Distinctive features
New growths on the skin are usually called tumors or neoplasia. Benign tumors on the skin have some distinctive criteria, thanks to which a specialist can differentiate these neoplasms from the malignant form. These criteria include:
- Slow growth.
- The neoplasm does not grow into nearby tissues.
- Cellular elements are not able to spread beyond the neoplasm.
- The size of the tumor increases evenly.
- Benign tumors on the skin are atypical structures that do not tend to metastasize.
- As benign tumors grow, they push adjacent tissues away, putting pressure on them, resulting in the appearance of a capsule.
It is important to note that benign tumors on the skin are not dangerous to humans, but it is worth noting that when exposed to certain factors, the formations can develop into cancer. Most often in practice, the following neoplastic benign tumors are observed:
- Fibroma.
- Hemangioma.
- Birthmark.
- Lymphangioma.
- Lipoma.
- Atheroma.
- Papilloma.
- Neurofibroma.
As a rule, the indication for removal is an unsuccessful localization, for example, on the head, face, or in a place of constant friction with clothing. In addition, large size, as well as disruptions in the functioning of other organs that provoke neoplasm, are also indications for removal. Such benign neoplasms on the skin respond well to both surgical and hardware therapy. Only sometimes tumors can recur.
Description and features
Hanging growths on the skin are most often diagnosed; such formations have their own characteristics. First of all, pedunculated warts are benign in nature. Doctors have extremely rarely observed the degeneration of a hanging wart into a malignant tumor. Malignization is possible only in cases where the formation is large or is often injured, as a result of which its integrity is damaged.
Such a wart has a thin stalk, inside of which there are blood vessels that feed the neoplasm. A hanging wart looks unsightly and is often noticeable. Such formations can be dark or light in color. Pedicled lesions appear predominantly in older people. This is explained by the physiological processes that occur in adulthood: the decline of the protective functions of the immune system and hormonal imbalance.
It is extremely rare that a pedunculated wart can be diagnosed in a child.
A hanging wart never goes away on its own, unlike other neoplasms. If a person wants to get rid of the growth, he should go to a special clinic where pedunculated warts are removed. Since it is not recommended to resort to home methods for removing the growth, this can cause a number of complications.
Structure and growth
A pedunculated wart can grow up to 0.7 cm in size, being soft to the touch and flesh-colored.
The wart includes epithelial cells of the skin and small thrombosed vessels that have altered walls. A pedunculated wart is not characterized by rapid growth; it can remain small in size for many years. The growth of a wart occurs as follows:
- When it appears, the formation is a small round compaction. Its dimensions are about 1−2 mm. The color of the formation is flesh or light pink.
- Over time, the wart grows and becomes elongated, the stalk of the formation is clearly visible.
- The growth reaches a size of 6−7 mm. When several warts form at once, they merge into one large formation, reminiscent of cauliflower.
Main types
Doctors divide hanging warts into two types: acrochordons (thread-like or villous growths) and finger-shaped. Each formation has its own characteristics, which are shown in the table below:
| Characteristic | Filiform | Finger-shaped |
| External features | Thin growth with a small stalk | A rough, thick wart, the base is quite dense and looks like a pea |
| Distinctive features | Often merge into one neoplasm | Often injured |
| Location | Neck, facial skin, groin area, armpit, back. In women, a thread-like growth is often observed under the breasts. | The scalp along the line where the hair grows |
| Number of growths | There is a single growth or multiple neoplasms | As a rule, one finger-shaped wart is formed |
| Size | On average, the value ranges from 3 to 10 mm. In rare cases it reaches 12 mm. | A growth of 5 mm to 2 cm may be observed |
| Color | Flesh or brown | Pinkish tones |
Locations
Pedicled warts often grow in delicate places of the body: neck, groin, armpits, genitals.
Considering the location of localization, pedunculated warts are divided into the following:
- A hanging formation on the skin of the face or neck. In this case, the growth is often susceptible to ultraviolet radiation. This leads to blackening of the tumor.
- A wart on the head that is often injured when scratching.
- The growth on the pedicle under the arm requires special monitoring to avoid damage to its integrity. This is due to the fact that there are many sweat glands in the armpit, so at the slightest damage to the formation, it becomes infected. This complication is fraught with degeneration of the growth into a cancerous tumor.
