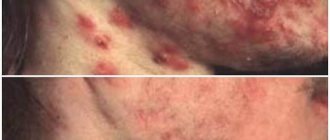
The concept of a defect and its types
Papules appear due to a malfunction of the immune system
The process begins with clogging of the skin pores with sebum, which continues to flow and stretches them, promoting the formation of peculiar cysts. The process ends with their rupture, followed by penetration of the pore contents into the upper layer of the skin. The immune system receives a signal of a violation and reacts, resulting in papules appearing on the epidermis.
These formations can be inflammatory or non-inflammatory in nature.
The former are distinguished by a reddish tint and can dissolve on their own without leaving any traces.
The latter are characterized by excessive growth of the epidermis in the absence of an inflammatory process and require mandatory treatment.
In appearance and shape, papules are:
- oval;
- round;
- cone-shaped or miliary;
- flat or lenticular.
Possible complications of rashes
If treatment is not started in a timely manner, there is a risk of complications. The most “harmless” continuation may be further progression and spread of the pustular lesion on the skin. In more serious cases, generalization of the infection may occur, spreading to internal organs. One of the dangerous options for the development of the disease is streptogenic toxic shock, in which waste products of bacteria enter the bloodstream, causing severe intoxication. Toxic shock develops in advanced cases of skin infection or in patients with severely weakened immune systems and is fatal in 5% of cases.
Causes of pathology
This skin condition is most often infectious in nature, provoked by the penetration of microbes and bacteria under the skin.
The disease begins as a result of exposure to the following factors:
- dysfunction of the sebaceous glands of the epidermis, occurring under unfavorable environmental conditions. Examples include environmental pollution and contact with hazardous toxic substances. Sometimes this condition can be caused by increased levels of cholesterol in cells;
- changes in the level of the body’s hormonal levels resulting from age-related changes in the body, under the influence of onset diseases or emotional instability;
- disruptions in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract due to poor nutrition, existing pathologies affecting metabolic processes in the body;
- a stressful lifestyle with frequent nervous shocks, mental overload, prolonged depression and constant stress.
It is very difficult for a person without medical education to distinguish papules from ordinary acne. It is imperative to contact a dermatologist, who will make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe a drug treatment regimen to successfully get rid of the defect that has arisen. Self-treatment can significantly complicate and worsen the course of the disease!
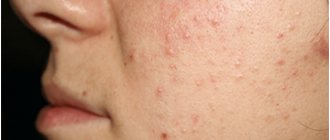
Pustule on the skin: photo, causes of formation
There are quite a few reasons for the appearance of pustules. It is impossible to determine exactly why ulcers began to appear on the body on your own. Therefore, you should definitely visit a dermatologist.
READ ALSO: Black face mask. TOP 5 best brands for cleansing
The main reasons for the formation of purulent pustules include:
- Bacterial infections, in which weak immunity can cause the appearance of numerous pustules.
- Irritations and injuries to the skin, for example, scratching with severe itching during allergies, burns, violations of the integrity of the skin due to small wounds, scratches and abrasions.
- Reduced immune defense, when any microbe or virus can become a real danger and cause disease, including pustules.
Pustules with pus also appear in such unpleasant diseases as acne, scabies, excessive sweating, hormonal imbalances, candidiasis, syphilis and many, many others.
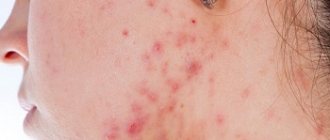
Signs characteristic of a pustule (abscess)
A pustule (abscess) on the surface of the skin can have a very different appearance. Most often it is an inflated ball or cone and sometimes a flat plaque. The purulent contents inside the pustule can also have a variety of colors - white (most often), gray, green or yellow.
Only a doctor can understand by the color of the pus what caused the appearance of these rashes.
The sizes of pustules can also be very different - from a couple of millimeters to several centimeters. There must be a white head, or abscess, at the top of the pustule. Also, the pustule is always surrounded by red, inflamed tissue.
You can see what a pustule looks like in the photo below.
The process of development of an abscess occurs in several stages.
- The first stage is the appearance of redness.
