1Why does androgenetic alopecia occur in women?
It is generally accepted that only men suffer from this type of baldness. This is an erroneous statement. Up to 30% of women over 50 years of age have this pathology.
The human body works under the power of hormones. In men, androgens predominate, and in women, estrogens predominate. Androgens are also present in small quantities in women.
They are produced by the adrenal glands, ovaries, peripheral tissues and organs (skin, liver, fat, muscle tissue). Normal hormonal levels determine the development of the genital organs, the functioning of the glands, as well as female or male hair growth.
If, for one reason or another, the level of male hormones in the female body increases, androgenetic alopecia may develop.
This type of baldness in women can occur without an increase in androgen levels if there is increased sensitivity of the hair follicles to male hormones.
Increased susceptibility in women is inherited genetically and is manifested by disruption and disorder of protein synthesis and hair nutrition. Because of this, the hair becomes thinner, turns into vellus hair and falls out.
Causes of the disease
The body of the fairer sex produces hormones, both female and male hormones (dihydrotestosterones) in a certain ratio. It can be disrupted under the influence of various factors. As a result, the amount of male hormones in the body increases, which becomes the cause of androgenic baldness in women.
The main factors provoking the disease include:
- Pregnancy. For the development of the fetus, nutrients, minerals, and vitamins are required from the mother’s body. As a result, a woman experiences a deficiency of useful microelements necessary for the functioning of organs and systems, including the condition of the hair. Added to the lack of nutrition is the hormonal surge caused by pregnancy.
- Androgenetic alopecia in women occurs as a result of hereditary predisposition. If older relatives have a problem with hair loss, it is necessary to begin prevention before the first signs of baldness appear.
- Adverse effects of external factors - ecology, use of low-quality dyes, hair styling products, perm.
- Taking medications, hormonal contraceptives.
- Presence of endocrine diseases, tumors.
- Gynecological problems often cause hair loss in women.
- Hormonal changes, as a result of which the amount of female hormones decreases.
The cause of baldness is often stress, depression and nervous overload. In this case, hair loss is detected 1–2 months after the stress.
2Symptoms
The main symptom of androgenetic alopecia is hair loss. It has its own characteristics for women.
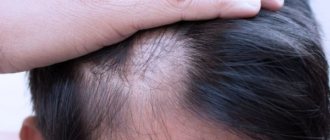
Initially, the hair thins from the forehead and crown. In the area of the central parting, the hair also thins out intensively, exposing a strip of bare scalp, which is visible through the remaining hair.
Androgenetic alopecia in women is characterized by the fact that in the occipital region the thickness and growth of hair usually remain the same. Only with a diffuse form can the occipital region also remain hairless.
What is the disease
Androgenic alopecia, or male pattern baldness, is a process that is manifested by increased hair loss in the forehead and crown of the head in men and in the parietal area, spreading to the lateral surfaces in women. In very rare cases, complete hair loss is possible.
Androgenetic alopecia is characterized by hair loss in the forehead and crown area in men and thinning of hair in the central parting area in women.
Some authors are not inclined to distinguish between the concepts of androgenic and androgenetic alopecia, although these diseases have different mechanisms of development. In androgenetic alopecia, the main role is played by the hereditary factor. Under the influence of male sex steroids, namely dihydrotestosterone, hair follicles shrink and weaken. In this case, thick pigmented hair is gradually replaced by thinner and less pigmented hair, eventually turning into vellus hair and falling out. With androgenetic alopecia, both men and women experience a high level of androgens in the blood. It is this increase that is responsible for hair loss. Dihydrotestosterone, a derivative of the steroid testosterone, causes dysfunction of the hair follicles, namely, it sharply shortens the anagen phase - the period of hair fiber growth. This leads to a failure of the entire life cycle of the follicles and diffuse hair loss in the telogen - resting phase.
The disease can develop at any age after puberty, but most often men begin to lose hair after 35–40 years of age and women after 50 years of age. In the latter, during premenopause, the amount of male steroids in the peripheral blood increases, which is natural, so the phenomena of hyperandrogenism in older women are not pronounced.
Androgenic alopecia is not inherited. It is secondary and occurs against the background of endocrine pathology or after taking certain medications.