- The groin area often becomes the site of formation of hanging condylomas. A person should be careful when shaving off unwanted hair in the groin area.
Classification of benign neoplasms on the skin
Benign neoplasms can be divided into the following types:
- Purchased.
- Congenital.
Acquired are neoplasms that arise on the skin due to pathologies such as papillomavirus, a weakened immune system, and metabolic disorders. With papillomavirus, papillomas and genital warts are formed. If a person has a weakened immune system, warts may appear on the palms and soles. When metabolism is disrupted, soft and hard fibromas are formed, for example, keratomas, xanthomas, nevi.
Congenital neoplasias include birthmarks, nevi whose area is more than 2 cm, and moles.
Reasons for appearance
The exact reasons for the appearance of neoplasms on the skin have not been established. However, experts have several theories about this. Provoking factors are as follows:
- Burdened heredity.
- Individual characteristics of the human body.
- Exposure to ultraviolet, x-ray and radiation.
- Presence of a viral infection.
- Long-term skin trauma.
- Chronic exposure of the skin to chemical carcinogens.
- Insect bites.
- Metastases in the presence of an oncological process in the patient’s body.
- Violation of skin trophism, which causes the formation of chronic ulcers.
- Weakened immunity.
Neck tumor treatment
For a tumor in the neck, conservative therapy is prescribed at the first stage. Treatments include chemotherapy, radiation therapy and medications.
Prescribed:
- Cetuximab. An anticancer drug prescribed as an intravenous infusion. Do not use the drug for tumors on the neck in childhood, during pregnancy and lactation, as well as in case of hypersensitivity to the composition of the drug.
- Fluorouracil belongs to the group of antitumor drugs and contains fluorouracil. The dosage is calculated individually, based on the severity and causes of the tumor (the patient’s general medical history is also taken into account). Before use, carefully read the instructions; there is a wide list of contraindications and side effects. Do not prescribe for hypersensitivity to the composition, during pregnancy or bone marrow bleeding. According to the doctor's indications, it is prescribed with caution to patients who have a history of acute infectious diseases.
- The drug Methotrexate has proven itself to be effective for tumors on the neck. Dispensed from the pharmacy strictly with a prescription, the drug has a pronounced antitumor spectrum of action, as it belongs to the group of antimetabolites - folic acid antagonists. Prescribed as injections, the dosage is selected individually. Methotrexate should not be used if liver or kidney function is impaired. Additional contraindications: pregnancy, thrombocytopenia.
Radiation therapy for malignant tumors in the neck: the main goal of the procedure is to destroy cancer cells. Currently, only two types of radiation treatment are used.
The first type is called external distance therapy. In this case, special radiation comes out of the device, which affects cancer cells.
The second type is called close focus therapy. The patient is injected with a radioactive substance that enters the bloodstream and then reaches the cancer cells and destroys them.
Traditional methods of treatment
For tumors in the neck, you can use folk remedies in combination with drug therapy.
At home, prepare a compress based on celandine. To prepare, you will need 2 parts of celandine infused in 100 ml of water or vodka. Infuse the alcohol tincture for 5-7 days.
Then soak gauze in the resulting solution and apply it to the tumor on the neck. Keep for 10-20 minutes. The course of treatment is at least 15 days.
The second remedy is based on onions and laundry soap. You will need 1 part of the onion and laundry soap (1 piece).
Preparation: bake the onion in the oven, then after cooling, grind everything in a meat grinder. Grate laundry soap into a separate container and mix with onions until smooth.
Application: apply the mixture to tumors on the neck 1-2 times a day. The course of treatment is 10-15 days.
For benign formations, you can use a beet-based recipe. You will need to grate the beets and mix with 350 ml of vegetable oil.
Symptoms and types of hemangioma
Quite often you can see hemangioma on the skin of adults. This is a tumor based on a vascular formation. Hemangioma can be divided into several types, they will depend on which specific vessels are involved in the process. Let's look at the types of hemangioma on the skin in adults and children:
- Cavernous. This hemangioma is located deep in the skin and is a limited subcutaneous node covered with a bluish-colored cover. As a rule, such a hemangioma is diagnosed immediately after the birth of a child, and it is localized on the head or neck.