- The second stage is the formation of a compaction (infiltrate) in the very center of the red spot.
- The third stage – the process of decay begins, which causes the appearance of pus, which means the pustule begins to increase in size, that is, it actively grows.
- The fourth stage is the maturation process.
- Fifth - the opening of the abscess begins, its contents burst out.
- The sixth stage is the appearance of a wound after the opening of the pustule. The wound gradually tightens and a scar appears on the surface of the skin.
Classification also involves dividing pustules according to their type. They can be:
- Follicular . In this case, a pustule (abscess) develops inside the hair follicle.
- Non-follicular . In this case, the abscess develops outside the hair follicle, for example, in the sebaceous gland, which happens with acne with pustules.
There is also a classification based on the depth of the lesion. If the abscess has formed in the epidermis, then it is considered superficial.
If the pustule appears in the dermis, it means it is deep. The formation of a pustule takes from several hours to a couple of days.
You suddenly have a pimple on:
And you don't know what to do? Don't panic! In our unique articles you will definitely find answers to all these and many other questions. Are you wondering if acne is hereditary or what daily habits can cause acne?
READ ALSO: Rash on the face of a newborn - types, treatment methods
Read, comment, ask questions. Together we will find a way to get rid of acne forever!
Diseases accompanied by the appearance of papules on the face
Such formations on the skin can serve as a factor accompanying the course of many diseases, namely:
- horny eczema, which occurs with the appearance of painful papules on the skin. This pathology usually occurs in people who are constantly in contact with chemically aggressive environments and can become chronic;
- amyloidosis, which is characterized by rashes concentrated near the mouth, eyes and in skin folds;
- syphilis associated with the formation of papules in the mouth and tonsils, causing severe pain in the throat with possible loss of voice. This type of formation is difficult to treat;
- psoriasis, characterized by the formation of a papular rash with white scales that easily separate from the surface and are most often located in the wrist area, on the backs of the feet, in the elbows and knee joints. If left untreated, they merge with each other, forming plaques that can cover the entire body;
- lichen spines, the development of which can be caused by a hereditary factor, vitamin deficiency, as well as a weakened immune system. This type of pathology is characterized by the appearance of small and rough papules when touched, having different shapes.
Pointed types of papules, constantly increasing in size, are considered the most dangerous, since they can degenerate into oncological tumors and become quite large tumors, so timely consultation with a dermatologist in this case is mandatory!
For each patient, the dermatologist prescribes his own treatment package depending on the stages of the papules.
What is a fibrous papule
A fibrous papule is a melanocytic nevus or mole. The phenomenon is familiar and common to the vast majority of people. The growths are classified as benign skin neoplasms. But this does not mean that they can be taken lightly. Under unfavorable circumstances, moles can degenerate into malignant melanoma or other types of cancer.
Fibrous papules are a rare form of nevus. In appearance, it is a dome-shaped formation in the form of a node or papule, which rises 5–7 mm above the surface of the skin of the nose. May occur on the face and body. The color of the fibrous capsule varies from pink and natural to brown and black.
Histological examination of tumor samples shows that the tissues are similar to angiofibromas. The skin is saturated with small blood vessels and fibrous. Currently, scientists tend to consider fibrous papules as a separate type of skin neoplasm, and not as a representative of the nevus class. But in the official WHO protocols the classification has not yet been changed. Therefore, involutional nevi are considered moles.
The reasons for the appearance of the tumor have not yet been clarified. Doctors identify a number of factors that contribute to the appearance of fibrous growths:
- hormonal imbalances of various kinds, even pregnancy and menopause can provoke the formation of nevi;
- heredity;
- frequent exposure of the skin to ultraviolet radiation;
- diseases of the dermis of various origins.
Under the influence of these factors, mutations occur during the development of melanoblasts. These skin cells degenerate into nevocytes, which accumulate in the layers of the dermis. In this case, a nevus appears.
Treatment options
Only a doctor is able to prescribe competent and qualified treatment after conducting a comprehensive examination of the patient’s body and passing all the tests necessary to establish an accurate diagnosis. In some cases, it is possible to take scrapings from the surface of the papules for histological examination in the laboratory.