The life cycle of hair consists of several phases, each of which is influenced by hormones, more precisely, androgens. Testosterone and its derivative dihydrotestosterone regulate the processes of growth and involution of each hair shaft, the follicles of which have androgen receptors. Anagen, that is, the stage of hair growth, is regulated by genes influenced by androgens. Excess of these steroids shortens the growth phase and the follicles degenerate over time. This can lead to total hair loss and the inability to naturally replace it with new ones.
Excessive amounts of dihydrotestosterone act on androgen receptors in the follicles, shortening the hair growth phase
Theoretically, it is believed that the process of hair loss due to androgenetic alopecia is reversible, since its cause is a violation of the correct hair growth cycle. But in some people, the rod cells of the follicles are damaged irrevocably, in which case hair loss therapy has no effect (especially in men).
Testosterone is converted to dihydrotestosterone, which inhibits hair growth, through the enzyme 5-alpha reductase
3 Stages of development
The following stages are distinguished during androgenetic alopecia:
Stage 1 – hair in the parting area in women begins to grow less frequently, becomes dull, and becomes more brittle.
Stage 2 – hair loss intensifies, hairless areas spread in the parietal region, affecting the frontal region.
Stage 3 – almost the entire parietal and frontal region is hairless. Partial hair in women is preserved on the back of the head and in the temple area. The head is covered with thin fluff. If the process progresses, then the back of the head and the temporal region also remain hairless.
Diagnostics
You can diagnose an excess or deficiency of androgens in the body by visiting a trichologist and passing all the necessary tests. The doctor will collect a history of complaints and diseases, where he will need to indicate when hair loss began and from which areas of the head.
During the appointment, you should give a detailed description of your family history and find out whether your relatives had similar pathologies. The trichologist must examine the scalp and lesions, and the condition of the skin at this stage.
The next step is to conduct trichoscopy, computer diagnostics of hair follicles under a microscope; for this, hair is taken from the parietal and occipital areas of the head.
4Causes of androgenetic alopecia
The following diseases and conditions can lead to hormonal imbalance with a predominance of androgens in the female body:
- Endocrine disorders. Pathological processes in the area of the adrenal glands and urogenital tract lead to disruption of the functioning of the endocrine glands, liver, and ovaries. This affects the woman’s hormonal background and creates the preconditions for hyperandrogenemia.
- Androgen-producing tumors of the ovaries, adrenal glands, and skin appendages are another serious pathology in which baldness is one of many symptoms indicating problems in a woman’s body
- Polycystic ovary syndrome
- Pregnancy, lactation, postmenopause
These periods in a woman’s life are the most vulnerable due to hormonal fluctuations. Any stress, physical or mental fatigue, colds can give impetus to the development of the pathogenesis of alopecia
- increased androgen production due to diseases such as acromegaly, hyperprolactinemia
- Long-term use by women of oral contraceptives, glucocorticosteroids, antidepressants
- genetic predisposition. As a rule, with an inherited form of baldness, there is a normal level of male sex hormones in a woman’s body, but the sensitivity of the hair follicle receptors to them is many times increased.
Drug therapy
The treatment of androgenic alopecia is based on taking medications that normalize hormonal levels and stimulate new hair growth.
Taking vitamins that activate the hair follicles is also indicated. To achieve maximum effect, drugs are combined to create an individual treatment regimen.
Headway, Rogaine, Regaine
All three drugs are trade names for Minoxidil. This is a local vasodilator aimed at improving blood circulation in the hair follicles.
The main purpose is to stimulate new hair growth. Available in lotion form for application to affected areas of the scalp.
The drug has different concentrations of the active substance. In the treatment of androgenetic alopecia in women, it is advisable to use 2% and 5% lotion. Higher concentrations may have the opposite effect.
The drug does not affect the hormonal background of a woman, exhibiting a local irritant effect. But when using the product in large dosages, it is possible for the active substance to penetrate into the blood. Therefore, you should strictly adhere to the recommended dosage.
Minoxidil (Headway, Rogaine, Regaine) has shown high effectiveness in the treatment of baldness. Thus, the first results were noted by women after just two months of regular use twice a day. And complete recovery is observed after six months to a year of use.
But, unfortunately, the products do not have a lasting effect, since they do not affect the cause of alopecia. Therefore, when the drug is discontinued, the hair condition returns to its original state, followed by progression of hair loss.