- Simple capillary. Such a neoplasm is detected on the surface of the skin. This hemangioma is very large in size. The color can range from reddish to dark blue. The tumor is growing around the periphery.
- Combined. This hemangioma is a combination of cavernous and simple forms of this tumor.
- Mixed. In this case, both blood vessels and nearby tissues are involved in the process. As a rule, connective tissues are involved.
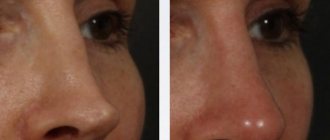
If the hemangioma is located on the eyelid or on the face, then radiation therapy is used for removal. In other situations, sclerotherapy, cryotherapy, and hormone therapy are prescribed. The surgical intervention method is used only if the hemangioma is located too deep.
Clinical picture
External manifestations and accompanying symptoms of a formation on the neck depend on its nature.
Phenomena accompanying cancer include:
- problems swallowing food;
- swelling in the neck and face;
- pain at the site of the tumor;
- Hoarseness, change in voice.
A tumor of the lymph nodes in the neck is manifested by the following symptoms:
- visually and upon palpation, an increase in the size of the organ is noted;
- the nodes are soft;
- when pressed, moderate to severe pain occurs;
- local redness of the lymph nodes may be observed;
- the temperature rises.
- if the lymph nodes are hard to the touch, this may cause suspicion of cancer.
During the examination, the doctor details the manifestations of the emerging pathology. Several aspects are important to make a diagnosis:
- localization of the tumor on the neck (right, left, back);
- dimensions;
- number of neoplasms;
- consistency (soft or hard).
Fibroma
So, we continue to consider the types of benign tumors on the skin. It is imperative to mention fibroma, which is a neoplasm formed from connective tissue. Quite often, fibroma is diagnosed in young people. This type of neoplasia occurs predominantly among the fair sex.
This neoplasia is characterized by its small size. The maximum fibroma reaches a diameter of 3 cm. The neoplasm is a spherical nodule, deeply embedded in the skin, which slightly rises above the surface. Fibroids can be of different shades, ranging from gray to black. As a rule, the surface is smooth, sometimes warty formations can be observed. Fibroids grow slowly.
It is important to note that, despite the fact that fibroma is a benign tumor, under favorable conditions there is a risk of degeneration into a cancerous form. To remove fibroids, laser, surgical, and radiosurgical methods are used. In addition, specialists may prescribe electrocoagulation for removal.
Nevi and moles
We continue to study the names of benign skin tumors. You can often see moles and nevi on the body. Such neoplasms can be either congenital or acquired.
The ICD-10 code for nevus is D22. It is a cluster of cells that have too much melanin. Such neoplasms are characterized by various shapes, shades, and textures. These tumors are most often removed due to possible degeneration into cancer, as well as due to localization in inconvenient places. The ICD-10 nevus table code may vary slightly depending on the specific type. Typically located somewhere on the face or in a place of friction with clothing, it is best to remove it. Currently, a variety of methods are used for excision.
Lipoma
But what can be said about lipoma, the causes and treatment of this neoplasm? This neoplasm is formed on the basis of the fat layer, which is why it is often called a wen. Lipomas are localized in the thickness of the connective tissues under the skin. Often the tumor penetrates deep into the underlying tissues, growing between the vessels and muscles and reaching the bones. Most often, lipoma is localized in areas with a thin layer of fat, for example, on the hips, shoulders, shoulder blade, and head.
A lipoma is a mobile and soft neoplasm that will be painful on palpation. This tumor is distinguished by its slow growth. Lipoma is not dangerous to health, but sometimes it can develop into cancer.
A lipoma can appear due to a violation of fat metabolism, genetic predisposition, due to an insufficient level of personal hygiene, or due to a violation of the mechanism of reverse regulation of fat metabolism.
What else can be said about the causes and treatment of lipoma? Mandatory removal is prescribed in case of intensive growth of this neoplasm, as well as compression of surrounding tissues or organs. You should pay attention to the fact that experts advise removing a lipoma if it has begun to grow and has not yet reached a small size. This will help avoid a large scar. To remove small lipomas, puncture-aspiration, laser, and radio wave therapy are used.
