of prolonged acne, when antibiotic therapy and topical isotretinoin are ineffective. Antiandrogens are used only after consultation with a gynecologist and endocrinologist. Oral intake of antiandrogens must be combined with the use of a complex of medicinal cosmetics.
Specific immunotherapy
Specific immunotherapy is indicated in the treatment of phlegmonous acne. Treatment is prescribed and carried out under the supervision of a doctor. Toxoid, antifagin, gamma globulin and other drugs are used.
Rice. 27. In the photo there are acne on the face. Heavy current. Systemic treatment is required.
Drawing conclusions
Acne vulgaris is often called a disease of adolescents. And indeed. This acne occurs before the age of 25 and then goes away. After all, the hormonal background begins to normalize and remains stable. And only in 10% of the adult population, acne, which is associated with hormones, does not go away for a longer time.
Diagnostics is an important step and should not be skipped. If necessary, you may need to consult not only a dermatologist, but also a gynecologist or urologist, an adolescent pediatrician, a cosmetologist, or an endocrinologist.
Under no circumstances should self-medication be allowed. It can cause many side effects and lead to pimples and acne being replaced by necrosis, scars and scars.
Author - Anna Mikhailova, dermatologist-cosmetologist of the first category, specialist at the Academy of Scientific Beauty. Especially for the site “Treating Acne”.