Androcur
Antiandrogenic drug. The active substance is cyproterone acetate. The action of the drug is aimed at blocking the influence of androgens. Prescribed only to women of reproductive age together with Diane-35 .
The effect achieved by taking Androcur is reversible. Therefore, the duration of the course and the dosage regimen are determined by the gynecologist-endocrinologist.
The minimum course is 4 months. According to the instructions, to achieve the desired therapeutic effect, Diane-35 and Androcur should be taken on the first day of the menstrual cycle.
Starting from day 16, Androkur is canceled, leaving only Diana-35. After the last 21 contraceptive tablets, a break is taken for a week, after which treatment continues according to the regimen.
Let's find out together how much a hair transplant on the head costs, depending on the technique used. Read here about the best vitamins against hair loss.
At this address https://cosmetolog-expert.ru/prochee/trihologiya/alopetsiya-vyipadenie-volos/posle-rodov-chto-delat.html we will tell you what to do if your hair falls out in clumps after childbirth.
Veroshpiron
Diuretic drug with antihypertensive effect. With regular use of a daily dose of 200 mg, a pronounced antiandrogenic effect is observed.
For the treatment of androgenic alopecia, it is prescribed to women over 30 years of age. The course of treatment is six months. Longer use increases the risk of developing breast cancer .
Due to the possible effect on the formation of a male fetus, contraception is indicated during treatment for baldness to prevent possible pregnancy.
Cimetidine
The drug belongs to the class of antihistamines. It is used primarily in the treatment of stomach ulcers and other diseases of the digestive system associated with increased production of hydrochloric acid.
It has proven itself well in the treatment of androgenetic alopecia in women when taken in large dosages for 9-12 months . Side effects include increased production of the hormone prolactin, which can lead to the development of breast diseases.
Diana-35
A complex hormonal drug that combines antiandrogens and estrogens.
The effect of the drug in the treatment of alopecia in women is based on blocking the influence of male sex hormones. In the long term, this helps not only stop the process of hair loss, but also allows you to restore lost volume.
The minimum course of treatment for Diane-35 is 3 months, but according to patient reviews, full recovery will require at least a year. Long-term use of the drug significantly increases the risk of developing side effects and undesirable conditions.
Therefore, the advisability of prescribing hormonal contraception is determined by the attending physician, and the selected treatment is reviewed every 3 months.
Yarina
Yarina also belongs to the class of antiandrogenic oral contraceptives. The action of the drug is based on blocking the production of androgens by the ovaries and reducing the concentration of male hormones in the blood.
Like any other drug to prevent unwanted pregnancy, it has many contraindications and side effects. The minimum course of treatment is 3-4 months to evaluate effectiveness. Treatment can be continued with the permission of the attending physician.
Finasteride
The action of the drug is aimed at blocking the production of enzymes that ensure the conversion of testosterone to dihydrotestosterone.
Finasteride has shown high effectiveness with long-term use for six months or longer. But the resulting effect is reversible, and when the drug is discontinued, the hair condition returns to its original appearance over the next few months.
Finasteride has a negative effect on the health of the unborn child, therefore it is not recommended for women of reproductive age planning pregnancy.
5Diagnostics in women
If a woman suspects that she has androgenetic alopecia, she should pay attention to whether her body, along with thinning the number of hairs on her head, has the following symptoms:
- menstrual irregularities (absence of menstruation, or, on the contrary, too much uterine bleeding, problems with fertility or pregnancy);
- excess hair growth on the body, neck, chin area;
- deepening of the voice;
- atrophy of the mammary glands;
- acne.
If alopecia is combined with one of the above symptoms, there is a very high probability that the woman will develop androgenetic alopecia. But an accurate diagnosis must be made by a doctor.
For the purpose of examination, you should visit the following specialists: a trichologist, a therapist, an endocrinologist, a gynecologist. Undergo a set of analyzes and studies, including:
- general clinical blood and urine tests, blood glucose test;
- biochemistry;
- blood test for thyroid and adrenal hormones, sex hormones (determination of testosterone and estrogen levels);
- Ultrasound of the kidneys and adrenal glands;
- CT, MRI of the hypothalamic-pituitary region;
- examination of hair structure under a microscope;
- phototrichogram (determination of hair growth density);
- scalp biopsy.