Lymphangioma
These tumors are formed on the basis of lymphatic vessels. In most cases, lymphangioma is congenital in nature, since it forms in an inconvenient period. This neoplasm is found in children less than 3 years old. Externally, lymphangioma is a cavity with thin walls. The size of the neoplasm ranges from 1 to 5 mm in diameter. Neoplasia grows quite slowly, but there may be cases of spasmodic growth, when lymphangioma increases in size very quickly. In such situations, surgical removal is indicated.
A surgical technique for the treatment of benign neoplasms is used in the case of lymphangiomas, which are located near the trachea, larynx, and other vital organs.
Warts and papillomas
Warts and papillomas on the body, the causes of which can be many, are neoplasms in the form of a nodule or flat papilla. In practice, you can find growths of various sizes, shades and shapes. The main reason for the appearance of papilloma and warts on the body is the papilloma virus, which has many different strains. This virus is activated in the human body due to stress, decreased immunity, and vegetative disorders.
There are certain types of warts that can transform into cancer. However, the bulk of these neoplasms are still safe. Immunomodulatory and antiviral agents are used for therapy. To remove a wart or papilloma, you can use any method, from acids to surgery.
Why do filamentous papillomas appear?
Papillomas and condylomas of any kind are formed in the body as a result of viral infection. The analysis reveals that the invading microorganism is the human papillomavirus. There are several ways to transmit it:
- sexual;
- as a result of childbirth;
- domestic;
- contact, through wounds and cracks in the skin.
An increased risk of pedunculated papillomas is observed in women of reproductive age. Neoplasms are especially common in patients who have skin problems:
- increased sweating;
- active work of the sebaceous glands;
- skin moisture.
Formations on a thin or wide stalk are caused by a special type of HPV. Their occurrence is influenced by 3, 5, 8 and 9 strains of the virus. After penetration into the body, the disease may not manifest itself. When the body’s immune defense decreases, infection activates.
After penetration into the epithelial tissue, the stage of active reproduction of the virus begins. At this moment, papillomas can appear.
Neoplasms appear as a result of HPV infection
Atheroma
According to the classification in the ICD-10 table, atheroma has a code from L60 to L75; it is a cyst from the sebaceous gland, which occurs due to blockage. Most often, atheroma is localized in the groin area, on the head, neck, and back. Thus, we can conclude that neoplasms are located in areas where a high concentration of sebaceous glands predominates.
The code in the international ICD-10 table for atheroma will depend on the specific type. But how can it be determined externally? The atheroma has clear contours, is very dense, elastic upon palpation, and does not bring any discomfort to the patient. If an infection is attached, then suppuration of the tumor may occur. In this case, the atheroma acquires a red tint, swelling and pain form. In a state of inflammation, atheroma can break through on its own, and purulent-greasy contents will come out of it.
Despite the fact that atheromas are benign neoplasms, they can degenerate into a malignant form. That is why it is necessary to remove such tumors on the body. This is done only by surgical intervention.
Neurofibroma
This neoplasia grows from cells that create nerve sheaths. Neurofibroma is localized in the subcutaneous tissue, as well as on the skin. Externally it is a tubercle, which has a dense consistency. Neurofibromas are about 3 cm in diameter. Neoplasia is covered with epidermis, which is heavily depigmented or pigmented. Such a tumor can be multiple in nature. This condition is commonly called neurofibromatosis. It is the result of a genetic failure, and can be inherited.
Single neurofibromas rarely degenerate into a cancerous form, but they can cause many problems for the patient. The fact is that such neoplasms can provoke various functional disorders and constant pain. Neurofibroma is treated with medication. Removal of neurofibroma is carried out using radiation therapy, as well as surgery.
Diagnostics
Regular examinations, as well as self-analysis, will be of great importance in early diagnosis. During an external examination, a specialist can accurately diagnose a particular pathological condition, as well as a neoplasm on the skin. After this, the patient is sent for further examination.
If you are attentive to your own health, you will be able to notice changes in your moles, birthmarks, and pigmentation in time. For example, if you notice new moles on your body, a doctor should determine the cause of their appearance. In some cases this is a warning sign.
If you notice skin changes that are observed without any reason, then it is imperative to undergo examination by an oncodermatologist or dermatologist, where, based on an external examination, an oncological examination, as well as an examination of the general condition of the patient’s body, the tumor-like nature of the neoplasm will be excluded or confirmed.