Treating only the external manifestations of the disease is not enough, since the disease can worsen and become chronic, which is especially difficult to eliminate.
Therapeutic methods for treating papules are selected strictly individually for each individual patient, depending on the cause of their occurrence, shape, depth, degree of growth and other factors.
For information: for minor rashes without the presence of a specific disease, the following are generally prescribed:
- local spot treatment of papules using special anti-inflammatory compounds;
- intravenous administration of medications;
- external treatment with antiseptic solutions, lotions, antibacterial creams;
- taking multivitamin preparations that increase the body's defenses.
Self-medication is dangerous for your health! Don’t take risks and immediately seek help from a specialist for an accurate diagnosis of the pathology!
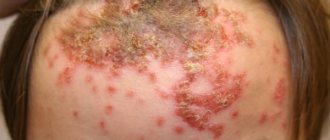
Localization on the body
Superficial pustules, however, like deep ones, can be located on different parts of the body. Based on the location, a preliminary diagnosis can be made.
On the face
External signs : resemble small rings with erosions. Most often, pustules in this area are located on the chin, nose or forehead.
Nature of the lesion : mostly always follicular.
Causes : acne, which happens most often, candidiasis, allergies to medications, aseptic skin lesions called pustulosis.
On the back
External signs : resembles a small ball, in the middle there is a white head. The swelling is small, the redness around is barely noticeable.
Nature of the lesion : most often located under the stratum corneum and are called superficial. Sometimes there may be deep abscesses.
Causes : acne, impetigo, bacterial damage, infections, pustular psoriasis.
On the arms and hands
External signs: rashes of various sizes with purulent contents inside. Most often appear in women.
Nature of the lesion : can be either follicular or non-follicular, deep or superficial, but more often the middle layer of the epidermis is affected.
Causes : insect bites, bacterial infection, use of household chemicals, vaccinations and vaccinations.
On the legs and buttocks
External signs : can have very different sizes. Inside there is purulent contents.
Nature of the lesion : located in the middle layer of the epidermis.
Causes: insect bites, bacterial damage, increased sweating, neglect of hygiene rules, psoriasis, allergies.
On the shoulders and neck
External signs : similar to small balls. In the center there is a white purulent head. There is a red rim of inflammation around the circumference.
Nature of the lesion : most often superficial, in rare cases it can be deep.
Causes : acne, skin infection, bacterial infection, impetigo.
Pustules on the body can appear for a variety of reasons. The tactics for treating rashes will depend on this.
Prevention measures
You can prevent the appearance of papules on the face with the following simple measures:
- frequent hand washing, especially after visiting public places;
- regular cleansing of the facial skin to remove contaminants, bacteria and fatty secretions accumulated on its surface, which can cause clogged pores;
- proper, nutritious, balanced nutrition with a sufficient supply of vitamins and microelements that increase the overall protection of the body;
- daily walks in the fresh air, strengthening the local immunity of the skin.
Do not neglect timely medical consultation and get better!
Papules and pustules
Both papules and pustules are very common types of skin rashes. They can appear on various parts of the body under the influence of many processes (from poor hygiene to various infectious diseases), but the rash causes the most discomfort if it forms on the face.
Sometimes various elements of rashes are found on the skin. Information about their type helps to make the correct diagnosis, determine the cause of the rash and choose the right treatment.
Differential diagnosis
If any skin defects are detected, you should consult a dermatologist. The diagnosis is made on the basis of visual examination, immune complex analysis and microscopy. You can differentiate a pustule from a papule, erythema, or vesicle using the following diagnostic features. The pustule has:
- the upper layer in the form of a parakeratotic stratum corneum;
- bottom consisting of granular liquid;
- swelling in the papillary layer;
- multiple perivascular infiltrates.
An immune complex analysis will reveal what caused the formation of pustules: a bacterial or fungal infection, an allergic reaction to medication, a change in blood composition.
Using microscopy, the contents of pus are studied, the causative agent of infection is identified, and the sensitivity of bacteria to medications is determined. A treatment regimen is developed based on the results obtained.