Reasons why baldness occurs in women
Trichologists have long been able to study baldness in women, the causes of which are noted below.
- Lack of iron in the blood. With anemia, there is a noticeable thinning of the hair, which disappears when its amount normalizes. Women may also experience hair loss as a result of heavy menstruation, which lasts for five to six days. Iron deficiency can be treated with the help of vitamins and a properly selected nutrition system. A lack of iron in the body can be identified by the following signs: pale skin, loss of strength, drowsiness and lethargy. To confirm the diagnosis, you just need to take a blood test from your finger. If necessary, the doctor will prescribe certain medications to raise iron levels in the blood.
- Periodic or constant stressful situations. It has been noted more than once that those who worry too often and too much usually have big problems with baldness, which is difficult to stop. If a stressful situation happens to you once, then your hair will quickly recover and there should not be excessive hair loss. With a single stress, the hair quickly returns to normal. But if, due to constant stressful situations, your blood vessels constantly narrow, then nutrients will poorly flow to the hair roots, which is why female pattern baldness may occur.
- Hair loss can also be caused by various diseases that seem to have virtually nothing to do with hair. We are talking about polycystic ovary syndrome, diabetes mellitus, sexually transmitted diseases, and various inflammatory processes in the body.
- Hair loss can sometimes be stopped by changing the medication. Sometimes hair falls out because a woman is taking antibiotics or other pills that adversely affect her hair. If you have been taking the drug for several days and notice increased hair loss, then contact your doctor and ask them to consider changing this medication, as it is not suitable for you.
- Female pattern baldness occurs because of this. That the fair sex often exposes their hair to the aggressive effects of strong chemicals such as styling products, dyes, perms and hair dryers. All these methods of creating a hairstyle are harmful to the hair, so they should be used much less frequently. In addition, trichologists do not recommend that those who want to have chic hair make themselves dreadlocks, tighten their ponytail and weave African braids.
- Dietary supplements do not always have a positive effect on the condition of the hair. Often women get too carried away by vaunted foreign remedies and suffer from it. It is wrong to treat yourself with products that contain selenium. Imported vitamins also contain heavy metals, so be careful with the medications you plan to take.
- Very often, baldness in women progresses during periods of hormonal decline. Then, when the amount of testosterone increases, and estrogen, on the contrary, decreases. This happens during puberty, pregnancy and with the onset of menopause. In any case, you should not ignore these changes in the body. As soon as you notice excessive hair loss during your hormonal changes, do not expect it to go away on its own, but contact a trichologist to solve this problem and not lose your hair.
- Quite often, in order to stop hair loss, it is enough for women to treat a violation of the blood supply to the blood vessels of the head. This disease is possible due to lack of sleep, stress, excessive consumption of coffee, alcoholic beverages, and smoking. All this makes the walls of blood vessels more fragile and narrows them. Without a healthy circulatory system, normal nutrition of the hair follicles is impossible.
6Principles of treatment of androgenetic alopecia
The sooner the disease is detected and the cause that provoked it is established, the greater the likelihood of successful hair restoration.
Therapy for androgenetic alopecia in women includes a complex effect on the cause of the disease, as well as symptomatic methods aimed at restoring hair growth.
Drug therapy is prescribed according to indications and includes:
- Antiandrogen drugs that lower the level of male hormones. Prescribed exclusively on the recommendation of a doctor: Marvelon, Logest, Janine, spironolactone.
- estrogen and progesterone preparations. Allows you to increase the level of female sex hormones, thereby blocking the production of androgens.
Symptomatic therapy for androgenetic alopecia in women is aimed at restoring the functioning of the hair follicles. The following have a good effect in the treatment of androgenetic alopecia:
- Minoxidil. Solution for external use 2.5%. It has a vasodilating effect, thereby helping to improve metabolic processes inside the follicles. Stimulates hair growth. It is recommended to apply the solution externally, twice a day, the effect of its use occurs after 2-3 months.
- Immunomodulators: immunobex, trimunal, echinin
- Vitamins B, D, A, E. Complex multivitamins with microelements: Zn, Se, Mg.
- ointments based on glucocorticosteroids, tinctures with pepper extract. Medicines are rubbed into intact scalp, they have an irritating effect, increase blood flow to the hair follicles, and accelerate metabolic processes.