Other diseases with skin manifestations
This group includes viral infections, which are also characterized by changes in the skin. The rash is often not the only symptom.
At the same time, the virus does not have a direct damaging effect on the skin, and rashes of various types appear in response to the action of toxins produced by the virus.
Infections in children
The group of diseases in which changes in the skin are observed includes measles, rubella, chickenpox, infectious mononucleosis, erythema infectiosum and roseola infantum.
It is worth remembering that in some cases, childhood infectious diseases may not be accompanied by the appearance of skin rashes. Therefore, it is important to know all the characteristic features of the disease and be able to distinguish it from similar pathological conditions.
Measles
The disease is caused by an RNA-containing pathogen from the genus Morbillivirus. Changes in the skin appear in the form of large-spotted, confluent rashes. They are visualized 5–6 days after the onset of the first symptoms.
The rash appears in stages, first on the face and behind the ears, and then spreads down the body.
In addition to skin rashes, the child’s body temperature rises (up to 40 °C) and specific Filatov-Koplik spots appear, which are located on the mucous membrane of the cheeks in the molar area. Their presence makes it easier to make a correct diagnosis.
Rubella
The disease develops when infected with togavirus. With it, there is often a significant increase in body temperature and always an increase in the size of the posterior cervical lymph nodes.
Skin rashes appear on the body 1–2 days after the onset of the described symptoms and spread throughout the body rapidly. The rash is small-spotted, pale pink in color, not merging, located on unchanged skin. It generously covers:
- Extensor surface of the arms.
- Lumbar region of the back.
- Sides of the legs.
- Buttocks.
The rash disappears within 2–7 days, leaving no visible traces behind.
Chicken pox
A disease caused by the Varicella-Zoster virus. The pathology is characterized by an increase in body temperature, accompanied by the appearance of rashes of different types (spots, papules, blisters), which is associated with the undulating course of the disease.
The rash occurs even on the scalp and mucous membranes of the oropharynx. In this case, the child is bothered by severe itching of the skin. The rash disappears by drying out and forming crusts.
The child remains infectious to others for another 5 days from the moment the last element appears.
Viral exanthema
The disease, otherwise known as enteroviral exanthema, occurs when infected with the Coxsackie virus. The nature of the rash is similar to that observed with rubella. The rash is small-spotted and localized mainly on the torso.
After 3–7 days from the onset of the disease, the rash disappears without a trace.
Roseola infantile
Known as sudden exanthema. The disease is caused by herpes virus type 6. The disease begins with an increase in body temperature, which returns to normal after 5 days. During this period, small and medium-spotted rashes appear on the skin. They are localized mainly on the torso and are not accompanied by pain or itching of the skin.
The rash disappears without a trace within 5 days.
Treatment and prevention
There is no specific prevention of tumors on the body. Preventive measures should include the removal of warts and moles at the initial stage of their development, especially if you observe a large number of them on your body. Persons who have a genetic predisposition to cancer should be more attentive to the treatment of benign skin tumors, as well as to prevention. To do this, you should avoid insolation, carefully select a workplace, and also avoid contact with carcinogenic substances. Experts also recommend excluding from your diet those foods that can cause the tumor to degenerate into a malignant form.
Treatment for a benign skin tumor on the face or other parts of the body will involve removing the affected area. Laser removal has the least relapses, since in this case the wound surface is cauterized and further dissemination of tumor cells is not allowed. Cryodestruction and electrocoagulation can also be used for these purposes. A specialist may prescribe a radio wave removal method depending on the type of tumor on the skin.
Types of viral diseases
Different viral skin diseases manifest themselves in different ways, but they all cause cosmetic defects of the skin and inflammation of the mucous membranes.
Most often, dermatologists diagnose:
- herpes (different forms, stages);
- condylomas;
- different types of lichen;
- pemphigus;
- pustular dermatitis;
- warts (papillomas);
- molluscum contagiosum.
Each pathology has its own course and characteristic features specifically for this type of virus.
We recommend studying this topic:
Pemphigus of newborns - how to save your baby from an infectious disease?
8339
0
1
reading information
Herpes
The pathology is caused by two types of viruses: HSV-1 and HSV-2. It is possible to distinguish asymptomatic herpes simplex, initial, primary and recurrent.
The manifestation of herpes near the mouth is a phenomenon familiar to many. It requires treatment.
The clinical picture of the disease can appear at any age. Most often, the primary variant is diagnosed in children and young people in the first weeks after contact with an infected person. The distinctive clinical picture of the pathology is the appearance of characteristic rashes covering a fairly large area. At the same time, there is an increase in temperature and an increase in lymph nodes.
The main danger with herpes is the dissemination of the virus, which occurs during the development of a primary disease affecting the gastrointestinal tract, respiratory tract and central nervous system.
Important! Herpes is considered a simple disease, but it can be fatal.
We recommend studying this topic:
Symptoms and treatment features of human papillomavirus (HPV) in women
6822
0
5
reading information
The initial form appears in people who have previously been infected with primary herpes. With this form, the general clinical manifestations are not so pronounced.
Viral skin diseases are not only a cosmetic defect, but are also fraught with various complications.
Skin viral diseases HSV-1 and HSV-2 have four stages of development:
- Erythematous. Initially, a pink spot forms in the affected area.
- Vesicular. Bubbles appear on the resulting stain. They can be located in groups or separately.
- Cortical. The bubbles dry out, forming crusts.
- Recovery. At this stage, the crusts fall off, the hyperemic spot gradually turns pale and disappears.
In addition to the classic forms of herpes, some people are diagnosed with atypical types. These types include:
- edematous form;
- migratory form;
- disseminated form;
- herpes simplex with an abortive type of course.
Remember! Herpes can appear not only on the skin, but also on the mucous membranes. Most often it is diagnosed on the oral mucosa, eyes, and genitals.
If left untreated, herpes can be fatal.
Condylomas acuminata
This acute viral disease affects the skin and mucous membranes of the genital organs, oral cavity and perianal area.
The appearance of genital warts in the perineal area should alert a person
Infection occurs through sexual contact. Infection occurs in 90% of cases through contact with a sick person.
During childbirth, the virus is transmitted from an infected woman to the child. With such transmission, laryngeal condyloma is diagnosed in children.
In most cases, the pathology occurs covertly, with periodic manifestations in the form of rashes. The incubation period can last up to several years.
During activation of condylomas, patients note the appearance of rashes on different parts of the body. Most often they form in the genital area, near the anus and in the mouth. Externally, the formations resemble fleshy warts the size of a pinhead.
Treatment of condylomas does not always give positive results. Even after the outward manifestation disappears, the virus remains in the body in an inactive state, and under special conditions it is activated.
Genital warts are dangerous because they can develop into malignant neoplasms.
For information! To avoid infection, it is recommended to use barrier contraception, but they do not guarantee complete protection against the virus.
Warts or papillomas
The most common viral skin diseases in humans are warts. They are caused by the human papillomavirus, which selectively affects the skin. Most often, the disease manifests itself on the hands.
Group accumulation of warts on the hands is a very common viral disease that is easily transmitted from one person to another
Infection occurs through contact between a healthy person and a sick person. The penetrated virus destroys the integrity of the stratum corneum. Infection can occur in any public place, at home, at school, etc.
Typically, warts do not cause any clinical complaints other than a cosmetic defect . The resulting papillomas are dense, rounded nodules. The surface is covered with cracks. Layers of the stratum corneum are visible on the surface.
Papillomas can be single or multiple. Their arrangement is random. After warts are removed, new formations may appear around them. In people with good immunity, the disease goes away on its own.
Remember. There is no point in waiting for the disease to go away on its own. It is better to immediately consult a doctor to prescribe treatment, rather than wait until the virus appears in different parts of the body where there are microcracks.
Molluscum contagiosum
Pathology occurs in children and adults. The latter become infected through sexual contact. Rashes appear on the genitals, in the perineal area. In children, poxvirus manifests itself in open areas of the body, then moves to closed areas.
An example of the formation of molluscum contagiosum on the skin. As a rule, the disease has no consequences
With pathology, pink papules with a small depression in the central part are formed. Apart from the skin defect, patients do not present any other complaints. However, some may complain of itching and mild soreness (these symptoms usually occur in people with high sensitivity).