Local therapy with which you need to be very careful!
Minoxidil is a drug for the treatment of AGA. It is recommended to apply daily every 12 hours. In approximately 40% of patients, after a couple of months of use, hair loss may stop and the first vellus hair will appear. That's where the positives end.
There are, in my opinion, much more disadvantages. More than half of patients are not sensitive to minoxidil. Vellus hair will most likely never turn into terminal hair. Therapy resistance will appear very soon. You will have to increase the concentration to higher doses, which is fraught with consequences in the form of seborrhea and dermatitis. Withdrawal syndrome, in case of refusal of therapy, occurs very quickly.
What was grown by back-breaking labor over months of therapy will leave your head in a matter of weeks. So what to do? Combine the use of Minoxidil (always in low concentration) with additional local therapy (5-alpha reductase inhibitors, melatonin, vitamin D, sex hormones: estrogens, testosterone and progesterone).
Antifungal shampoos, in addition to the main therapy, can enhance the effect due to antiandrogenic properties.
8Stimulation of hair growth through mesotherapy
A modern method of treating androgenic type alopecia is mesotherapy. This method is based on the administration of medications consisting of vitamins, microelements, and nutrients by injection - puncturing the scalp in areas of impaired hair growth.
The procedure for alopecia in women can be carried out using a small syringe, which is administered by the doctor himself, or using special devices for mesotherapy.
The course of injections and the method of their administration for androgenetic alopecia are determined by the doctor in each specific case.
Lifestyle and menu
Treatment of androgenetic alopecia is a long process that requires perseverance and a lot of patience. At the same time, successful therapy includes not only medications and physical procedures. You need to change your lifestyle and review your menu.
Tips from trichologists
To enhance the healing process and protect your strands from falling out, you need to follow a few simple recommendations. Such advice should be followed not only by those who have experienced alopecia, but also by absolutely healthy people - as a preventive measure against baldness. General recommendations:
- stop smoking;
- wash your hair only with natural shampoos;
- make sure you get enough rest;
- treat all diseases in a timely manner;
- undergo regular medical examinations;
- reduce your coffee intake (no more than three cups per day).
It would be a good idea to follow other tips:
- rinse your hair with herbal decoctions - use infusions of burdock, chamomile, peppermint, nettle;
- refuse styling products - if this is not possible, resort to their help extremely rarely;
- protect yourself from stress and depression - if necessary, consult a psychologist or psychiatrist;
- do not use hormonal contraceptives - except for drugs prescribed by a doctor;
- be sure to wear a hat - this advice is relevant if the air temperature drops below 0ºC;
Dietary ration
Baldness is often accompanied by a lack of nutrients in the body. To replenish them, the patient is prescribed vitamin and mineral complexes. However, proper nutrition should also contribute to the restoration of the body. The products required for treatment are listed in the table below.
Table - Recommended food groups for alopecia
| Group | Products |
| Sources of Omega Fats | — Fish (mackerel, pink salmon, hake, herring, trout, mackerel, salmon, tuna, cod, chum salmon, herring, flounder, sprats, sardines, halibut, stellate sturgeon, eel, mullet); — sea shellfish (squid, octopus, oysters); - soy; - nuts: cashews, almonds; — unrefined vegetable oils (sunflower, olive, flaxseed) |
| Easily digestible proteins, carbohydrates | - Spinach; - broccoli; - lettuce; - parsley; — cabbage (white, red, cauliflower, Beijing); - leek |
| Sources of vitamin B12 | — Meat (beef, rabbit, lamb, chicken); - eggs; — offal (liver, heart, tongue); — dairy products (cottage cheese, sour cream, kefir, milk, cheese); – fish (herring, sardine, trout, mackerel, sea bass) |
| Sources of fiber | - Carrot; - eggplants; - beet; - zucchini; - cucumbers; - celery |
| Sources of microelements – zinc and iron | — Legumes (peas, beans, lentils); - flakes (oatmeal, buckwheat); - porridge (barley, buckwheat, wheat); - whole wheat bread; - citrus fruits (grapefruit, lemon, orange); - vegetables (potatoes, garlic, radish); - hard cheese; - meat (chicken, turkey); - berries and fruits (apples, black currants, raspberries); - green tea |
Semi-finished products and fast foods are completely unhelpful and even harmful for androgenetic alopecia. It is recommended to avoid smoked foods, baked goods and sweet desserts.