Pemphigus viral
Viral diseases of the mucous membranes and skin include pemphigus. Most often it is diagnosed in children at an early age. Lesions can be observed on the feet, hands, and oral mucosa. Often the pathology manifests itself in the form of stomatitis with exanthema.
Doctors diagnose the formation of viral pemphigus on the hands most often in children
In addition to the external manifestations of the disease, general clinical symptoms and syndromes are observed: patients may experience an increase in body temperature, a headache, and exanthema in the throat. During examination of the oral cavity, red spots, ulcers and blisters are visible on the surface of the mucous membrane.
We recommend studying this topic:
Removal of condylomas during pregnancy: risk or justified treatment?
6659
0
0
reading information
Pustular dermatitis (eczema contagiosum)
This pathology is often called contagious eczema. It is caused by a virus transmitted by contact from sick animals (goats, sheep, cows).
A variant of the manifestation of viral pustular dermatitis on the fingers
With the disease, the appearance of dense nodules is observed, which over time develop into crusts with depressions in the central part.
Good to know! The localization of formations is most often recorded on the forearms and hands. Without treatment, pustular dermatitis goes away on its own in 5-7 weeks.
When is there danger?
So, above we looked at the names of benign tumors on the skin, as well as methods of treating these tumors. But when can such a neoplasm develop into a malignant form? First of all, it should be noted that this will not be typical for all tumors. Only an experienced specialist can determine specifically which mole on your body is potentially dangerous. If you notice that your birthmark is enlarging, be sure to seek help from a medical facility.
It has been proven that the most dangerous are nevi, which are birthmarks and moles that have a convex shape, and they are located on the skin from birth. In such situations, it is necessary to make a timely diagnosis. First of all, experts advise removing keratomas from your body. Due to severe discomfort, condylomas, papillomas, warts, and xanthomas are removed.
Prevention of complications
No specialist will give clear recommendations for the prevention of malignant tumors of the neck. There is no clear idea about the mechanism of cancer in this part of the body. To prevent an advanced form of the tumor, it is necessary to promptly consult a doctor if you detect even a small lump or swelling on the neck.
As a preventive measure it is suggested:
- quitting smoking and drinking large amounts of alcohol;
- use of protection in production with toxic substances;
- complete treatment of infectious diseases.
If a tumor appears on the neck, no matter on the left or right, you should not wait for it to disappear on its own. Check its nature for the safety of your own health.
When should I delete it?
There are cases when a neoplasm on the skin must be removed, regardless of the type. For example, if there are about 20 moles on a small area of the skin, then there is a risk of developing melanoma, that is, a malignant form.
If neoplasias are located on the neck, arms, or face, then it is best to remove them, since tumors are exposed to ultraviolet radiation, which increases the risk of degeneration into a malignant form.
If someone in the family has previously suffered from skin cancer, then there is a hereditary factor. In this case, you should also seek advice from a specialist who will prescribe removal of the tumors.
If the neoplasia is often injured, then it is best to remove it.
Never delay a visit to the doctor if a new growth on the skin begins to grow, hairs begin to fall out from the surface, the shade has changed, the consistency has changed, bleeding has appeared, the size has decreased, the shape has changed, the contour has become blurred, inflammation and itching have appeared, and cracks have formed on the surface . If you do not consult a doctor with these signs, then there is a possibility of degeneration into a malignant form.
Symptoms
If we talk about the clinic of neoplasms on the body, it is not very pronounced. In this case, it is important to pay attention to:
- color;
- location;
- size of neoplasia.
If the neoplasm is quite large in size, it can compress the tissue in its location. This, in turn, leads to pain and discomfort. When blood vessels are compressed, blood circulation in them and nearby organs is disrupted, and this is fraught with much more serious consequences.
You should immediately seek help from a doctor and undergo a thorough examination if the following alarming symptoms occur:
- pain in the area of the tumor that does not go away for a long time;
- bleeding neoplasia;
- blackening of the tumor;
- rapid proliferation of growth;
- increase in tumor volume;
- itching, discomfort and burning in the area of neoplasia;
- the appearance of a red halo around the skin growth.
Such symptoms may indicate inflammation of the growth or, even worse, its degeneration into a malignant tumor. Of course, not all types of neoplasia are accompanied by such anomalies, but, nevertheless, they should alert you.