Do not forget that it is very difficult to independently determine the symptoms of androgenetic alopecia in women in the initial stages. If you suspect something is wrong, then count how much hair falls out during the day. Normally, in a healthy person, this amount varies from 50 to 150. If you lose more than 150 hairs, this does not mean that you are going bald, but it is a serious reason to consult a doctor.
9Diet
Nutrition for patients suffering from androgenetic alopecia should be complete and balanced in terms of fats, carbohydrates, enriched with proteins, vitamins, and microelements.
Coffee, alcohol, marinades, and sweets should be excluded from the diet.
You can’t starve or limit the protein content in your diet. For alopecia, it is advisable to eat boiled meat, sea fish, walnuts, liver, boiled eggs, corn, and legumes.
Oats are useful for hair loss - they are a storehouse of vitamins, microelements and amino acids. Oat porridge can strengthen hair and stop hair loss due to alopecia.
10Folk methods in treatment
A good addition to the main treatment of androgenetic alopecia may be therapy using unconventional methods: applying masks, compresses to the scalp, made according to recipes from traditional healers and healers.
The only condition that doctors call for, before starting treatment of androgenetic alopecia with non-traditional medicine, is to consult a doctor.
Popular recipes for androgenic type alopecia “from the people” in women are the following:
- Grate the head of garlic and the head of onion on a fine grater, squeeze out the released juice through double gauze. Rub once a day into bald areas of the head.
This method should not be used if there is an individual intolerance, as well as if there are abrasions, scratches, or redness of the skin.
- Grate fresh burdock root, mix it with aloe juice and burdock oil in a ratio of 2:1:1. Make a mask from the resulting mixture once every 2-3 days for 20-30 minutes, wrapping your head in cellophane and a towel. Then rinse the mixture with warm water.
- Mix the yolk of a chicken egg, a tablespoon of linden honey, and a dessert spoon of aloe juice. Apply to the roots of the hair, wrapping it in a cellophane cap for 20 minutes. Afterwards, rinse with warm water.
- After each shampooing, rinse your hair with a warm decoction of fresh stinging nettle leaves. Nettle accelerates hair growth and follicle regeneration.
Norm and deviation
If the androgen hormone is normal in the body, then it is responsible for normalizing the amount of blood sugar, improves metabolism, and has a positive effect on hair growth. If it is present in excess, then the follicles begin to be damaged at the cellular level, and baldness begins.
The causes of androgenetic alopecia are most often associated with other disorders:
- hormonal imbalances;
- endocrine diseases;
- problems with the digestive tract;
- chronic stress, lack of sleep, depression, nervousness;
- inflammatory lesions on the scalp;
- malfunctions of the immune system.
Over time, hair thins, becomes spotted, becomes thinner, and dandruff appears. This disorder worries women aged 30 to 50 years, and the disease progresses at 60-70 years.
Attention! Cases have been recorded where complete baldness occurred in just 2 months, but most often this is a chronic process that lasts for years.
Symptoms can be expressed in different ways, but the main manifestation of the disease is the rapid loss of strands. Most often it starts from the frontal zone and spreads to the crown. New follicles may appear in place of the bald patch, but they also die over time.
11Prevention
Prevention of androgenic type alopecia in women consists of maintaining a healthy lifestyle, proper nutrition, timely medical examination and monitoring one’s own health.
If symptoms indicating increased androgen levels appear, such as: irregular menstruation, increased body and facial hair, deepening of the voice, you should not delay a visit to the doctor.
Stress, poor nutrition, and excessive physical activity can also become a trigger factor in the development of androgenetic alopecia.
Try to be exposed to stressful situations as little as possible, eat balanced foods, and adhere to a diet.
12Questions from women with alopecia
Most often, women suffering from androgenetic alopecia ask the following questions:
13Will my hair grow back on my head?
It is impossible to give a definite answer. Much depends on the cause that caused androgenetic alopecia, as well as on the stage and degree of neglect of the process.
As a rule, genetically determined alopecia in women is difficult to treat. Other reasons, with timely treatment, can be eliminated, a woman’s hormonal levels can be adjusted, in this case there is every chance of success in acquiring beautiful hair.